41 cn molecular orbital diagram
Molecular Orbital Theory Heteronuclear Diatomic (Cyanide ... Dr. Shields shows you how to draw the MO correlation diagram for cyanide (CN-), calculate the MO bond order, and write the MO electron configuration with an ... Molecular Orbital diagram of CN- - YouTube
CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... Molecular Orbital Diagram Molecular Orbital Theory is slightly different from VBT and orbital hybridization. Here, AOs from different atoms inside the molecule can come together to form molecular orbitals or MOs. Therefore, valence electrons are shared inside the molecule. The electronic configuration of both C and N are as follows:
Cn molecular orbital diagram
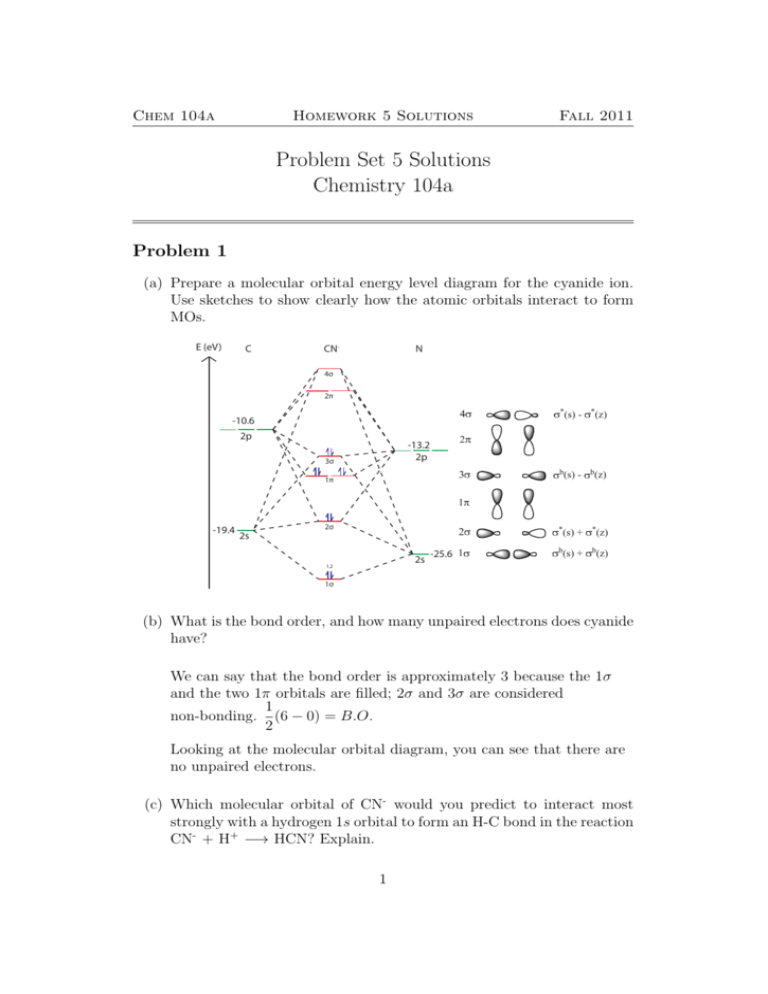
What is the bond order of CN-? - Quora Answer (1 of 6): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i... PDF Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. Describe The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Co - 17 images ... [Describe The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Co] - 17 images - solved 13 choose the orbital diagram that represents the, linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao, explain step by step how to draw molecular orbital diagram, choose the orbital diagram that represents the ground,
