39 enzyme reaction coordinate diagram
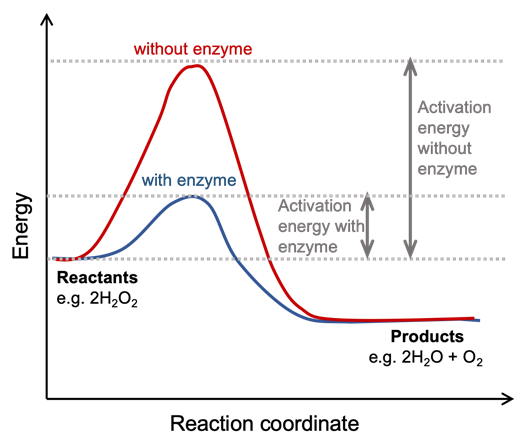
Covalent modifications to enzymes (video) | Khan Academy And looking at a reaction coordinate diagram you notice that enzymes do this by lowering the reaction's activation energy. Also, before we talk about covalently modified enzymes, I want to remind you that not all enzymes are proteins. And often, when we think of enzymes we think of proteins, which are amino acid polymers with primary, secondary ... Enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams (1) Quiz This is an online quiz called Enzyme reaction coordinate diagrams (1) There is a printable worksheet available for download here so you can take the quiz with pen and paper. Your Skills & Rank. Total Points. 0. Get started! Today's Rank--0. Today 's Points. One of us! Game Points. 8.
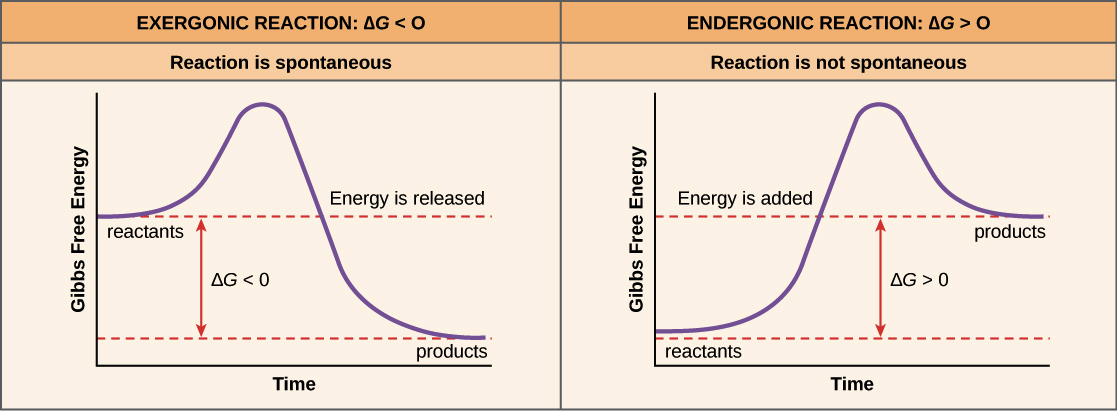
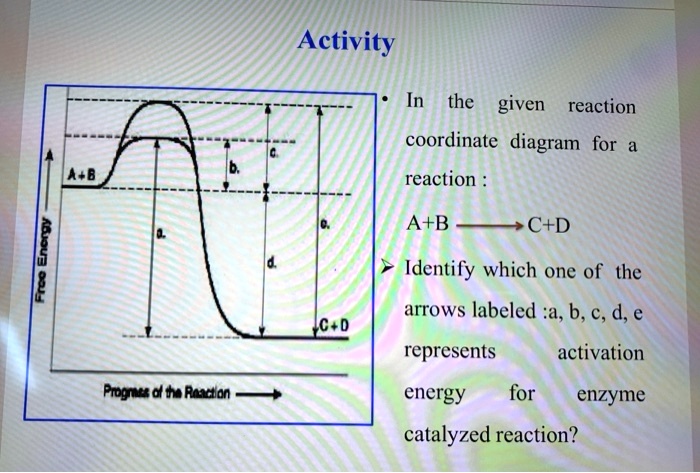
Solved Use the reaction coordinate diagram of an enzyme ... Transcribed image text: Use the reaction coordinate diagram of an enzyme catalyzed reaction shown below to answer Questions 5 through 10 From this diagram you can conclude: (A) The forward reaction is endergonic. (B) The forward reaction is exothermic. (C) The forward reaction is endothermic. (D) The forward reaction is at equilibrium.
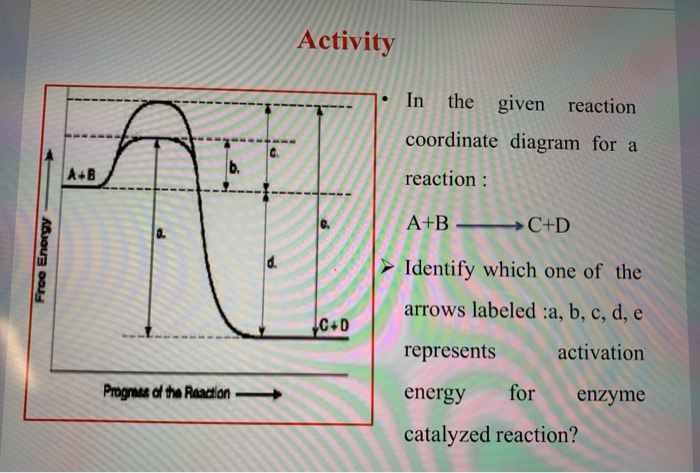
Enzyme reaction coordinate diagram
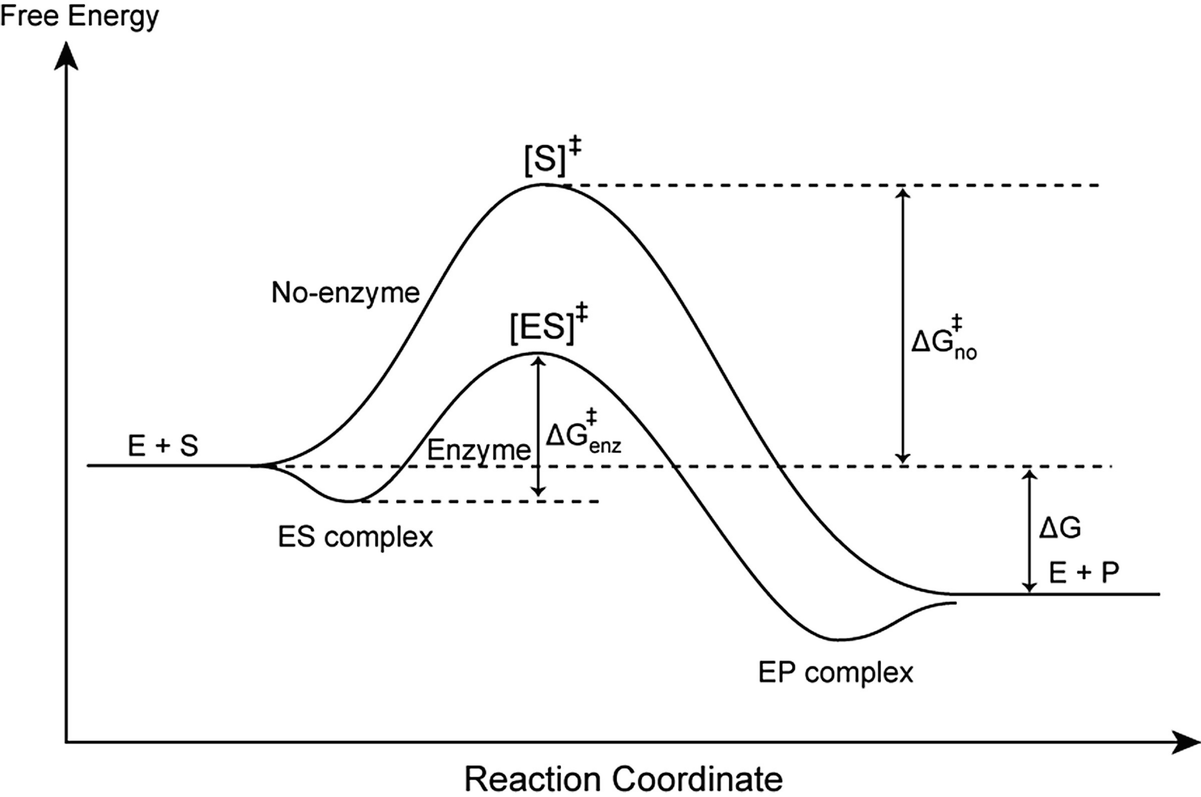
Biochem Exam 2 Flashcards - Quizlet A reaction coordinate diagram comparing an uncatalyzed reaction with an enzyme-catalyzed reaction can directly illustrate that the enzyme _____, but will not directly illustrate that the enzyme _____. PDF Enzyme An introduction to enzymes - University of Houston ... Fig. 1 Reaction coordinate diagram for a chemical reaction Fig. 2 Reaction coordinate diagram comparing enzyme-catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. 3 of 16 As shown in Fig. 1, from starting material to product, the highest point in terms of energy is called transition 04.02 Reaction Coordinate Diagrams and Stability Trends ... General structure of a reaction coordinate diagram, including transition states and intermediates. Overall free energy change and activation energy. Definiti...
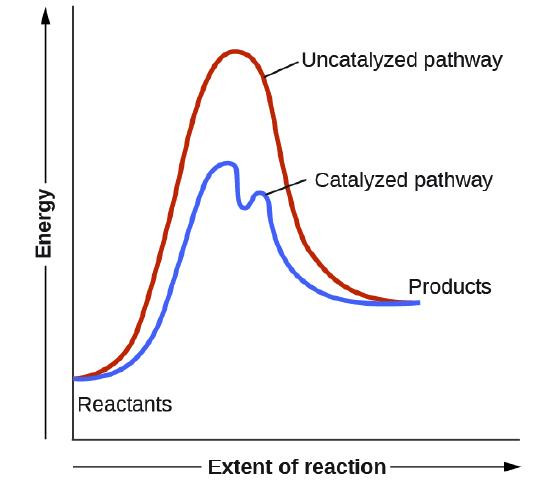
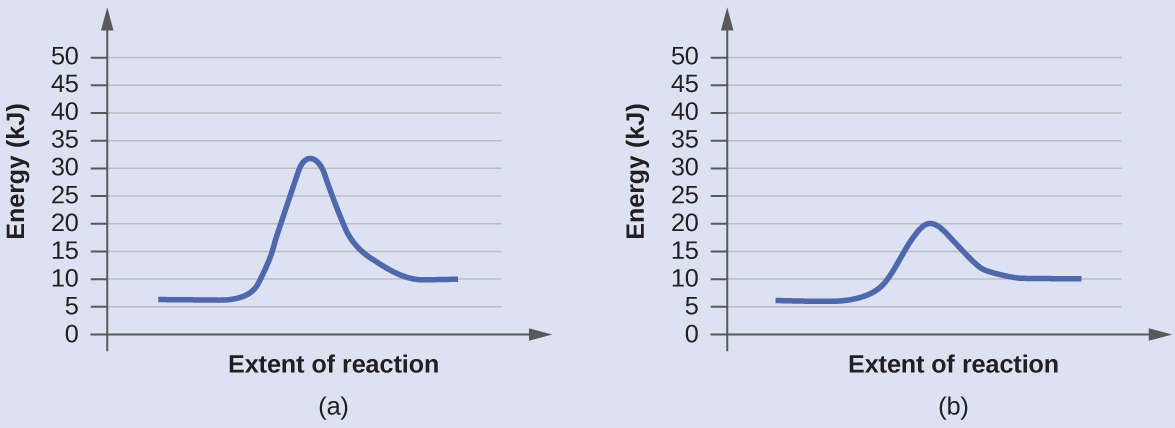
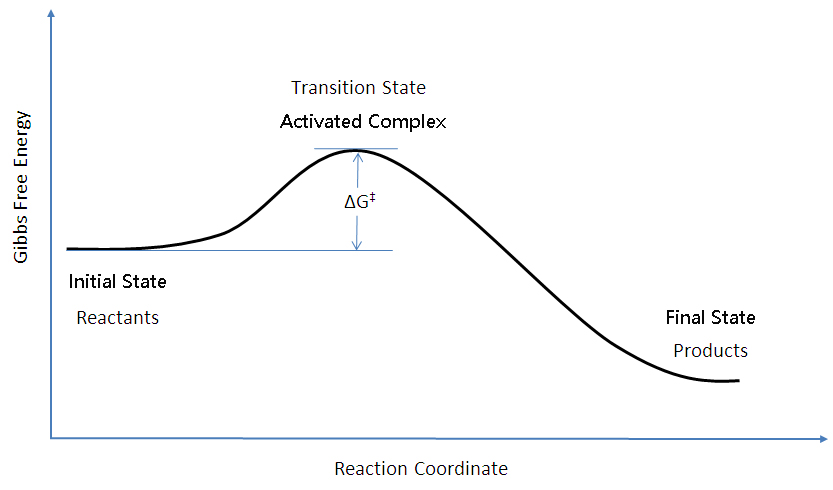
Enzyme reaction coordinate diagram. Reaction Coordinate Diagrams - College Chemistry The fully filled in reaction coordinate diagram is displayed below. The arrow marked in the question represents the activation energy, which is the energy barrier that must be overcome in order for the reactants to form products. This reaction is also exothermic because the energy of the products is lower than that of the reactants. Enzymes | Biology I - Lumen Learning Enzymes. A substance that helps a chemical reaction to occur is a catalyst, and the special molecules that catalyze biochemical reactions are called enzymes. Almost all enzymes are proteins, made up of chains of amino acids, and they perform the critical task of lowering the activation energies of chemical reactions inside the cell. Reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed ... Download scientific diagram | Reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. from publication: Design, synthesis and characterization of enzymeanalogue-built polymer catalysts as ... Enzymes - University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Reaction Coordinate Diagram We've already seen that the rate of a chemical reaction depends on the height of the activation barrier in the reaction coordinate diagram.Consider the reaction below where reactants A and B combine to form the product C.
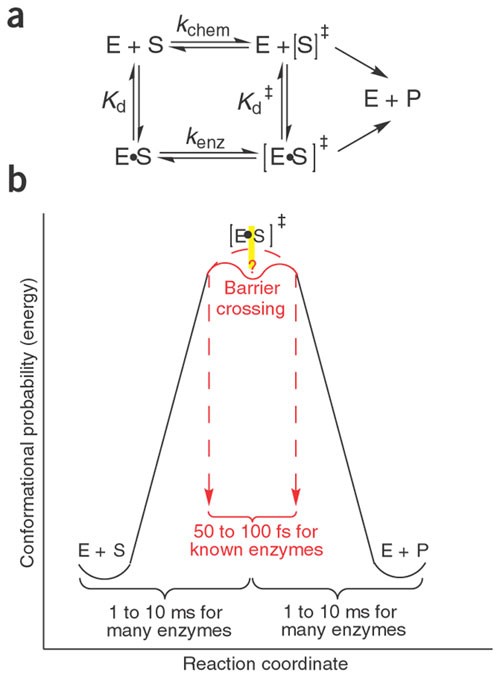
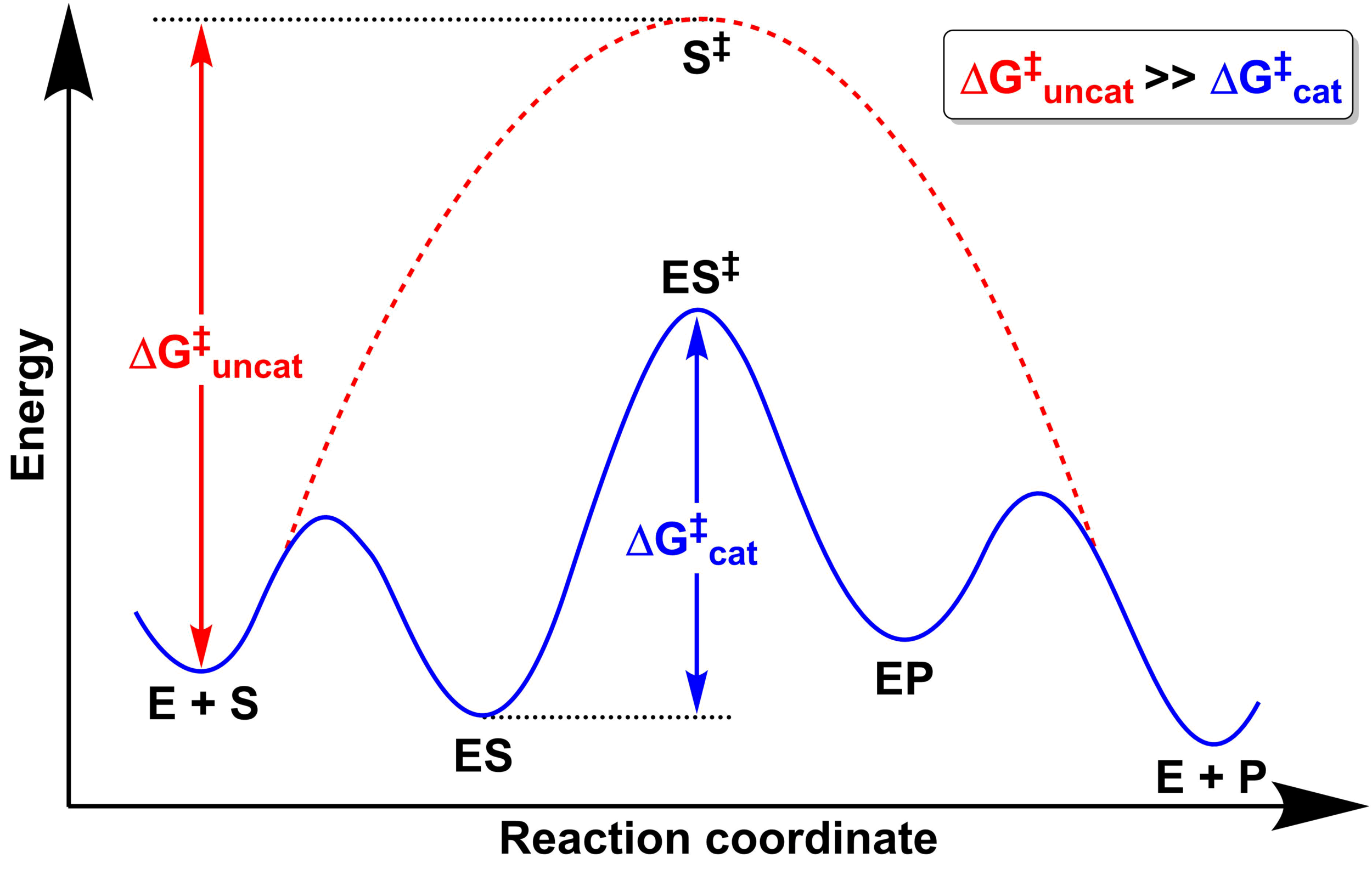
Compare and contrast the reaction coordinate diagrams for ... Volume 24 February 15, 2013 Reaction coordinate diagrams | 435 chain. Thus the reaction coordinate diagram (Figure 3C) reflects a pathway that proceeds via four transition states, two tetrahedral in-termediates and a covalently bonded acyl enzyme intermediate. In this reaction, the overall ΔG is negative and the formation of the first Biochem Chapter 6 question flashcards Flashcards - Quizlet 12) Which of the following is seen in a reaction coordinate diagram for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction that uses covalent catalysis? A) an intermediate B) two distinct transition states C) reactants that are lower in energy than an intermediate D) products that are lower in energy than an intermediate E) all of the above Chapter 6 - Enzymes. Practice Questions Flashcards - Quizlet A molecular form that occupies the highest point on a reaction coordinate diagram. Substrate. The molecule that undergoes chemical change within an enzymatic reaction. Kinetically Stable. ... All of the above are roles that an enzyme will play in increasing reaction rates. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › UreaseUrease - Wikipedia Sumner's work was the first demonstration that a protein can function as an enzyme and led eventually to the recognition that most enzymes are in fact proteins. Urease was the first enzyme crystallized. For this work, Sumner was awarded the Nobel prize in chemistry in 1946. The crystal structure of urease was first solved by P. A. Karplus in 1995.
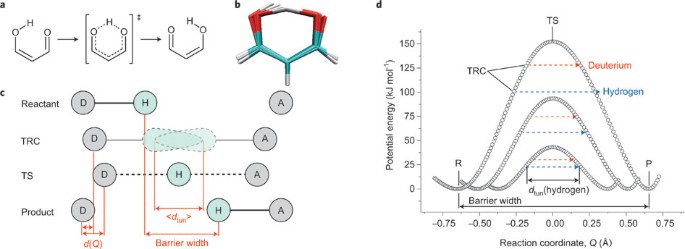
Enzymes and activation energy (video) - Khan Academy Now, we can look at the process of this reaction using something called a reaction coordinate diagram. And here, we'll plot the energy state of our molecules against the progress of the reaction. So essentially, using this graph, we'll follow the energy level of molecule A as it's converted to molecule B. Remember that a molecule's energy level ... EOF Exam 2 HW 6 Flashcards | Quizlet A reaction coordinate diagram comparing an uncatalyzed reaction with an enzyme-catalyzed reaction can directly illustrate that the enzyme _____, but will not directly illustrate that the enzyme _____. A. stabilizes the transition state; orients the substrates appropriately for the reaction to occur en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Kinetic_isotope_effectKinetic isotope effect - Wikipedia Note that in this schematic diagram, the curves actually represents (3N-6)- and (3N ‡-7)-dimensional hypersurfaces, and that the vibrational mode whose ZPE is illustrated at the transition state is not the same one as the reaction coordinate. The reaction coordinate represents a vibration with a negative force constant (and imaginary ...
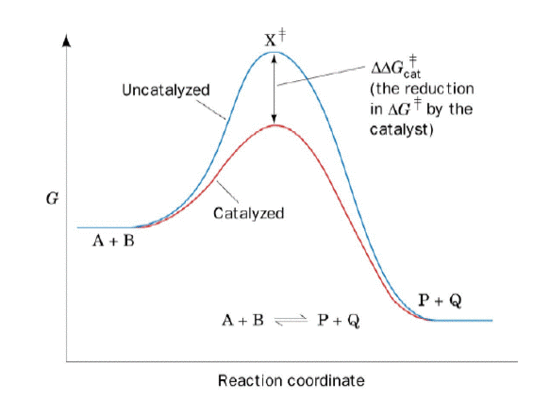
PDF The Molecular Basis of Enzymatic Catalysis Shown are two reaction coordinate diagrams for a catalyzed reaction (blue line) and its corresponding uncatalyzed reaction (red line). The Gibbs free energy difference of the products and reactants is the same regardless of whether or not the reaction is catalyzed; consequently, ΔG° rxn is the same for both the catalyzed and uncatalyzed ...
Enzyme reactivity Flashcards - Quizlet Enzyme-catalyzed reaction coordinate diagrams have an initial intermediate that represents an _____. enzyme binding to the substrate Consider the following enzyme-catalyzed reaction (where E = enzyme, S = substrate, and P = product):
CHEM 440 - Enzyme kinetics - Gonzaga University reaction coordinate diagram shows that the energy of activation for the reverse reaction is lowered by the catalyst as well. Enzymatic catalysis The ability of enzymes to catalyze reactions depends on their ability to interact directly and specifically with
04.02 Reaction Coordinate Diagrams and Stability Trends ... General structure of a reaction coordinate diagram, including transition states and intermediates. Overall free energy change and activation energy. Definiti...
PDF Enzyme An introduction to enzymes - University of Houston ... Fig. 1 Reaction coordinate diagram for a chemical reaction Fig. 2 Reaction coordinate diagram comparing enzyme-catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. 3 of 16 As shown in Fig. 1, from starting material to product, the highest point in terms of energy is called transition
Biochem Exam 2 Flashcards - Quizlet A reaction coordinate diagram comparing an uncatalyzed reaction with an enzyme-catalyzed reaction can directly illustrate that the enzyme _____, but will not directly illustrate that the enzyme _____.


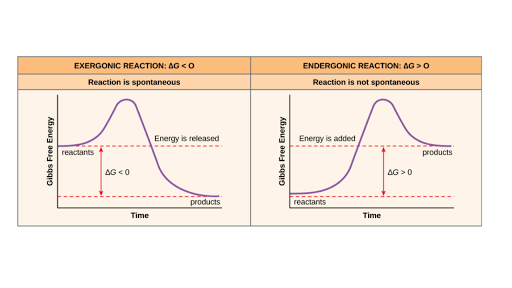
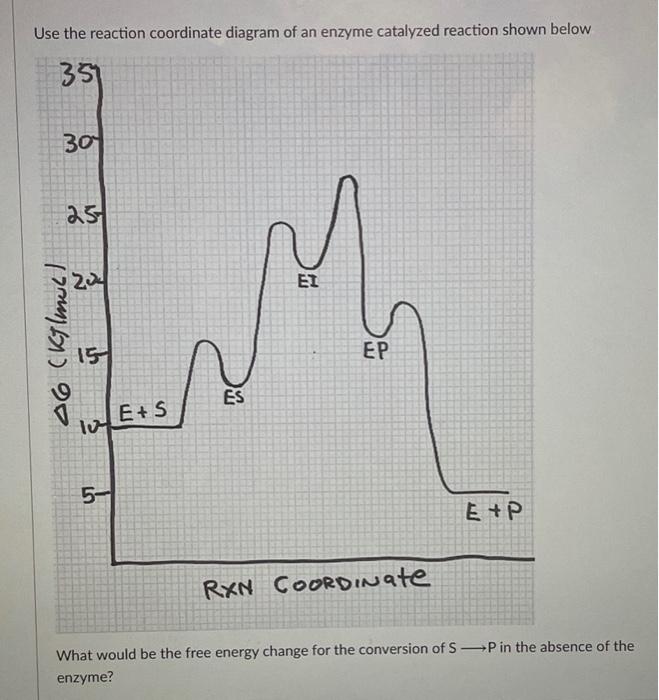
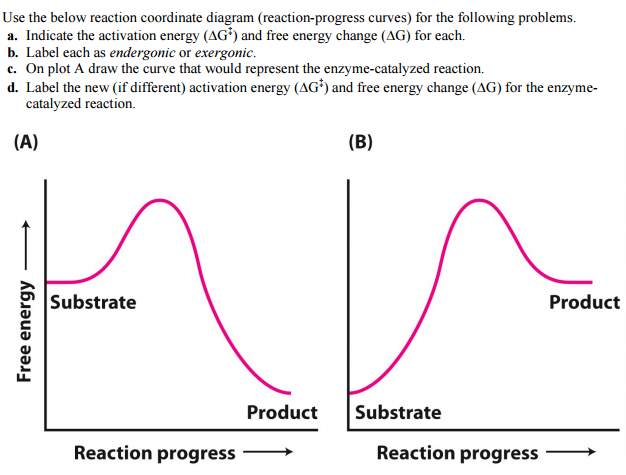




.png)








0 Response to "39 enzyme reaction coordinate diagram"
Post a Comment