38 cross bridge cycle diagram
Muscle Physiology: Troponin, Tropomyosin, and ... - YouTube About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators ... Muscle Contraction - Cross Bridge Cycle, Animation ... (USMLE topics) Molecular basis of the sliding filament theory (skeletal muscle contraction) - the cross bridge cycle. This video is available for instant dow...
when does cross bridge cycling end - Lisbdnet.com A single cross-bridge cycle consists of four basic stages. First, myosin binds actin, forming the high-energy/attached state. The power stroke occurs when myosin changes its shape, pulling the thin filaments towards the middle of the sarcomere - that's what causes sarcomere shortening in muscular contraction.Aug 24, 2021

Cross bridge cycle diagram
PPT PowerPoint Presentation Diagram the chemical and mechanical steps in the cross-bridge cycle and explain the effect on the muscle fiber length. Describe the end of contraction mechanisms. Muscle excitation and energy sources. Three roles of ATP in muscle function. Three sources of ATP for muscle function. Focus Figure 9.3: Cross Bridge Cycle Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Focus Figure 9.3: Cross Bridge Cycle. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Cross-bridge Cycle During Muscle Contraction | Biology | JoVE 20.8: Cross-bridge Cycle. As muscle contracts, the overlap between the thin and thick filaments increases, decreasing the length of the sarcomere—the contractile unit of the muscle—using energy in the form of ATP. At the molecular level, this is a cyclic, multistep process that involves binding and hydrolysis of ATP, and movement of actin ...
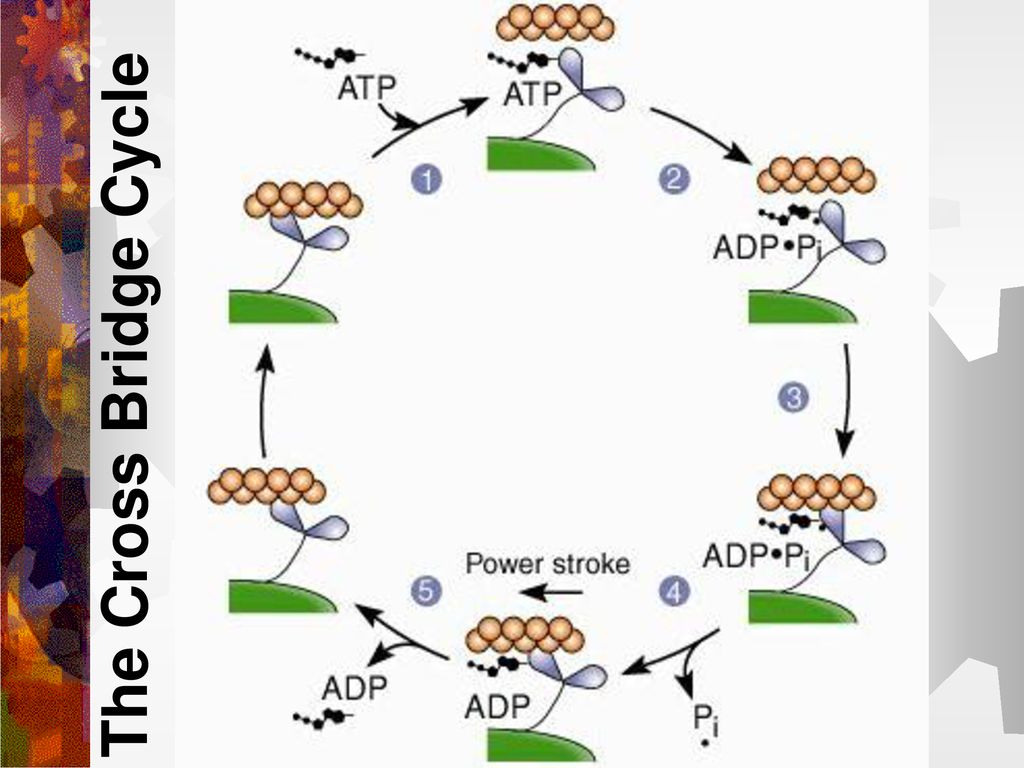
Cross bridge cycle diagram. A cross-bridge model that is able to explain mechanical ... A cross-bridge model that is able to explain mechanical and energetic properties of shortening muscle. ... responses of muscle to steady and stepwise shortening are simulated with a model in which actin-myosin cross-bridges cycle through two pathways distinct for the attachment-detachment kinetics and for the proportion of energy converted into ... Myosin isoforms and the mechanochemical cross-bridge cycle ... A minimal ATPase cycle for the actin and myosin cross-bridge cycle. Filled circles represent the actin monomers in a thin filament and the blue shape represents the motor domain of myosin. M is myosin, A is actin, T is ATP, D is ADP and Pi is inorganic phosphate. AMD, for example, represents a complex between actin, myosin and ADP. Learn About Cross Bridge Cycle Activity | Chegg.com The cross-bridge cycle refers to the cascade of repeated events where thin filaments slide over the thick filaments during muscle contraction with the help of myosin heads pulling the actin at the binding sites followed by detaching itself and then attaching to more binding sites and then keep detaching and binding to another site. actin myosin cross bridge cycle mnemonic? : Mcat Not really a mnemonic but I think of it like a golf swing in my head. Also I haven't seen this diagram before but I typically think of the cross bridge cycle beginning with the power stroke, so: Taking the club back to gain energy (ATP) Right as you make contact with the ball, energy is released (ATP hydrolysis now forms ADP + Pi) The ball gets ...
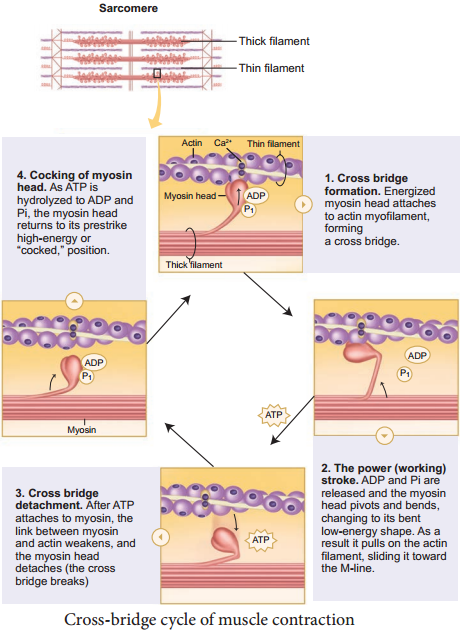
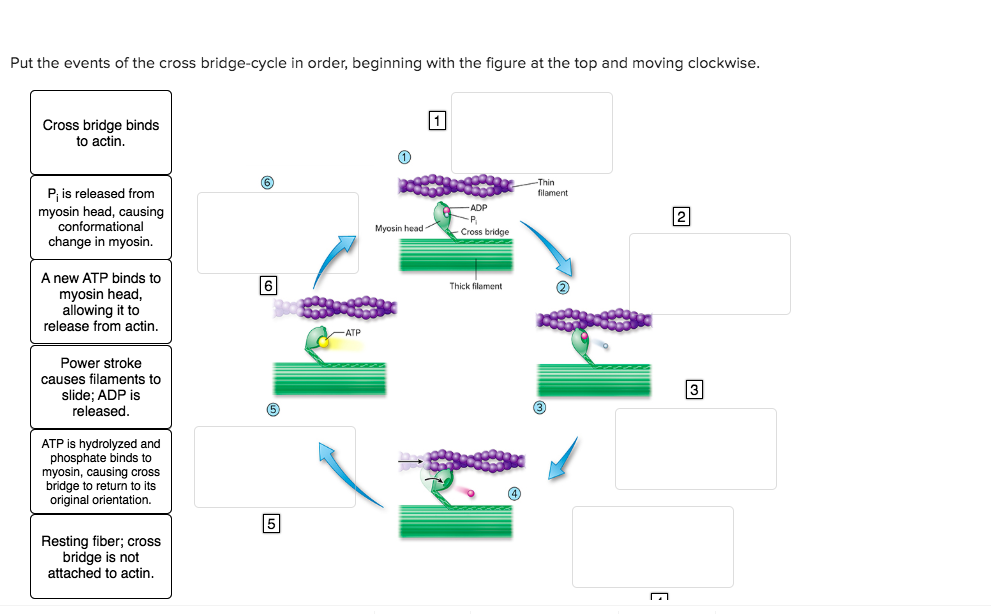
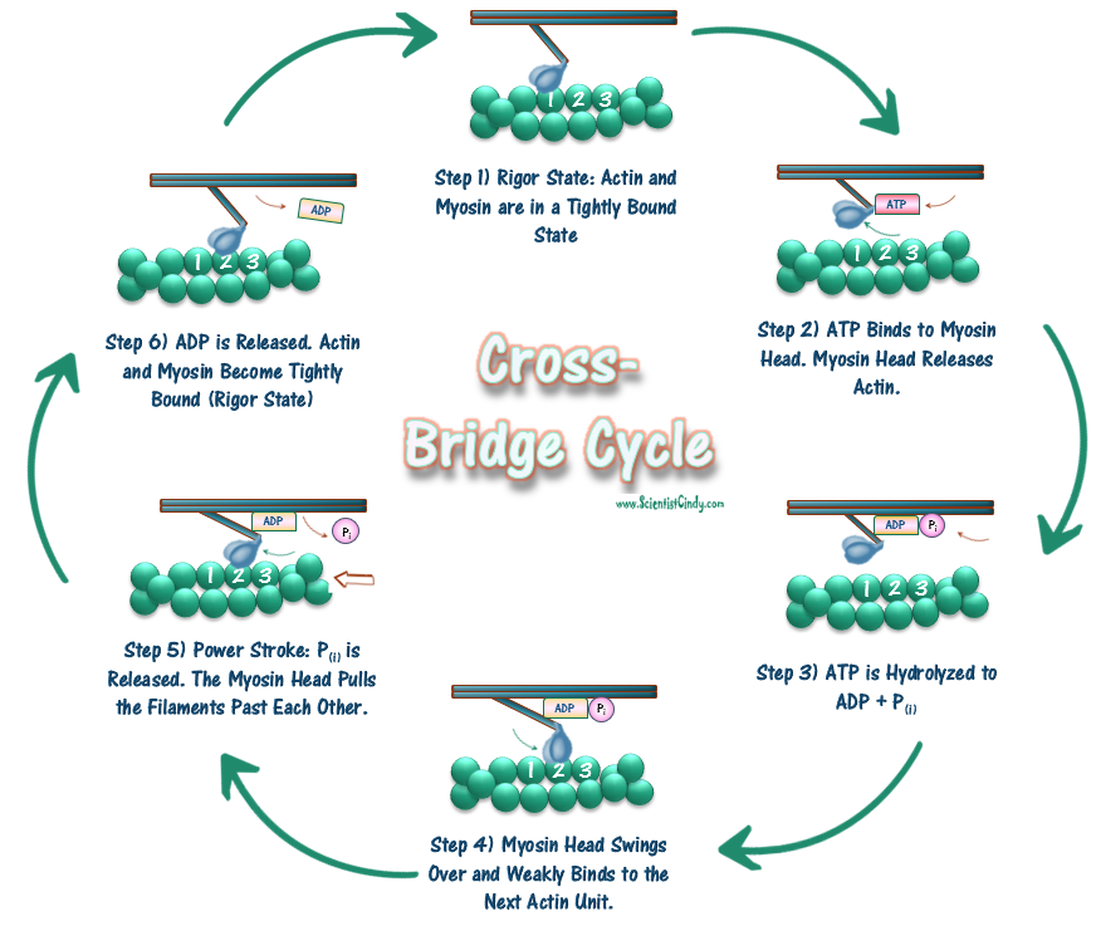
cross bridge | biology | Britannica In muscle: Cross-bridge cycle and ATP breakdown. Smooth muscle contraction requires the release of chemical energy stored in ATP molecules. The release of this chemical energy by the myosin cross bridge and the resultant mechanical work is commonly referred to as the cross-bridge cycle, which in smooth… Read More 10.3 Muscle Fiber Excitation, Contraction, and Relaxation ... Diagram the process of cross-bridge cycling; ... As long as ATP is available, it readily attaches to myosin, the cross-bridge cycle can recur, and muscle contraction can continue. Note that each thick filament of roughly 300 myosin molecules has multiple myosin heads, and many cross-bridges form and break continuously during muscle contraction. ... Steps of the Crossbridge Cycle Flashcards CardsReturn to Set Details. Term. Step 1: Binding of myosin to actin. [image] Definition. ADP and Pi are bound to ATPase site of myosin head. Creates high affinity for actin and the myosin head binds to thin filament. Term. Step 2: Power Stroke. Cross Bridge Cycle Diagram - Quizlet Start studying Cross Bridge Cycle. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Learn About Cross Bridge Cycle Diagram | Chegg.com Cross Bridge Cycle Diagram Definition The overlap between the thin and thick filaments increases as the muscle contracts, reducing the length of the sarcomere, the muscle's contractile unit, using ATP-like energy. At the molecular level, this is a cyclic, multistep mechanism involving binding and hydrolysis of ATP and movement of actin by myosin. Muscle Contraction and Locomotion | Boundless Biology After the power stroke, ADP is released, but the cross-bridge formed is still in place. ATP then binds to myosin, moving the myosin to its high-energy state, releasing the myosin head from the actin active site. ATP can then attach to myosin, which allows the cross-bridge cycle to start again; further muscle contraction can occur. Cross-bridge Cycle During Muscle Contraction | Biology | JoVE 20.8: Cross-bridge Cycle. As muscle contracts, the overlap between the thin and thick filaments increases, decreasing the length of the sarcomere—the contractile unit of the muscle—using energy in the form of ATP. At the molecular level, this is a cyclic, multistep process that involves binding and hydrolysis of ATP, and movement of actin ... Focus Figure 9.3: Cross Bridge Cycle Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Focus Figure 9.3: Cross Bridge Cycle. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
PPT PowerPoint Presentation Diagram the chemical and mechanical steps in the cross-bridge cycle and explain the effect on the muscle fiber length. Describe the end of contraction mechanisms. Muscle excitation and energy sources. Three roles of ATP in muscle function. Three sources of ATP for muscle function.














![PDF] Kinetic coupling of phosphate release, force generation ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/f75aa2a1cf0fe8e64333406ff2a56dd60fcd43ba/2-Figure1-1.png)











0 Response to "38 cross bridge cycle diagram"
Post a Comment