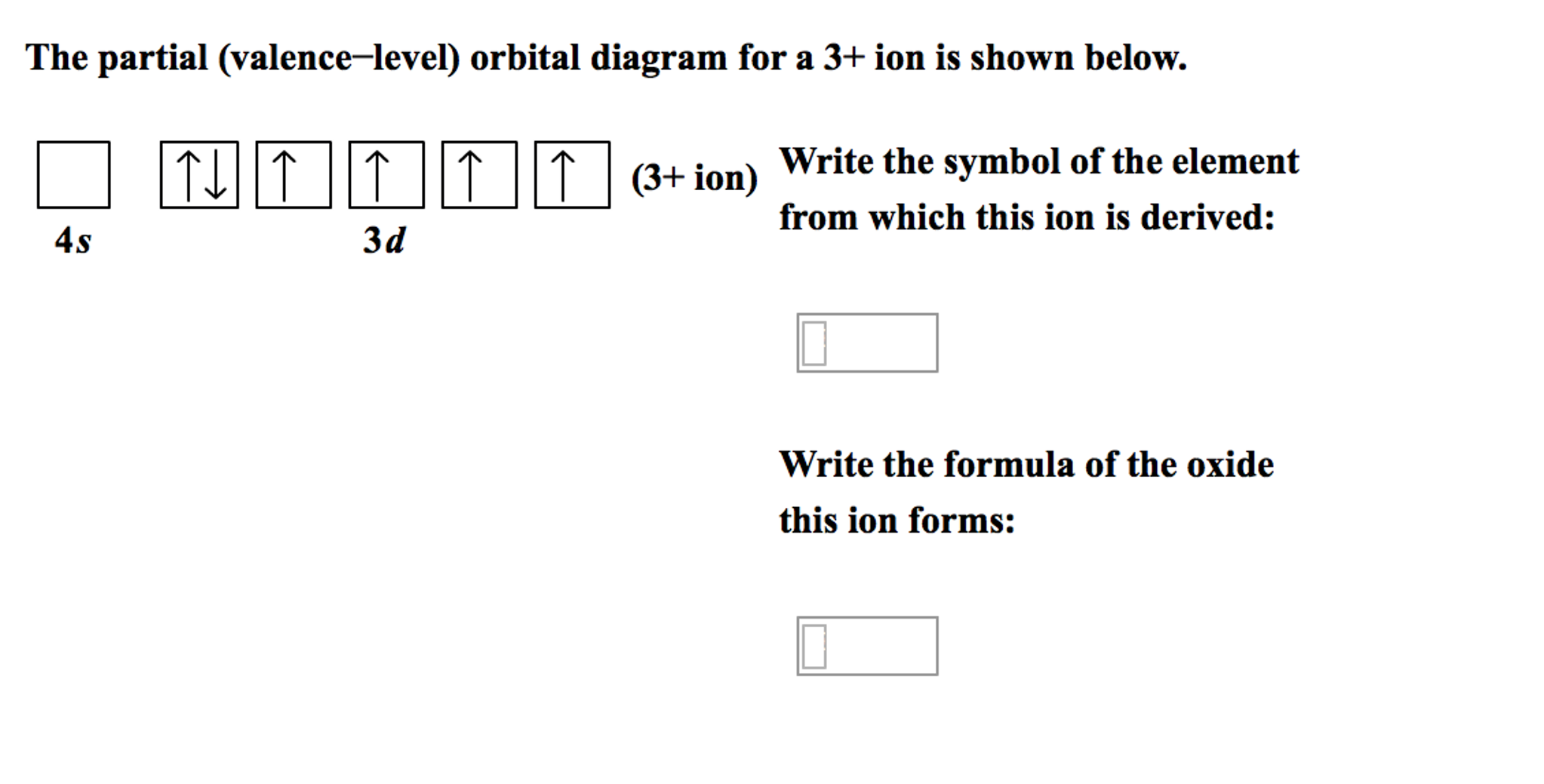
38 the partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below.