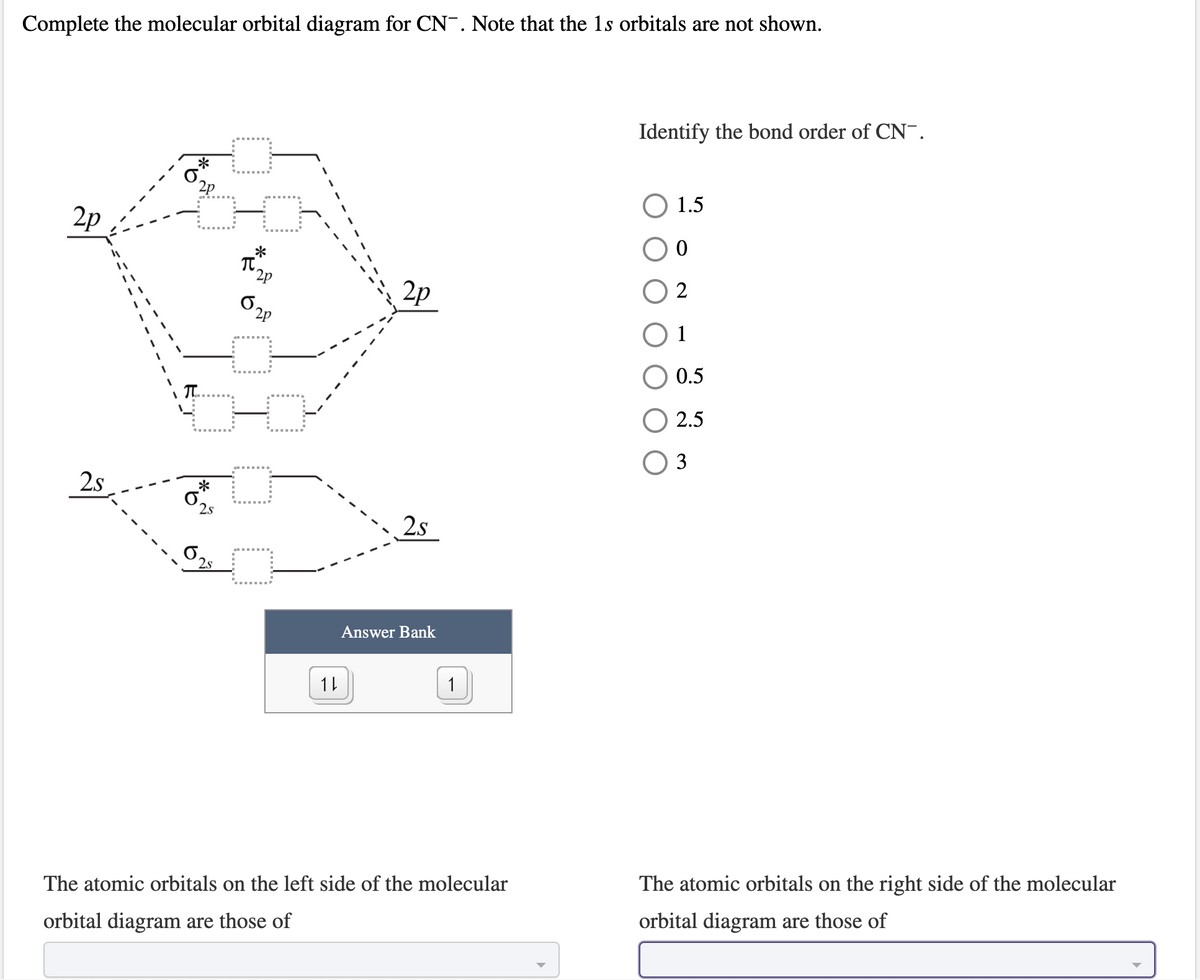
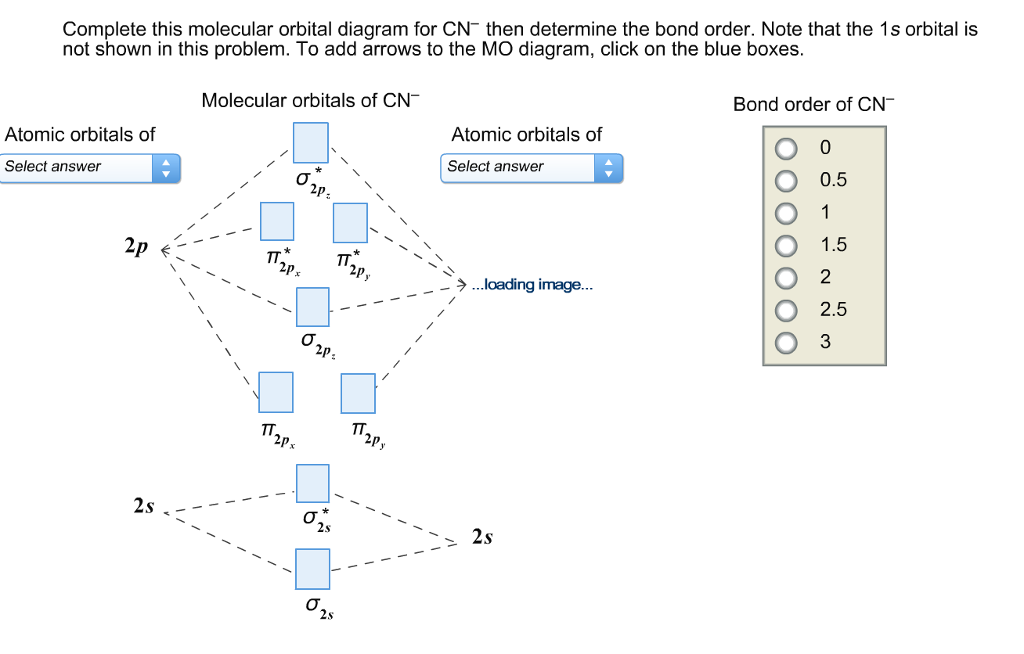
Cn molecular orbital diagram. Properties of water - Wikipedia The molecular orbital theory explanation (Bent's rule) is that lowering the energy of the oxygen atom's nonbonding hybrid orbitals (by assigning them more s character and less p character) and correspondingly raising the energy of the oxygen atom's hybrid orbitals bonded to the hydrogen atoms (by assigning them more p character and less s ... Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN- then ... Question "Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN- then determine the bond order" Complete this molecular orbital diagram for CN - then determine the bond order. Note that the 1s orbital is not shown in this problem. To add arrows to the MO diagram, click on the blue boxes. Bond order of CN - 0. 0.5. 1. 1.5. 2. 2.5. 3. Answer CN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond order Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital or hetero-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital. Clearly, CN is hetero orbital. 3. Molecular cloud - Wikipedia A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen, H 2), and the formation of H II regions.
