37 two component phase diagram
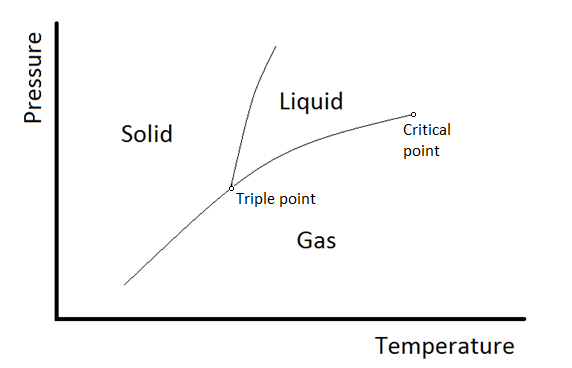
Below the graph, the two component system, which are phenol and water exists as two phase, so the degrees of freedom is F = C - P +2 = 2 - 2 + 2 = 2 This shows that the system has 2 independent variables which is temperature and concentration. 2D phase diagram. A phase diagram. The simplest phase diagrams are pressure-temperature diagrams of a single simple substance, such as water. The axes correspond to the pressure and temperature. The phase diagram shows, in pressure-temperature space, the lines of equilibrium or phase boundaries between the three phases of solid, liquid, and gas.
Experimental Methods for The Determination of Phase Diagram of Two-Component Systems The most common approaches for the determination of phase diagram of two-component systems are “cooling curve” and “thaw melt” methods. These methods are quite popular due to their easiness and practicability to many systems. 1.

Two component phase diagram
May 18, 2020 — Obviously the two phases must have different compositions or they would be identical; the difference is called a miscibility gap. A binary ... 13.1.2 Two volatile components. In an ideal solution, every volatile component follows Raoult's law. Since the vapors in the gas phase behave ideally, the total pressure can be simply calculated using Dalton's law as the sum of the partial pressures of the two components \(P_{\text{TOT}}=P_{\text{A}}+P_{\text{B}}\).The corresponding diagram is reported in Figure 13.2. Phase diagrams (of two component systems) In general in a binary phase diagram the temperature or the pressure is plotted versus the molar fraction of one the two components. The variable of state that is not plotted is constant. The lines in the phase diagram are curves that divide different phases.
Two component phase diagram. 2-component phase diagrams Due Friday, Dec. 4 Mathcad can be used to construct quantitative two-component phase diagrams. Reproduce the following phase diagram calculations and then perform a similar calculation on a real chemical system. Below are the pure vapor pressure (in torr) of a two component system (A & B). The mole fraction TWO COMPONENT EUTECTIC SYSTEMS Figure 1 shows the simplest of two component phase diagrams. pure crystals of B, and liquid with compositions ranging between pure A and pure B. Compositions are plotted across the bottom of the diagram. Note that composition can be expressed as either a percentage of A or a percentage of binary phase diagrams (isomorphous phase diagram) this is a two component system. in this phase diagram, temperature and composition are variable parameters, and pressure is held constant normally 1 atm. temperature is taken on y-axis and various compositions of the two components on x-axis. ni-cu, au-ag, cr-mo are examples of binary phase … Ternary phase diagram books by D.R.F. West - there are several . Ternary grid . Space diagram . C A B . Space diagram . Usually have elements at the corners as the constituents, but can have compounds: ← For "normal diagrams", where interested in all . components, use the . Normal equilateral . triangle.
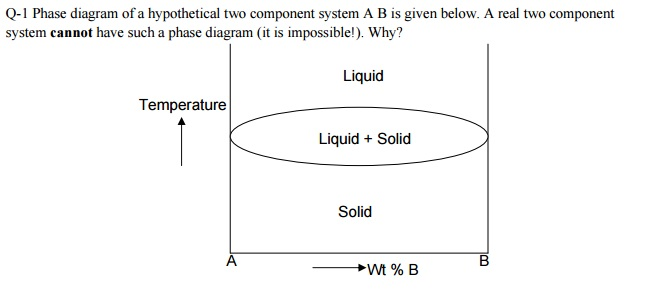
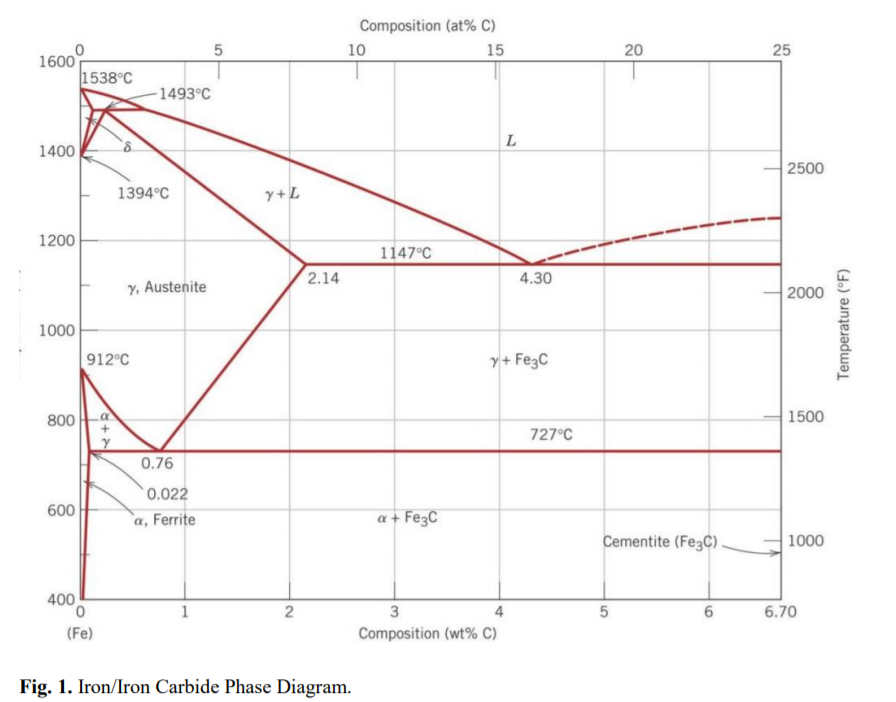
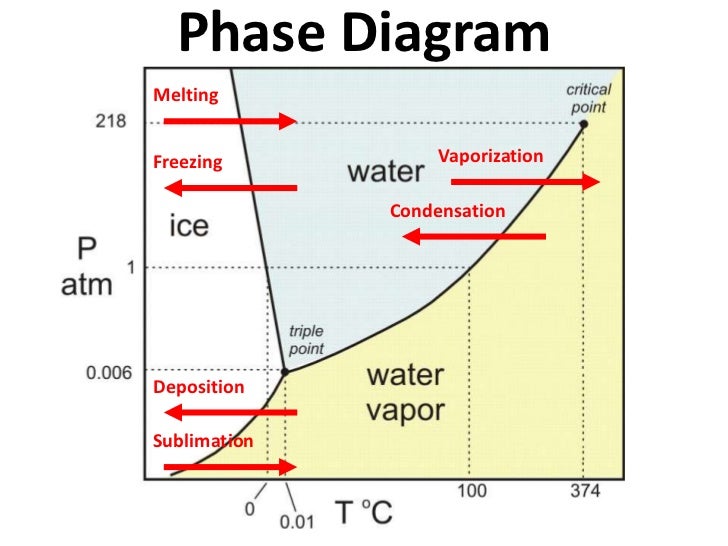
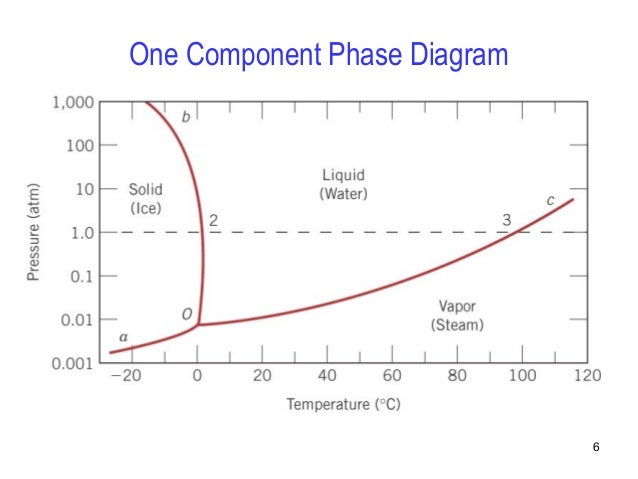
A diagram which illustrates the conditions of equilibrium between various phases of a substance is called a "phase diagram.". 14. Two component system: In a system of two components, when p = 1 F = C - p + 2 = 2 -1 +2 =3 • This means that three variables must be specified in order to describe the condition of the phase. The regions in which the various phases of a binary mixture are in equilibrium can be described by a so-called twocomponent phase diagram in which the temperature is plotted as a function of composition. The term eutectic melting diagram is also used if we are dealing with solid-liquid transitions. This Lecture talks about Phase Diagram of Two Component System 2. THE ONE-COMPONENT PHASE DIAGRAM . Figure 1 illustrates the temperatures and pressures at which water can exist as a solid, liquid or vapor. The curves represent the points at which two of the phases coexist in equilibrium. At the point T. t . vapor, liquid and solid coexist in equilibrium. In the fields of the diagram (phase fields) only one ...
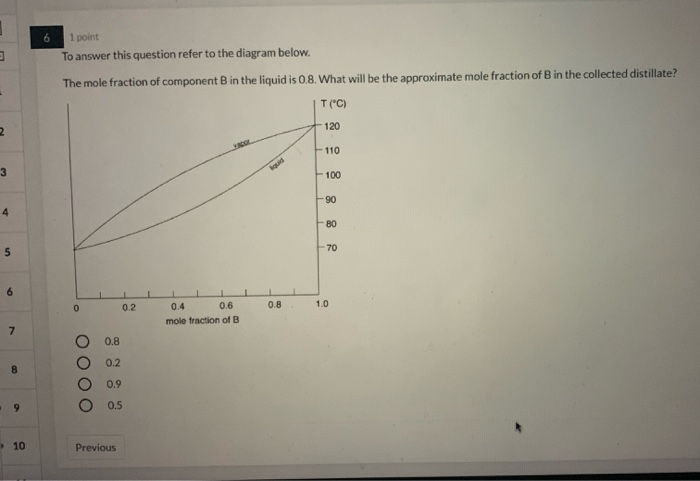
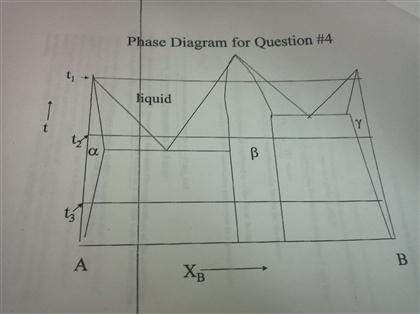
Question: Reading phase diagrams of a two-component system 1. Mark all fields on the phase diagram. 2. Draw the liquidus and solidus lines and mark characteristic points on the phase diagram 3. Draw a cooling curve for the composition. 4. Specify the composition and mass ratio of the coexisting phases for the selected point t, °C 8001 1800 700 ... 8.6 Liquid-solid phase diagram Consider the two-component liquid of composition a1 in the diagram above. The changes can be described as follows: (1) a1®a2. The system enters the two phase region labeled 'liquid + B'. Pure solid B begins to come out of solution and the remaining liquid becomes richer in A. (2) a2®a3. In the phase diagram to the right, the boundary curve between the liquid and gas regions maps the constraint between temperature and pressure when the single-component system has separated into liquid and gas phases at equilibrium. The only way to increase the pressure on the two phase line is by increasing the temperature. If the temperature is decreased by cooling, some of the gas condenses ... # Phase Diagram # Two component system # Priyanka jain chemistry # csir net chemistry Other Related videos-PHASE DIAGRAM 2- component system -https://youtu.b...
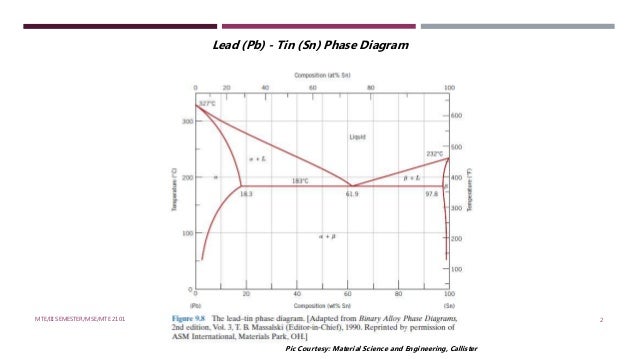
Phase Diagrams 10 Indicate phases as function of T, C o, and P. For this course:-binary systems: just 2 components.-independent variables: T and C o (P = 1 atm is almost always used). • Phase Diagram for Cu-Ni system Adapted from Fig. 9.3(a), Callister 7e. (Fig. 9.3(a) is adapted from Phase Diagrams of Binary Nickel Alloys, P. Nash (Ed.), ASM
Nov 10, 2008 — Here is another example of a two component phase diagram. The materials being combined are actually liquid crystals.
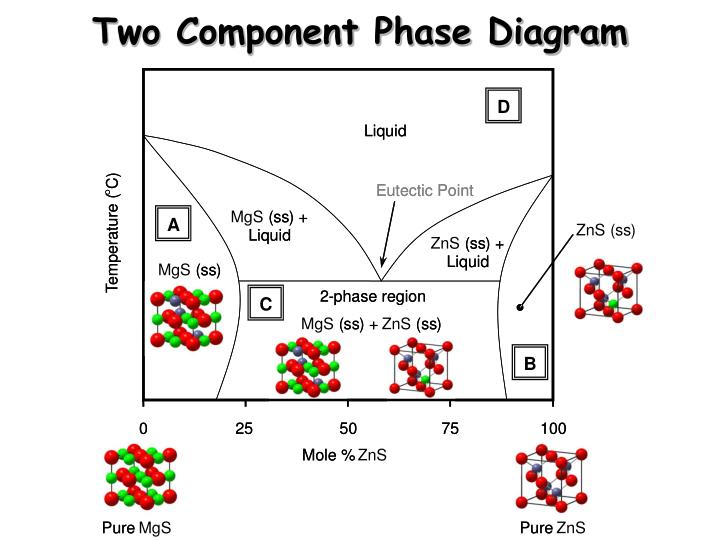
• The phase diagram consists of: Curves AC and CB Points A, B, and C Areas ADC, D`CB, OO`DD`, and area above the curve ACB Description Point A. It represents the melting point of the pure component A. Point B. It represents the melting point of the pure component B. Point C. It is known as the eutectic point.
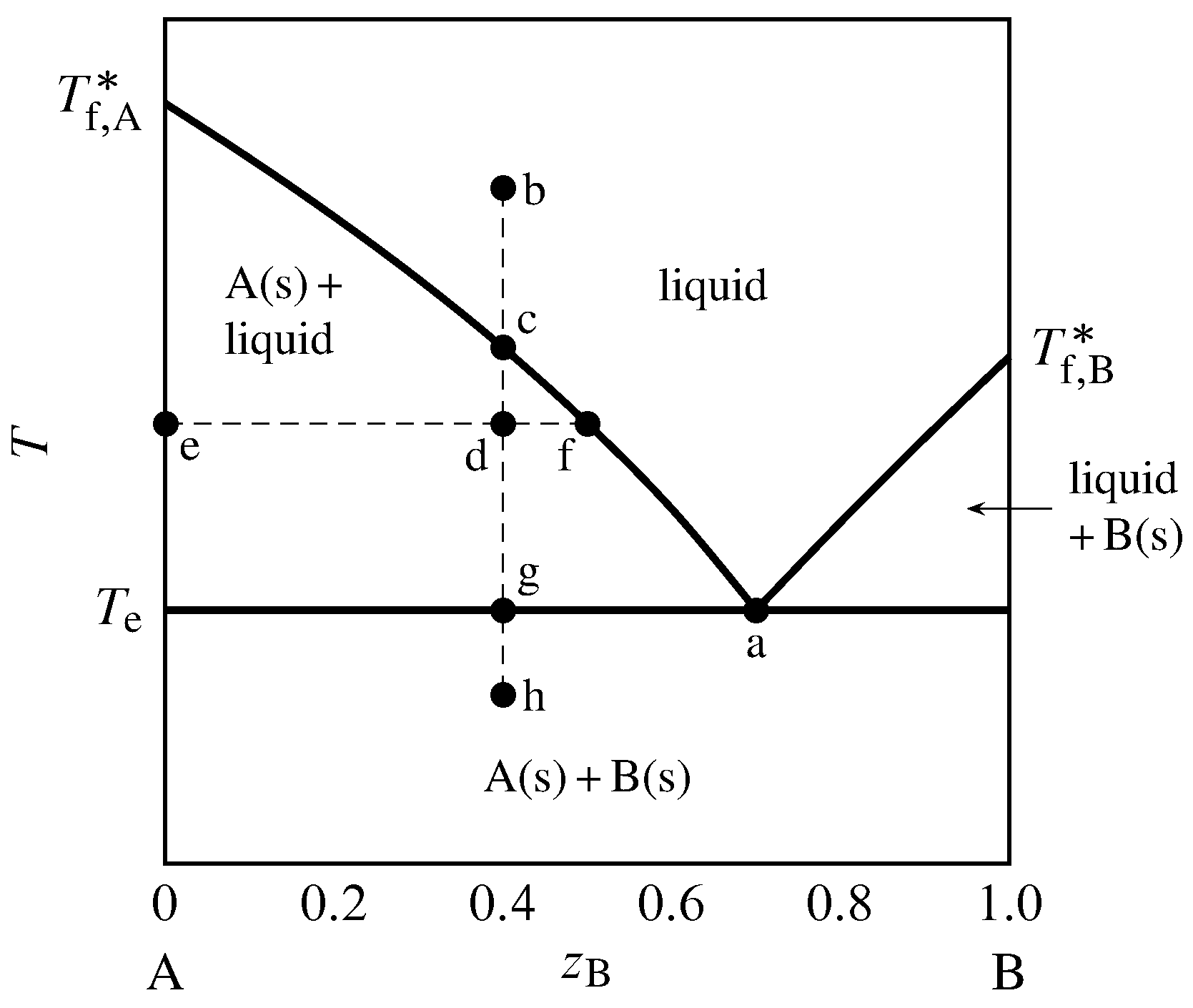
TWO COMPONENT EUTECTIC SYSTEM ! Phase rule: f = c + 2 – p ... Eutectic point: the point on a phase diagram where the maximum number of allowable phases are in equilibrium. When this point is reached, the temperature must remain constant until one of the phases disappears. A eutectic is an
Phase diagramis a graphical representation of all the equilibriumphases as a function of temperature, pressure, and composition. For one component systems, the equilibrium state of the system is defined by two independent parameters (P and T), (T and V), or (P and V). Phase diagram Pressure-temperature phase diagram for H2O:
You can drag the locator over various regions of the phase diagrams. For one-component systems, this selects values for the pressure and temperature. For two-component systems, this selects the temperature and composition. The two-component phase diagram should actually be three-dimensional, with pressure providing an additional degree of freedom.
PPT - Solid State Synthesis, Phase Diagrams and Solid Solutions PowerPoint Presentation - ID:1790511
prism is a two-component temperature-composition phase diagram with Pb Triple Eutectic 3-Dimensional Depiction of Temperature-Composition Phase Diagram of Bismuth, Tin, and Lead at 1atm. The diagram has been simplified by omission of the regions of solid solubility. Each face of the triangular a eutectic.
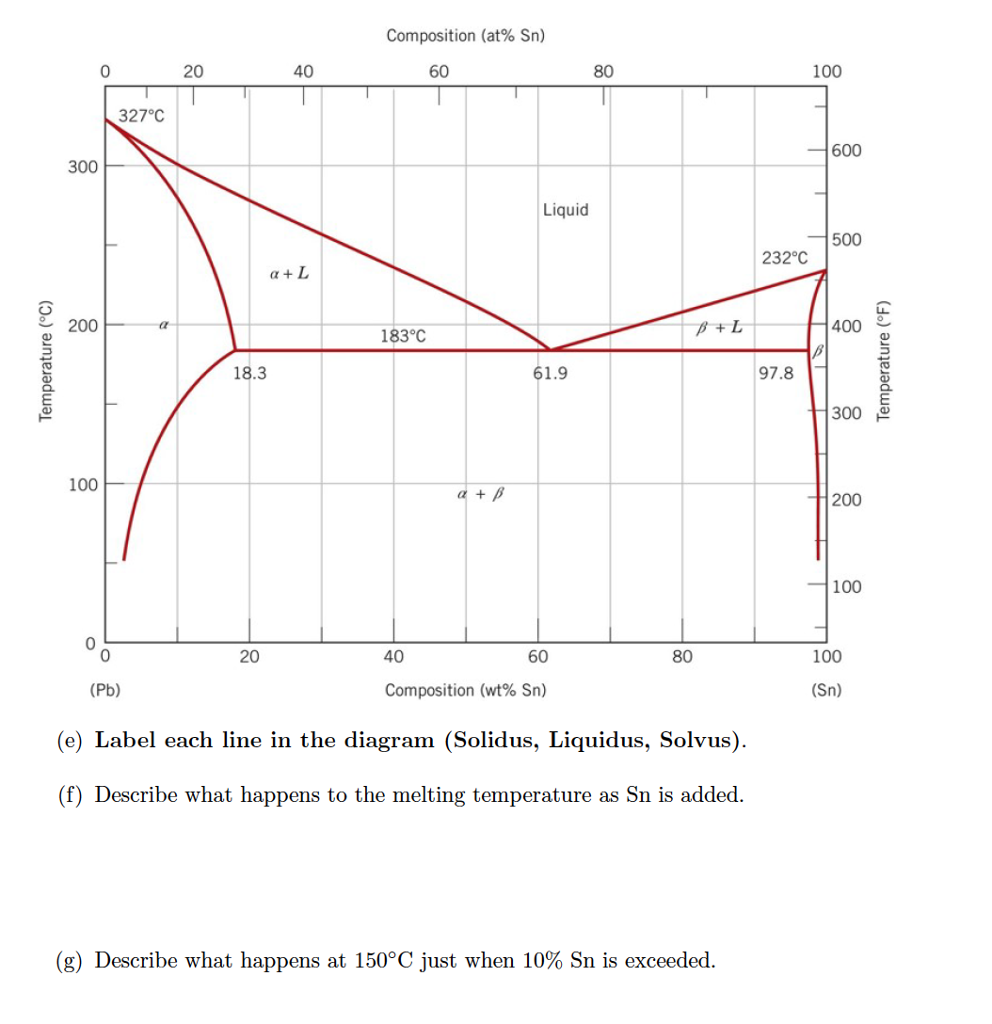
Determining phase composition in 2-phase region: 1. Draw the tie line. 2. Note where the tie line intersects the liquidus and solidus lines (i.e. where the tie line crosses the phase boundaries). 3. Read off the composition at the boundaries: Liquid is composed of CL amount of Ni (31.5 wt% Ni). Solid is composed of Cαααα amount of Ni (42.5 wt% Ni).
This section includes a discussion of systems, phases, components, the phase rule, two component eutectic systems, incongruent melting, rocks of varying composition and fractional crystallization, solid solution and exsolution. The lecture notes contain text, definitions and annotated phase diagrams. This resource is part of the Teaching ...
in the case of this lab) in a two-phase, two-component system when the temperature and pressure are known, as well as the overall composition. ... Phase diagrams are graphs that give information on the equilibrium temperature and pressure for a particular compound. The equilibria occur for the solid- liquid plateau,
Another type of binary phase diagram is a boiling-point diagram for a mixture of two components, i. e. chemical compounds. For two particular volatile components at a certain pressure such as atmospheric pressure , a boiling-point diagram shows what vapor (gas) compositions are in equilibrium with given liquid compositions depending on temperature.
Two components diagrams Two components diagrams The lever rule nl nlααββ= Relative amount and the composition of phases in equilibrium can be found on the phase diagram Two-components diagrams Temperature-composition diagrams •Distillation of mixtures number of theoretical plates Fractional distillation Two-components diagrams
Expt. 5: Binary Phase Diagram CHEM 366 V-2 P1=X1P1 0 (3) where X1+X2=1 (4) for a two component systems. Let us consider the situation of our mixtures of diphenylamine (A) and naphthalene (B). There are four possible combinations, neglecting the vapors of the two substances, a reasonable assumption at temperatures just above their melting points ...
Two types of phase diagrams are suitable for alloys composition which are binary and ternary phase diagrams. The binary phase diagram is used for system of two components and its classifications...
Phase diagrams (of two component systems) In general in a binary phase diagram the temperature or the pressure is plotted versus the molar fraction of one the two components. The variable of state that is not plotted is constant. The lines in the phase diagram are curves that divide different phases.
13.1.2 Two volatile components. In an ideal solution, every volatile component follows Raoult's law. Since the vapors in the gas phase behave ideally, the total pressure can be simply calculated using Dalton's law as the sum of the partial pressures of the two components \(P_{\text{TOT}}=P_{\text{A}}+P_{\text{B}}\).The corresponding diagram is reported in Figure 13.2.
May 18, 2020 — Obviously the two phases must have different compositions or they would be identical; the difference is called a miscibility gap. A binary ...







![Diode Ring Modulator [Analog Devices Wiki]](https://wiki.analog.com/_media/university/courses/electronics/drm_f4.png?w=500&tok=43bcab)








![Two-component phase equilibrium diagram Co-Cr [3] | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Wlodzimierz_Dudzinski/publication/267781823/figure/fig1/AS:295627746496514@1447494555952/Two-component-phase-equilibrium-diagram-Co-Cr-3_Q320.jpg)


0 Response to "37 two component phase diagram"
Post a Comment