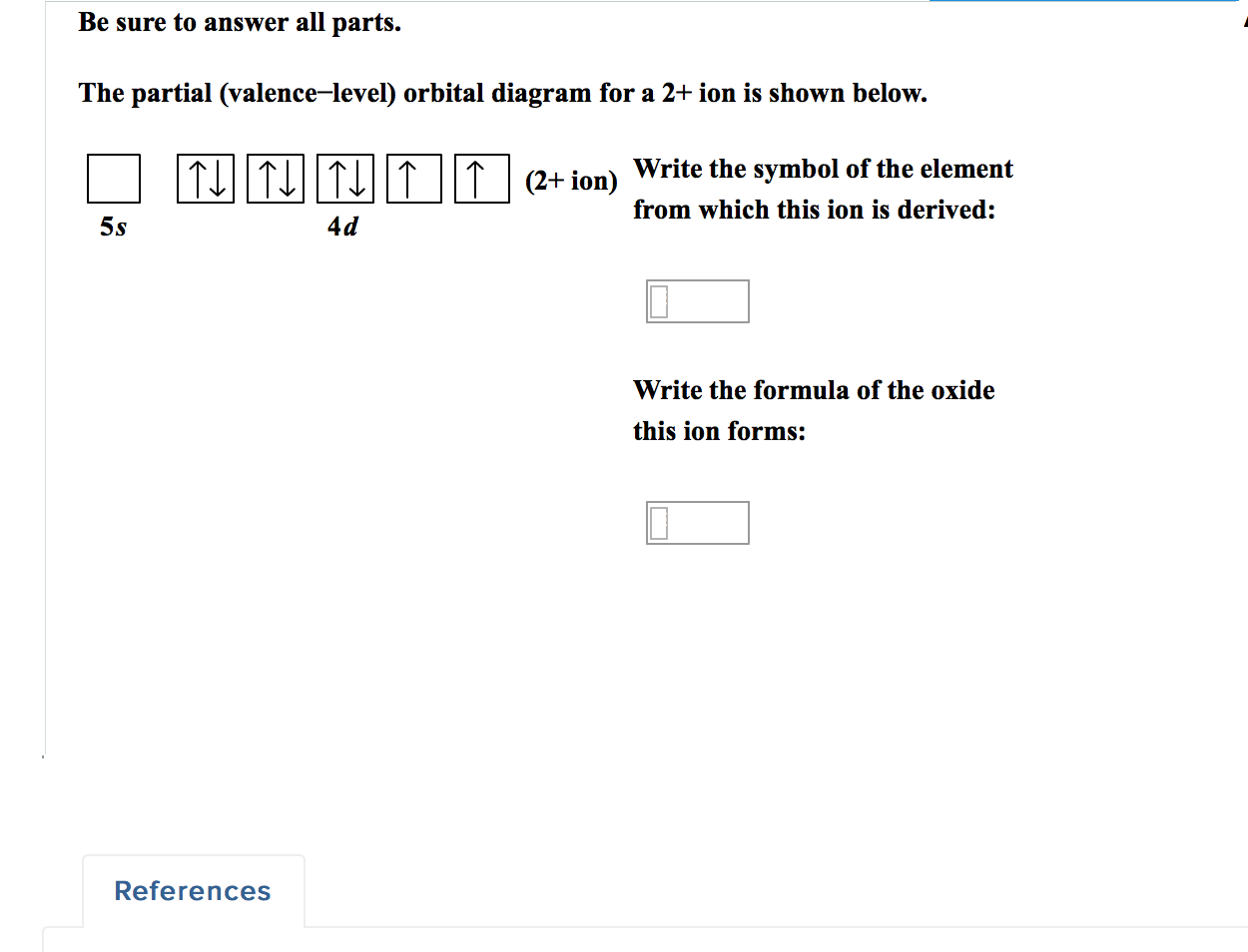
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived: Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms: Question: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived: Write the ... • The molecular orbital energy level diagrams for F 2 and B 2 are shown below. Fill in the valence electrons for each species in its ground state. Hence calculate the bond order for F 2 and B 2 and indicate whether these molecules are paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Marks 3 F 2 B 2 Bond order Paramagnetic or diamagnetic σ σ∗ σ π π∗ σ ...
