42 trigeminal nerve branches diagram
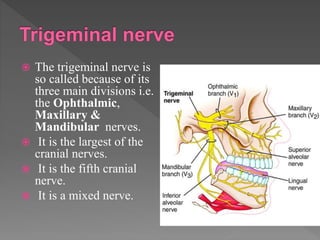
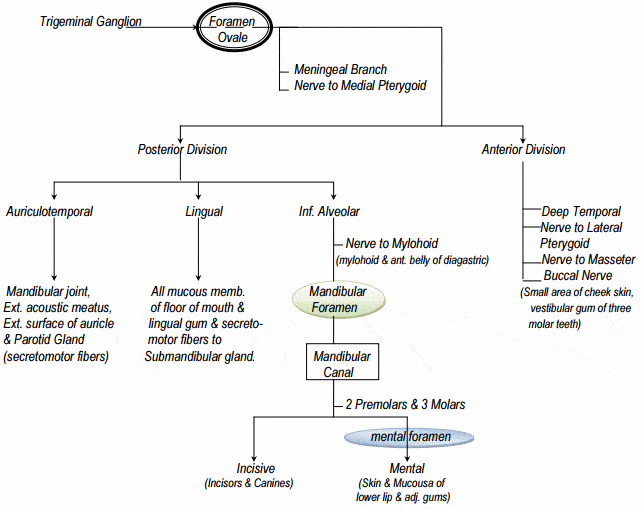
Diagram of the third branch (mandibular) of the trigeminal ... Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy: Gross Anatomy, Branches of the Trigeminal Nerve, Microscopic Anatomy The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head. Trigeminal nerve (illustration) | Radiology Case ... Diagram Simplified diagrams of the main branches and sensory supply of the trigeminal nerve. Case Discussion Simplified illustrations of the trigeminal nerve, its main branches, and its sensory supply. See article for more information. References 11 article feature images from this case 1 public playlist includes this case
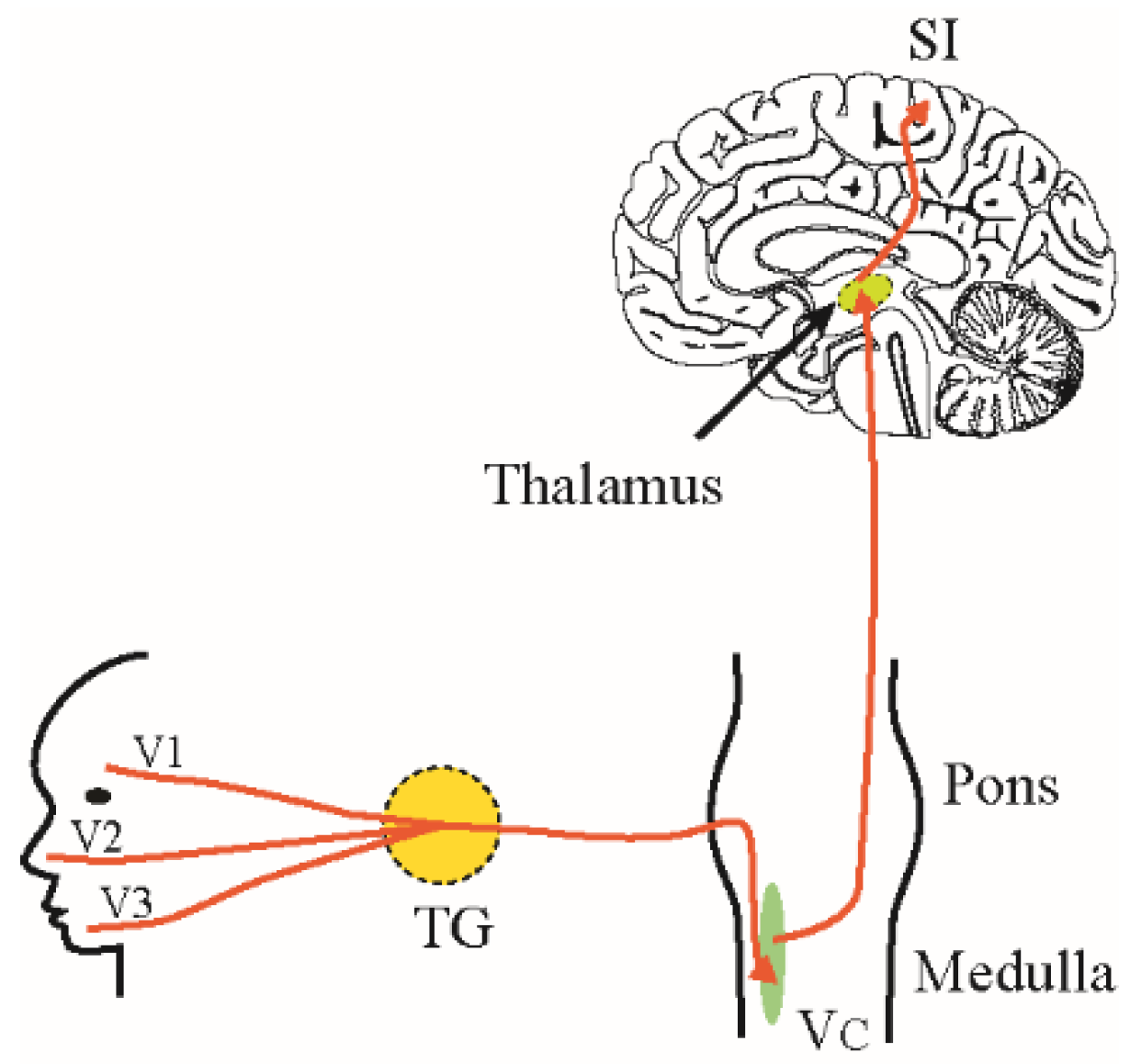
Trigeminal nerve route of entry. (A) Schematic showing the ... (A) Schematic showing the three branches of the trigeminal nerve: V1, V2, and V3. Branches V1 and V2 innervate the nasal cavity and project to the brain stem (BS).

Trigeminal nerve branches diagram
Trigeminal Nerve Distribution Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Trigeminal Nerve Distribution. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Trigeminal nerve | Radiology Reference Article ... Although the trigeminal nerve is usually described singularly, it actually emerges/enters from the brain stem as multiple nerve roots 8. The sensory root is large and single and enters the anterolateral aspect of the pons. Usually superomedial to, and within 4 mm of the sensory root, one or more motor roots emerge. radiopaedia.org › articles › temporal-bone-1Temporal bone | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org Jul 01, 2021 · The temporal bone is situated on the sides and the base of the cranium and lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebrum. The temporal bone is one of the most important calvarial and skull base bones. Gross anatomy The temporal bone is divided ...
Trigeminal nerve branches diagram. Trigeminal nerve (CN V) - Kenhub The principal regulator of the sensory modalities of the head is the trigeminal nerve. This is the fifth of twelve pairs of cranial nerves that are ...Divisions: Ophthalmic nerve (CN V1); Maxillary ...Field of innervation: Motor: Muscles of masticat...Nuclei: Motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve; Prin...Type: Mixed (motor and sensory) Trigeminal Cardiac Reflex: New Thinking Model About the ... The peripheral TCR is further subdivided based on the branch of the affected trigeminal nerve into the oculo-cardiac reflex (V1) and the maxilla-mandibulo-cardiac reflex (V2-V3). A TCR, triggered at the Gasserian ganglion has, according to the latest studies, 23 , 25 its own entity and is classified as a separate subtype. 25 In all the ... The Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) | Cranial Nerves | Geeky Medics Cranial nerves and cranial foramina diagram. 