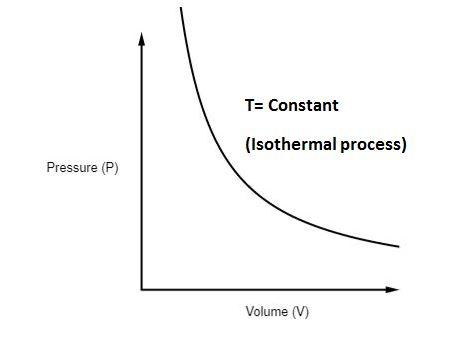
39 pv diagram constant temperature
The pressure falls from P3 to P4, Volume increases from V3 to V4, the temperature falls from T3 to T4 and entropy remains constant (i.e. S3=S4). Process 4-1: Constant Volume Heat Rejection In this process, the piston rest at BDC for a moment and the cold body is brought in contact with the cylinder and the heat rejection takes place at constant ...
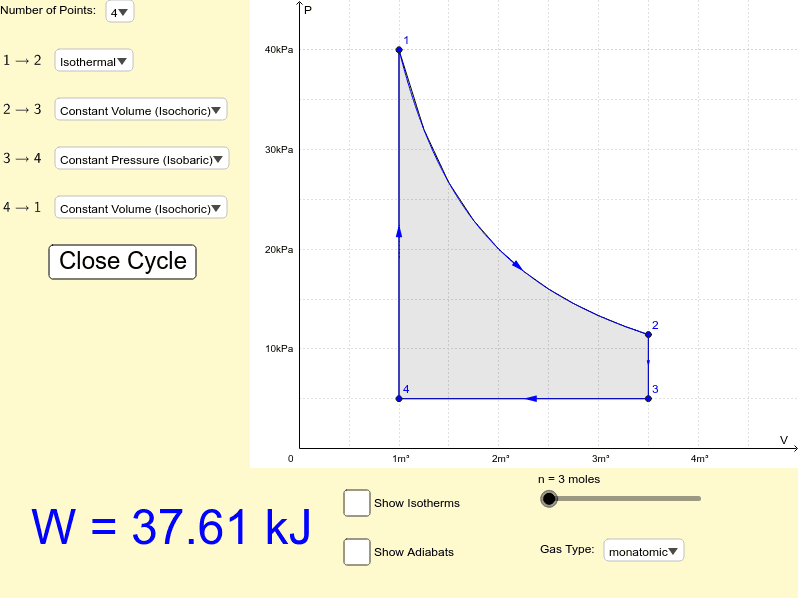
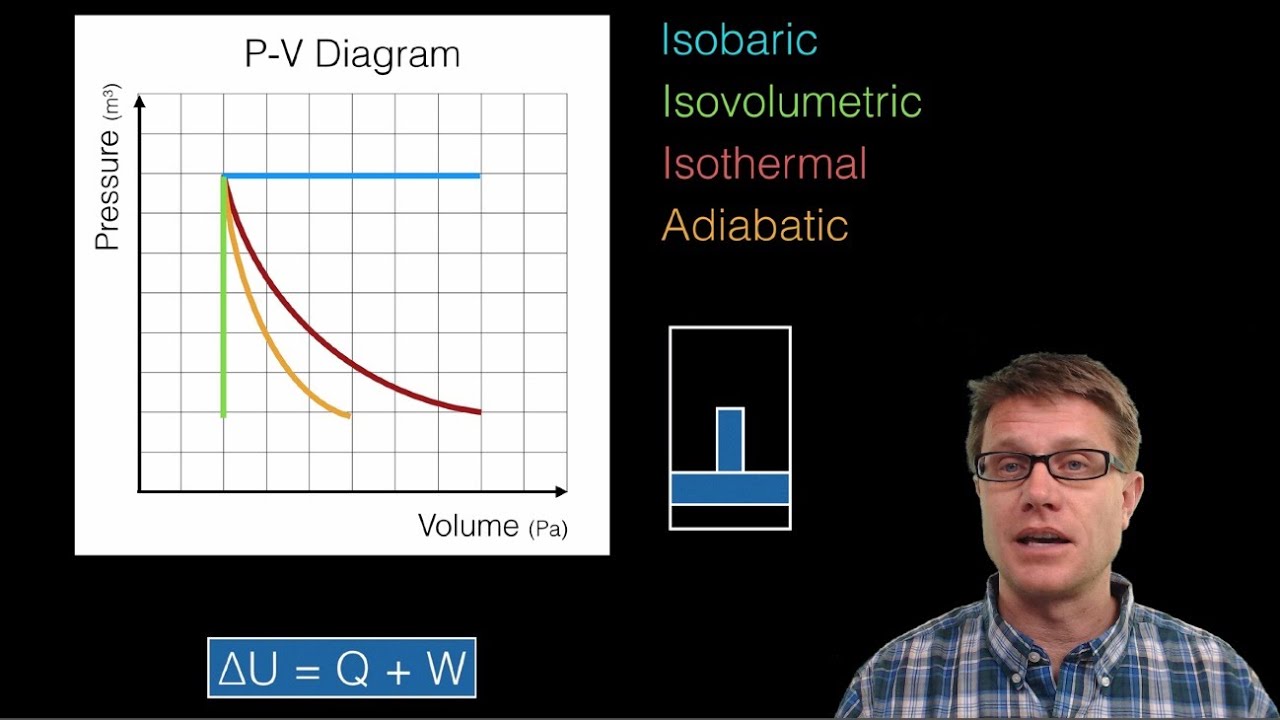
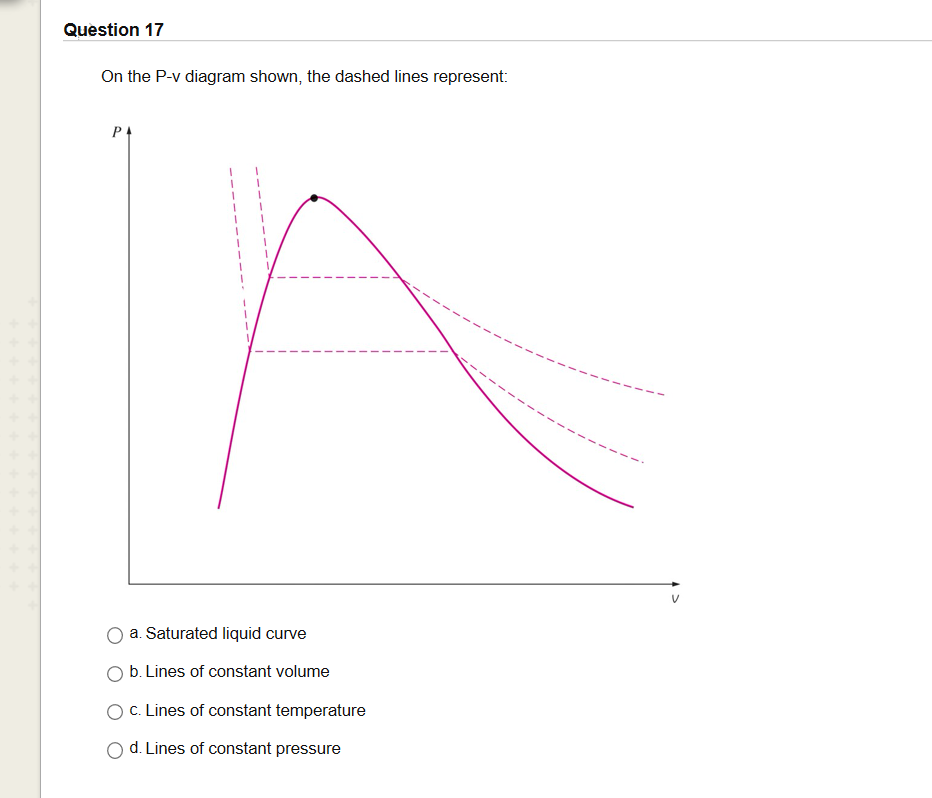
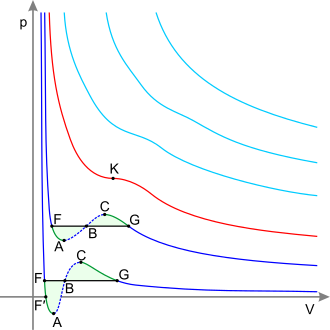
A pressure-volume diagram, also known as an indicator diagram is used to show changes to the pressure and volume in thermodynamic cycles. The area under a p-V curve represents the work done on or by a gas. Some p-V diagrams are shown below: Constant Pressure and Constant Volume. A constant pressure process is represented as a horizontal line.
pV γ=constant =1 1 =constant pV γ pVγ 1 constant 2 2 1 1 1 = = T Vγ− T V γ− pV =nRT During an adiabatic expansion process, the reduction of the internal energy is used by the system to do work on the environment. During an adiabatic compression process, the environment does work on the system and increases the internal energy.

Pv diagram constant temperature
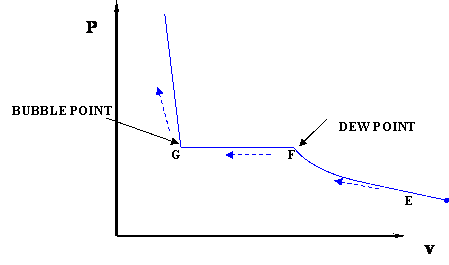
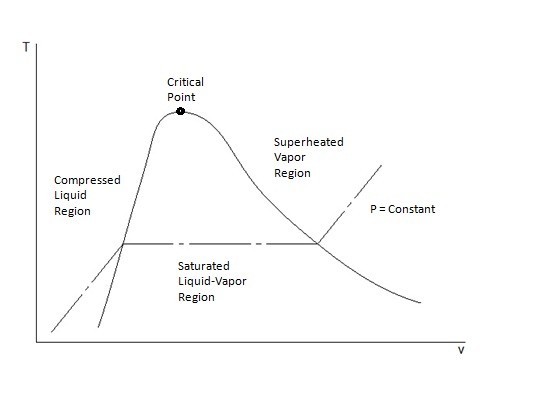
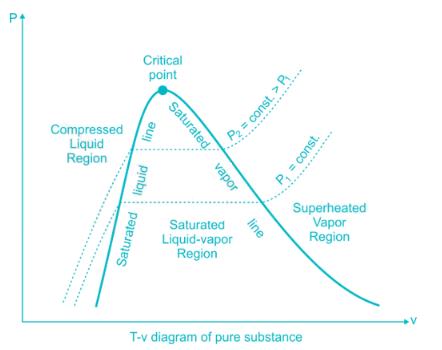
Let us draw the PV diagram, Pressure will be shown on vertical axis i.e. Y axis and volume will be shown on horizontal axis i.e. X axis. We will consider the cooling process in order to understand the PV diagram for a pure substance here. We will start our discussion with point A. At point A, working fluid will be in the phase of vapour.
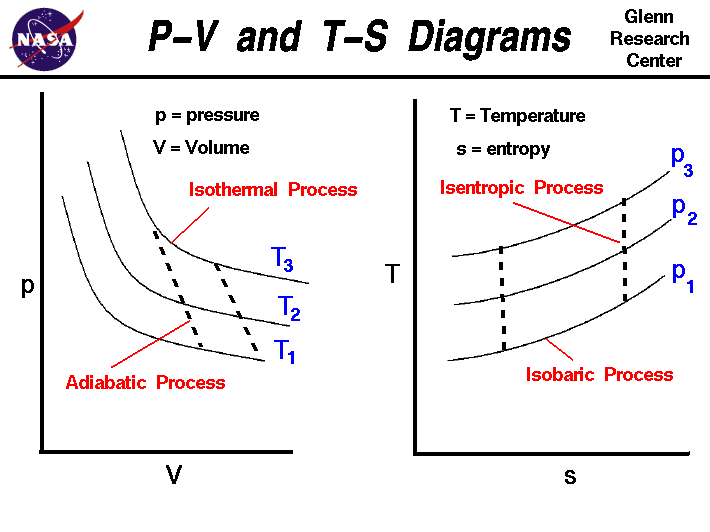
The PV diagram for an adiabatic process show a special result. • An adiabatic process looks very much like an isothermal process, but it drops off to a lower point. This means it is on a different isotherm. Remember, isotherms are just lines that show where the temperature stays constant.