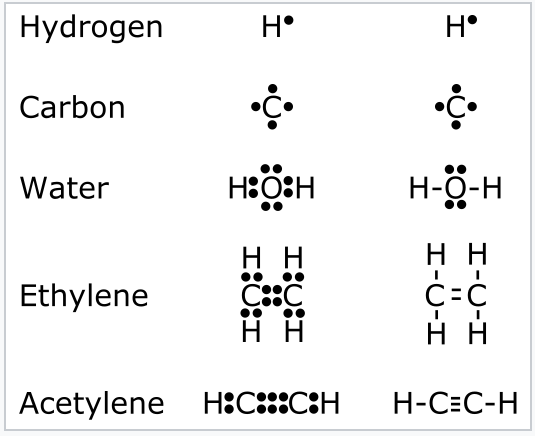
This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic orbitals.
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below.
a) The 1s orbital in H is more stable than the 1s orbital in He+ b) The 2s orbital in He atom is less stable than the 2s orbital in He+ c) The 2s subshell in Li is more stable than the 2p subshell in Li a. a) only b. a) and b) only c. a) and c) only d. c) only e. None of these The partial (valence level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below... Then it shows a box with no arrows for the 5s orbital (aka no electrons) then it shows the 4d orbital with five boxes the first 3 boxes have an up and down arrow in each box (indicating the electrons spin (spin up spin down)) and the last 2 boxes only have spin up arrows. Transcribed image text: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 4+ ion is shown below. What is the symbol of the element from which this ion is ...
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below.. A 4s orbital is higher in energy than a 3s orbital. As increases, orbital energy increases. In the n = 3 shell, 3s < 3p < 3d. As n increases, the subshell energies become more closely spaced and overlapping occurs. The 4f orbital is higher in energy than the 5s orbital, despite its lower n value. 7.3 Electron Configuration of Elements Transcribed image text: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3-ion is shown below. What is the symbol of the element from which this ion is ... Consider the following portion of the energy-level diagram for hydrogen: n = 4-0.1361 × 10-18 J n = 3-0.2420 × 10-18 J n = 2-0.5445 × 10-18 J n = 1-2.178 × 10-18 J For which of the following transitions does the light emitted have the longest wavelength? Beyond the second energy level, the filling of atomic orbitals does not follow a simple pattern. For example, the 5s orbital is of lower energy than the 4d orbital (see Figure 3 for a complete pattern of orbital levels). Ca electron occupancy The orbital notation of calcium (Ca) is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 Or short-hand: [Ar] 4s2.
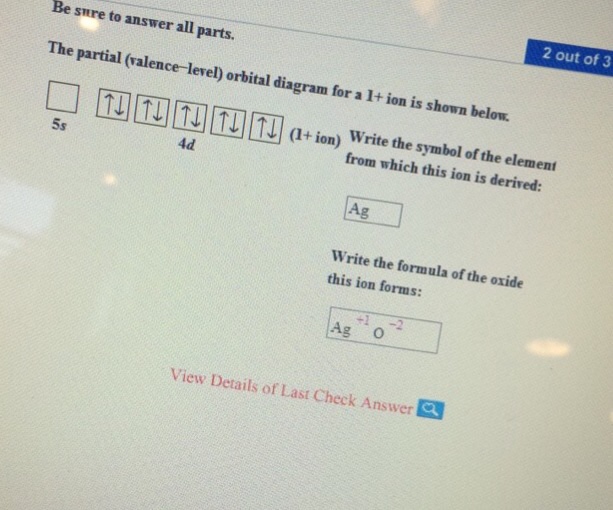
In peroxide ion, the bonding σ O (2 p )O (2 p) orbital is calculated to be below the π bonding orbitals in energy, as is the corresponding MO in F 2, whereas with antibonding character it appears above the π bonding levels in N 2. The idea that bonding by the σ O (2 s )O (2 s ) orbital is cancelled out by antibonding by the σ* O (2 s )O (2 ... 10 polnts The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 1+ ion is shown below. + ion 4d Print References Write the symbol of the element from which this ion ... Draw a partial (valence-level) orbital diagram, and write the condensed ground-state electron configuration for each: $$ \begin{array}{llll}{\text { (a) Ti }} & {\text { (b) } \mathrm{Cl}} & {\text { (c) } \mathrm{V}}\end{array} ... Period 4 transition element that forms $3+$ diamagnetic ion (n) Period 4 transition element that forms $2+$ ion ... 2s. 20.3. N. 2p. 14.5. Transformation of the valence atomic orbitals in C3v symmetry. The following table summarizes how the nitrogen and hydrogen atomic orbitals transform. Additional discussion follows regarding the assignment of characters for the 2px and 2py orbitals which transform together as a pair. C 3v.
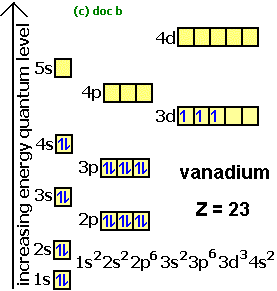
• The molecular orbital energy level diagrams for F 2 and B 2 are shown below. Fill in the valence electrons for each species in its ground state. Hence calculate the bond order for F 2 and B 2 and indicate whether these molecules are paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Marks 3 F 2 B 2 Bond order ½ (8 – 6) = 1 ½ (4 – 2) = 1 Paramagnetic or ... Transcribed image text: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is ... 5.13 The energy level diagram for SH- is shown below. A bond order of 1 is predicted. The S orbital energies are -22.7 eV (3s) and -11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of -13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the An atom of vanadium (Z=23) in its ground state has _____ valence electrons. 5. Rank the following elements in order of increasing metallic character (from least metallic at the top of the list to most metallic at the bottom). Al, P, Cs, Zn.

1 2 Valence Bond Theory Lewis Dot Structures The Octet Rule Formal Charge Resonance And The Isoelectronic Principle Chemistry Libretexts
388 chApTer 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories • Count the number of electrons in a delocalized p system.(Section 9.6) • Explain the concept of bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals and draw examples of s and p MOs. (Section 9.7) • Draw molecular orbital energy-level diagrams and place electrons into them to obtain the bond orders and electron configurations of diatomic

Electrostatic Charging Due To Separation Of Ions At Interfaces Contact Electrification Of Ionic Electrets Mccarty 2008 Angewandte Chemie International Edition Wiley Online Library
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. tutt 11 (3+ ion) 4s 3d Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is ...
molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule.
Which best describes the outermost energy level in the orbital diagram for Carbon (C)? A pair of electrons in the 2s and 2 single electrons in the 2p Based on the periodic trends, which atom below is least likely to form a cation?

Transition Metal Impurities In Carbon Based Materials Pitfalls Artifacts And Deleterious Effects Sciencedirect
a. the n = 3 shell has no f subshell b. there are three p orbitals in every shell of an atom except the n = 1 shell c. all s orbitals have spherical shapes d. each d subshell has five d orbitals e. the energies of subshell in the shells (energy levels) of a hydrogen atom vary as s < p < d, etc.
100% (5 ratings) there are 6 electrons in d orbital of …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived: Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms:
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below. quifditu1 (2+ion) 5s 4d Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived.
Relative AO Energies for MO Diagrams F 2s orbital is very deep in energy and will be essentially nonbonding. H He Li Be B C N O F Ne B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar Al Si P S Cl Ar 1s 2s 2p 3s -13.6 eV 3p -18.6 eV -40.2 eV
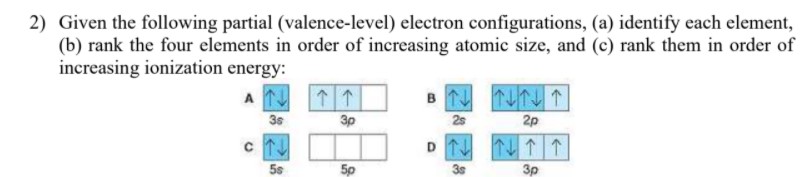
a. Mg 1s22s22p63s13p1 b. Cl 1s22s22p63s23p44s1 c. Mn 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d 44p1 d. Ne 1s22s22p53s1 8.46 Given the following partial (valence‐level) electron configurations, a. identify each element, A Si B F C Sr D S b. rank the four elements in order of increasing atomic size, and F, S, Si, Sr
required and write a partial orbital diagram. PROBLEM: Use partial orbital diagrams to describe how mixing of the atomic orbitals of the central atom(s) leads to hybrid orbitals in each of the following: (a) Methanol, CH. 3. OH (b) Sulfur tetrafluoride, SF. 4 (a) CH. 3. OH. The electron- group arrangement is tetrahedral around both the C and ...
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. __ 4s (no arrows) __ __ __ __ __ 3d (two arrows in the first box, up and down) (One up arrows in the rest of the boxes, 6 arrows total) Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived. Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms. The answer is not Fe or Cr.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Chemistry questions and answers. Be sure to answer all parts. Re The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 1+ ion is shown below. 5s 4d Gu Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms. Question: Be sure to answer all parts.
- electrons in the highest energy level that contains electrons Valence electrons ... this energy is a measure of how easily the element forms an ion with a ____ charge. ... Which sub levels may be utilized in constructing a partial orbital diagram for a period 3 element? select all that apply - 3p

1 Write Orbital Diagrams For Each Of These Ions A V5 B Cr3 C Ni2 D Fe3 2 Determine If The Ion Is Diamagnetic Or Paramagnetic A V5 B Cr3 C Ni2
2 BH 3 B2H6 The BH 3 molecule is trigonal planar and we will make the C 3 principal axis of symmetry the z axis, with the x and y axes in the plane of the molecule. The y axis (arbitrary) will be along one of the B-H bonds. Molecular Orbital Theory - D3h Character Table D3h E 2C 3 3C 2 σh 2S 3 3σv A1' 1 1 1 1 1 1 A2' 1 1 -1 1 1 -1 E ...
M.O.Energy Level Diagram for A2 (A = Li, Be) Li2 Only two valence electrons, i.e. σs 2σ*s 0. Bond order = 1. Diamagnetic Li2 exists in gas phase over metallic lithium. "Be2" σ s 2σ* s 2 B o ndr e= 0 - t b i g energy, so molecule does not exist. Beryllium in gas phase is monatomic. Use Aufbau, Pauli, Hund - just as in filling atomic orbitals