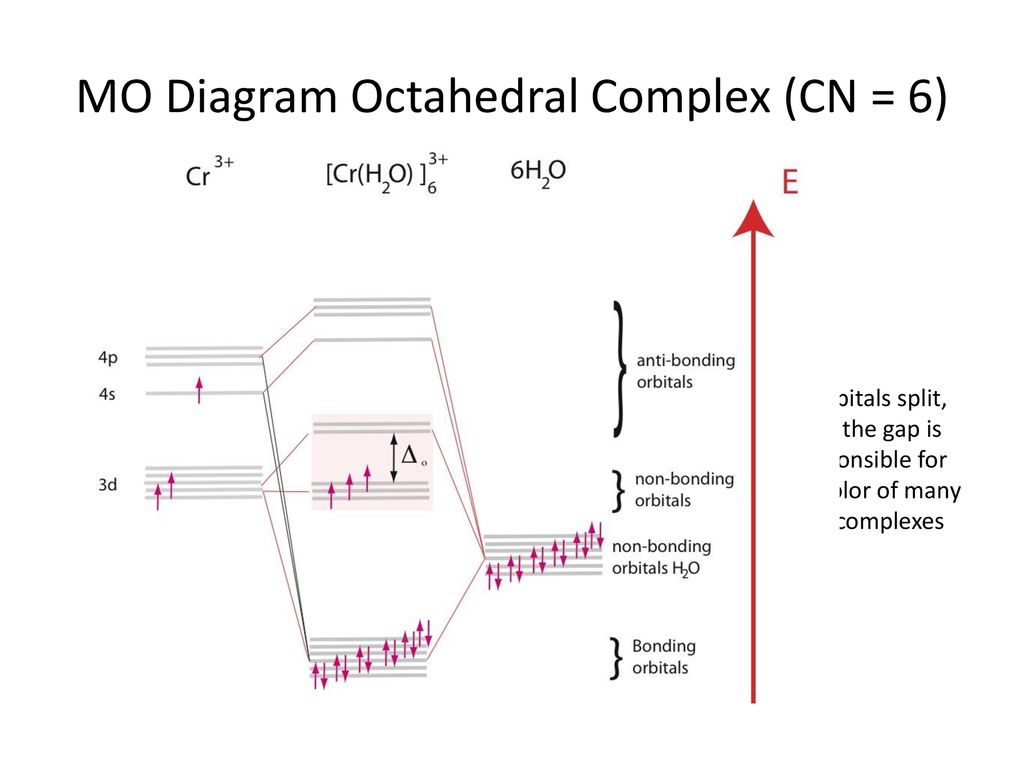
MO Diagram of CN-< - Hunt Research Group Molecular Orbital Mixing. More detail was added to this answer in response to input and questions from students in the class of 2008. If you have suggestions or contributions please e-mail me. First of all while the stage 1 (pre mixing diagram) of diatomics is very easy to produce, the mixing in diatomics is very difficult to evaluate because ... Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals - Chemical ... Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons . Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by N b and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.. 1) If N b > Na,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than ... Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram - wiringall.com The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN- (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion). Figure \ (\PageIndex {2}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for \ (\ PageIndex {12}\) to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). In the traditional Lewis picture there are two lone pairs on the cyanide ion. Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Molecular Orbital Theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds.