Process 4-1 - Constant Pressure Heat Rejection in Condenser. At this process the low temperature and low pressure vapour will be condensed in the condenser. It will be converted into saturated liquid. So, these are the four process in the ideal Rankine cycle.
Pv diagram constant temperature.
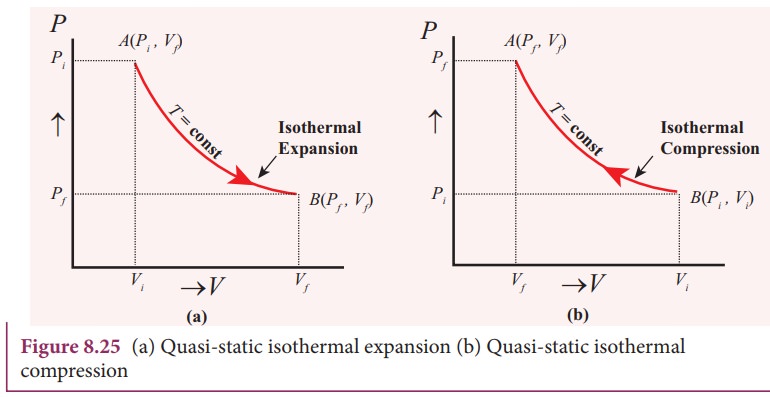
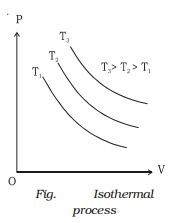
14 Feb 2017 — In P-V graph of constant temperature pressure and volume are variables. But since temperature is constant the ideal gas law can be modified; PV= nRT. now ...3 answers · Top answer: * Constant temperature means an isothermal process. • PV=nRT 1. 1. This is the ideal ...How can I calculate the temperature in a P-V diagram ...1 answer21 Dec 2017What is the slope of a constant temperature line in a ...1 answer31 Jul 2017In a PV diagram, how do you know the process is ...2 answers25 Sept 2018How is PV CONSTANT in a isothermal process? - Quora6 answers1 Jan 2017More results from www.quora.com
Isochoric Process - Ideal Gas Equation - pV Diagram. An isochoric process is a thermodynamic process in which the volume of the closed system remains constant (V = const). It describes the behavior of gas inside the container that cannot be deformed. Since the volume remains constant, the heat transfer into or out of the system does not the ...
13. Starting from the initial state shown, draw a pV diagram for the p. three—step process: i. A constant-volume process that halves the temperature. ii. An isothermal process that halves the pressure, then iii. An isobaric process that doubles the volume. Label each of the stages on your diagram.
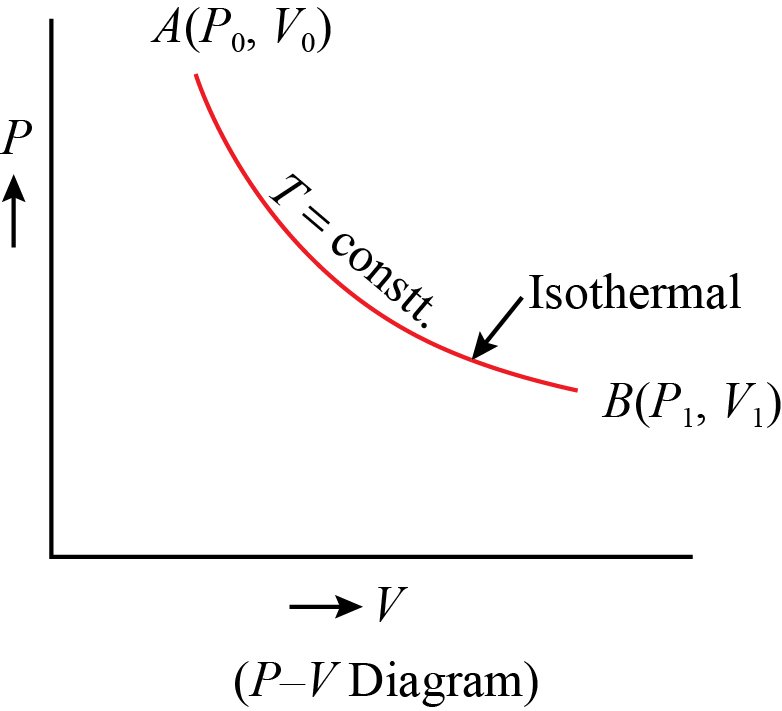
On a p-V diagram, lines of constant temperature curve from the upper left to the lower right. A process performed at constant temperature is called an isothermal process. During an adiabatic process no heat is transferred to the gas, but the temperature, pressure, and volume of the gas change as shown by the dashed line.
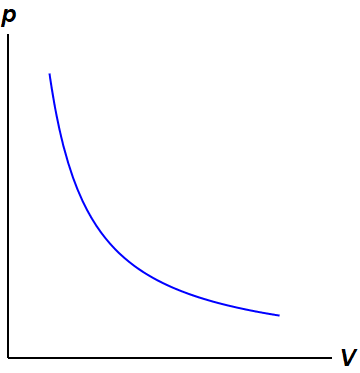
PV = constant (ideal gas, constant temperature). PV = constant ( ideal gas, constant temperature). For example, the volume of the gas will decrease as the pressure increases. If you plot the relationship PV = constant PV = constant on a PV PV diagram, you find a hyperbola. The figure below shows a graph of pressure versus volume.
During this process, volume remains constant (V = C) and is represented on a PV-diagram by means of vertical line as shown. When unit mass of a gas is heated in a closed vessel (i.e., V = C), then, since volume remains constant, no external work is done. But as temperature of the gas increases I.E. increases. (a) Work Done:
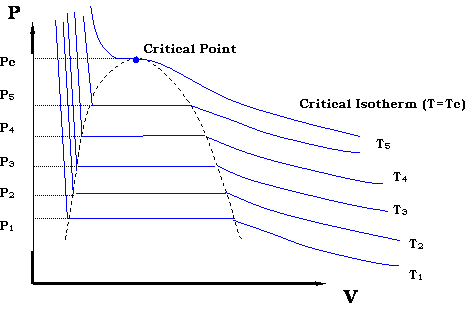
Ideal Gas p-V, p-T Diagrams NkT p V = increasing T Volume Pressure p vs V at various constant T's 0 Pressure Temperature 0 Pressure →zero as T →absolute zero, because the thermal kinetic energy of the molecules vanishes. p vs T at constant V Isotherms. ... pV = constant γ= (α+1)/α. Lecture 3, p 19 ...
On a pV diagram, the process occurs along a line called isothermal curve or an isotherm. This curve has the equation p = constant / V. It can be derived from ideal gas law. In an ideal gas, molecules have no volume and do not interact. According to the ideal gas law, pressure varies linearly with temperature and quantity, and inversely with volume.
PV = nRT = constant. In state 1, Table 14.2 tells us ... sketch isotherms on the P-V diagram to convey temperature information - an isotherm is a line of constant temperature. Related End-of-Chapter Exercises: 11, 12, 49 - 52. Figure 14.13: A P-V diagram showing two
EXPLORATION 15.3A - A constant-volume process A sample of monatomic ideal gas is initially at a temperature of 200 K. The gas occupies a constant volume. Heat is then added to the gas until the temperature reaches 400 K. This process is shown on the P-V diagram in Figure 15.8, where the system moves from state 1 to state 2 by the process ...
Temperature: This simulation introduces the P-V (pressure-volume) diagram. when the temperature of the ideal gas or the volume is changed (at constant temperature). You can also sketch a pressure vs. volume graph for a given temperature, by choosing a temperature and then using the volume slider to
in thermodynamic pv diagram or pressure-volume diagram is most basic in mechanical engineering,this video gives only basic idea how to draw pv diagram for be...
3. Sketch a PV diagram of the following process: 2.0 L of ideal gas at atmospheric pressure are cooled at constant pressure to a volume of 1.0 L, and then expanded isothermally back to 2.0 L, whereupon the pressure is increased at constant volume until the original pressure is reached. (Table of contents)
Pressure = NKT/V. Now lookit. N number of molecules in here, that's a constant we're not letting any gas molecules in or out. K, that's Boltzmann's Constant, that number doesn't change. For an isothermal process, temperature's also a constant.
12 Sept 2018 — The isothermal process is represented by a P-V curve at constant temperature. As pressure changes and volume changes within a closed system, ...
A convenient way to visualize these changes in the pressure and volume is by using a Pressure Volume diagram or PV diagram for short. Each point on a PV diagram corresponds to a different state of the gas. The pressure is given on the vertical axis and the volume is given on the horizontal axis, as seen below.
constant temperature "therm" comes from the greek work for heat: θερμότητα [thermotita] examples: "slow" processes, breathing out through a wide open mouth; PV graph is a rectangular hyperbola
pV = constant. or. p 1 V 1 = p 2 V 2. Yes, it seems to be identical as isothermal process of ideal gas. In fact, during their experiments the temperature remain constant as was assumed by Mariotte. These results are fully consistent with ideal gas law, which determinates, that the constant is equal to nRT. pV = nRT. where: p is the absolute ...
constant volume. (b) Heating at constant volume followed by cooling at constant pressure. Calculate the heat and work requirements and ΔU and ΔH of the air for each path. The following heat capacities for air may be assumed independent of temperature: C V = 20.78 and C P =29.10 J mol-1 K-1 Assume also for air that PV/T is a constant ...
(E) The temperature of the gas remains constant. 37. A constant amount of an ideal gas undergoes the cyclic process ABCA in the PV diagram shown above. The path BC is isothermal. The work done by the gas during one complete cycle, beginning and ending at A, is most nearly (A) 600 kJ (B) 300 kJ (C) 0 (D) -300 kJ (E) -600 kJ 38.
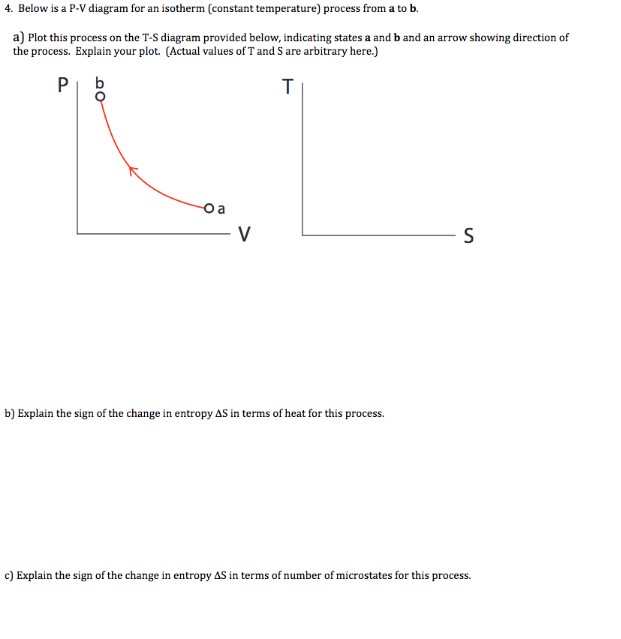
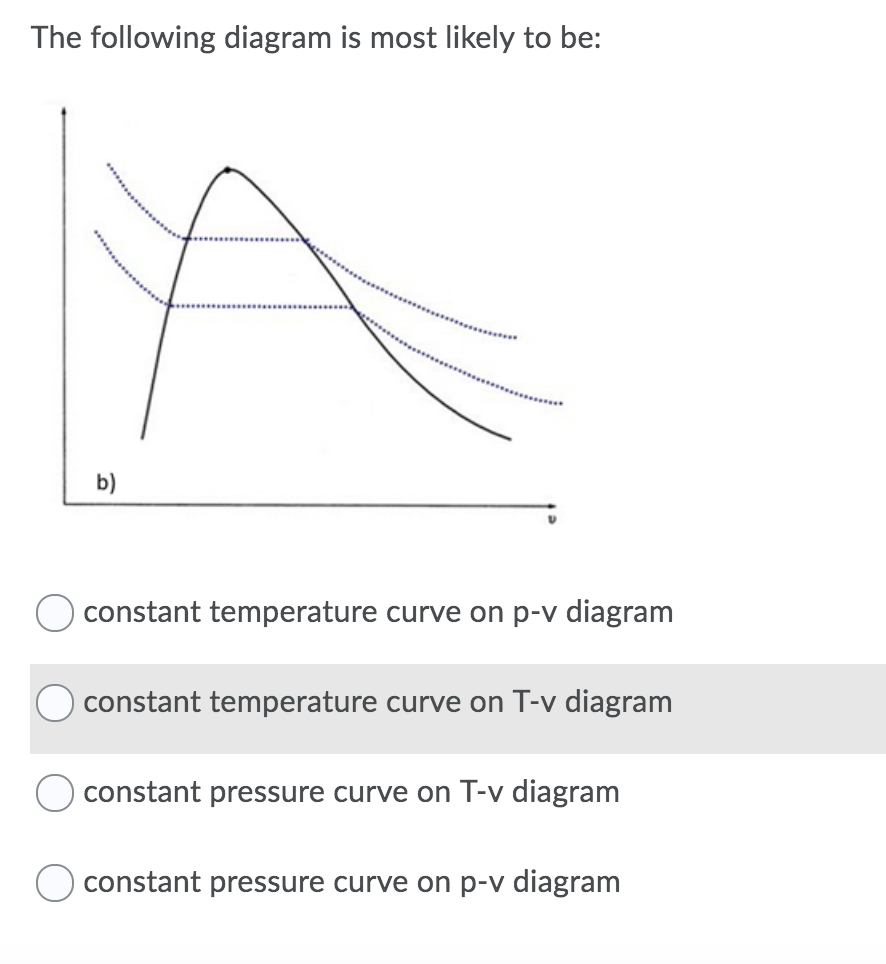
If we want to follow changes in volume, we may construct P-v or T-v diagrams, in which we hold temperature (T) or pressure (P) constant. Let us consider the case of a P-v Diagram (Figure 3.4). Figure 3.4: P-v Diagram For A Pure Component In this case temperature is being held constant; our substance is undergoing an isothermal compression process.
For example, the equation of state for an ideal gas is PV = nRT. So if your process has a fixed amount of the gas (constant number of moles, n) you can calculate the temperature T for every point in the P-V diagram. Other materials, like a magnet, have other state variables (magnetization instead of volume being one).
The PV diagram models the relationship between pressure (P) and volume (V) for an ideal gas.An ideal gas is one that never condenses regardless of the various changes its state variables (pressure, volume, temperature) undergo. In addition, the processes plotted on PV diagrams only work for a closed system (in this case the ideal gas), so there is no exchange of matter, but still an exchange ...
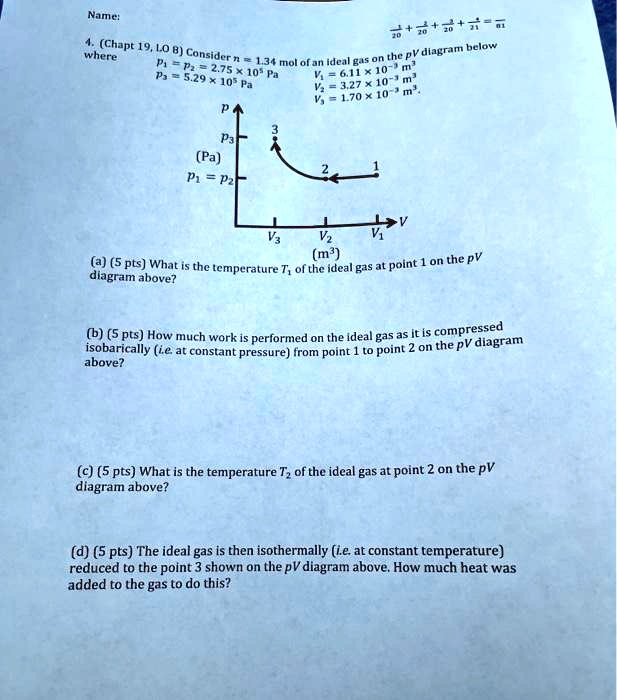
1. Two moles of an ideal gas are heated at constant pressure from 27°C to 107°C. (a) Draw a pV-diagram for this process. (b) Calculate the work done by the gas. 2. Two moles of an ideal gas are compressed in a cylinder at a constant temperature of 85.0°C until the original pressure has tripled. (a) Sketch a pV-diagram for this process. (b ...
















0 Response to "39 pv diagram constant temperature"
Post a Comment