1. Embryology. The name trigeminal is derived from the Latin "tri-" meaning three, and "-geminal" meaning a group attached to a common point. There are 'three' major branches of the trigeminal nerve, coming from four distinct nuclei in the brainstem. Mandibular nerve: Anatomy and function - Kenhub The trigeminal nerve is the fifth of the twelve Cranial Nerves. It consists of both afferent and efferent motoric and sensory fibers as well as proprioceptive, sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers that are divided into three main branches: the ophthalmic nerve, the maxillary nerve, and the mandibular nerve.
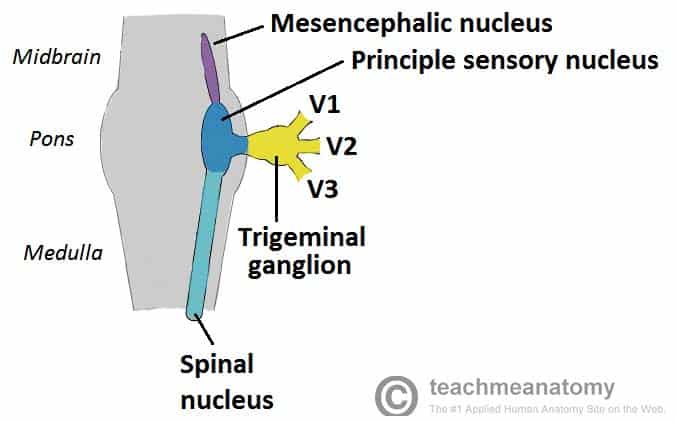
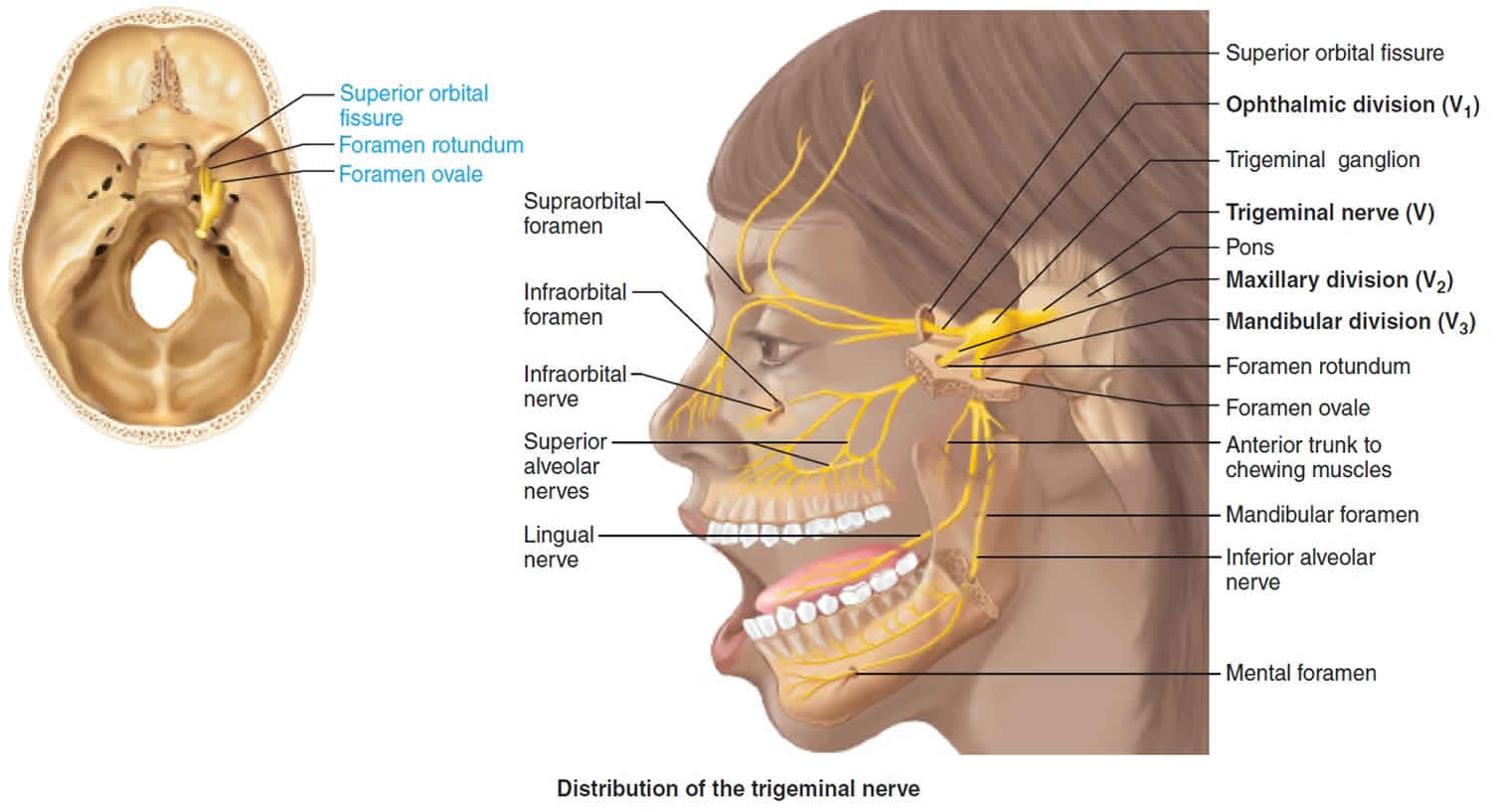
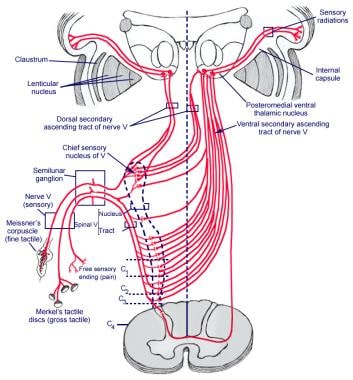
PDF 5. THE TRIGEMINAL SYSTEM Somatic Sensation of the Face and ... 2. Three nerve roots give rise to: a. Ophthalmic nerve, (CN V-1) b. Maxillary nerve, (CN V-2) c. Mandibular nerve, (CN V-3) 3. Peripheral distribution of three branches. Back of head and the angle of the jaw are not supplied by the trigeminal (Areas around ear supplied by CNs 42 trigeminal nerve branches diagram - Wiring Diagram Source Trigeminal nerve branches diagram The great auricular nerve is a cutaneous nerve of the head. It originates from the cervical plexus, with branches of spinal nerves C2 and C3. It provides sensory nerve supply to the skin over the parotid gland and the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and surfaces of the outer ear. Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve Anatomy, Function ... 19-01-2018 · Neuropathies (nerve damage) of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve can arise from many different clinical situations, and often manifest as sensory loss or pain, which can be tingling, aching, or ... These Are the 12 Cranial Nerves and Their Functions 14-03-2019 · The 12 cranial nerves are pairs of nerves that start in different parts of your brain. They control everything from your facial expression …
