39 electron transport chain diagram
These data show that the structure of M. tuberculosis Sdh1 is significantly different by comparison with the human counterpart making a good antituberculosis drug target. Keywords: succinate dehydrogenase, Mycobacterium smegmatis, electron transport chain, cryoelectron microscopy. The structure and function of each of these complexes are usually described in separate sections of a biochemistry textbook because they are so complex but we've always known that they function together as an electron transport chain. When I first started writing this section of my textbook it was obvious that the three complexes would cluster ...
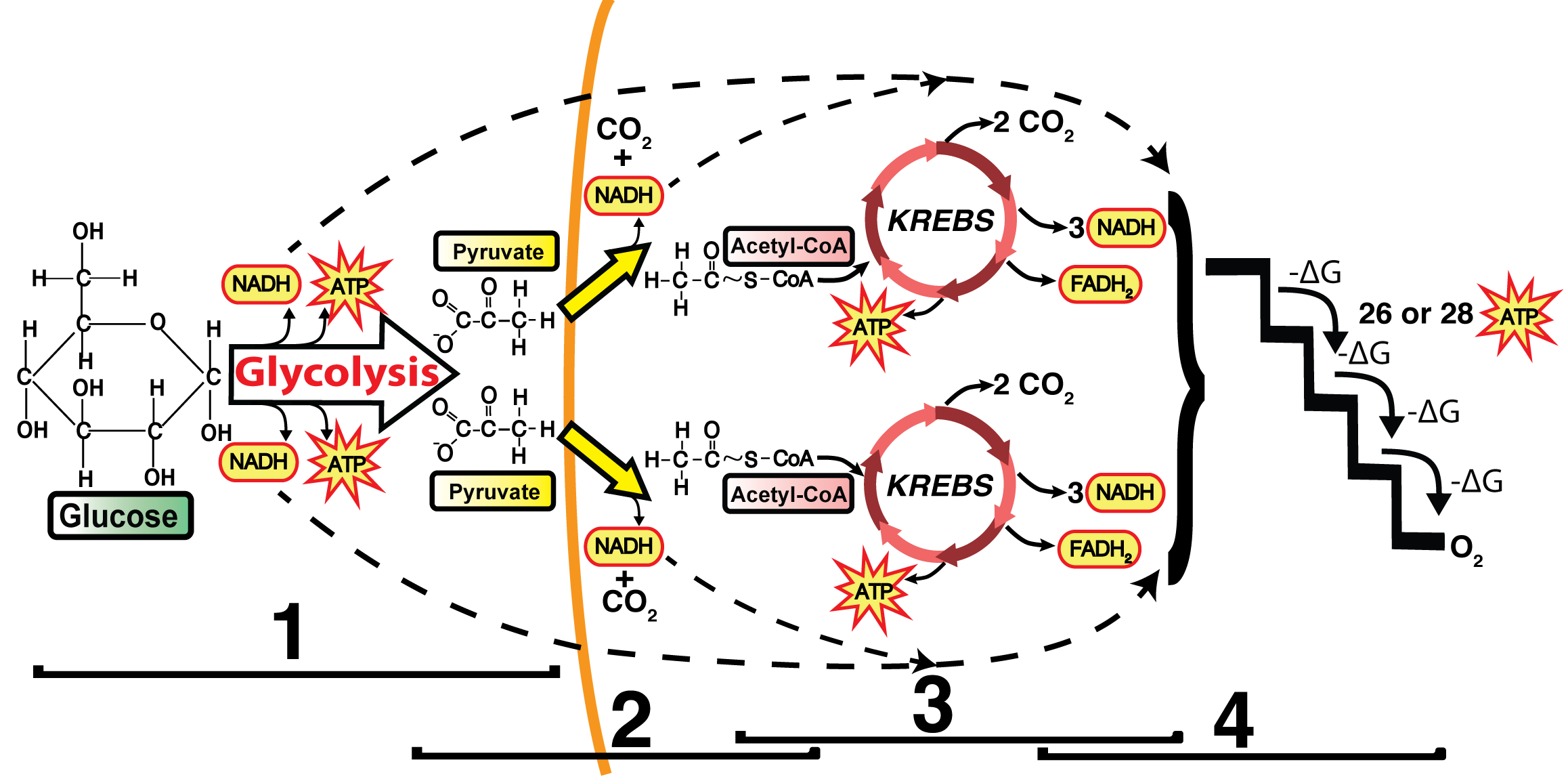
The final stage, the electron transport chain, is where the bulk of the ATP is formed. About 32 molecules of ATP are formed in this section, bringing the total of ATP from cellular respiration up ...

Electron transport chain diagram
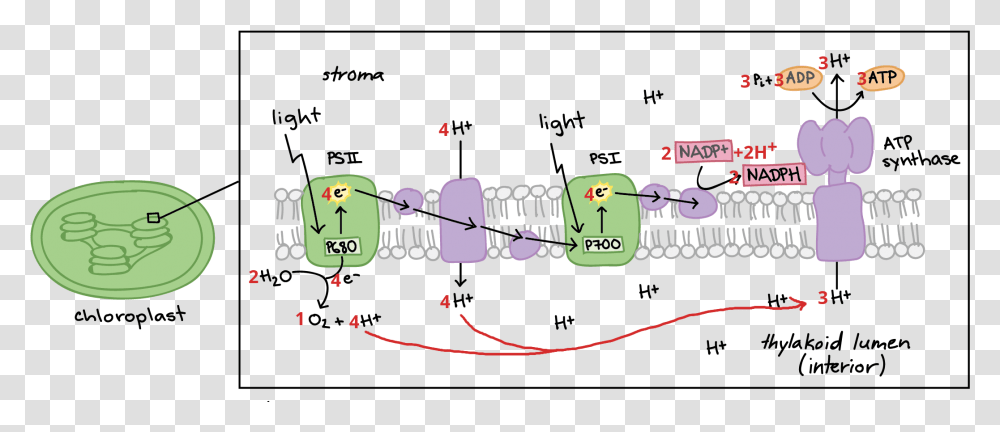
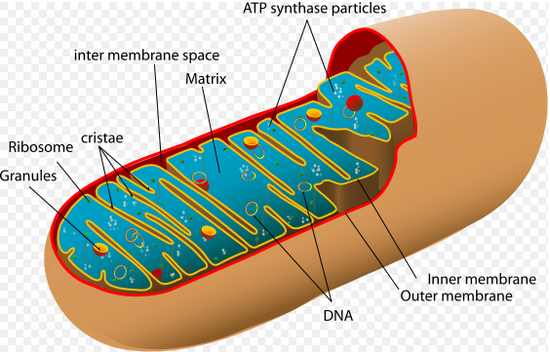
Mitochondria is a decisive organelle of cells that produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the process of oxidative phosphorylation of the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain system of mitochondria embodies multiple enzyme supercomplexes including complex I to V which located in the inner membrane. Although the simple enzyme activity of some as-isolated ... Fig: Electron Transport Chain in Chloroplast Splitting of Water or Photolysis of Water (i) The supply of electrons continuously is achieved by the splitting of water involving PS-II located on the inner side of the thylakoid membrane. (ii) Water is split into 2 H +, [ O] and electrons. The electron transport chain and chemiosmosis are collectively known as oxidative phosphorylation. Pyruvate oxidation is the reaction that connects glycolysis to the Krebs cycle because pyruvate ...
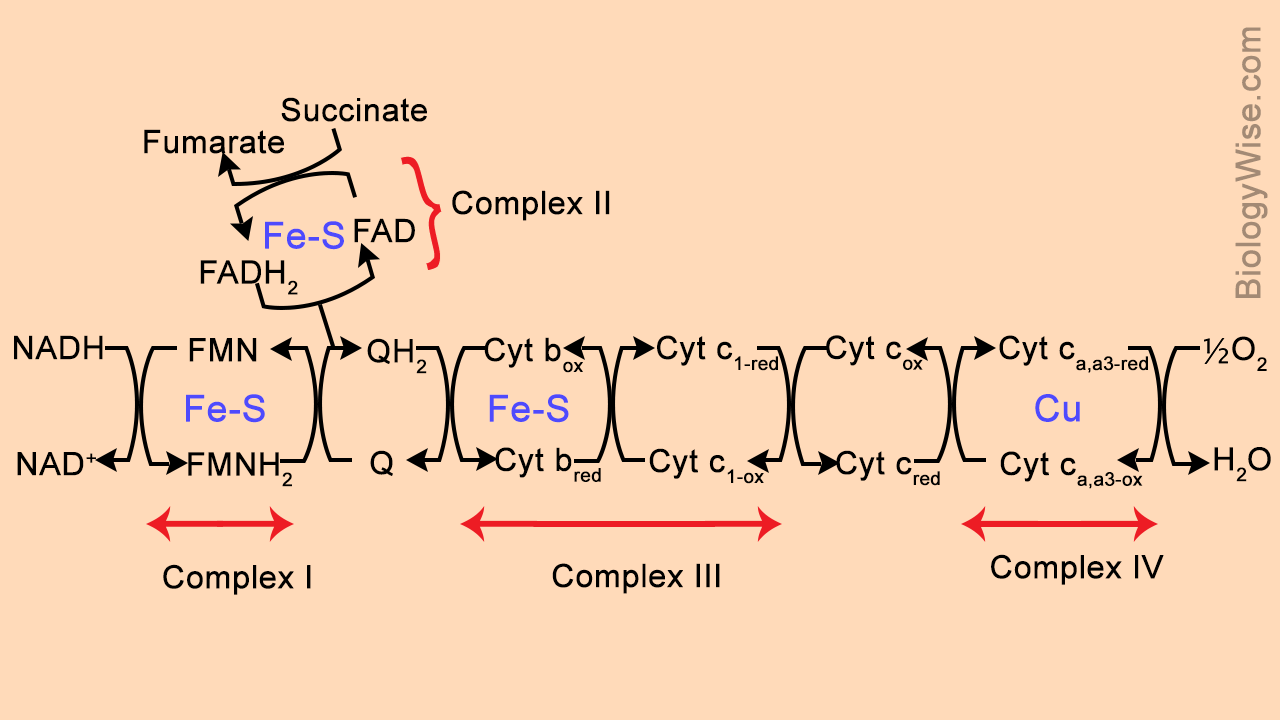
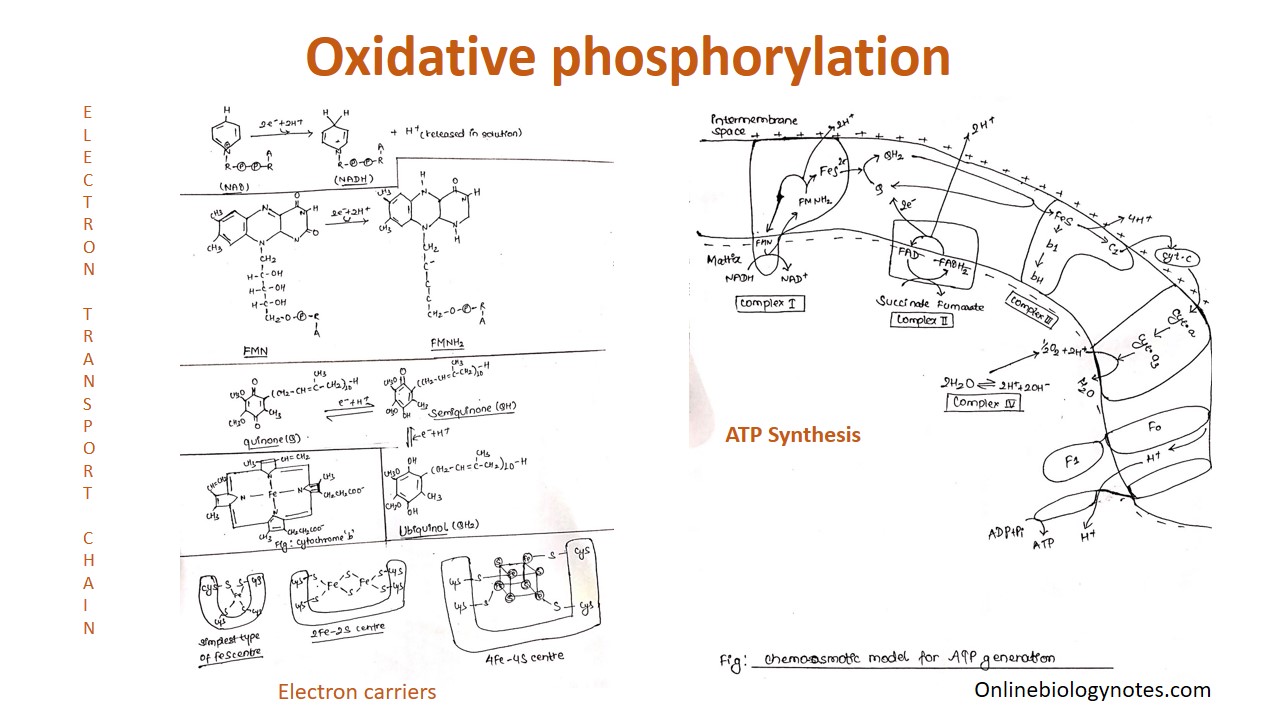
Electron transport chain diagram. Here are a number of highest rated Redox Potential Electron Transport Chain pictures on internet. We identified it from reliable source. Its submitted by admin in the best field. We bow to this nice of Redox Potential Electron Transport Chain graphic could possibly be the most trending subject following we portion it in google help or facebook. The electron transport chain is made up of a series of spatially separated enzyme complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron receptors via sets of redox reactions. This is also accompanied by a transfer of protons (H + ions) across the membrane. This leads to the development of an electrochemical proton gradient across the membrane that activates the ATP synthase proton pump, thereby, driving the generation of ATP molecules (energy). Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis a) Illustrate drawing informative diagram to explain electron transport chain: The pathway of electron transport is NADH dehydrogenase, Ubiquinone/ CoQ, cyt c reductase, cyt c oxidase. b) Explain chemiosmosis: proton motive force. c) Explain complete oxidation of one molecule of Fig 1 - Diagram to summarise the electron transport chain. Uncoupling Uncoupling proteins provide an alternative route for proteins to pass into the matrix through the membrane. This is due to reduced gradient between the matrix and the intermembrane space. Therefore, there is less ATP formed, and, instead, more heat generated.
Electron Transport Chain Diagram. A major source of cellular energy production, in the form of ATP, is derived from the proton motive force supplied to mitochondrial ATP synthase. The main driver of the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane is the electron transport system. NADH and FADH2 produced by glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation and the TCA cycle serve as a electron donors and cofactors for the protein complexes involved in the electron transport system. Subject Matter of Electron Transport Chain: The primary function in photosynthesis is the raising of an electron to a higher energy level in chlorophyll. Then the electron is transferred to an acceptor. It is, as if, there is a hole in the chlorophyll which invites filling. This hole is plugged by electrons from water. Electron Transport Chain Definition. The Electron Transport System also called the Electron Transport Chain, is a chain of reactions that converts redox energy available from oxidation of NADH and FADH 2, into proton-motive force which is used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex through a process called oxidative phosphorylation. In bacteria and archaea, the cytoplasmic membrane also contains all membrane-bound reactions, including those related to the electron transport chain, ATP synthase, and photosynthesis. The cell wall of archaea is pseudopeptidoglycan, as they have ether bonds with the branching of aliphatic acids, whereas bacteria have lipid membrane ester bonds ...
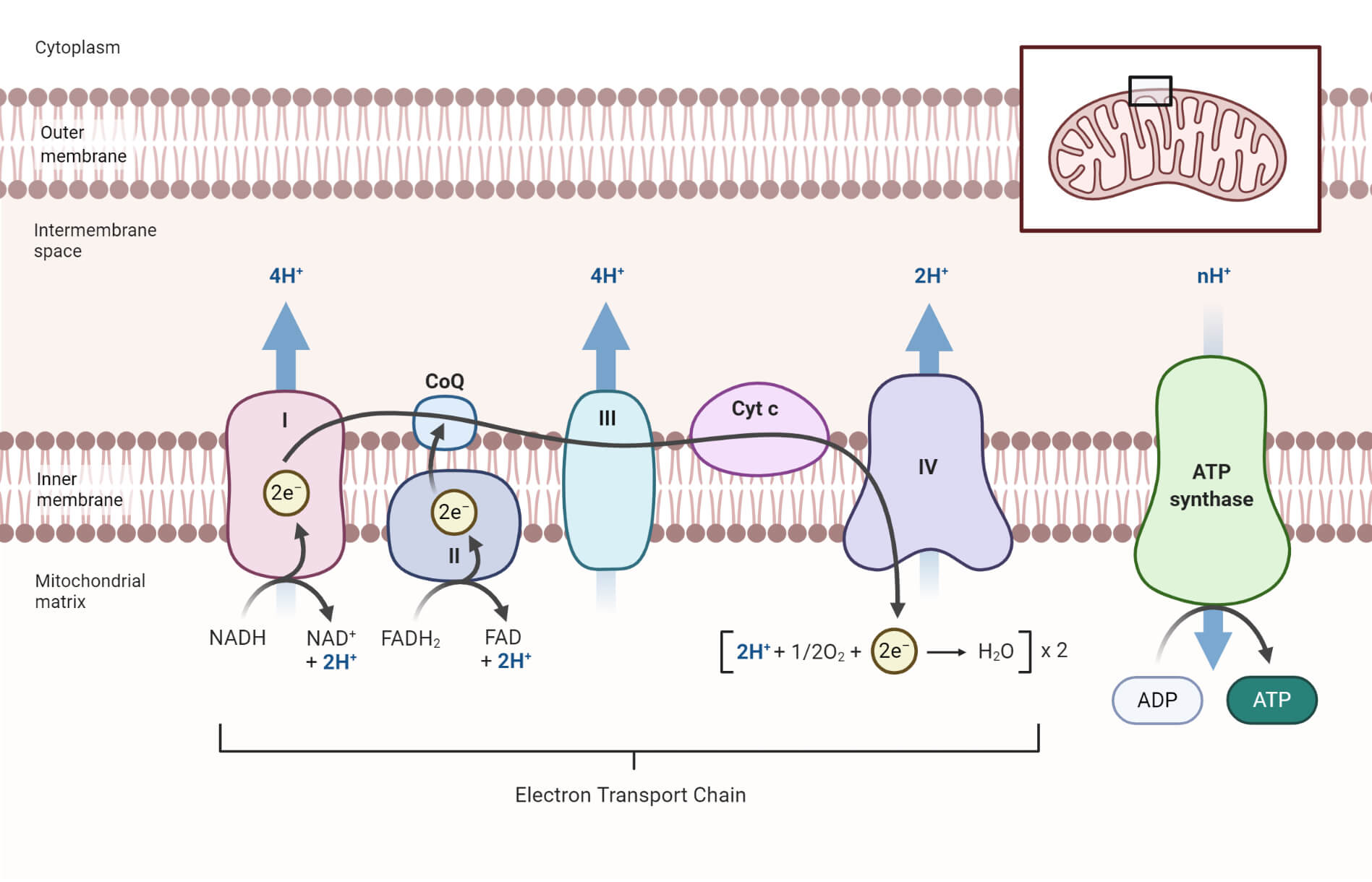
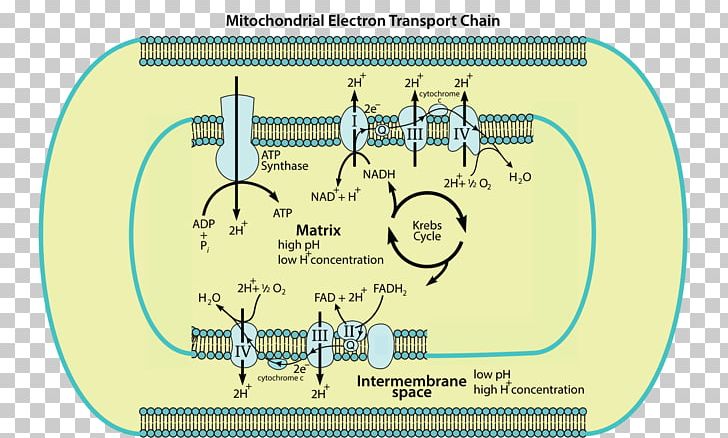
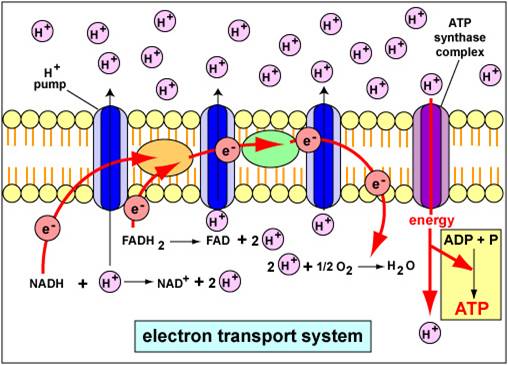
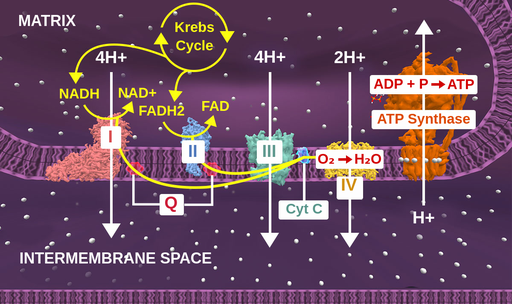
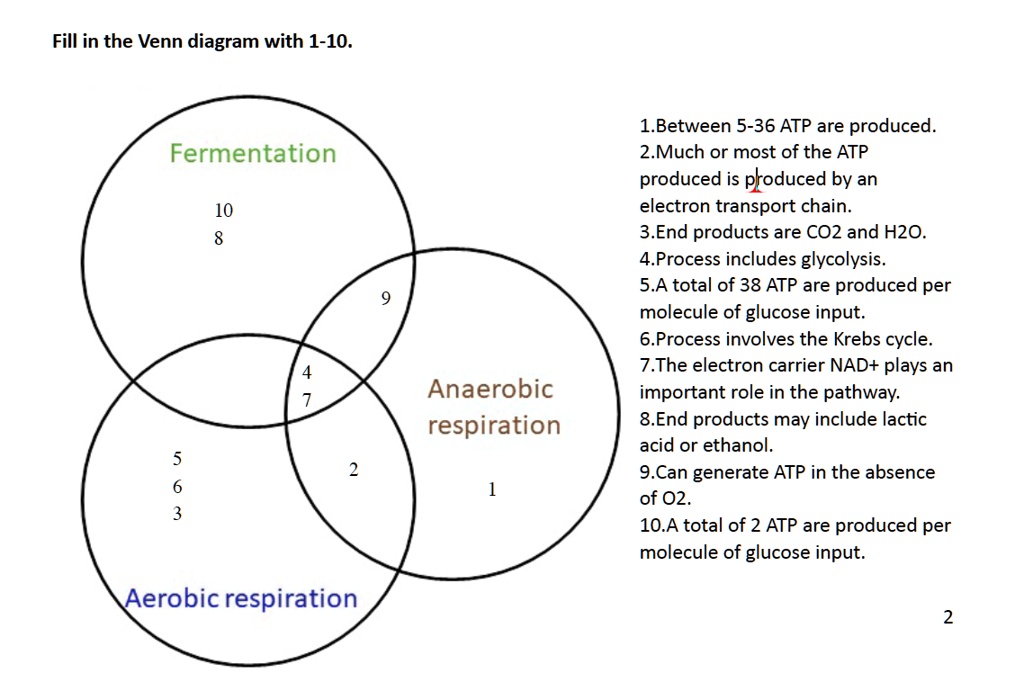
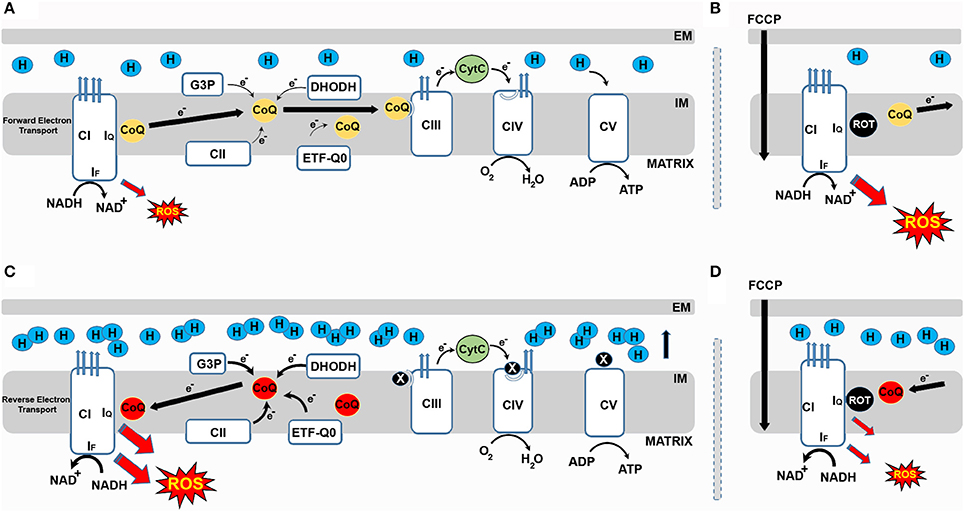
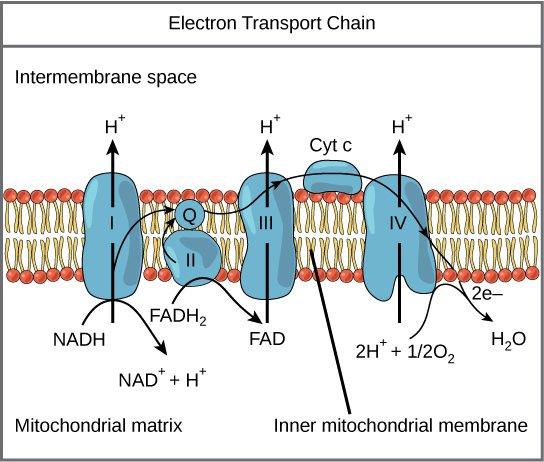
Electron Transport Chain is a series of protein complexes that transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons across a membrane. The electron transport chain is built up of peptides, enzymes, and other molecules Instead, another high-energy electron carrier, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) acts as the hydrogen acceptor resulting in the formation of FADH 2. The FADH 2 then enters the electron transport chain via the complex II transferring the electrons to ubiquinone, finally forming 2ATPs. Step 7: Hydration of fumarate to malate Electron Transport Chain (overview) • The NADH and FADH2, formed during glycolysis, β-oxidation and the TCA cycle, give up their electrons to reduce molecular O2 to H2O. • Electron transfer occurs through a series of protein electron carriers, the final acceptor being O2; the pathway is called as the electron transport chain. electron transport chain ( mitochondrial respiratory chain ) is embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane and consists of four electron carrier complexes ( complexes I-IV) that transfer electrons from nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide ( NADH ) and flavin adenine dinucleotide ( FADH2 ) to oxygen, thereby generating water (H 2 O).
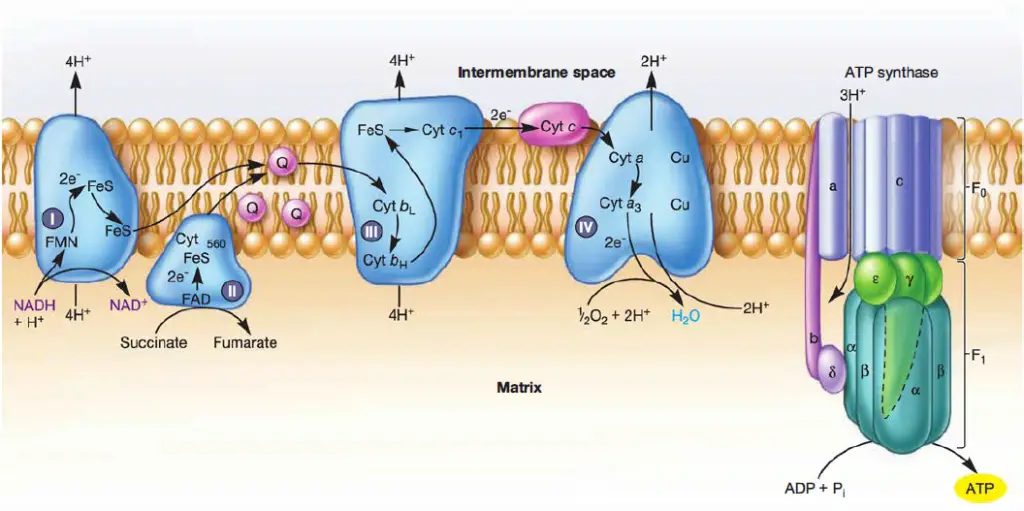
Electron Transport Chain in Mitochondria. A complex could be defined as a structure that comprises a weak protein, molecule or atom that is weakly connected to a protein. The plasma membrane of prokaryotes comprises multi copies of the electron transport chain. Complex 1- NADH-Q oxidoreductase: It comprises enzymes consisting of iron-sulfur and FMN. Here two electrons are carried out to the first complex aboard NADH.
Protein machinery of respiration becomes visible. Imaging of the cytochrome bcc-aa3 supercomplex using a cryogenic electron microscope allows a detailed understanding of the molecular structure ...
The key difference between the glycolysis krebs cycle and electron transport chain is the net yield. Glycolysis produces two pyruvates, two ATP, and two NADH, while Krebs cycle produces two carbon dioxide, three NADH, one FADH 2, and one ATP. Electron transport chain, on the other hand, produces thirty-four ATP and one water molecule. Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic reactions ...
Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell.
Cytoplasm 2 molecules of ATP. Glycolysis Electron transport chain Krebs cycle. If cellular respiration took place in just one step most of the ENERGY would be lost in the form of. The loss of electrons from a molecule d. Bio 1107 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation. The chemistry of cellular respiration worksheet answer key.
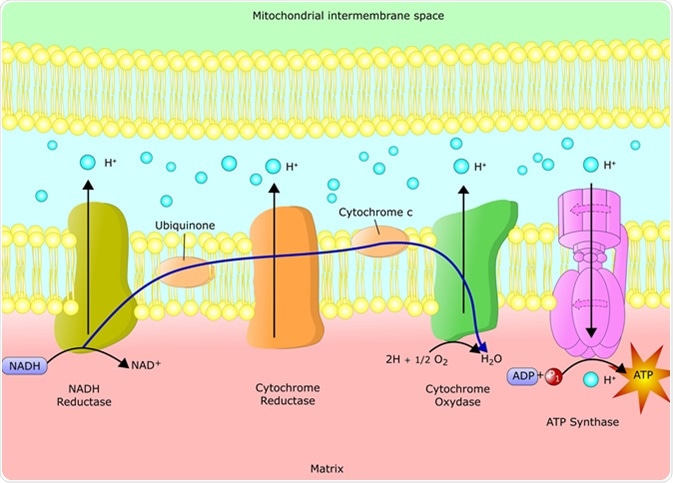
Figure 1.The Electron Transport Chain. This is a general overview of The Electron Transport Chain (ETC). The ETC is a series of four protein complexes: NADH dehydrogenase, succinate dehydrogenase, cytochrome bc 1, and cytochrome c oxidase, embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria.As electrons are transferred through these protein complexes, a proton (H +) gradient accumulates in the ...
In a new study, researchers provide a detailed atomic view of one key component of mitochondrial energy metabolism—respiratory complex I. The first enzyme in the electron transport chain of ...
The chain works in the same way as the electron transport chain in photosynthesis. A concentration gradient is formed, and ATP synthase is responsible for creating ATP. When hydrogen ions are dropped off by electron carriers to the electron transport chain, the hydrogen ion is pumped across the plasma membrane to form a high concentration ...
In order for ATP to be produced through oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are required for ATP to pass down the electron transport chain. These electrons come from electron carriers such as NADH and FADH₂, which are produced by the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (TCA cycle, also known as the Kreb's/Citric Acid cycle). In this article we will outline the steps and regulation of this essential ...
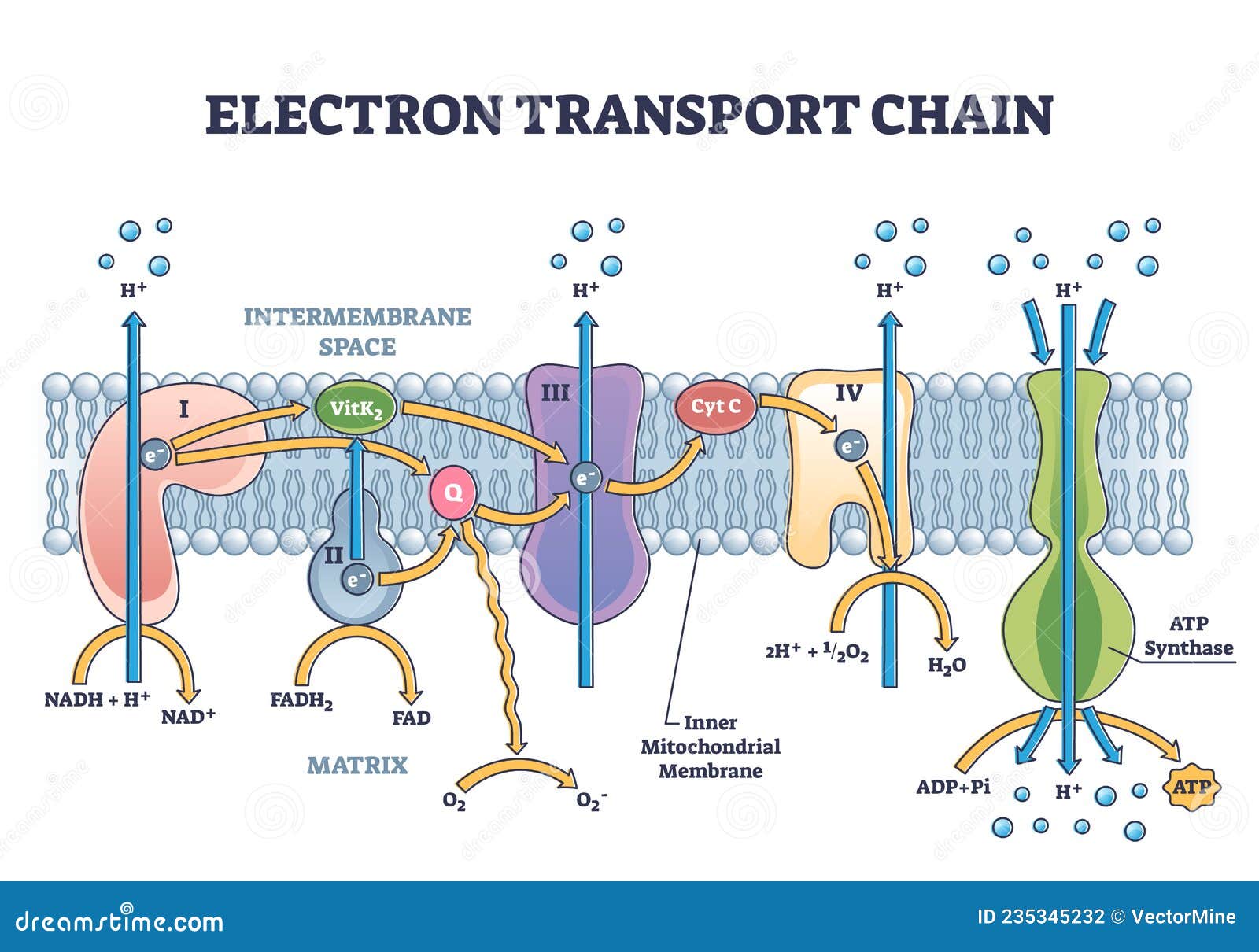
Concentration-response data for 3 respiration phases confirmed activity and indicated a mechanism for 193 mitochondrial toxicants: 149 electron transport chain inhibitors (ETCi), 15 uncouplers and 29 adenosine triphosphate synthase inhibitors. Subsequently, an electron flow assay was used to identify the target complex for 84 of the 149 ETCi.
The electron transport chain is a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation. It occurs in mitochondria in both cellular respiration and photosynthesis. In the former, the electrons come from breaking down organic molecules, and energy is released.
The first electron is donated to the ISP, due to the higher potential of the Fe-S cluster and haem c 1 compared with haems b 75, while the second electron can follow the low-potential chain once ...
What are the 4 steps of the electron transport chain? The key steps of this process, shown in simplified form in the diagram above, include: Delivery of electrons by NADH and FADH 2 start subscript, 2, end subscript. … Electron transfer and proton pumping. … Splitting of oxygen to form water. … Gradient-driven synthesis of ATP.
Where is the electron transport chain associated with Photophosphorylation located in plant cells? Diagram of non-cyclic photophosphorylation. The photosystems and electron transport chain components are embedded in the thylakoid membrane.When light is absorbed by one of the pigments in photosystem II, energy is passed inward from pigment to pigment until it reaches the reaction center.
The electron transport chain is a series of electron transporters embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular oxygen. In the process, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, and oxygen is reduced to form water.
This is a unique example where ATP can be produced at substrate level without participating in electron transport chain. This type of reaction where ATP is formed at substrate level is called as Substrate level phosphorylation. Step 8 : Conversion of 3-Phosphoglycerate to 2-Phosphoglycerate
The electron transport chain and chemiosmosis are collectively known as oxidative phosphorylation. Pyruvate oxidation is the reaction that connects glycolysis to the Krebs cycle because pyruvate ...
Fig: Electron Transport Chain in Chloroplast Splitting of Water or Photolysis of Water (i) The supply of electrons continuously is achieved by the splitting of water involving PS-II located on the inner side of the thylakoid membrane. (ii) Water is split into 2 H +, [ O] and electrons.
Mitochondria is a decisive organelle of cells that produces adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the process of oxidative phosphorylation of the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain system of mitochondria embodies multiple enzyme supercomplexes including complex I to V which located in the inner membrane. Although the simple enzyme activity of some as-isolated ...
















0 Response to "39 electron transport chain diagram"
Post a Comment