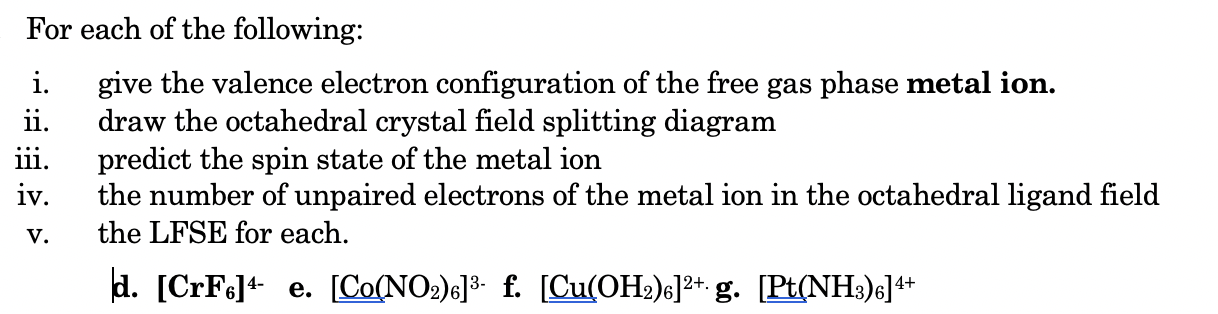
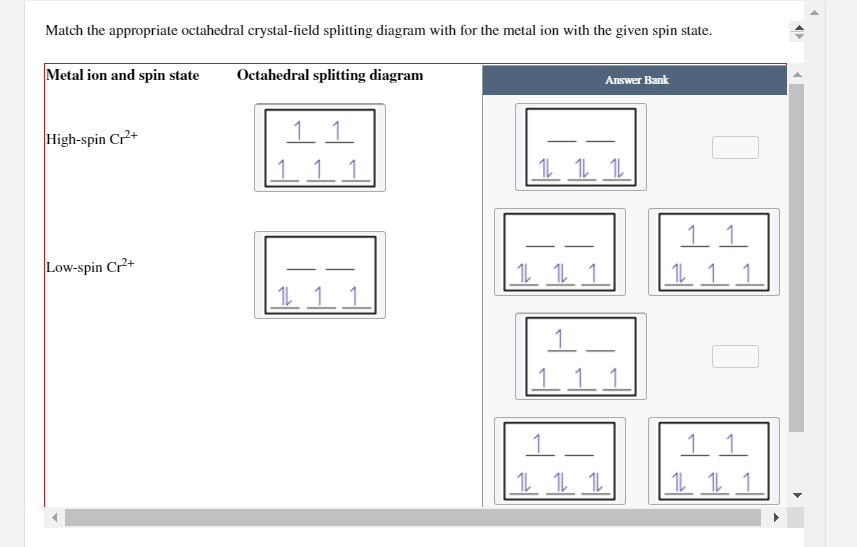
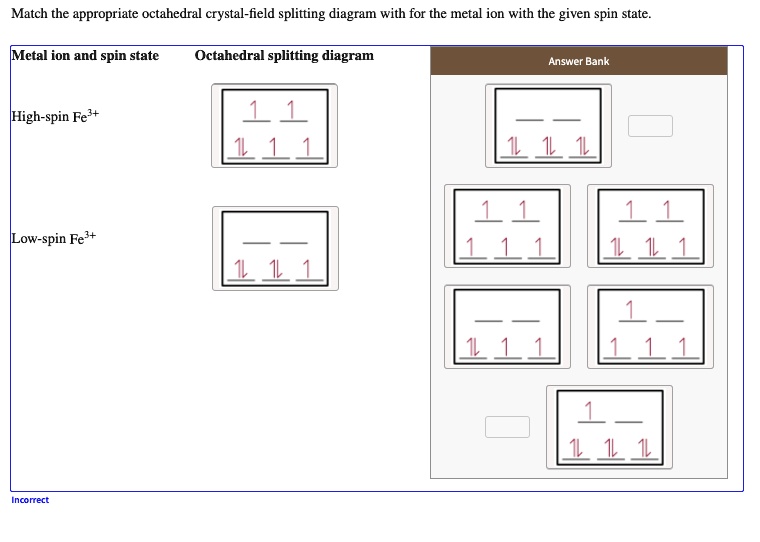
38 draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion.
PDF D-orbital splitting diagrams - University of California ... D-orbital splitting diagrams Use crystal field theory to generate splitting diagrams of the d-orbitals for metal complexes with the following coordination patterns: 1. Octahedral 2. Tetrahedral 3. Trigonal bipyramidal 4. Square pyramidal d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz 5. Square planar d z2x2-y d xy d yzxz d z2 d x2-yxy d yz d xz d z2 d x2-y2 d xy d yz d ... Energy storage through intercalation ... - OUP Academic Intercalation is the process by which a mobile ion or molecule is reversibly incorporated into vacant sites in a crystal lattice. Despite modest capacities, this mechanism minimizes volume change and mechanical strain during repeated insertion and extraction of alkali ions. As a consequence, this mechanism leads to good cycling performance and governs the operation of …
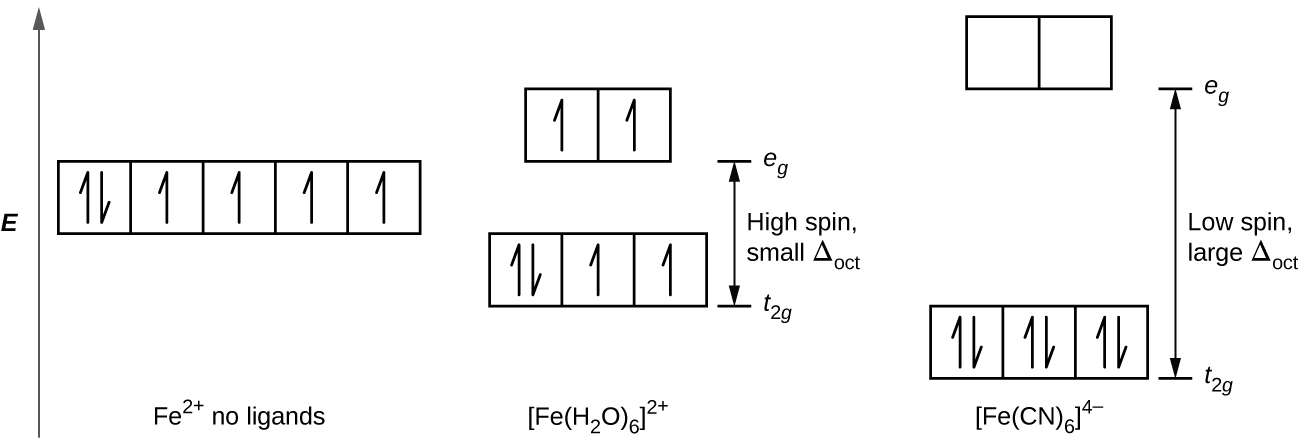
4.3: High Spin and Low Spin Complexes - Chemistry LibreTexts 28/01/2022 · Crystal Field Splitting Electron Count. In order to make a crystal field diagram of a particular coordination compound, one must consider the number of electrons. This can be done simply by recognizing the ground state configuration of the electron and then adjusting the number of electrons with respect to the charge of the metal. For example ...

Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion.
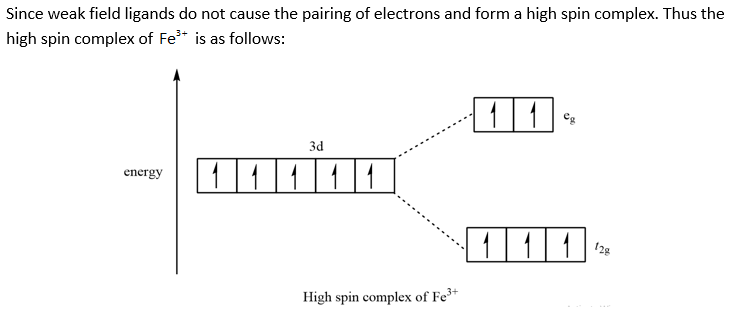
SOLVED:Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram ... Answer. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. a. Zn2+ b. Fe3+ (high- and low-spin) c. V3+ d. Co2+ (high-spin) Solved Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram ... Solved Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. Cr3+ Cu2+ Mn3+ (high-spin) Mn3+ (low-spin) Fe2+ (low-spin) Question: Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. Crystal Field Theory (CFT) - Detailed Explanation with ... The splitting of fivefold degenerate d orbitals of the metal ion into two levels in a tetrahedral crystal field is the representation of two sets of orbitals as T d. The electrons in d x 2 -y 2 and d z 2 orbitals are less repelled by the ligands than the electrons present in d xy , d yz , and d xz orbitals.
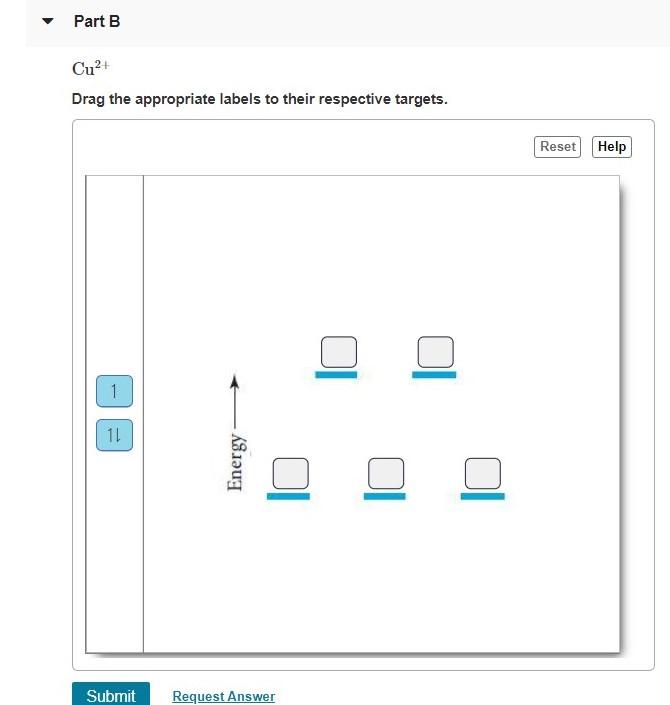
Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion.. PDF Molecular Orbital Theory - Octahedral, Tetrahedral or ... The crystal field theory fails to explain many physical properties of the transition metal complexes because it does not consider the interaction between the metal and ligand orbitals. The molecular orbital theory can be very well applied to transition metal complexes to rationalize the covalent as well as the ionic character SOLVED:Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram ... Problem 42 Medium Difficulty. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. a. Cr3+ b. Cu2+ c. Mn3+ (high- and low-spin) d. Fe2+ (low-spin) A review of Ni based powder catalyst for urea oxidation in ... 10/01/2022 · Metal oxide of Fe 2 O 3 was employed to promote Ni/NiO for urea-assisted water splitting with controllable iron oxide content . The catalyst with Fe/Ni ratio of 0.5:1 was demonstrated to exhibit the best performance due to the enlarged surface area and improved kinetics in the rate-determining step. In a two-electrode system, 10 mA cm Videos on physics, organic chemistry, biochemistry, and ... Complex ion geometries (octahedral, square planar, tetrahedral, linear). Isomerism. ... Transition metals and the crystal field model. Strong-field case and weak-field case; low-spin case and high-spin case; paramagnetism and diamagnetism; spectrochemical series; colors of complex ions. The localized electron model of bonding in complex ions, also known as the valence bond …
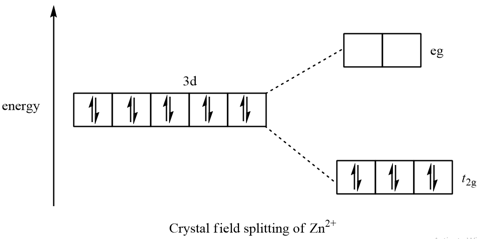
[Yu Yue question bank] Shaanxi Normal University 600003 ... 03/02/2022 · 9. Coordination with metal ions can occur σ+π Synergistic bonding is ( ) (A) CO (B) H2O NH3 (D) C6H6 10. Which of the following ions has the largest stabilization energy of crystal field in octahedral strong field ( ) (A) d3 (B) d4 d5 (D) d6 11. It is known that [PdCl2(OH)2]2- There are two different structures , The type of central ... PDF The Catholic University of Eastern Africa ii. Draw and label the Crystal Field splitting diagram for the 3d atomic orbitals in an octahedral field and tetrahedral field (5 marks) b. For the complex ion [Fe(Cl) 6]3- determine the number of d electrons for Fe, sketch the d-orbital energy levels and the distribution of d electrons among them, list the number of Answered: For each of the following metals, write… | bartleby For each of the following metals, write the electronic configuration of the atom and its 3+ ion: (a) Fe. Draw the crystal-field energy-level diagram for the d orbitals of an octahedral complex, and show the placement of the d electrons for each 3+ ion, assuming a weak-field complex. Solved 1) Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting | Chegg.com Chemistry questions and answers. 1) Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion: a. Zn2+ b. V3+ c. Fe3+ (high- and low-spin) d. Co2+ (high-spin) Question: 1) Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion: a. Zn2+ b.
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram ... Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram, write electronic configuration of the central metal atom/ion and determine the magnetic moment asked Aug 26, 2019 in Chemistry by Anup Agrawal ( 72.9k points) Construction of Pyrazine-Appended 1D and 3D Cobalt(II ... 10/02/2022 · These observations draw conclusions from single-ion anisotropy and antiferromagnetic (AF) interactions mediated by ligands bridging the cobalt(II) centers. (42,43,48,61) So, to gather evidence on the AF interactions persisting in the compound, we performed various temperature susceptibility (χ M ) measurements on compound 1 . OneClass: 42. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting ... Get the detailed answer: 42. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. a. Cr3+ b. Cu2+ c. Mn+ (high- and low-spin) d. Fe2+ (l Electron Configuration - Chemistry | Socratic Electron Configurations are an organized means of documenting the placement of electrons based upon the energy levels and orbitals groupings of the periodic table.. The electron configuration for the first 10 elements. H #1s^1# He #1s^2# Li #1s^2 2s^1# Be #1s^2 2s^2# B #1s^2 2s^2 2p^1# C #1s^2 2s^2 2p^2# N #1s^2 2s^2 2p^3# O #1s^2 2s^2 2p^4# F #1s^2 2s^2 …
Crystal field theory - Wikipedia If the splitting of the d-orbitals in an octahedral field is Δ oct, the three t 2g orbitals are stabilized relative to the barycenter by 2 / 5 Δ oct, and the e g orbitals are destabilized by 3 / 5 Δ oct.As examples, consider the two d 5 configurations shown further up the page. The low-spin (top) example has five electrons in the t 2g orbitals, so the total CFSE is 5 x 2 / 5 Δ oct = 2Δ oct.
PDF Crystal Field Splitting in Octahedral Transition Metal ... d‐Subshell Splitting in an O h Field • In the octahedral (O h) environment of three acac ligands, the fivefold degeneracy among the d orbitals in Mn3+ islifted. • To a first approximation, the ligand field is of O h symmetry, and the 3 d orbitals will separate into a set of three degenerate orbitals (t 2g = dxy, dyz, dxz) and a set of two
Solved 1) Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting - Chegg Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. 1) Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. a) V3+ b) Co2+ (high-spin) 2)The [CrCl6]3− ion has a maximum in its absorption spectrum at 735 nm. Calculate the crystal field splitting energy (in kJ/mol) for this ion. 3) Which complex ion is diamagnetic? Which complex ion is.
Crystal Field Theory - Purdue University The d x 2-y 2 and d z 2 orbitals on the metal ion at the center of the cube lie between the ligands, and the d xy, d xz, and d yz orbitals point toward the ligands. As a result, the splitting observed in a tetrahedral crystal field is the opposite of the splitting in an octahedral complex.
Domain Wall Dynamics in a Ferroelastic Spin Crossover ... Pinned and mobile ferroelastic domain walls are detected in response to mechanical stress in a Mn3+ complex with two-step thermal switching between the spin triplet and spin quintet forms. Single-crystal X-ray diffraction and resonant ultrasound spectroscopy on [MnIII(3,5-diCl-sal2(323))]BPh4 reveal three distinct symmetry-breaking phase transitions in the polar space …
Construct The Octahedral Crystal-field Splitting Diagram Answer to Construct the octahedral crystal-field splitting diagram for the metal in each species. V (H2O)63+ Co (CN)63 - Mn (H2O)62+. A d1 octahedral complex is found to absorb visible light, with the absorption maximum occcurring at nm. a) Calculate the crystal-field splitting energy, Δ, in.
OneClass: Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting ... Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. Zn^2+ Fe^+ (high- and low-spin) The [Mn(NH_3)_6]^2+ ion is paramagnetic with five unpaired electrons. The NH_3 ligand is usually a strong field ligand. Is NH_3 acting as a strong field ligand in this case?
Worksheet - Crystal Field Theory 5. Draw the expected splitting for a Cu(ox) 3 4-complex. Would the splitting pattern change if two of the Cu-O bond lengths were longer than the other four? 6. Using the Tanabe-Sugano diagrams, give the ground states for the free metal, high spin and low spin d 5 complexes. What are the first excited state for each of these?
SOLVED:Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram ... Problem 42 Hard Difficulty. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. a. $\mathrm{Cr}^{3+}$ b. $\mathrm{Cu}^{2+}$ c. $\mathrm{Mn}^{3+}$ (high-and low-spin)
SOLVED:Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram ... A) The octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for the given metal ion is as follows:IMAGE NOT AVAILABLEB) The octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for F e 3 + in low spin complex is as follows:IMAGE NOT AVAILABLEC) The octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for V 3 + i s shown below:IMAGE NOT AVAILABLED) The octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for F e 3 + in high complex is as follows:IMAGE NOT AVAILABLE.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 ... - VEDANTU Free PDF download of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 - Coordination Compounds solved by Expert Teachers as per NCERT (CBSE) textbook guidelines. All Chapter 9 - Coordination Compounds Exercises Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and boost your score more in examinations.
Answered: 12. Draw the octahedral crystal field… | bartleby Solution for 12. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. a. Cr³+ b. Cu²+ c. Mn³* (high- and low-spin) d. Fe²+ (low-spin)
Draw figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an ... Draw energy level diagrams and indicate the occupancy of the orbitals in the following complexes : (a) d 6 octahedral, low-spin (b) d 9 octahedral with tetragonal elongation (c) d 8 square planar (d) d 6 tetrahedral. Calculate in units 0 the difference in crystal field stabilization energy between complexes (a) and (b) assuming that the ligands are strong field ligands.
SOLVED:Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram ... Problem 41 Easy Difficulty. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. $$ \begin{array}{ll}{\text { a. } Z n^{2+}} & {\text { b. } F e^{3 ...
CHEM 2P32 Assignment 4 Hints - Brock University Multiply this number by Avogadro's number to get the octahedral splitting in kJ/mol. CFSE = 170 kJ/mol Question 3 Answer The metal ion in both complex ions is Ni(II), a d 8 ion. The crystal field splitting diagrams for tetrahedral and square planar d 8 complexes are shown below.
Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field Crystal Field Splitting in an Octahedral Field eg Energy 3/5 o o 2/5 o t2g e g - The higher energy set of orbitals (d z2 and d x2-y2) t 2g - The lower energy set of orbitals (d xy, d yz and d xz) Δ o or 10 Dq - The energy separation between the two levels The eThe eg orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0 6orbitals are repelled by an amount of 0.6 Δo The t2gorbitals to be stabilized to the ...
Balbharati solutions for Chemistry 12th ... - Shaalaa.com Balbharati solutions for Chemistry 12th Standard HSC for Maharashtra State Board chapter 9 (Coordination Compounds) include all questions with solution and detail explanation. This will clear students doubts about any question and improve application skills while preparing for board exams. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and …
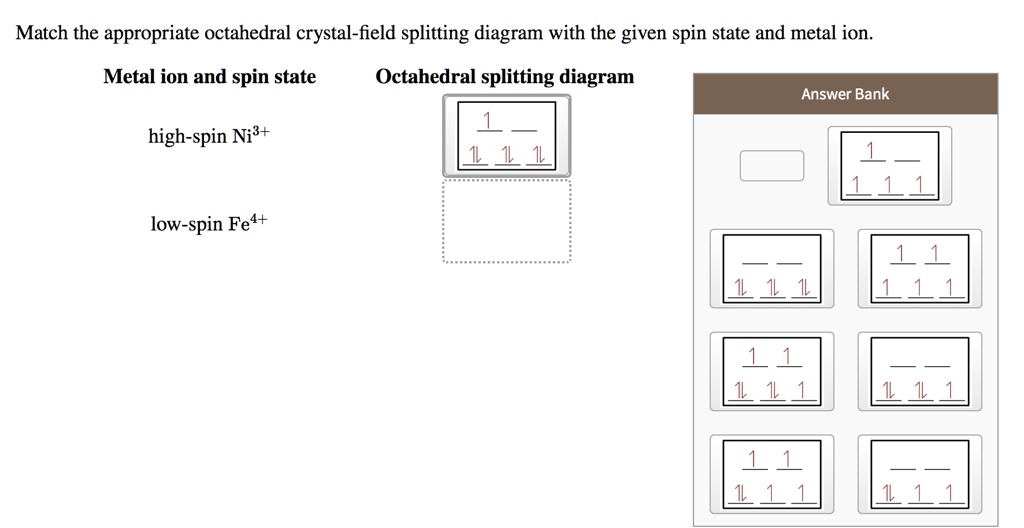
PDF Principles of Chemical Science, Solutions for Lecture 28 ... 1. For each of the following ions, (i) draw. an crystal field splitting diagrams to show orbital occupancies in both weak and strong octahedral fields, and (ii) indicate the number of unpaired electrons in each case. Label . the diagrams (iii) weak or strong field, (iv) high spin or low spin (as appropriate), (v) with the names of the d ...

draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion beginarraylltext a z n2 tex 2
d-metal complexes Practice Problems Answers [Cr(ox) 3] 3- has Cr in the +3 oxidation state, which is d 3, and approximately an octahedral crystal field so LFSE = -12Dq. b) hexacyanoferrate(II) ion [Fe(CN) 6] 4- has Fe in the +2 oxidation state, which is d 6, and a strong octahedral crystal field so LFSE = -24Dq + 2P. c) tetrachloro-η 2 -etheneplatinate(II) ion
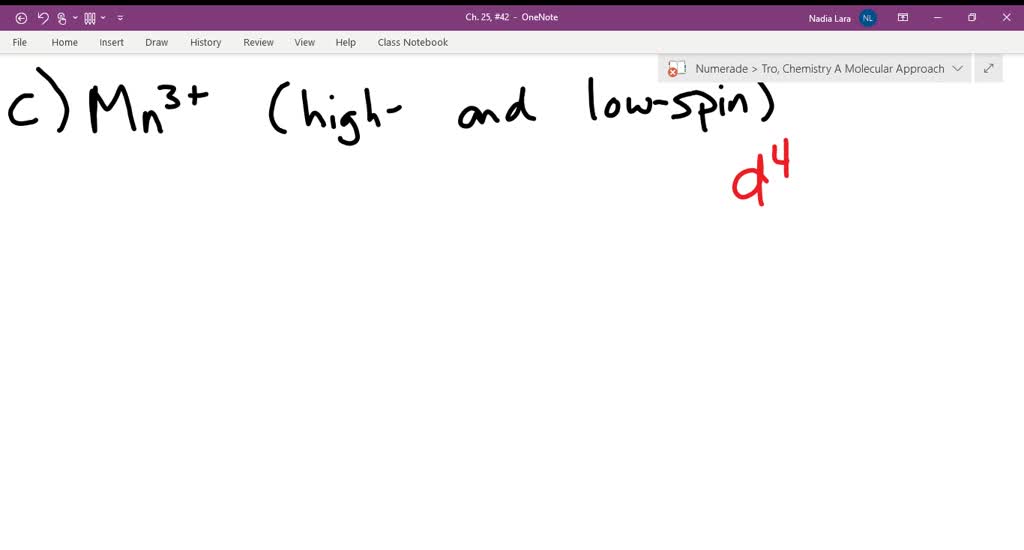
draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion a mathrmcr3 b mathrmcu2 c mat
Draw figure to show the splitting of d ... - SaralStudy Draw figure to show the splitting of d orbitals in an octahedral crystal field. Answer The splitting of the d orbitals in an octahedral field takes palce in such a way that d x 2 y 2 , d z 2 experience a rise in energy and form the eg level, while d xy , d yz and d zx experience a fall in energy and form the t 2g level.
Crystal Field Theory (CFT) - Detailed Explanation with ... The splitting of fivefold degenerate d orbitals of the metal ion into two levels in a tetrahedral crystal field is the representation of two sets of orbitals as T d. The electrons in d x 2 -y 2 and d z 2 orbitals are less repelled by the ligands than the electrons present in d xy , d yz , and d xz orbitals.
Solved Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram ... Solved Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. Cr3+ Cu2+ Mn3+ (high-spin) Mn3+ (low-spin) Fe2+ (low-spin) Question: Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion.
SOLVED:Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram ... Answer. Draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion. a. Zn2+ b. Fe3+ (high- and low-spin) c. V3+ d. Co2+ (high-spin)










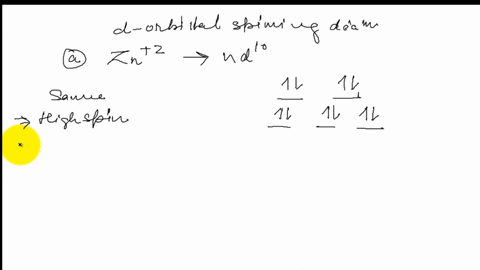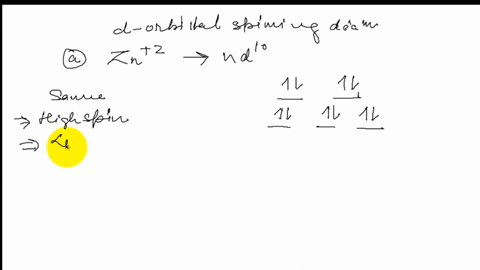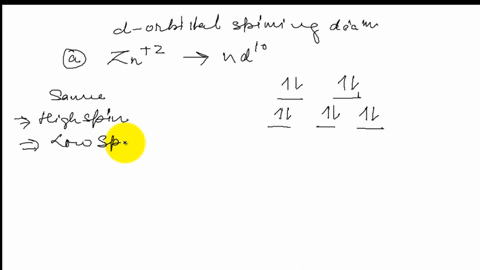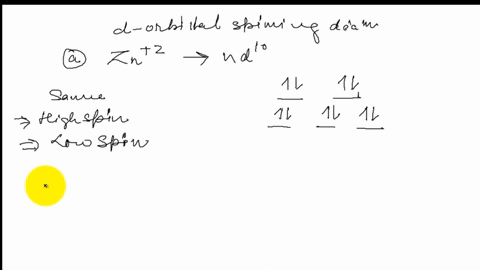








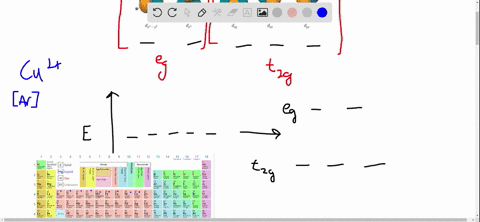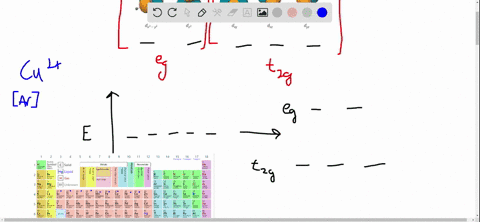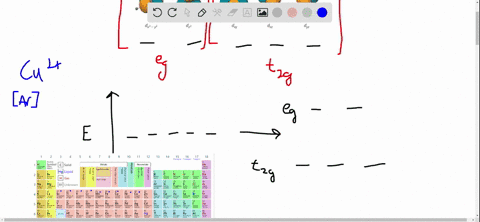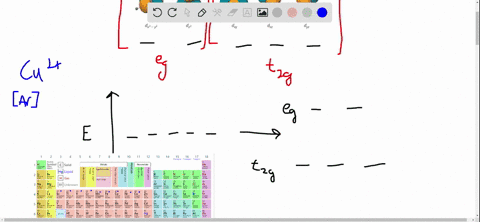





0 Response to "38 draw the octahedral crystal field splitting diagram for each metal ion."
Post a Comment