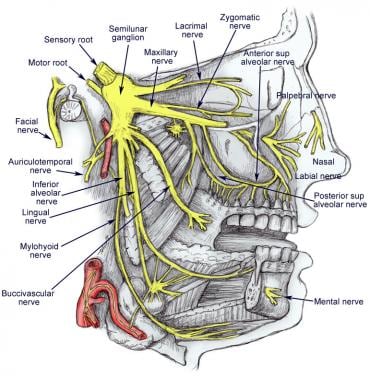
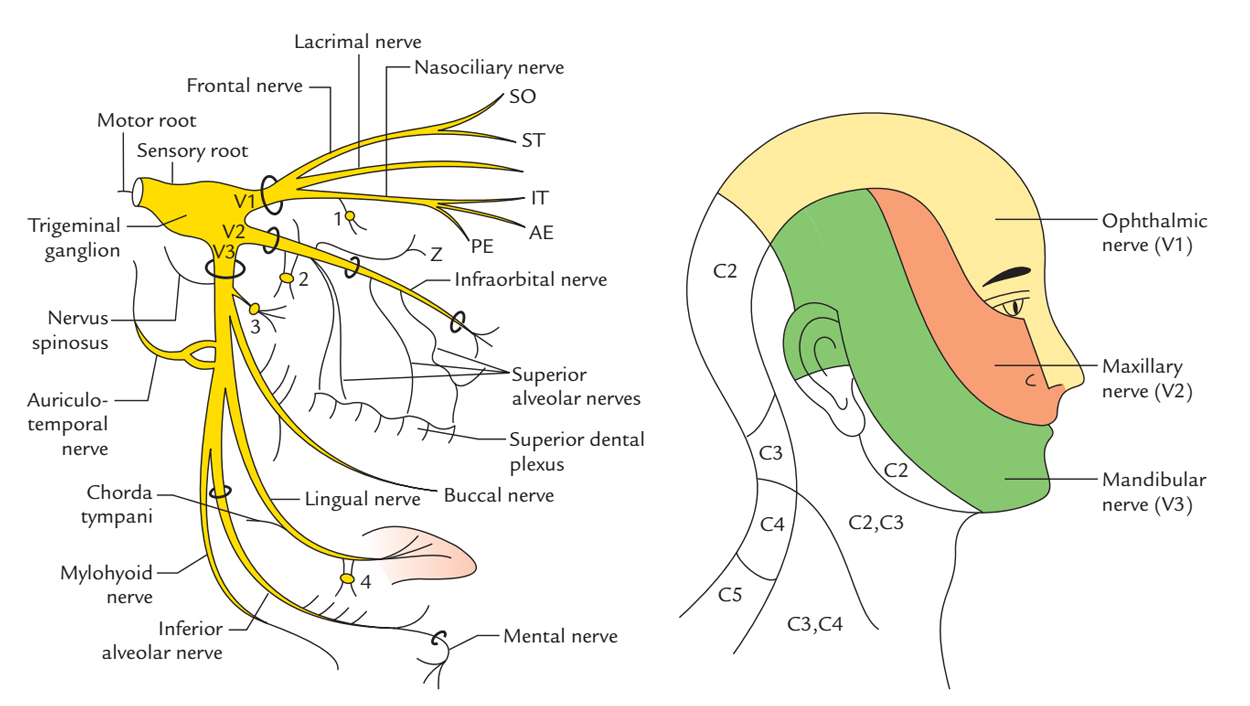
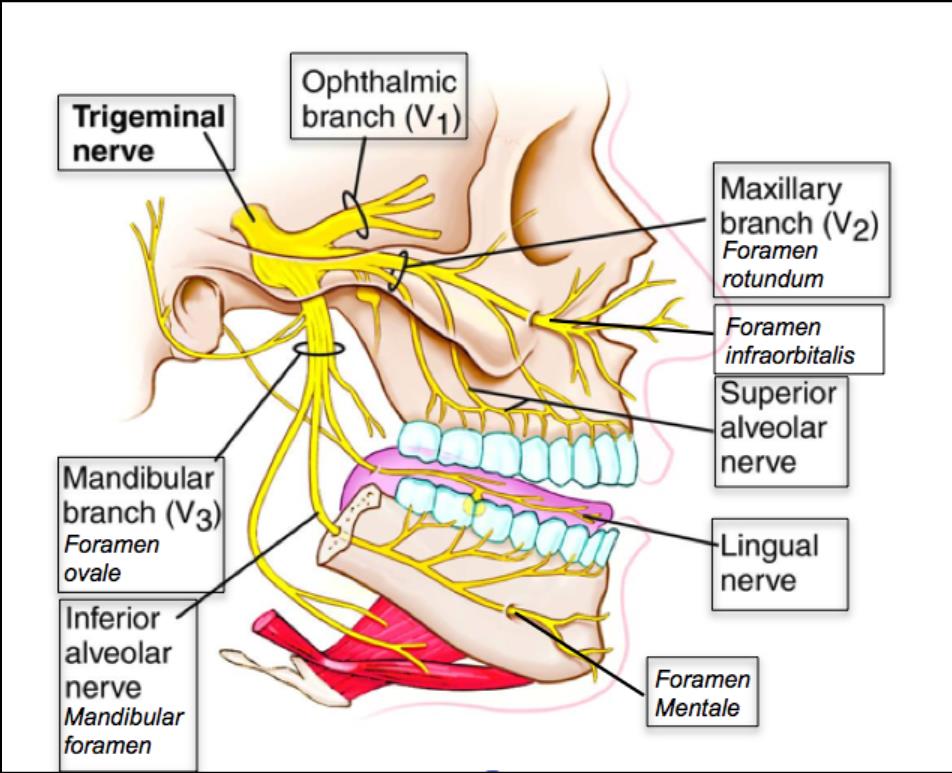
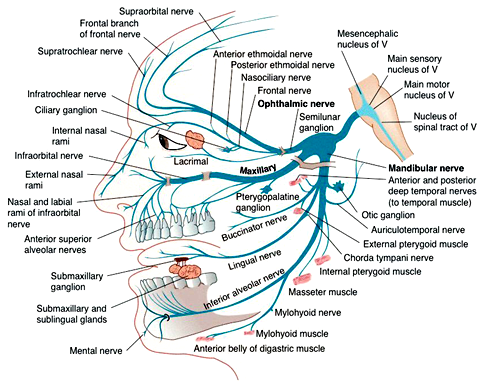
Trigeminal Nerve Diagram - Trigeminal Neuralgia - MedHelp Thanks for the diagram. What I've learned over the last year and a half is that there are little branches from the TN nerve that go to each of the teeth -- that's why a lot of us experience 'toothache' like pain. And the diagram shows that it connects into the nose area -- that's where I had my first electric zap. Trigeminal Neuralgia: Current Approaches and Emerging ... Schematic diagram of treatment modalities for trigeminal neuralgia. (A) ... Peripheral neurectomy involves the surgical disconnection of peripheral branches of the trigeminal nerve. 276-283 The procedure is usually performed as an outpatient procedure for patients who have failed medical therapy, or those who have severe medical comorbidities ... Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Diagram shows trigeminal nerve (TGN), trigeminal ganglion, and peripheral divisions and their branches. From fora- men rotundum ossis sphenoidalis, maxil- lary nerve (thin underline) gains access to pterygopalatine fossa and continues in floor of orbit as infraorbital nerve. Inferior alveolar and lingual nerves ( thick underline ) The Trigeminal Nerve: Anatomy, Function, and Treatment The small sensory branches of the trigeminal nerve have sensory endings located throughout the face, eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and chin. The branches of the trigeminal nerves travel along the pathways listed below. Ophthalmic The frontal nerve, the lacrimal nerve, and the nasociliary nerves converge in the ophthalmic nerve.
› ~brmacp › oralhistOral Histology: Dental Pulp Lecture - University of Kentucky These arise from the maxillary and mandibular branches of the fifth cranial nerve (trigeminal). They are predominantly myelinated fibers and may terminate in the central pulp. From this region some will send out small individual fibers that form the subodontoblastic plexus (of Raschkow) ( Lab Image 5 ) just under the odontoblast layer.
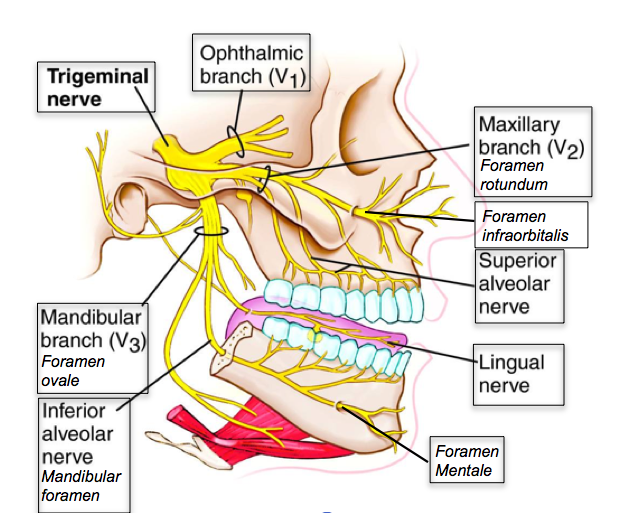
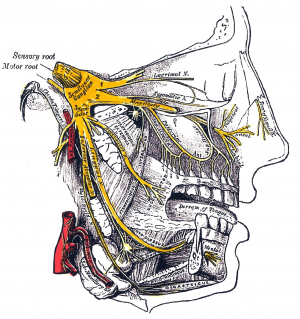
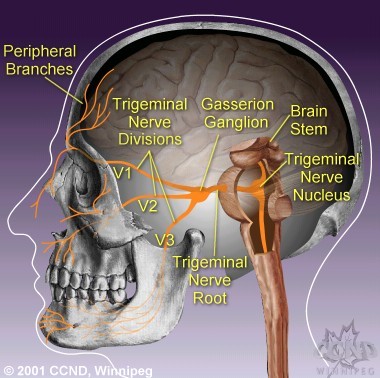
Trigeminal nerve - Wikipedia The three major branches of the trigeminal nerve—the ophthalmic nerve (V 1 ), the maxillary nerve (V 2) and the mandibular nerve (V 3 )—converge on the trigeminal ganglion (also called the semilunar ganglion or gasserian ganglion), located within Meckel's cave and containing the cell bodies of incoming sensory-nerve fibers.
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy - Medscape Reference 28 Nov 2017 — It contains the sensory cell bodies of the 3 branches of the trigeminal nerve (the ophthalmic, mandibular, and maxillary divisions). The ...Main location: Trigeminal areaPain intensity: SeverePain duration: Seconds to 2 minutes
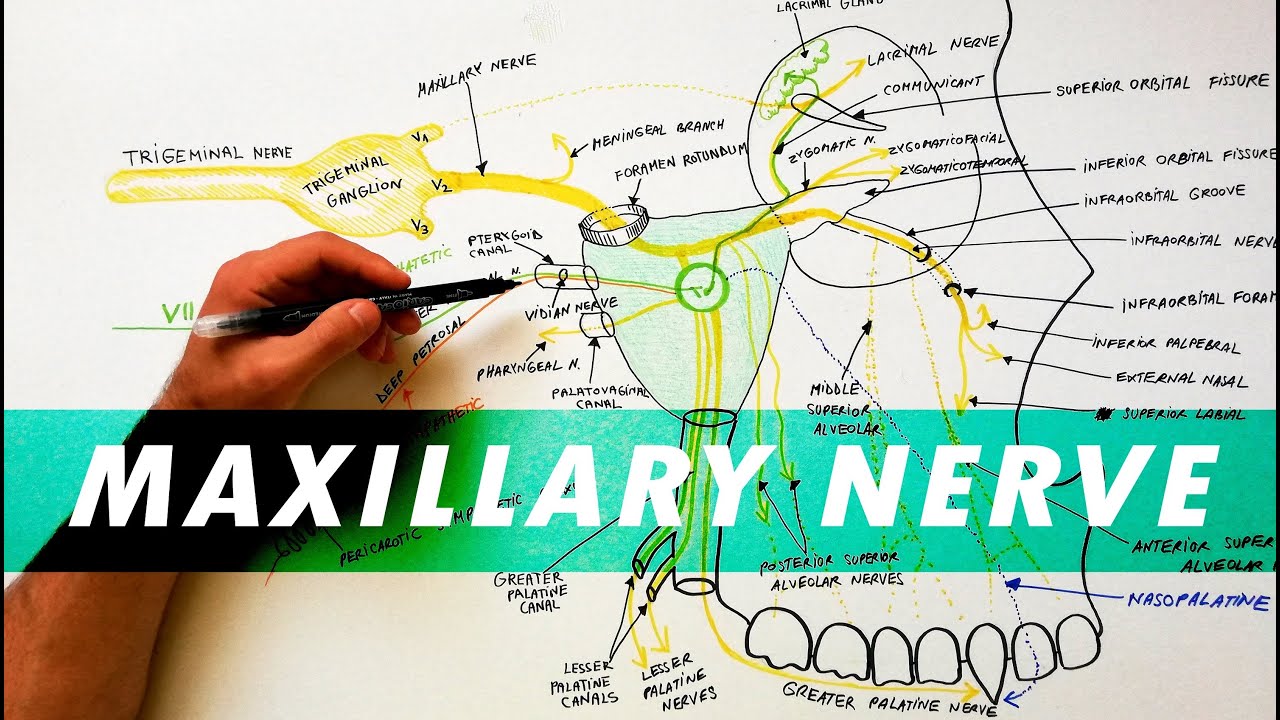
Diagram of the second branch (maxillary) of the trigeminal ... Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy: Gross Anatomy, Branches of the Trigeminal Nerve, Microscopic Anatomy The trigeminal nerve is the largest and most complex of the 12 cranial nerves (CNs). It supplies sensations to the face, mucous membranes, and other structures of the head.
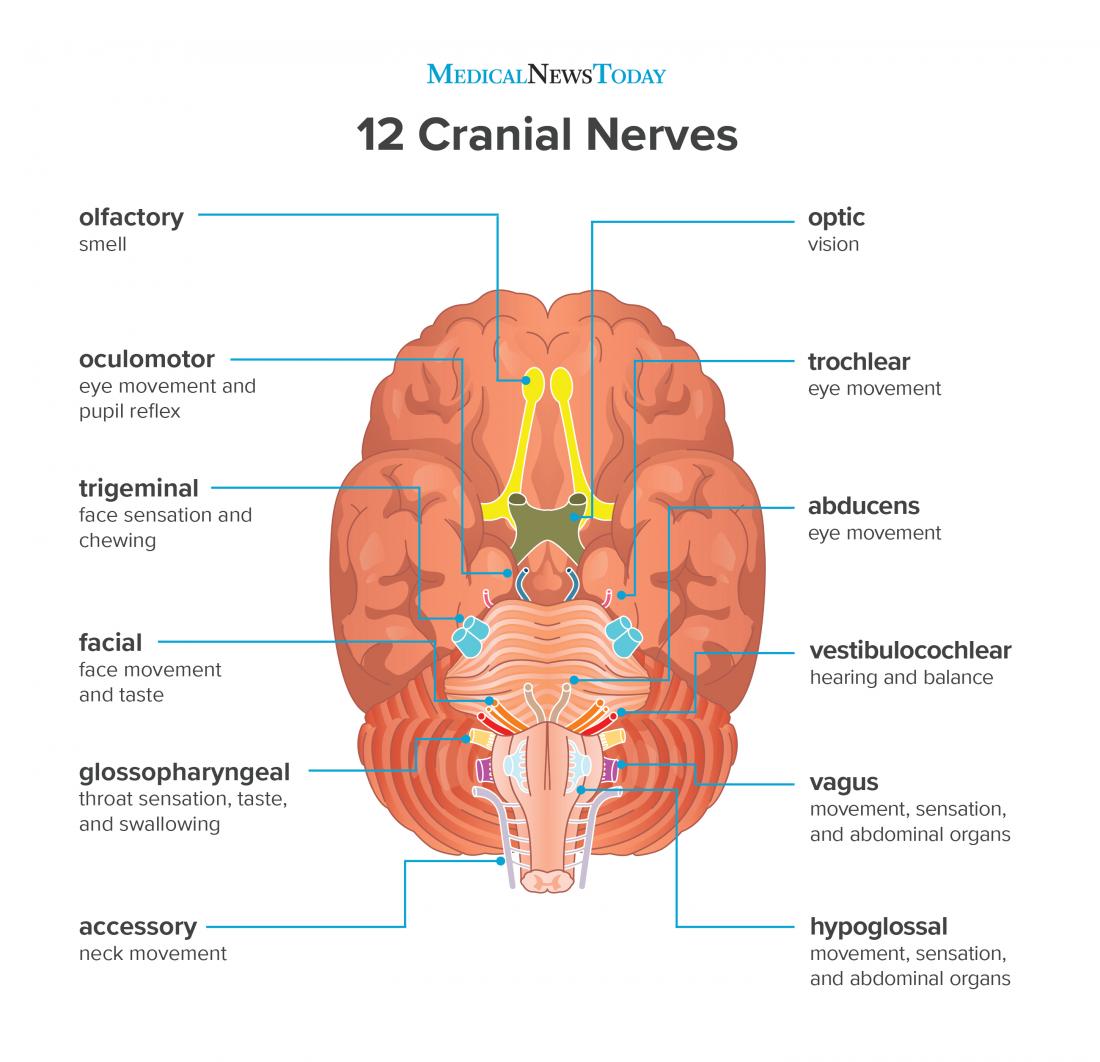
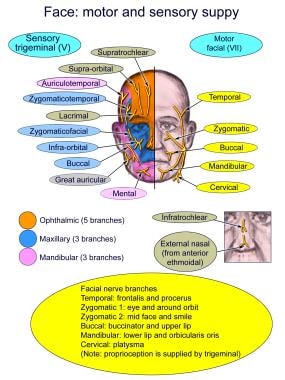
Illustrations and diagrams of the 12 pairs of cranial ... Oculomotor nerve [III] , Trochlear nerve [IV] , Abducent nerve; Abducens nerve [VI] : Anatomy atlas. The dermatomes of the trigeminal nerve (V) are represented on a diagram of the face. The branches of the trigeminal nerve (V) are represented in three different diagrams. The ophthalmic nerve (V1) in the orbital cavity with its main branches ...
The Trigeminal Nerve (CN V) - Course - Divisions ... The trigeminal nerve, CN V, is the fifth paired cranial nerve. It is also the largest cranial nerve. In this article, we shall look at the anatomical course of the nerve, and the motor, sensory and parasympathetic functions of its terminal branches. The trigeminal nerve is associated with derivatives of the 1st pharyngeal arch.
Trigeminal Nerve: Function, Anatomy, and Diagram Explore the interactive 3-D diagram below to learn more about the trigeminal nerve. Testing The trigeminal nerve plays a role in many sensations that are felt in different parts of the face. As a...
Branches of the trigeminal nerve - Mayo Clinic Branches of the trigeminal nerve Print Sections Products and services Trigeminal neuralgia results in pain occurring in an area of the face supplied by one or more of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the
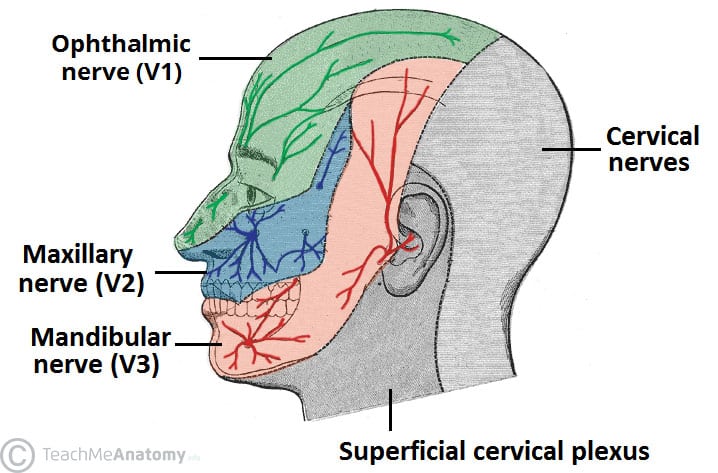
Trigeminal Neuralgia Fact Sheet | National Institute of ... The trigeminal nerve is one of 12 pairs of nerves that are attached to the brain. The nerve has three branches that conduct sensations from the upper, middle, and lower portions of the face, as well as the oral cavity, to the brain. The ophthalmic, or upper, branch supplies sensation to most of the scalp, forehead, and front of the head.
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy : American Journal of ... The motor root of the trigeminal nerve bypasses the trigeminal ganglion and reunites with the mandibular nerve in the foramen ovale basis cranii . As the mandibular nerve enters the masticator space, it divides into several sensory branches to supply sensation to the lower third of the face and the tongue, floor of the mouth, and the jaw ( Fig ...
The Ophthalmic Division of the Trigeminal Nerve (CNV1 ... The cutaneous innervation to the face and scalp by the three branches of the trigeminal nerve have sharp borders and little overlap. The cutaneous innervation of CNV1 can be seen in the image below: Fig 4 - Cutaneous innervation to the head and neck. Autonomic Functions The ophthalmic nerve itself does not contain any autonomic fibres.
Trigeminal nerve anatomy, branches, distribution, function ... Trigeminal nerve. The large trigeminal nerve or 5th cranial nerve has three branches: ophthalmic (V1), maxillary (V2), and mandibular (V3) divisions. Trigeminal nerve is a mixed nerve providing sensations of the face for touch, temperature, and pain from the upper, middle, and lower portions of the face, as well as the oral cavity, to the brain.
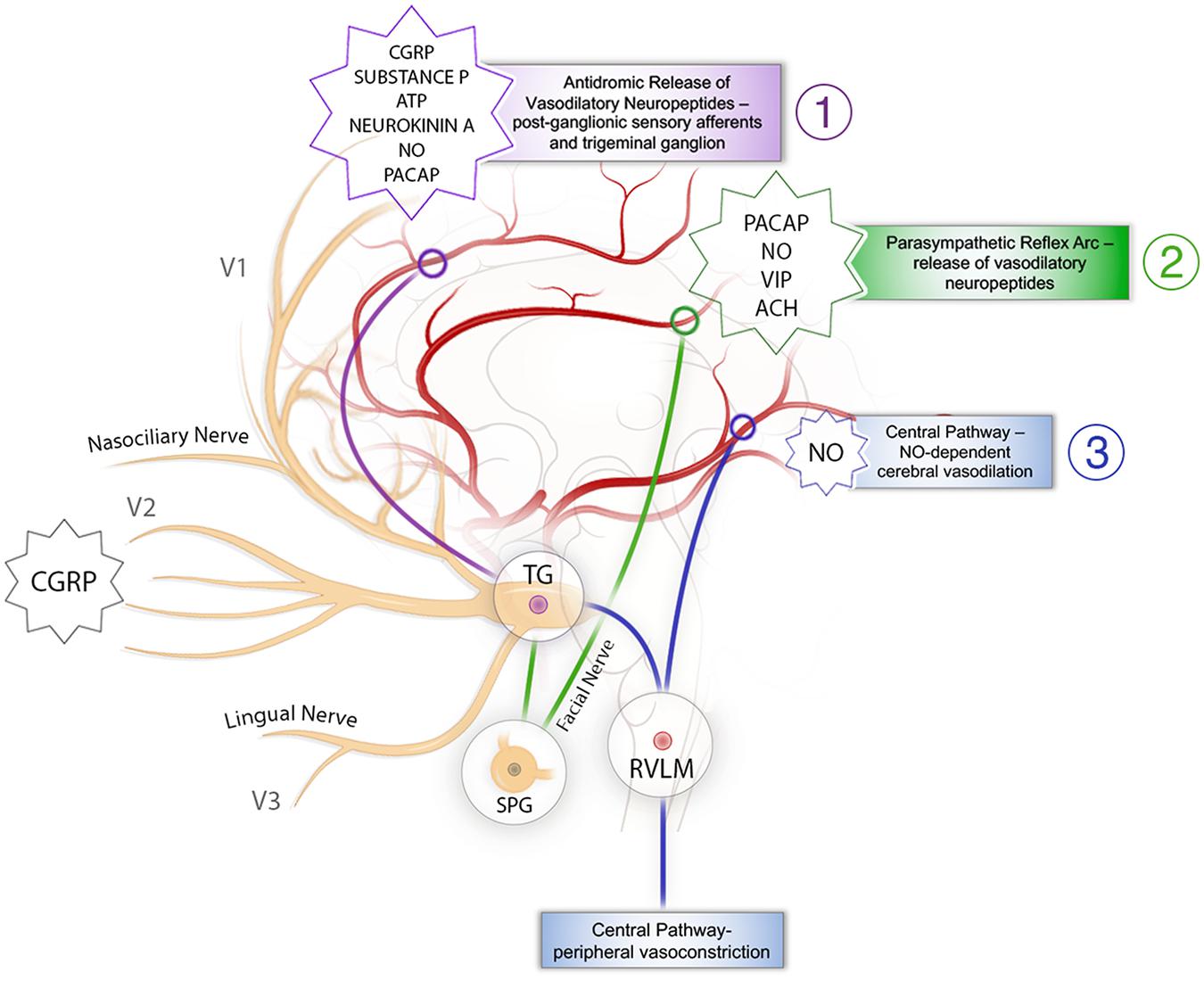
Illustration of a tentorial branch arising from the ... Supratentorial sensory perception, including pain, is subserved by the trigeminal nerve, in particular, by the branches of its ophthalmic division, which provide an extensive innervation of the ...
Trigeminal Nerve - SmartDraw Trigeminal Nerve Create healthcare diagrams like this example called Trigeminal Nerve in minutes with SmartDraw. SmartDraw includes 1000s of professional healthcare and anatomy chart templates that you can modify and make your own. 71/75 EXAMPLES EDIT THIS EXAMPLE Text in this Example: Trigeminal Nerve
radiopaedia.org › articles › temporal-bone-1Temporal bone | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org Jul 01, 2021 · The temporal bone is situated on the sides and the base of the cranium and lateral to the temporal lobe of the cerebrum. The temporal bone is one of the most important calvarial and skull base bones. Gross anatomy The temporal bone is divided ...
Trigeminal nerve | Radiology Reference Article ... Although the trigeminal nerve is usually described singularly, it actually emerges/enters from the brain stem as multiple nerve roots 8. The sensory root is large and single and enters the anterolateral aspect of the pons. Usually superomedial to, and within 4 mm of the sensory root, one or more motor roots emerge.
Trigeminal Nerve Distribution Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Trigeminal Nerve Distribution. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.








![trigeminal_nerve [Operative Neurosurgery]](https://operativeneurosurgery.com/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=trigeminal_nerve.jpg)
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/522/hefybIAztz3WDIDI33S06g_the-mandibular-nerve_english.jpg)



:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/274/CKsWYOqMbRE3da7XY9Ssw_the-maxillary-nerve_english.jpg)





0 Response to "42 trigeminal nerve branches diagram"
Post a Comment