The placement of the next electron must follow Hund's rule. The orbital diagram shows three unpaired electrons. The electron configuration for nitrogen is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. For oxygen the eighth electron must pair with one of the electrons in the 2p orbitals. The orbital diagram for oxygen is shown on the left.
Transcribed image text: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 4+ ion is shown below. What is the symbol of the element from which this ion is ...
The partial (valence level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below... Then it shows a box with no arrows for the 5s orbital (aka no electrons) then it shows the 4d orbital with five boxes the first 3 boxes have an up and down arrow in each box (indicating the electrons spin (spin up spin down)) and the last 2 boxes only have spin up arrows.
a) The 1s orbital in H is more stable than the 1s orbital in He+ b) The 2s orbital in He atom is less stable than the 2s orbital in He+ c) The 2s subshell in Li is more stable than the 2p subshell in Li a. a) only b. a) and b) only c. a) and c) only d. c) only e. None of these
Symmetry Free Full Text Chemical Reasoning Based On An Invariance Property Bond And Lone Pair Pictures In Quantum Structural Formulas Html

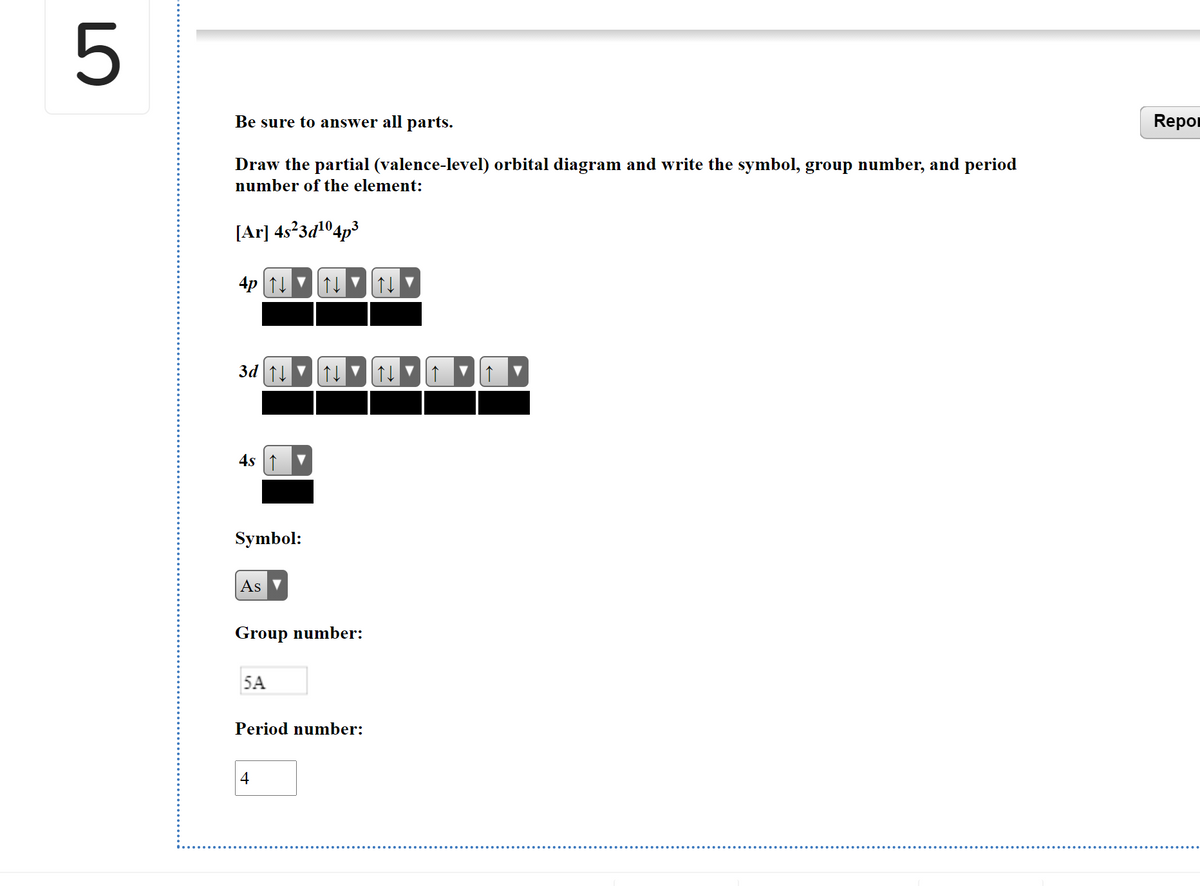
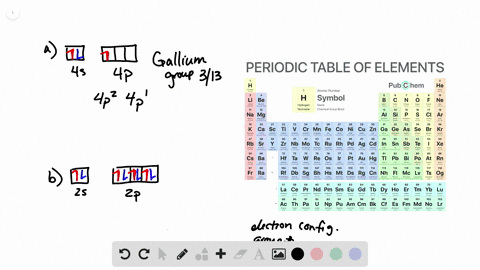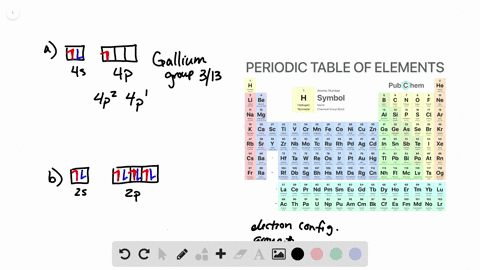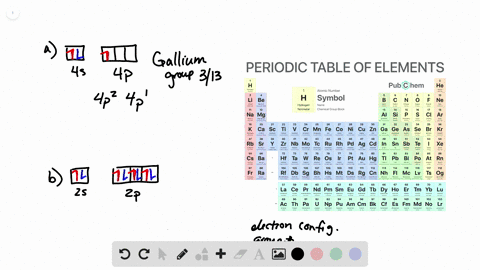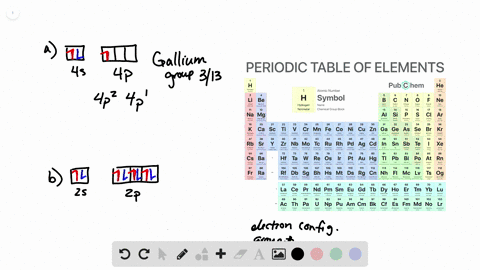
Draw The Partial Valence Level Orbital Diagram And Write The Symbol Group Number And Period Number Of The Element Ar 4s 2 3d 10 4p 3 Image Src Orbital9195593143458043682 Jpg Alt Orbital C Study Com
Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes
Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes

Solved Partial Valence Level Electron Configurations For Four Different Ions Are Shown Below Identify The Elements From Which The Ions Are Derived And Write The Formula Of The Oxide Each Ion Forms








0 Response to "38 the partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below."
Post a Comment