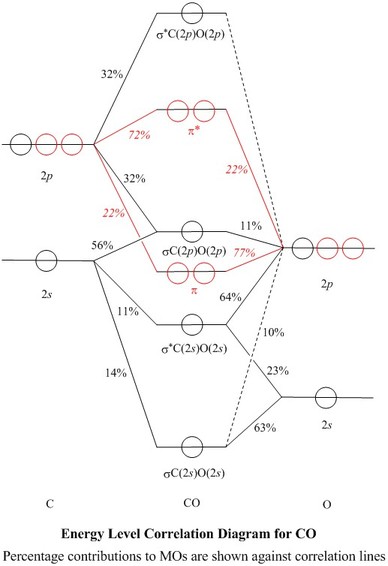
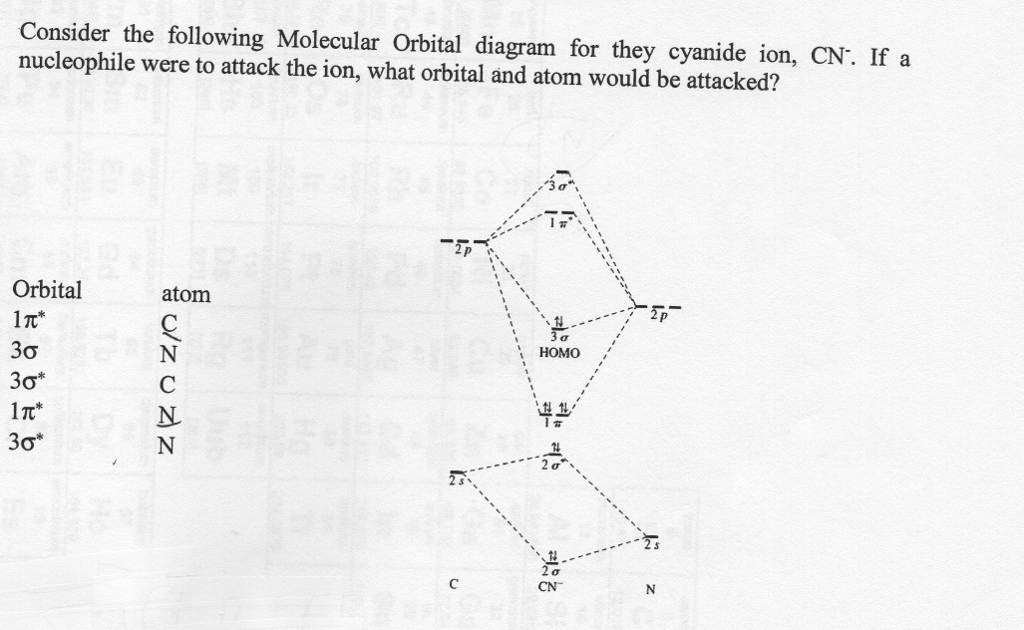
The molecular orbital configuration of CN^+ is - Toppr Ask The molecular orbital configuration of C N + is K K σ (2 s) 2, σ ∗ (2 s) 2, π (2 p x ) 2, π (2 p y ) 2. Bond order is 2 . All the electrons are paired and ion is diamagnetic. Molecular Orbital - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The occupied molecular orbitals and conduction molecular orbitals contain DOS. In bulk particles, DOS is a continuous function of energy, while in CNTs (and other 1D nanoparticles), DOS is made of discontinuous spikes, ascending and then descending sharply—the Van hove singularities ( Figure 39 ; v1, v2 and v3 are DOS for HOMO and c1, c2 and ... SOLVED:Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the cyanide ... uh, molecular orbital represents. So they have, like, behavior off electron. They're formed into the linear combination for atomic orbital spawned in there at them. So fair manicure. Um, the the electronic configuration off carbon and nitrogen is carbon is one is to toe to toe pay two and a nitrogen is 12 tourist to and to be three. So the total electron in the Hadron ah, hit your own nuclear ... Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above.
Solved Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note ... Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Answered: 1. Draw the molecular orbital diagram… | bartleby Solution for 1. Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the following molecules: (a) NH3 (b) CO (c) CN 2. Explain how the backbonding occur between metal and CO…
Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide - ChemTube3D Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules.
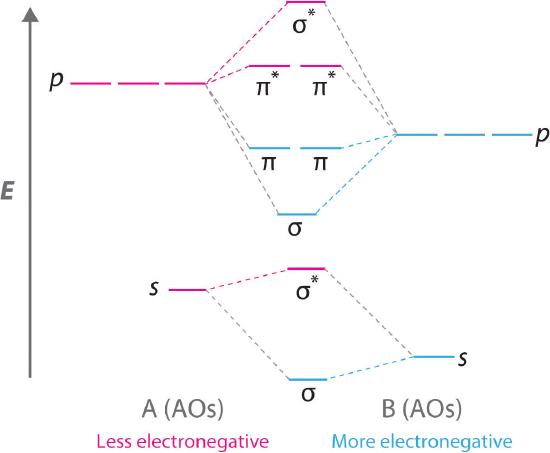
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia Molecular orbital diagrams are diagrams of molecular orbital (MO) energy levels, shown as short horizontal lines in the center, flanked by constituent atomic orbital (AO) energy levels for comparison, with the energy levels increasing from the bottom to the top. Lines, often dashed diagonal lines, connect MO levels with their constituent AO levels.
PDF Simple Molecular Orbital Theory - University of California ... Using Symmetry: Molecular Orbitals One approach to understanding the electronic structure of molecules is called Molecular Orbital Theory. • MO theory assumes that the valence electrons of the atoms within a molecule become the valence electrons of the entire molecule.
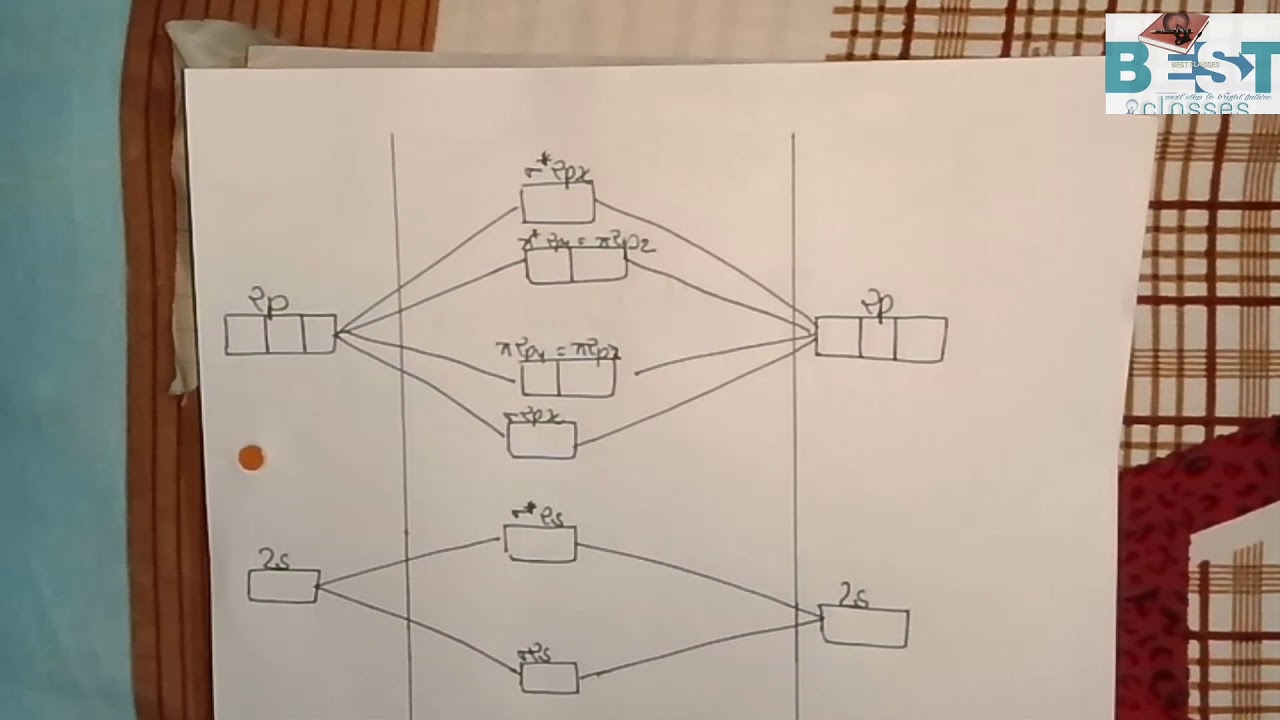
Molecular Orbital Theory - Purdue University Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram - schematron.org CN- (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in carbon is six.MOLECULAR ORBITAL DIAGRAM KEY Draw molecular orbital diagrams for each of the following molecules or ions.
What is the molecular orbital diagram for C_2^-? | Socratic The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the neutral C2 molecule is -- I'll use the notation given to you in the diagram. C2:(1sσ)2(1s* σ)2(2sσ)2(2s* σ)2(2pπ)4. The electron configuration of the C− 2 ion will be.
OneClass: What are the molecular orbital diagram, bond ... The molecular orbital diagram of NO shown in Figure 10.47 also applies to the following species. Write the molecular orbital electron configuration of each, indicating the bond order and the number of unpaired electrons.
Describe The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Co - 17 images ... [Describe The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Co] - 17 images - solved 13 choose the orbital diagram that represents the, linear combination of atomic orbitals lcao, explain step by step how to draw molecular orbital diagram, choose the orbital diagram that represents the ground,
PDF Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
What is the bond order of CN-? - Quora Answer (1 of 6): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here's a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i...







![Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT), Bonding in [Fe(CN)6]4– ion ...](https://ebrary.net/htm/img/33/1908/304.png)







![On the gold–ligand covalency in linear [AuX 2 ] − complexes ...](https://pubs.rsc.org/image/article/2015/DT/c4dt04031g/c4dt04031g-f5_hi-res.gif)





0 Response to "41 cn molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment