39 flat mirror ray diagram
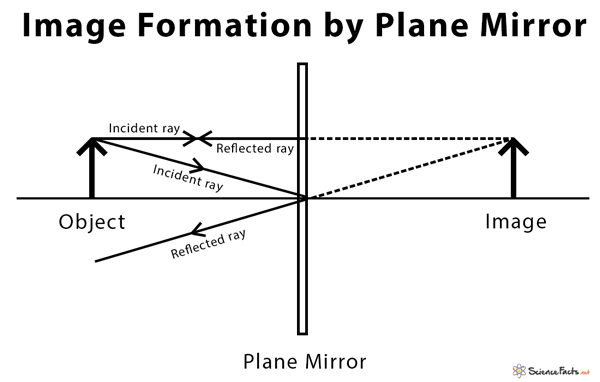
The ray diagram below uses three reflected rays to illustrate how the image can appear to be enlarged and upright. The image formed is a virtual image. Figure 6 . How to draw a ray diagram for a plane (flat) mirror.Please visit www.studyphysics.ca.
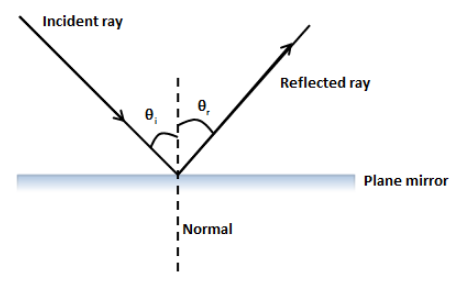
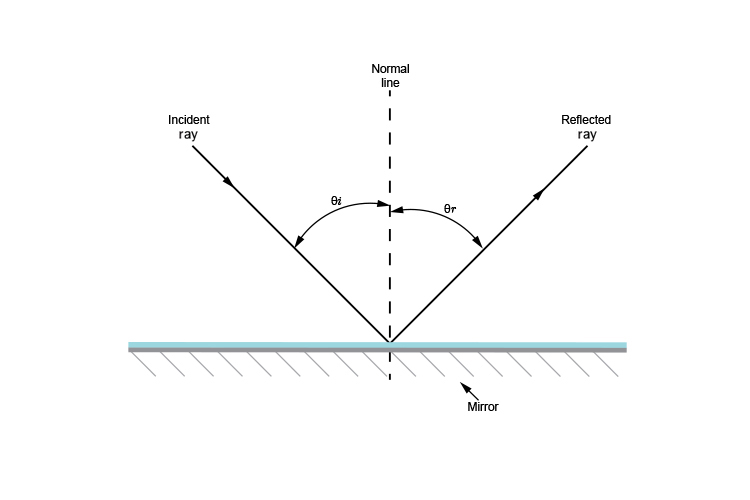
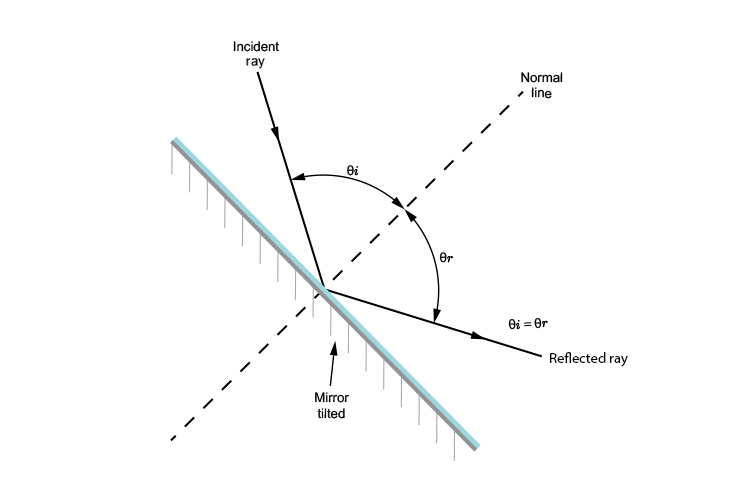
A ray diagram for reflection at a mirror. In the ray diagram: ... The reflection of light from a flat surface such as a mirror is called specular reflection - light meeting the surface in one ...

Flat mirror ray diagram
Ray Diagrams J.M. Gabrielse Outline • Reflection • Mirrors • Plane mirrors • Spherical mirrors • Concave mirrors • Convex mirrors • Refraction • Lenses • Concave lenses • Convex lenses J.M. Gabrielse A ray of light is an extremely narrow beam of light. ... (flat mirrors) How do we see images in mirrors? Flat Mirror Diagrams . Overall Information In this diagram you can see how an image is formed. 1. Light leaves the object and hits the mirror ... Drawing Ray Diagrams •For our ray diagrams you will need to determine the location of the top of the object and the location of the bottom of the object. Use the following steps to do that. Step 1 ... How to draw a light ray diagram for a flat mirror and locate the looking glass' virtual image. Locating Flat Mirror Virtual Images Top » Consulting » Tutorials » Flat Mirror Images: Flat Mirror Ray Diagram. Translatable page. Shop for neat science stuff. ...
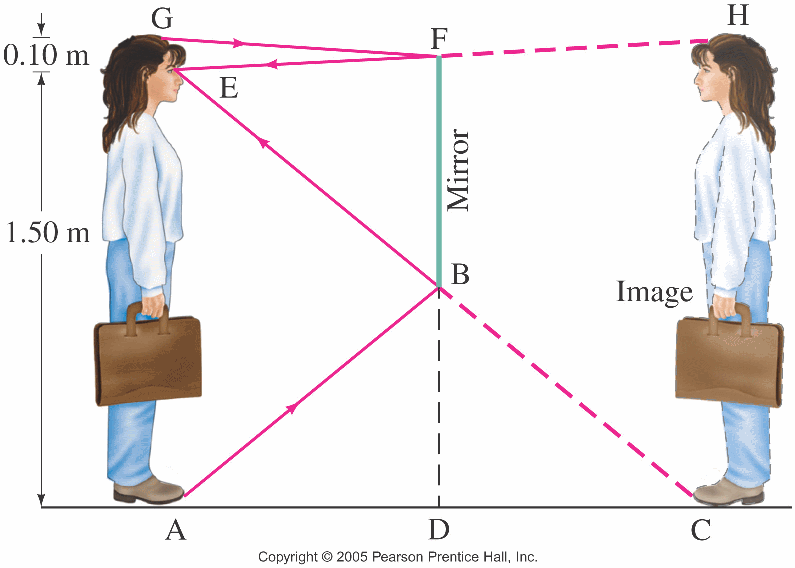
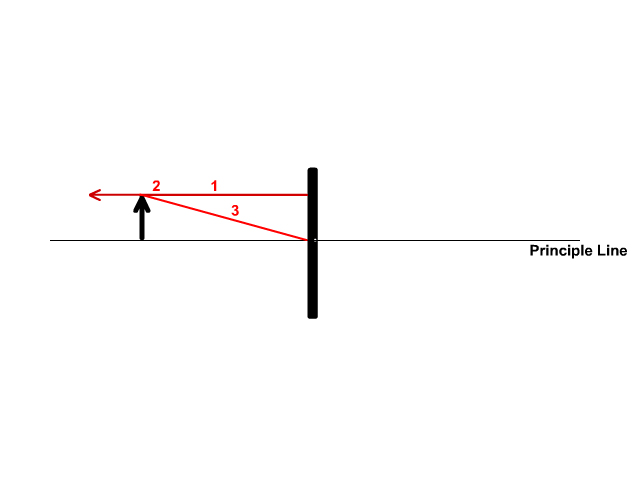
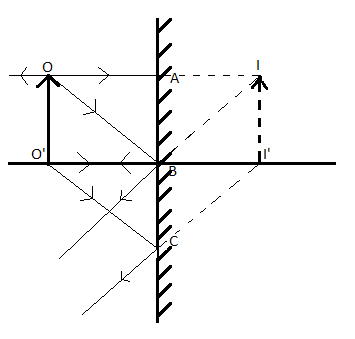
Flat mirror ray diagram. In the case of a flat mirror, no light from the object goes behind the mirror. It bounces off the surface and comes back the other way. So, the image location in this case isn't actually where the light is coming from. (That is true for some images, "real" ones.) Thus this is a "virtual" image. 3) Consider two mirrors arranged at right angles. Mirrors: Principal Ray Diagram of a Flat Mirror Uses of Ray Diagrams. Ray diagrams can be particularly useful for determining and explaining why only a portion of the image of an object can be seen from a given location. The ray diagram at the right shows the lines of sight used by the eye in order to see a portion of the image in the mirror. 4) A object is a distance d = 5cm in front of a flat mirror, make a ray diagram showing location of image. 5) Discribe the image in the previous question (question 4) and find the magnification.
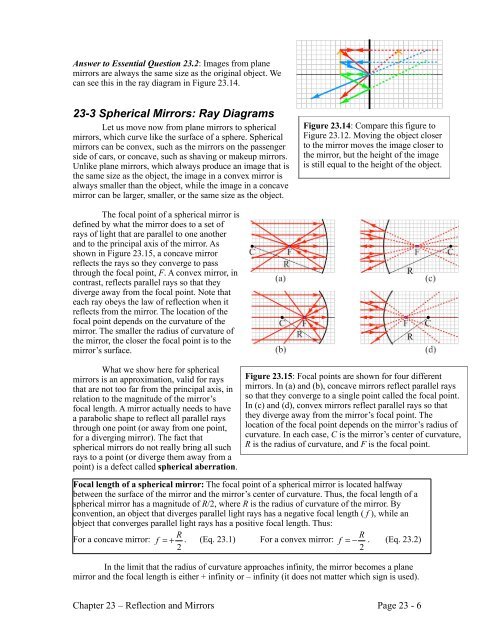
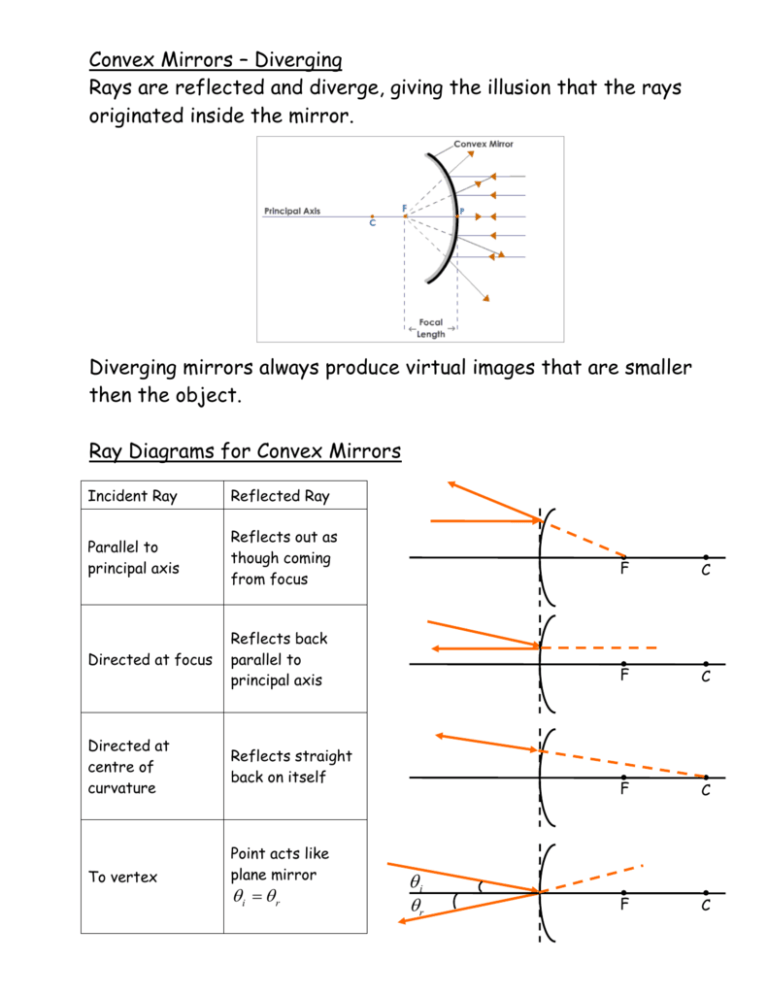
Plane mirror- Definition, Properties and Ray Diagram. Mirrors are defined as one side-polished surface that can reflect the light rays. Plane mirrors in physics are the ones that have a flat reflecting surface and produce always a virtual image. In this tutorial, we review the most important topics in the plane (flat) mirrors in physics ... Determine the minimum height of a vertical flat mirror in which a person 5' 10" in height can see his or her full image. (A ray diagram would be helpful). A. 2' 11" B. 3' 9" C. 5' 10" D. Depends on distance to mirror. Answer klm In what location will the image form? 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D Answer klm Which ray is correct? ray A ray B ray C ray D ... Concave Mirror Ray Diagram. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p.
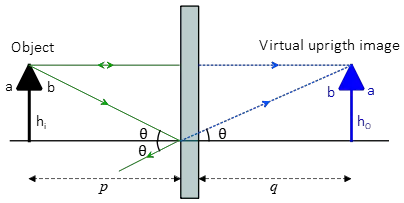
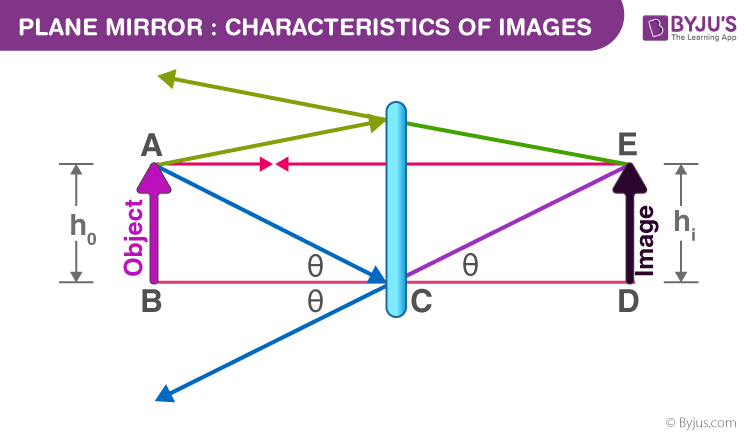
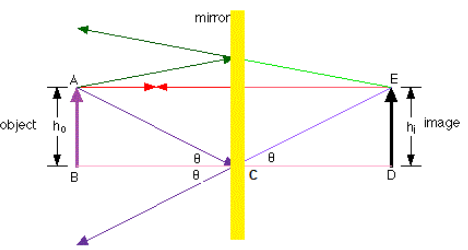
diagrams for lenses and mirrors. Concave Mirror Ray Diagrams For mirrors, the following set of rays are typically used in ray diagrams. Ray # 1 The flrst ray starts at the top of the object, parallel to the optical axis and is re°ected through the focus of the mirror just as is shown in Figure 3. In Figure 2, Plane Mirrors. Drawing a ray diagram is fairly simple for a plane mirror. Firstly we should draw an incoming ray: Figure 1: A diagram showing a ray incident on a plane mirror from an object. Notice that the object is clearly labelled and the direction of travel is indicated with an arrow on the ray. How to draw a ray diagram that shows the formation of a virtual image in a plane mirror. How to draw a ray diagram that shows the formation of a virtual image in a plane mirror. For flat mirrors the Law of Plane Mirrors states that "the image is always the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror." The image, I, and the object, O, always line up along the same normal. The image is upright, but left-right reversed. Notice that the rays entering the eye are diverged from the mirror's surface.

With The Help Of A Ray Diagram State And Explain The Laws Of Reflection Of Light At A Plane Mirror Mark The Angle Of Incidence And Reflection Clearly In The Diagram If
The virtual images in a plane mirror have a left-right inversion. Drawing a ray diagram is a way to predict what a reflected image will look like.
Infinite reflections may terminate. For instance, two mirrors at right angles form three images, as shown in part (a) of . Images 1 and 2 result from rays that reflect from only a single mirror, but image 1,2 is formed by rays that reflect from both mirrors. This is shown in the ray-tracing diagram in part (b) of . To find image 1,2, you have ...
Mirror mini lab. Review of drawing ray diagrams. Mirror worksheet 1 - ray diagrams. Refraction: If one has ever used a pool skimmer, gone fishing, played with a stick in the water one would notice objects in the water tend to bend. They are not where they are suppose to be. This is refraction.
Drawing a ray diagram would be helpful. A convex spherical mirror has a radius of curvature of magnitude 40.0 cm. Determine the position of the virtual image and the magnification for object distances of 30.0 cm and (b) 60.0 cm. (c) Are the images in parts (a) and (b) upright or inverted?
Drawing ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Refraction of light. Total internal reflection. This is a short tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors. Click on the images to view a larger version. Initially, we have an object in front of a plane mirror.
Give Mr. H just 6 minutes to explain what a ray diagram is and to demonstrate how to construct a ray diagram for a point object and an arrow ...
How to draw a light ray diagram for a flat mirror and locate the looking glass' virtual image.
Explain with ray diagrams the formation of an image using spherical mirrors. Determine focal length and magnification given radius of curvature, distance of object and image. We only have to look as far as the nearest bathroom to find an example of an image formed by a mirror.
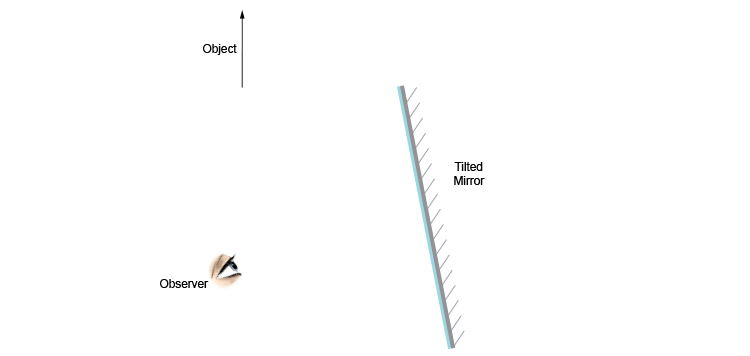
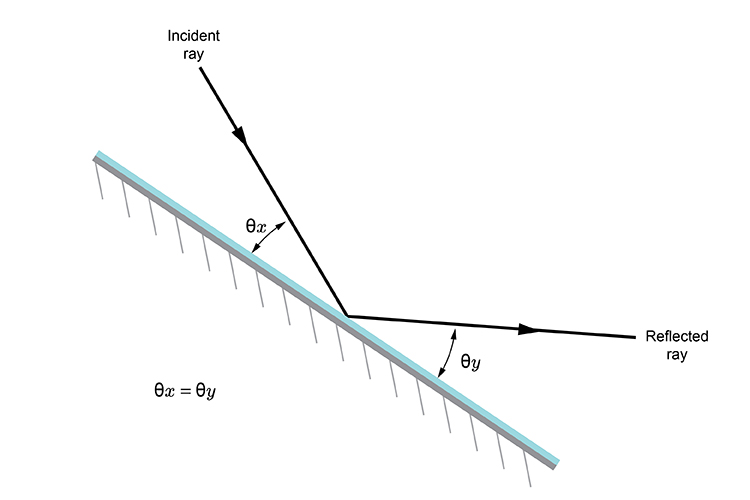
Flat mirror, tilted, ray diagram. How do you draw the ray diagram for a flat mirror which has been tilted, an object and an observer, as below: The way to draw the ray diagram for this situation is to carry out the three stages as we have previously learnt as follows:
Practice: Ray diagrams and curved mirrors. This is the currently selected item. Mirror formula derivation. "Objects in the mirror are ..." actually images in the mirror. Cartesian sign conventions mirrors. Practice: Sign convention. Solved example: Mirror formula. Practice: Using the mirror formula.
Flat Mirror •Properties of the image can be determined by geometry. •One ray starts at P, follows path PQ and reflects back on ... Ray Diagram for a Concave Mirror, p < f •The object is between the mirror and the focal point. •The image is virtual. •The image is upright.
Description of how to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors for grade 10 science.
Using flat mirrors ray diagram rules. How do we draw the ray diagram for a flat mirror, an object and an observer using flat mirror ray diagram rules? See below: The first stage is to draw an image on the other side of the mirror perpendicular (at 90°) to the mirror. Behind the mirror Equal distance The same size
Convex Mirror Image. A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign convention is used here.. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror.
• Ray diagrams are based on the premise that to view an object in a mirror, one must sight along a line at the image of the object. When one does, light travels along that line to your eye. • Ray diagrams can be drawn for all types of mirrors. This video focuses on plane mirrors. Proceure for Drawing Ray Diagram Step 1 Locate the Image:
How to draw a light ray diagram for a flat mirror and locate the looking glass' virtual image. Locating Flat Mirror Virtual Images Top » Consulting » Tutorials » Flat Mirror Images: Flat Mirror Ray Diagram. Translatable page. Shop for neat science stuff. ...
Flat Mirror Diagrams . Overall Information In this diagram you can see how an image is formed. 1. Light leaves the object and hits the mirror ... Drawing Ray Diagrams •For our ray diagrams you will need to determine the location of the top of the object and the location of the bottom of the object. Use the following steps to do that. Step 1 ...
Ray Diagrams J.M. Gabrielse Outline • Reflection • Mirrors • Plane mirrors • Spherical mirrors • Concave mirrors • Convex mirrors • Refraction • Lenses • Concave lenses • Convex lenses J.M. Gabrielse A ray of light is an extremely narrow beam of light. ... (flat mirrors) How do we see images in mirrors?













0 Response to "39 flat mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment