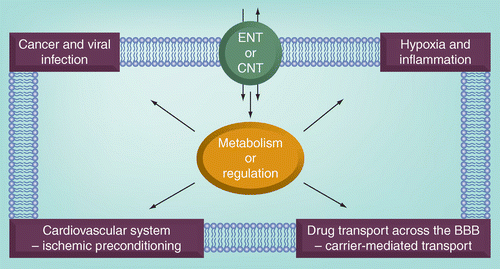
39 in the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion?
In the diagram, this structure directs cellular activities. C In the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion? C In the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution C In the diagram, which panel shows the kinetochore of the centromeres aligning along the center of the mitotic spindle of the cell? A & F briefly describe the fluid mosaic model the fluid mosaic model states that the molecular arrangement of the plasma membrane resembles an ever-moving sea of fluid lipids containing a mosaic of many different proteins the three main components of lipid bilayer portion of plasma membrane are a. phospholipids, glycoproteins, & water
What is the major function of histones? help organize coiling and folding of the DNA This portion of a DNA segment does not code for a protein. introns In the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion? C In the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution C

In the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion?
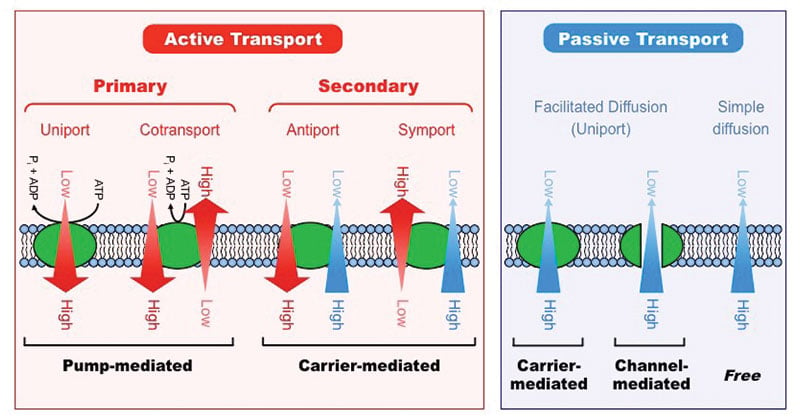
Molecules such as glucose are transported across plasma membranes by special protein carriers. Carrier-mediated transport in which the net movement is down a concentration gradient, and which is therefore passive, is called facilitated diffusion. Carrier-mediated transport that occurs against a concentration gradient, and which therefore requires metabolic energy, is called active transport. A membrane carrier is used for the transported substance. The carriers (as in the active transport) are proteins embedded in the cell membrane. The facilitated diffusion is faster than simple diffusion, but as the concentration of the transported substance increases, the carrier is saturated and the rate of facilitated diffusion stops increasing. In the diagram which one represents carrier mediated School Naugatuck Valley Community College Course Title BIO 211 Type Test Prep Uploaded By angelavalenti90 Pages 59 Ratings 50% (2) This preview shows page 28 - 32 out of 59 pages. View full document See Page 1 59) In the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion?
