38 octahedral molecular orbital diagram
For this we need to picture atomic and molecular orbitals. l = 0 2. ATOMIC ORBITALS 2p x 2p y 2p z l = 1 x y z n = 2 This is an accurate representation of a 2p x orbital. This is a common picture of a p x orbital This simplifi ed p x orbital is often useful. A hand drawn version does not have to be exact. Molecular orbital diagram for a simple octahedral complex. This is qualitatively equivalent to the results of the simpler crystal field theory, which ignores orbital overlap with the ligand orbitals and uses just the electrostatic repulsion of the metal d-orbitals and the negative charges of the ligands.
On the other hand, the bonding molecular orbitals of t2g are higher in energy than all σ bonding molecular orbitals. The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for this type of π-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 21. The generation of π and σ-molecular orbitals in octahedral complexes.

Octahedral molecular orbital diagram
The CFT diagram for tetrahedral complexes has d x 2 −y 2 and d z 2 orbitals equally low in energy because they are between the ligand axis and experience little repulsion. In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane. High‐Spin and Low‐Spin Configurations • In an octahedral complex, electrons fill the t 2g and e g orbitals in an aufbau manner, but for configurations d4 - d7 there are two possible fillingschemesdependingon the magnitudeof o. • The relative magnitudes of o and the mean pairing energy, P, determine whether a high spin or low spinstate isobserved inoctahedralcomplexes. In about 15 minutes animated video, the concept of Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), symmetry of metal atomic orbitals in different ligand environment and mole...
Octahedral molecular orbital diagram. σ‐MOs for Octahedral Complexes Γσ= A1g+ Eg+ T1u Reading off the character table, we see that the group orbitals match the metal s orbital (A1g), the metal p orbitals (T1u), and the dz2and dx2-y2 metal d orbitals (Eg). We expect bonding/antibonding combinations. The remaining three metal d orbitals are T2gandσ-nonbonding. 5. In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry describes a molecular geometry in which 6 ligands are symmetrically arranged around a central atom in an octahedral geometry. All six ligands are chemically equivalent. The central atom is often a transition metal.The octahedron has eight faces (hence the prefix octa) and thus is one of the Platonic solids (although octahedral molecules typically ... Download scientific diagram | Qualitative valence molecular orbital (MO) diagram of an octahedral iron hexacyanide complex with Fe-centered nominal 3d and ligand-centered CN − MOs. The ferrous ... A molecular orbital diagram which estimates the energies of the bonding (show above) antibonding and non-bonding orbitals is shown below. Since there is a large disparity in energy between the ligand orbitals and the metal orbitals, the lower lying molecular orbitals in the diagram are essentially ligand orbitals.
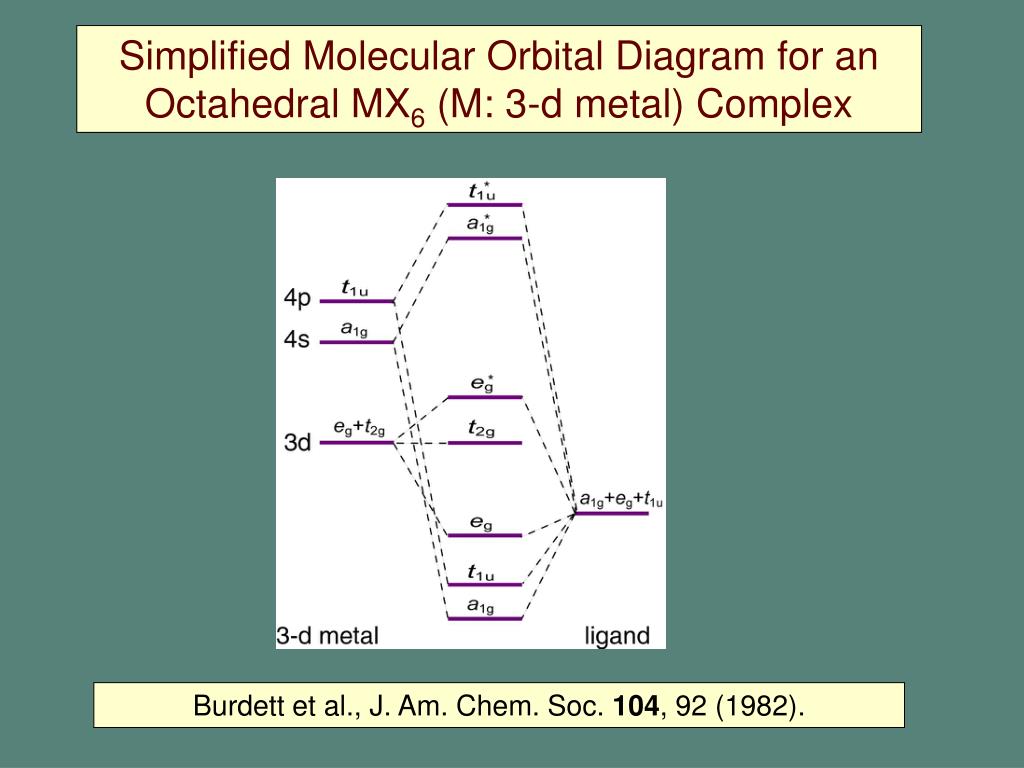
molecular orbital diagram for a coordination complex? - Assume central atom has s, p, d orbitals in valence shell = 9 orbitals - Assume each ligand atom, L, has s and p orbitals 4 x n ligands = 4n orbitals Octahedral ML 6 metal 9 orbitals ligands 4x6 = 24 orbitals Thirty – three orbitals sounds like a lot! Ligand Field Theory The molecular orbital diagram is consistent with the crystal field approach. Note that the t2g set of orbitals is non-bonding, and the eg set of orbitals is antibonding. 27. Ligand Field Theory The electrons from the ligands (12 electrons from 6 ligands in octahedral complexes) will fill the lower bonding orbitals. { 28. Molecular orbitals for Octahedral complexes The combination of the ligand and metal orbitals (4s, 4p x, 4p y, 4p z, 3d z2, and 3d x2-y2) form six bonding and six antibonding with a 1g, e g, t 1u symmetries. The metal T 2g orbitals do not have appropriate symmetry - nonbonding Electron in bonding orbitals provide the potential energy that holds ... Molecular orbital theory Octahedral complexesDiagrams with examplesExplainedThanks for watching!!!!!#chemistry
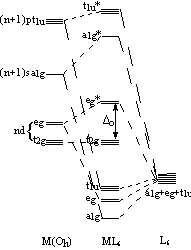
The tetrahedral MO diagram is similar to the octahedral molecular orbital diagram. On the left, the metal ion orbitals are present, and on the right side are the ligand orbitals. The center depicts the orbitals of the metal complex. There are four ligands in tetrahedral complexes. Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. Transcribed image text: Shown below is a molecular orbital diagram for an octahedral ML. complex and the character table. Assume there are no ligand orbitals with pi symmetry that interact with the metal. All Ngond orbitals are fully filled. Guiding fines connecting atomic orbitals to their corresponding molecular orbitals have been omitted. In octahedral complexes, the molecular orbitals created by the coordination of metal center can be seen as resulting from the donation of two electrons by each of six σ-donor ligands to the d-orbitals on the metal. The metal orbitals taking part in this type of bonding are nd, (n+1)p and (n+1)s. It should be noted down
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix octa. The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between the ligand atoms. A perfect octahedron belongs to the point group Oh. Examples of octahedral compound

Marina City Theater, Chicago, Illinois, Roof and Partial Concrete Frame Development Drawing (1961-1962) // Bertrand Goldberg American, 1913-1997
A qualitative molecular orbital diagram for octahedral compounds like W0 3. Electrons Per Shell, 2 8 18 32 12 2. Electron Configuration, [Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2. 1s 2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 4f14 5d4 6s2. Orbital Diagram. manual for problem e states that the electron configuration for Tungsten is [ Xe] 4f^14 5d^4 6s^2.
Show below is a molecular orbital diagram for an octahedral ML 6 complex and the O h character table. From the ligand pi orbitals, only the t 2g set is considered. All ligand orbitals are fully filled. Guiding lines connecting atomic orbitals to their corresponding molecular orbitals have been omitted.
Fig. 2. Simplified molecular orbital diagram for a low spia octahedral complex, such as [Co(NH3 )g, where A = energy difference a, e, and t may be antisymmetric (subscript ungerade) or centrosymmetric (subscript, gerade) symmetry orbitals.
1. Molecular orbital theory and the octahedron 2. The MO energy diagram and Δo 1. Octahedral transition metal complexes utilize s, p and d-orbitals in their bonding. For a first row transition metal, these are the 3d, 4s and 4p orbitals (the valence orbitals). Here we will create a molecular
This generates an octahedral molecular and electron geometry. You can see the final shape of this at the bottom. PRINCIPLES OF ORBITAL HYBRIDIZATION Orbital hybridization in "PF"_6^(-) requires that all six "P"-"F" bonds are identical; not necessarily in bond angle, per se, but in the orbitals used to construct the bond.
CONTROLS. This series of diagrams illustrate the symmetry adapted linear combinations of ligand σ orbitals, which are represented by spheres. The metal s orbital has a 1g symmetry as it is symmetric to all operations. Hence it bonds with all the ligand σ orbitals in phase. The p orbitals have t 1u symmetry.
Octahedral molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds wherein six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands are symmetrically arranged around a central atom. The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix octa-. An example of an octahedral compound is molybdenum hexacarbonyl (Mo(CO) 6).
Molecular Orbital Theory of Octahedral Complexes. Molecular Orbital Theory of Octahedral Complexes. In contrast to crystal field theory, molecular orbital included the covalent nature of the metal-ligand bond interaction. No Metal- Ligand -bonding ( bonding only) Let’s take [Co(NH3)6]3+ as an example. Using the LGO method, one can construct a qualitative MO diagram for bonding in a [ML6]n+ complex.
π‐MOs for Octahedral Complexes The reducible representation for the π‐ligand orbitals in O h: E 8C3 6C2 6C4 3C2′ i 6S4 8S6 3σh 6σd Γπ 12000-400000T1g + T2g + T1u + T2u irreducible representations x and y axes on each ligand The non-bonding t2gorbitals of an octahedral metal complex are oriented perfectly to form π-bonds with ligands
Transition Metal Oxide Perovskites: Band Structure, Electrical and Magnetic Properties Chemistry 754 Solid State Chemistry Lecture 22 May 20, ppt download
Molecular orbital diagram corresponding to an octahedral MX N complex. Atomic levels of the transition-metal impurity, M, (ligand anions, X) are depicted on the left-hand (right-hand) side of the ...
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. O22+ ... Identify the number of electron groups around a molecule with an : octahedral shape. 6. Give the approximate bond angle for a molecule with an : octahedral shape. 90. The bond angle in NH3 is. 107. Give the major force between acetone and ...
#bondingincoordinationcompounds #octahedralcomplex
In about 15 minutes animated video, the concept of Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), symmetry of metal atomic orbitals in different ligand environment and mole...
High‐Spin and Low‐Spin Configurations • In an octahedral complex, electrons fill the t 2g and e g orbitals in an aufbau manner, but for configurations d4 - d7 there are two possible fillingschemesdependingon the magnitudeof o. • The relative magnitudes of o and the mean pairing energy, P, determine whether a high spin or low spinstate isobserved inoctahedralcomplexes.
The CFT diagram for tetrahedral complexes has d x 2 −y 2 and d z 2 orbitals equally low in energy because they are between the ligand axis and experience little repulsion. In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane.
Figure 3 | The 18-electron rule and electron counting in transition metal compounds: theory and application | SpringerLink

Mobile Delousing Unit, Truck Equipment, Plan of Operation and Erection Procedure, Presentation Drawing (1943) // Bertrand Goldberg American, 1913-1997

Sky Frame Orbit (1964–73) // Helen Frankenthaler (American, 1928-2011) printed by Zigmunds Priede and Donn Steward published by Universal Limited Art Editions (American, founded 1955)














![Molecular orbital diagram of [CoF 6 ] 3-complex with six p ...](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Majid-Monajjemi/publication/257140982/figure/tbl4/AS:669050661244944@1536525516817/continued_Q640.jpg)







0 Response to "38 octahedral molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment