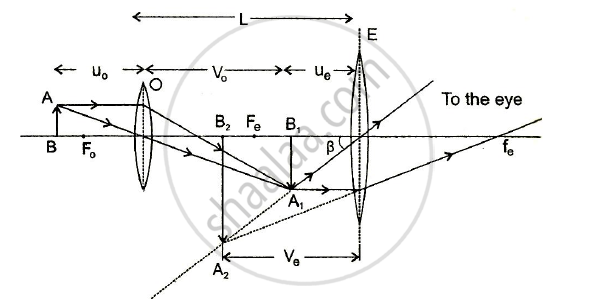
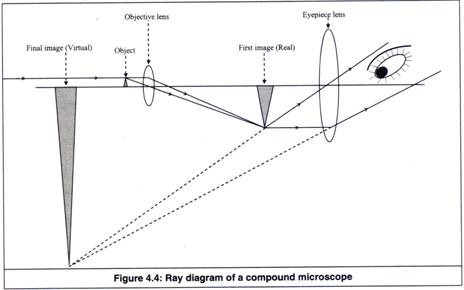
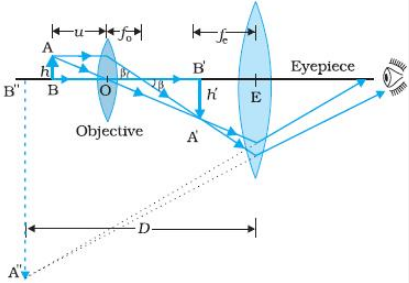
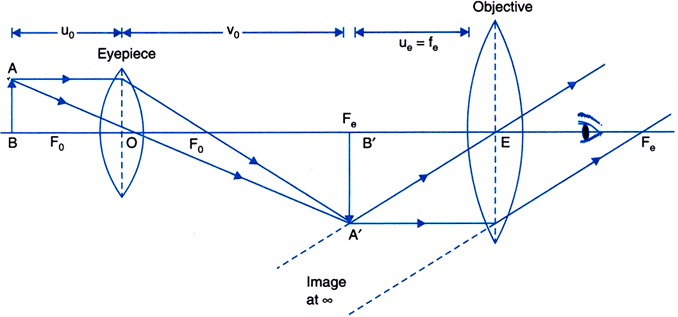
39 diagram of compound microscope
Structure of Cell: Definition, Types, Diagram, Functions ... The ordinary compound microscope of today is a greatly improved design of the original Hooke’s microscope. However, the cells which Hooke observed had no information about the organelles which are to be present inside the cell in most living organisms. In \(1674\), Antony Van Leeuwenhoek, a Dutch microscopist, made an important contribution to the cell theory. He was … How does a microscope work? - Explain that Stuff 05/12/2020 · A compound microscope uses two or more lenses to produce a magnified image of an object, known as a specimen, placed on a slide (a piece of glass) at the base. The microscope rests securely on a stand on a table. Daylight from the room (or from a bright lamp) shines in at the bottom. The light rays hit an angled mirror and change direction, traveling …
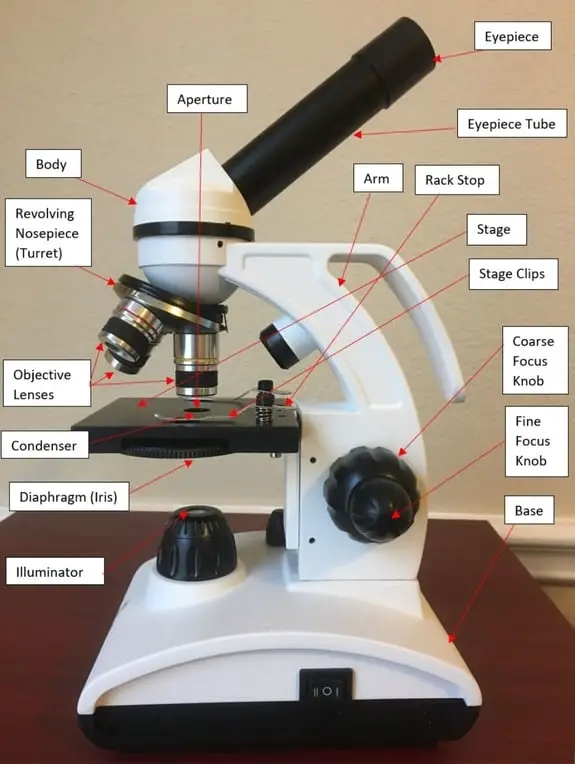
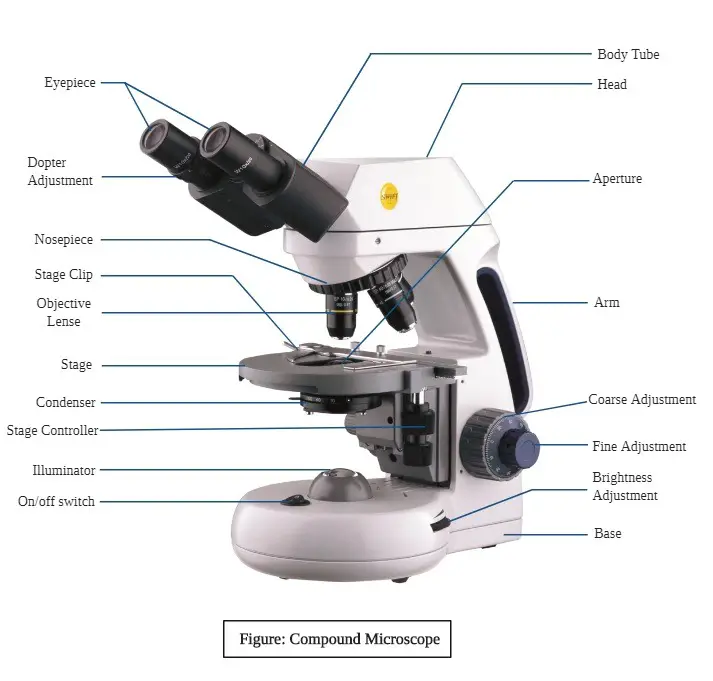
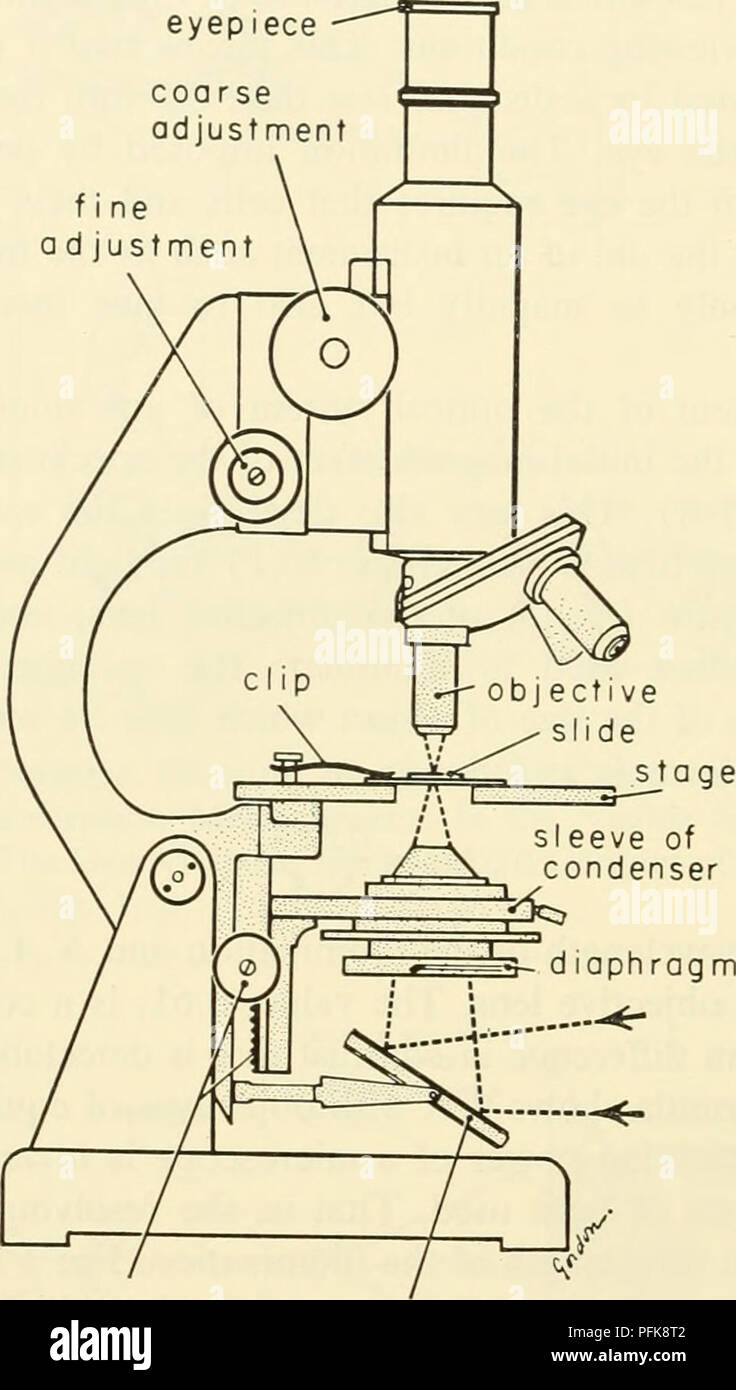
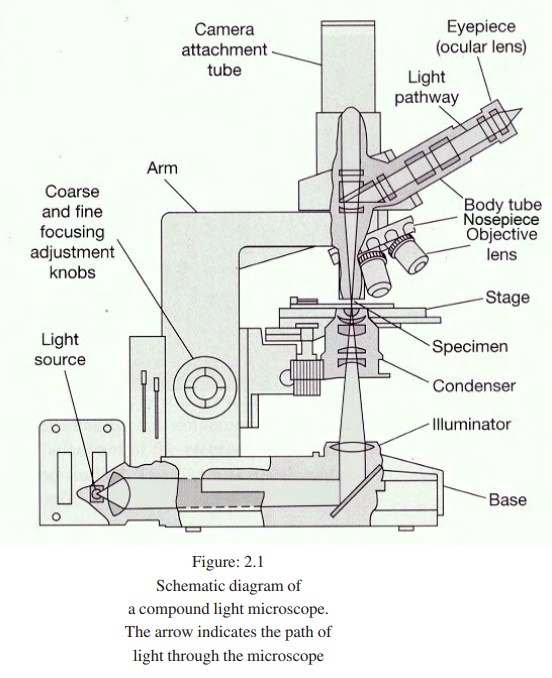
Lab 1A: Microscopy I - University of Kentucky diagram of the compound light microscope in Figure 1. Describe the function of each lens in producing the magnified image of a specimen: Condenser Lens: (#4) gathers light from light source and allows a small cone of light to reach a portion of the specimen. Objective Lens: (#5) gathers light diffracted from . the specimen and focuses it into a magnified image in the …

Diagram of compound microscope
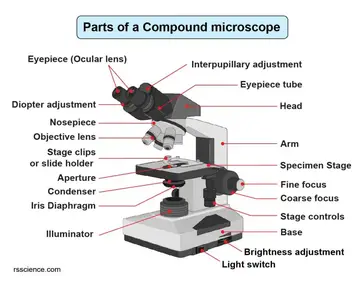
Ternary Phase Diagram - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The ternary phase diagram of the Mg–Nd–Ag system is rather incomplete (Berger and Weiss, ... This compound contains 23–26% Mn and 5.6–9.5% Ni and has an orthorhombic structure (space group Bbmm, Bbm2, or Bb2m, ~160 atoms per unit cell) with lattice parameters a = 2.38 nm, b = 1.25 nm, c = 0.755 nm; and density, 3.62 g/cm 3. The projection of liquidus surface and the … Parts of the Light Microscope - Science Spot B. NOSEPIECE microscope when carried Holds the HIGH- and LOW- power objective LENSES; can be rotated to change MAGNIFICATION. Power = 10 x 4 = 40 Power = 10 x 10 = 100 Power = 10 x 40 = 400 What happens as the power of magnification increases? Electron Microscope- Definition, Principle, Types, Uses ... 04/11/2021 · An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. It is a special type of microscope having a high resolution of images, able to magnify objects in nanometres, which are formed by controlled use of electrons in a vacuum captured on a phosphorescent screen.
Diagram of compound microscope. Electron Microscope- Definition, Principle, Types, Uses ... 04/11/2021 · An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination. It is a special type of microscope having a high resolution of images, able to magnify objects in nanometres, which are formed by controlled use of electrons in a vacuum captured on a phosphorescent screen. Parts of the Light Microscope - Science Spot B. NOSEPIECE microscope when carried Holds the HIGH- and LOW- power objective LENSES; can be rotated to change MAGNIFICATION. Power = 10 x 4 = 40 Power = 10 x 10 = 100 Power = 10 x 40 = 400 What happens as the power of magnification increases? Ternary Phase Diagram - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The ternary phase diagram of the Mg–Nd–Ag system is rather incomplete (Berger and Weiss, ... This compound contains 23–26% Mn and 5.6–9.5% Ni and has an orthorhombic structure (space group Bbmm, Bbm2, or Bb2m, ~160 atoms per unit cell) with lattice parameters a = 2.38 nm, b = 1.25 nm, c = 0.755 nm; and density, 3.62 g/cm 3. The projection of liquidus surface and the …
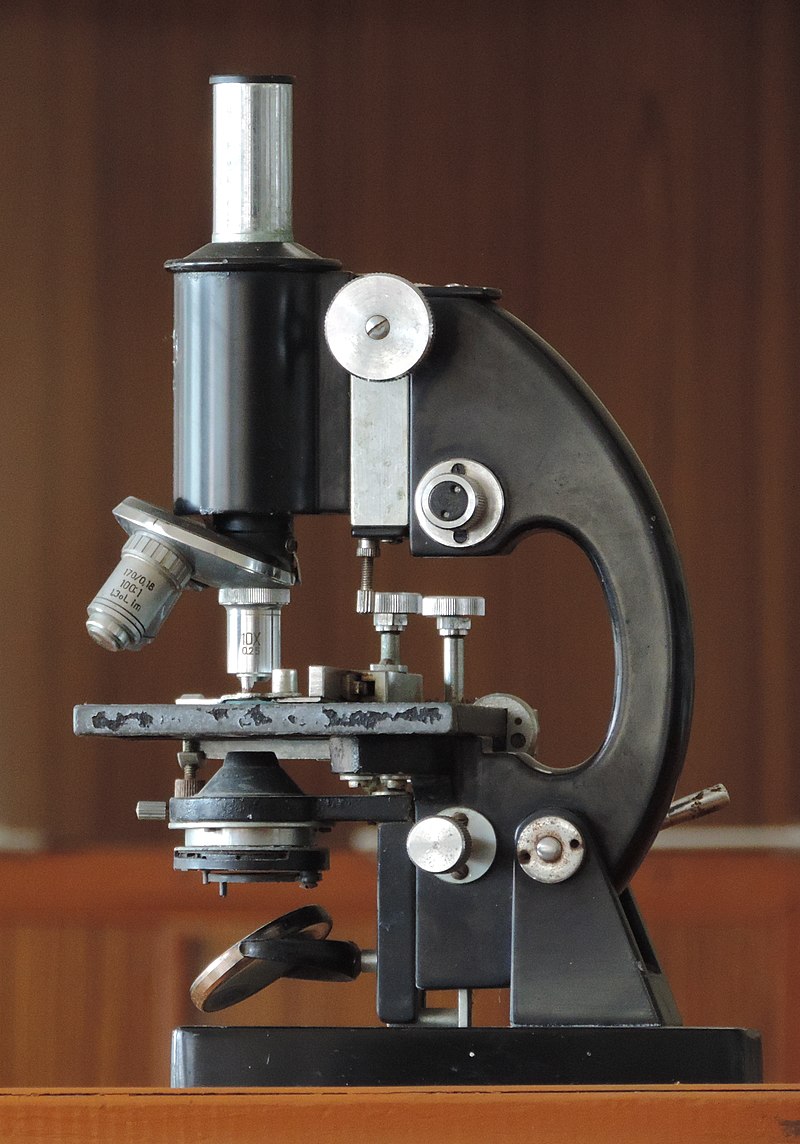
















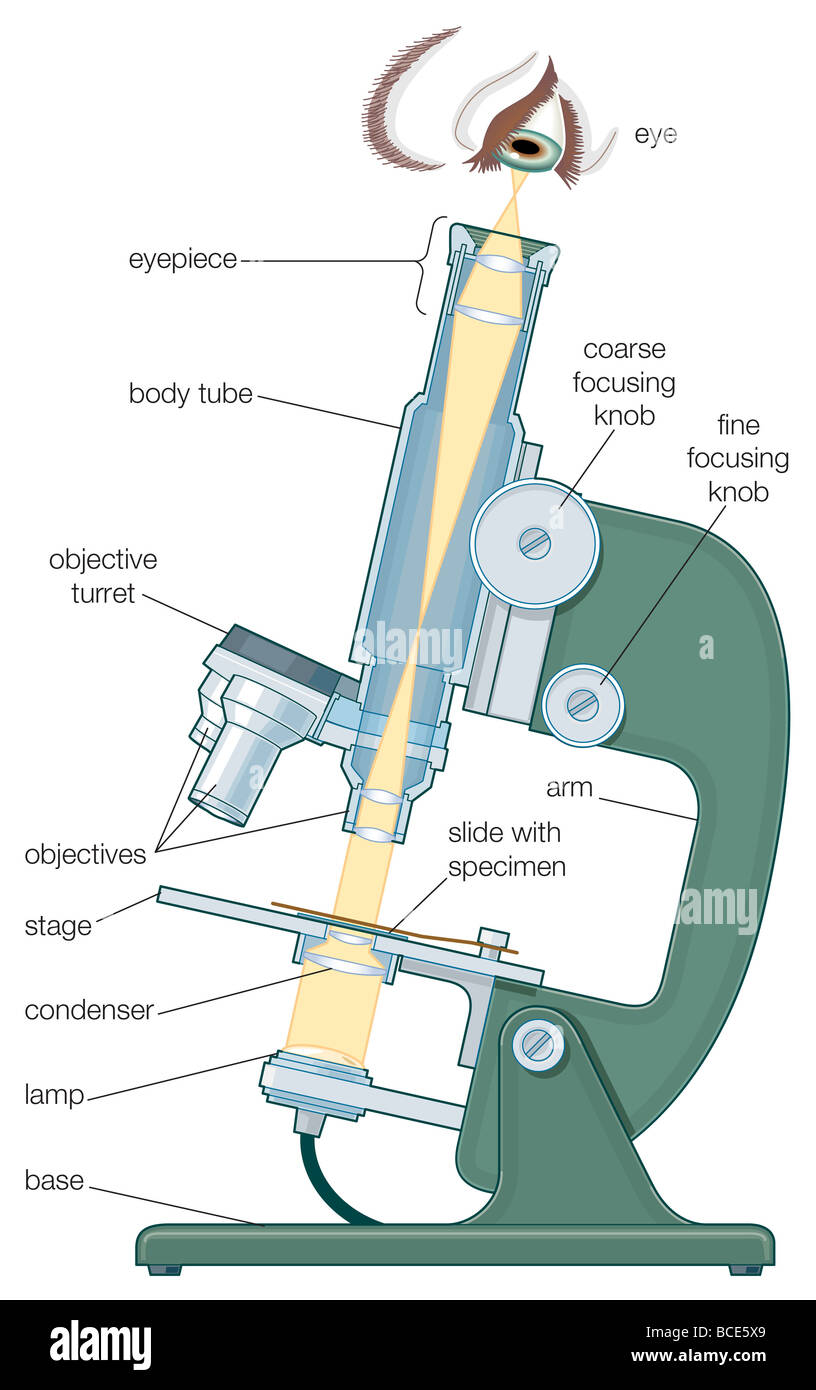


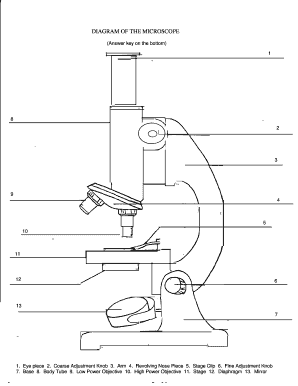



0 Response to "39 diagram of compound microscope"
Post a Comment