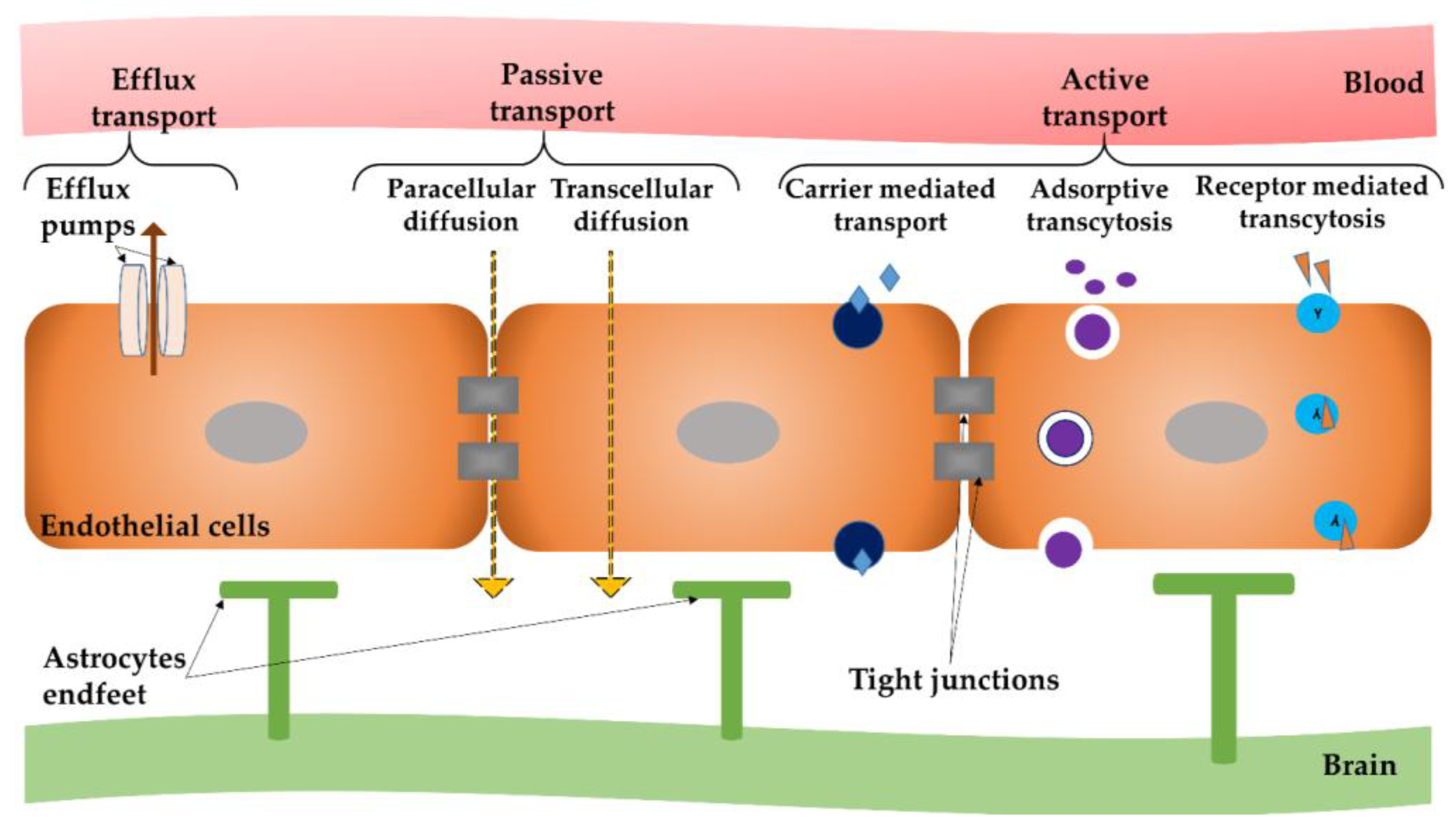
In the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion?. Facilitated diffusion is a form of facilitated transport involving the passive movement of molecules along their concentration gradient, guided by the presence of another molecule - usually an integral membrane protein forming a pore or channel. Facilitated Diffusion | Definition, Factors, and Example ... In The Diagram Which One Represents Carrier Mediated ... 29.08.2012 · In addition, there is minimal fluid-phase pinocytosis in brain capillary endothelium. 2 The absence of paracellular or transcellular channels within the BBB means that molecules in the circulation gain access to brain ISF (interstitial fluid) via only one of the two mechanisms: (1) lipid-mediated free diffusion through the BBB or (2) carrier- or receptor-mediated transport (RMT) … 47) In the diagram, this structure directs cellular activities. a) D; b) F; c) G; d) A; e) H . Answer: c . Difficulty: Medium. Study Objective 1: SO 3.5 Describe the structure and function of the nucleus. Section Reference 1: Sec 3.5 Nucleus . 48) In the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion? a) A; b) B; c) C; d ...
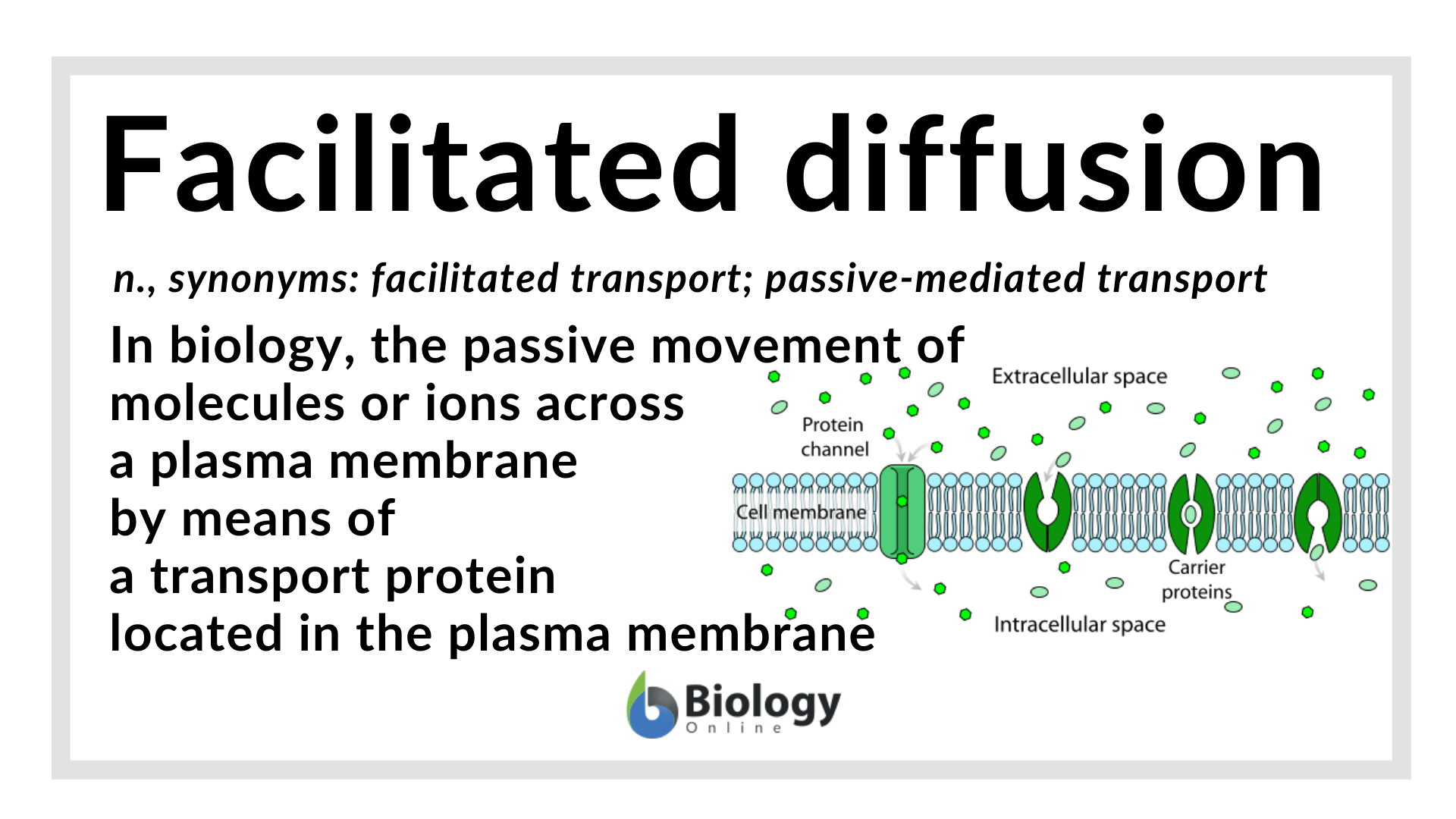
Hiring good writers is one of the key points in providing high-quality services. That’s why we have entry tests for all applicants who want to work for us. We try to make sure all writers working for us are professionals, so when you purchase custom-written papers, they are of high quality and non-plagiarized. Our cheap essay writing service employs only writers who have outstanding … The simplest forms of transport across a membrane are passive. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend any energy and involves a substance diffusing down its concentration gradient across a membrane. A concentration gradient is a just a region of space over which the concentration of a substance changes, and substances will ... Facilitated diffusion... In this type of transport process, a solute (e.g. glucose) binds to a specific carrier protein on one side of the membrane. This binding induces a conformational change in the carrier protein that results in the solute moving down its concentration gradient to the other side of the membrane primary active transport Uniporter is a carrier that transports only one substrate in a complete cycle; the process is known as facilitated diffusion or uniport, and is always passive. Shown in the figure is a glucose uniporter at the basolateral membrane. Symporter is a carrier that transports at least two substrates in the same direction in each cycle.
Ans: This figure represents protein synthesis. Step one, the initiator tRNA attaches to a start codon. In step two, the large and small ribosomal subunits join to form a functional ribosome and initiator tRNA fits into P site. In step three, the anticodon of an incoming tRNA pairs with the next mRNA codon at A site. Step four, the amino acid on the tRNA at P site forms a peptide bond with the ... Section Reference 1: 3.6 Protein Synthesis Solution: This figure represents protein synthesis. Step one, the initiator tRNA attaches to a start codon. In step two, the large and small ribosomal subunits join to form a functional ribosome and initiator tRNA fits into P site. In step three, the anticodon of an incoming tRNA pairs with the next mRNA codon at A site. Facilitated diffusion Active transport Ionic or electrochemical diffusion Ion-pair transport Endocytosis. Passive Diffusion A lso called nonionic diffusion, it is the major process for absorption o f more than 90% o f the drugs. The driving force for this process is the concentration or electrochem ical gradient. It is defined as the differ ence in the drug concentration on either … Hopkins W.,Huner N.-Introduction to plant physiology-2008.pdf
In the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution. Image: A. A red blood cell placed in a solution of 5% NaCl would lose water. This is because the solution is _____ to the cell: hypertonic. A low-density lipoprotein is transported into the cell through a clathrin coated receptor and is degraded. ...
Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Carrier-mediated diffusion is a type of facilitated transport, which utilises carrier proteins to help with the movement of substances across the plasma membrane. Carrier-mediated active transport, another type of facilitated transport. Osmosis The passive movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called osmosis.
Facilitated diffusion is a type of absorption that requires a special carrier to transport a molecule across the cell membrane and During carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion, the cell will increase its transport maximum if the concentration gradient is increased. Which of the following are consistent with facilitated diffusion?
The primary difference between simple and facilitated diffusion is that facilitated diffusion requires a membrane protein to act as a channel or carrier for a substance while simple diffusion means substances can slip through the lipid bilayer without a channel or carrier being needed. askedJun 27, 2020in Biology & Microbiologyby Kuloteyn
Our online assignment help is one of the best essay writing help in the world as we work with international students from the most prestigious universities in the world. We write quality papers for our clients as we have employed highly qualified academic writers from all over the world. Our writers are able to handle complex assignments from their field of specialization. When it …
(1) Movement is against a concentration gradient (2) Movement is with a concentration gradient (3) Involves a carrier molecule (4) Involves cotransport (5) Involves counter transport (6) Exhibits competition and saturation Facilitated diffusion and active transport require a carrier protein to mediate the movement across the plasma membrane.
Facilitated diffusion is the passive movement of molecules along the concentration gradient. It is a selective process, i.e., the membrane allows only selective molecules and ions to pass through it. It, however, prevents other molecules from passing through the membrane. The electric charge and pH helps in the diffusion across the membrane.
In the diagram which one represents a hypertonic solution The Grape Lab. Purpose: To determine how osmosis occurs in hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solutions. Background information: Osmosis is the diffusion of water from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. beaker of 40% sucrose solution.
In the diagram, which one represents facilitated diffusion? In the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution. 48. Compare and contrast primary and secondary active transport. 49. Compare mitosis to meiosis. Briefly describe the two ways water molecules pass through a plasma membrane. Briefly list the steps involved in receptor ...
KIN 267 Midterm Exam 1 U of R 13 50. In the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion? a. A b. B c. C d. Both A and C e. Both B and C c. C 51. In the diagram, which one represents a hypertonic solution a. A b. B c. C d. Both B and C e. All of these choices are correct. c ) C
Diffusion, Osmosis, Active Transport There are two ways in which substances can enter or leave a cell: 1) Passive a) Simple Diffusion b) Facilitated Diffusion c) Osmosis (water only) 2) Active a) Molecules b) Particles Diffusion Diffusion is the net passive movement of particles (atoms, ions or
31) In the diagram, which panel shows cells that are in interphase? 1 A 2 C 3 F a) 1 only b) 2 only c) 3 only d) 1 and 3 e) 1, 2, and 3 32) Briefly state the functions of the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
The diagram represents a cell expressing three membrane transporters. Top: Primary-active transport of Na ... The first one is the dihydroxylation at the vinyl group at C18 found in the first NCC identified in the senescent leaves of barley (Hv-NCC1) [1,56]. Since then, it has been characterized in other senescent material, but at the moment the nature of the biochemical …
E) it is needed to transport K+ out of the cell C In the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion? A) A B) B C) C D) Both A and C E) Both B and C C Match the letter from the figure with the following organelle name or description: Synthesizes fatty acids and steroids; stores and releases calcium ions in muscle. C D H J C
3. Facilitated Diffusion. Facilitated diffusion (also known as carrier-mediated diffusion) is, like simple passive diffusion, dependent on the inherent energy in a solute gradient. No additional energy is required to transport the solute and the final solute distribution reaches equilibrium across the membrane.
The second period (1972 to 1992) was inaugurated by the simultaneous publication of two seminal papers, one by Kokko and Rector and one by Stephenson, proposing that a “passive mechanism” provides the single effect for countercurrent multiplication in the inner medulla [7;8]. According to the passive mechanism hypothesis, a net solute efflux from thin ascending limbs of the loops of …
In the diagram which one represents carrier mediated School Naugatuck Valley Community College Course Title BIO 211 Type Test Prep Uploaded By angelavalenti90 Pages 59 Ratings 50% (2) This preview shows page 28 - 32 out of 59 pages. View full document See Page 1 59) In the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion?
A membrane carrier is used for the transported substance. The carriers (as in the active transport) are proteins embedded in the cell membrane. The facilitated diffusion is faster than simple diffusion, but as the concentration of the transported substance increases, the carrier is saturated and the rate of facilitated diffusion stops increasing.
Molecules such as glucose are transported across plasma membranes by special protein carriers. Carrier-mediated transport in which the net movement is down a concentration gradient, and which is therefore passive, is called facilitated diffusion. Carrier-mediated transport that occurs against a concentration gradient, and which therefore requires metabolic energy, is called active transport.






















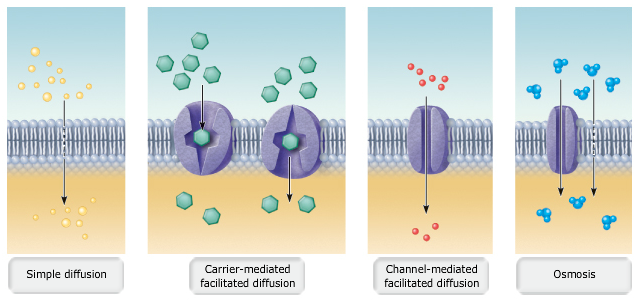



0 Response to "39 in the diagram, which one represents carrier-mediated facilitated diffusion?"
Post a Comment