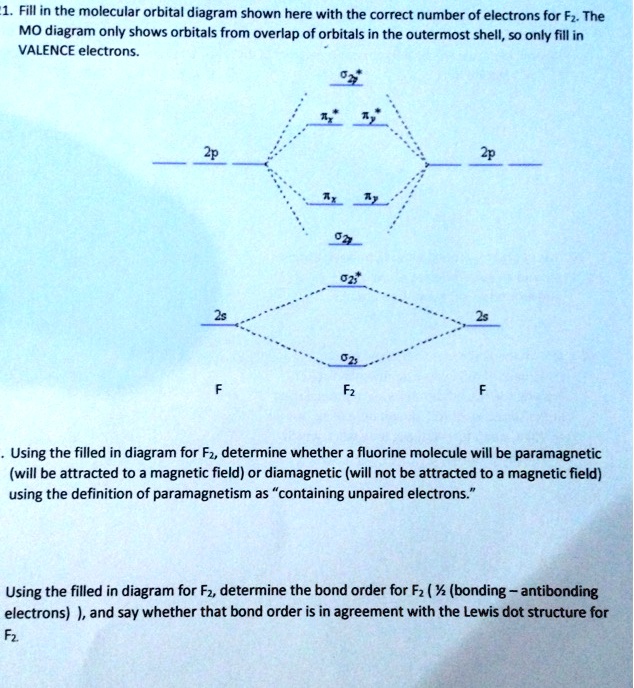
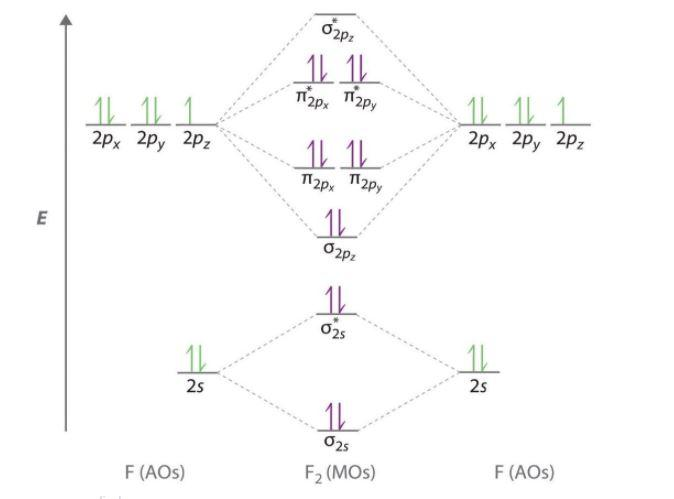
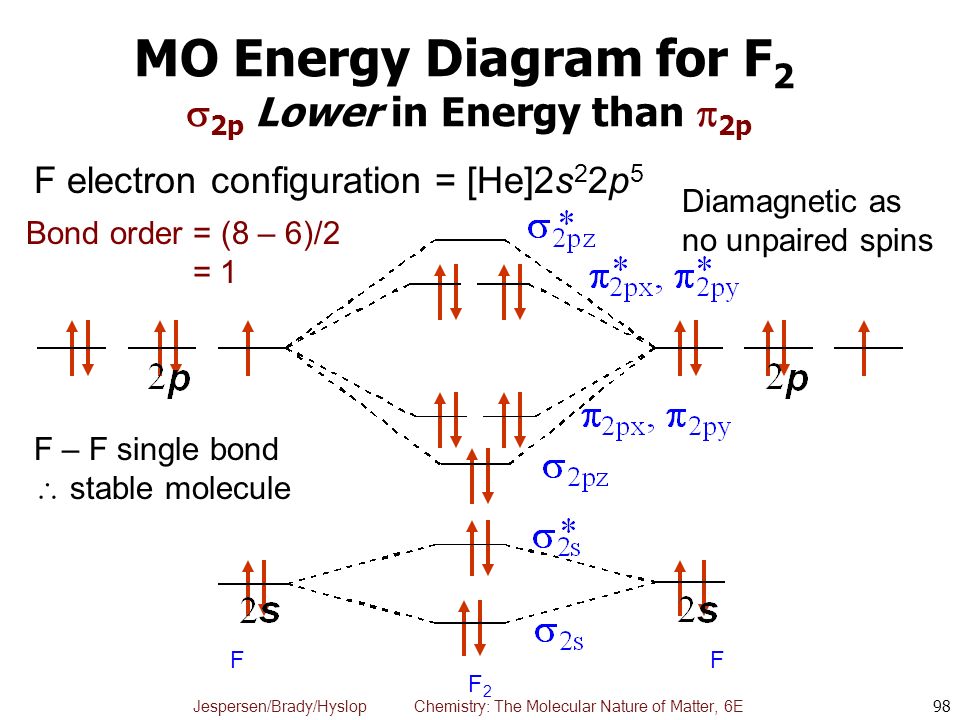
41 molecular orbital diagram for f2
Molecular Orbital Theory Diagram Of F2 - The 31 Best ... The answer is n (nonbonding) ---> pi antibonding (look at the picture I drew above), which makes sense cause the ***non-electron excites to the next higher energy leve***l, which is the antibonding level in Molecular orbital diagram. 3 questions: Draw and write the molecular configuration of nitrogen ... Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule. Also, give its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. 138. Solve the following: Open in App. Solution. Verified by Toppr. Solve any question of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure with:-Patterns of problems >
Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram for F2(2+) - YouTube When two fluorine atoms bond, the sigma(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the pi(2p) bonding orbitals.F2(2+) has a bond order of 2, so ...

Molecular orbital diagram for f2
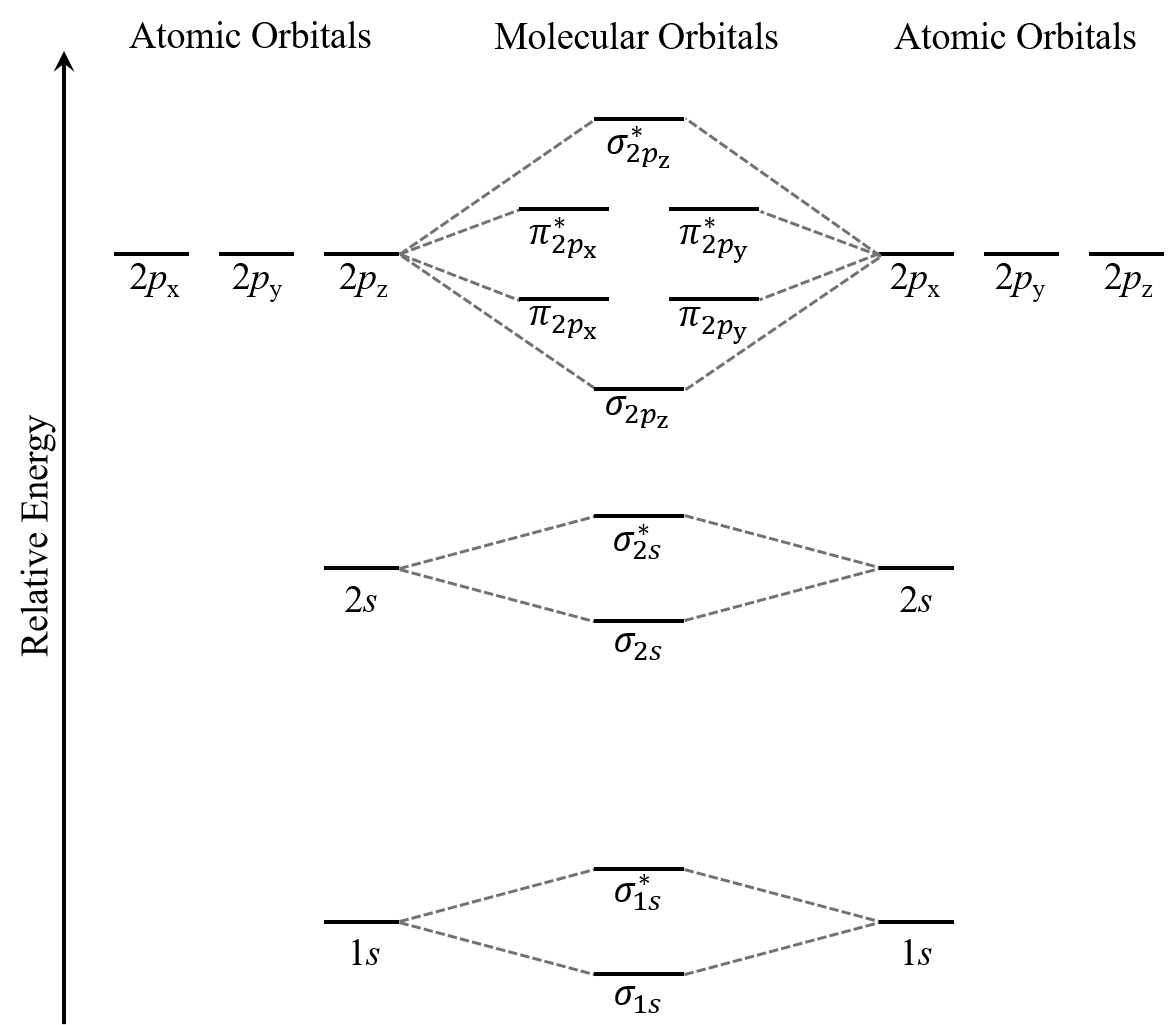
What is are the intermolecular forces of HF? - Quora Answer (1 of 5): HF is a polar molecule dipole-dipole forces. Hydrogen is bounded to F. Hydrogen bonds exist. There are also dispersion forces between HBr molecules. 7.7 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Fundamentals Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 7.7.9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right. Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals - Chemical ... Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... If N b = Na,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order.
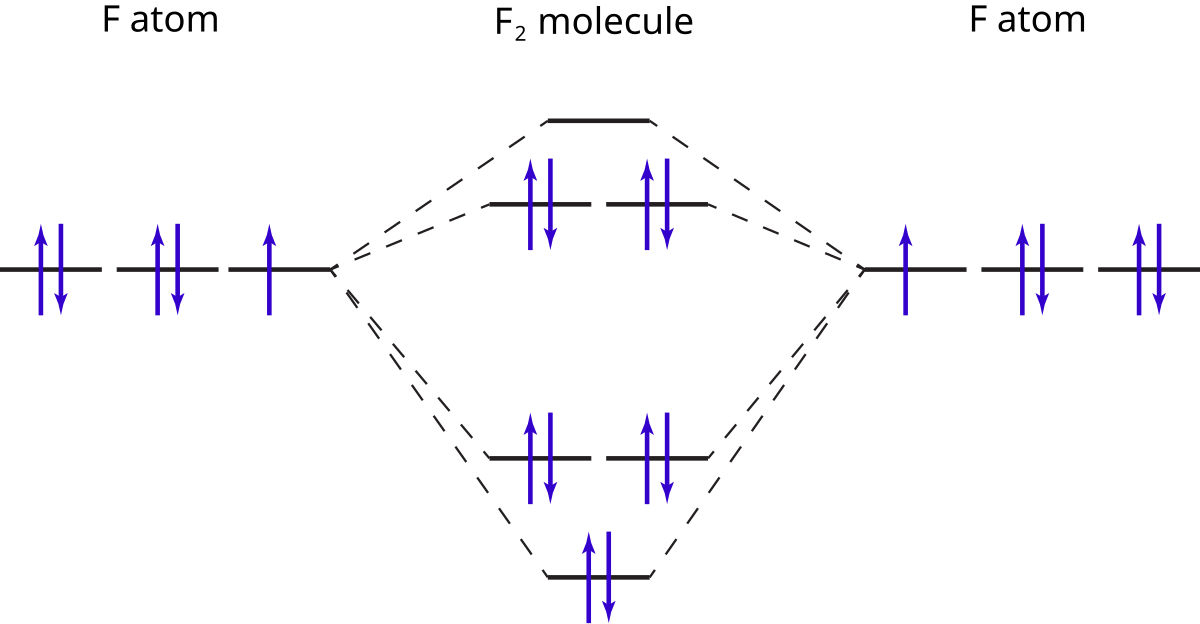
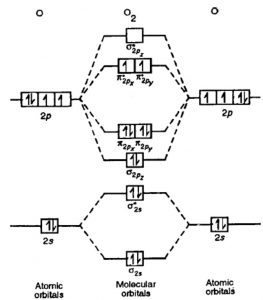
Molecular orbital diagram for f2. What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2? - Quora Answer (1 of 6): Here is the solution, > * For O2 molecule, > * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading. 40 o2+ molecular orbital diagram - Wiring Diagrams Manual 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science The way these bonds are placed on any molecular orbital diagram is according to how the atomic orbitals that make the MOs mix. In that mixing, there are two factors to consider: (1) atomic symmetry and (2) mixing. PDF Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules together to produce a sigma molecular orbital [σ = (1sa + 1sb)]. Since the electrons in this orbital are more stable than on the individual atoms, this is referred to as a bonding molecular orbital. A second molecular orbital is also created, which we simplistically show as a subtraction of the two atomic 1s orbitals [σ* = (1sa - 1sb)]. This ... Molecular Orbital Diagram Ne2 - schematron.org Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways. Page 1. MO Diagrams for Elements Li2 through Ne2. (Don't memorize.) Li2 through N2. O2 through Ne2.
Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic \ ( {\text {Be}}_ {2} {}^ {\text {+}},\) showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals, using the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule. Bond Order Cl2 Molecular Orbital Diagram Click here to get an answer to your question how to drew molecular orbital diagram of Cl2. bond order = 1 (like F2) Cl2 has the weakest bond. b. + would be weaker than in Cl2, the Ar-Ar distance would be molecular orbitals in the diagram suggest. Cl atom has 17 electrons, so chlorine molecule has (Cl2) has 34 electrons. so, bond order of ... Answered: a. Using the molecular orbital diagram,… | bartleby Using the molecular orbital diagram, calculate the bond order of F 2+. Show show your work or give a brief explanation of the process. b. Do you expect this to have a shorter or longer bond length than F 2? Explain your answer. c. Do you expect F 2+ to be paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Explain your answer. Molecular Orbital Diagram For Li2 - schematron.org Molecular orbital (MO) diagram for N2 and N2^- $-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction moving from $\ce{Li2}$ to $\ce{F2}$. The $\mathrm{s}$-$\mathrm{p}$ interaction is the bonding interaction between the $\mathrm{2s}$ orbital of one atom and the $\mathrm{2p_{z}}$ orbital of another atom which (among other things) increases the energy of the $\mathrm ...
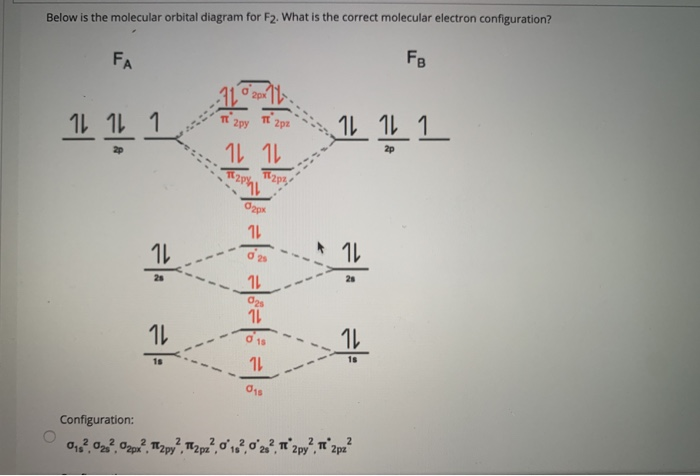
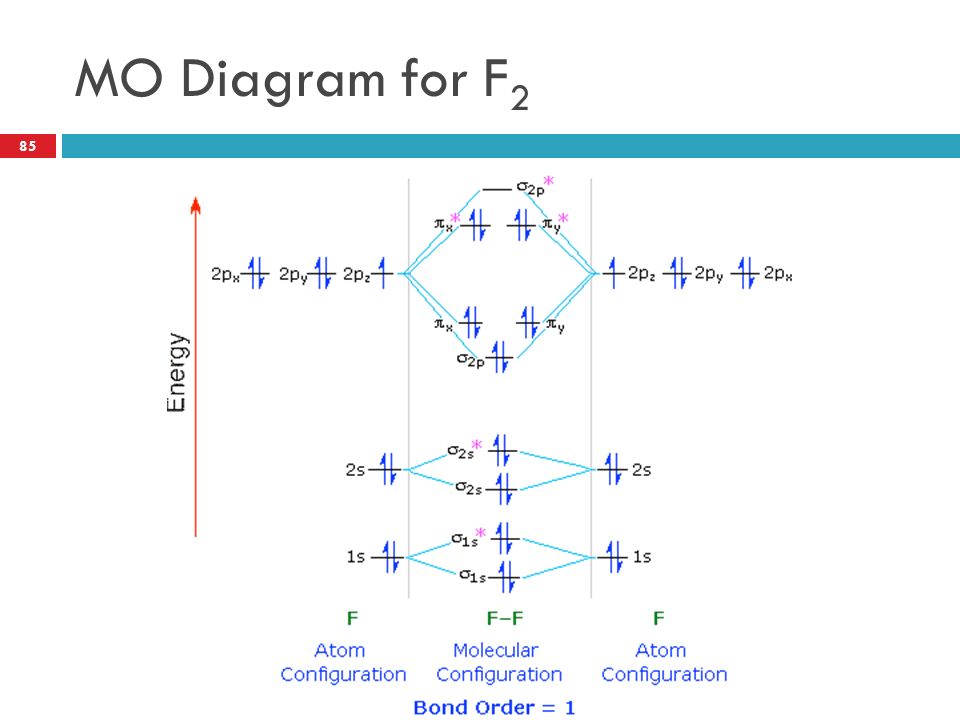
MO Diagram #2 - F2 - YouTube This video is about MO Diagram #2 - F2 electronic configuration - Molecular orbital (MO) diagram ... The short answer is: we could not tell it using the primitive molecular orbital theory introduced in the general chemistry courses. In exact same way we could not tell why $\mathrm{\sigma_{2p_{z}}}$ MO becomes lower in energy than $\mathrm{\sigma_{2p_{z}}}$ MO to the left of $\ce{N2}$ and not to the left of, say, $\ce{C2}$. F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram - 17 images - what is the ... F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. Here are a number of highest rated F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram pictures upon internet. We identified it from well-behaved source. Its submitted by processing in the best field. We take this kind of F2 Molecular Orbital Diagram graphic could possibly be the most trending subject in the manner of we share it in ... F2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... Mar 31, 2022 · F2 Molecular Orbital (MO) Diagram. As per molecular orbital (MO) theory, all the constituent atoms in a molecule contribute to the formation of molecular orbitals. These MOs are a linear combination of the atomic orbitals. Thus, the electrons in a molecule are not individually assigned to atomic orbitals but to molecular orbitals. Let us have a ...
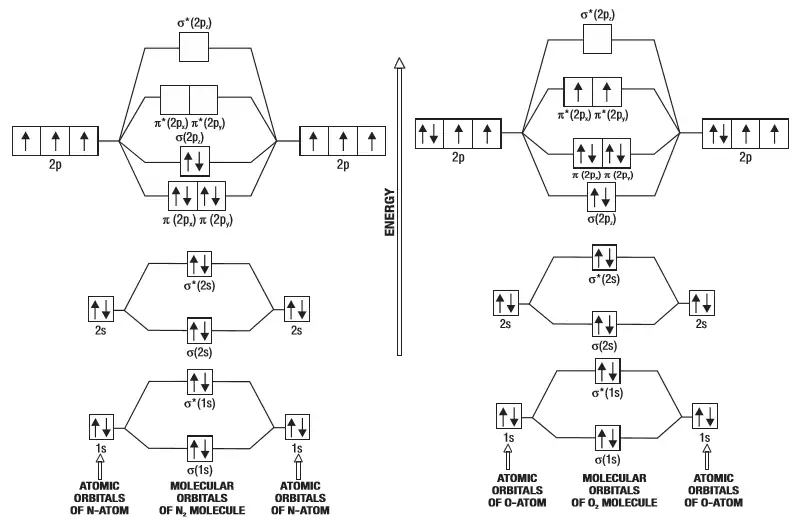
Draw a molecular orbital diagram of N2 or O2 with magnetic ... Verified. Hint: Generally the molecular orbital diagrams are used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. You should know that molecular orbital diagrams are used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule; they also help us to find out the bond order of the molecule. First let us understand the concept of molecular orbital theory.
(PDF) James E. Brady The Molecular Nature of Matter (6th ... James E. Brady The Molecular Nature of Matter (6th Edition) Copia. Eduardo Silva. Download PDF
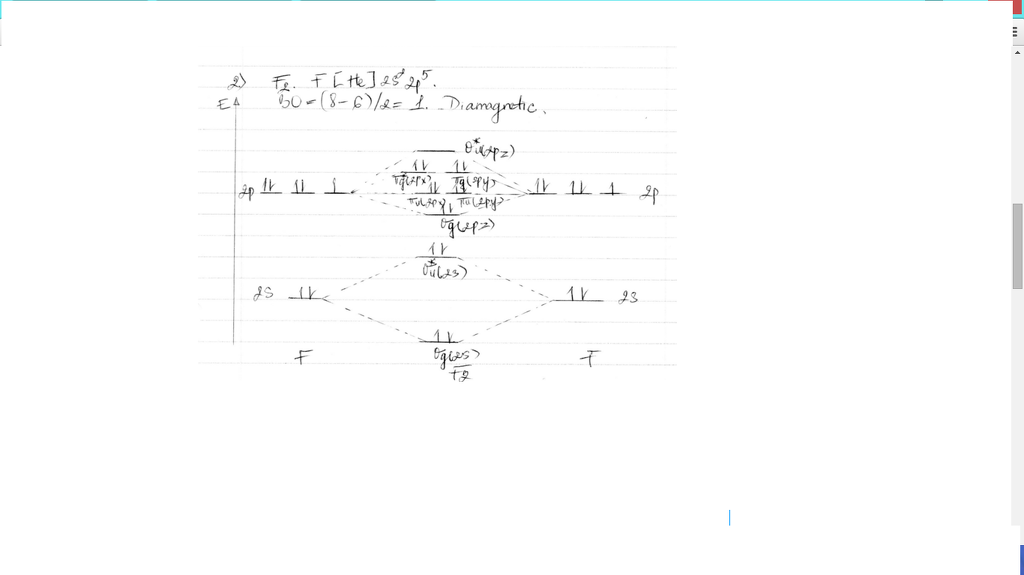
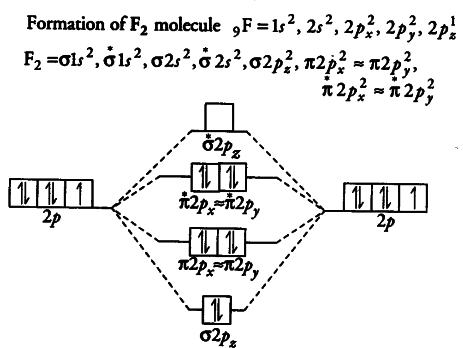
Draw molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule Also class ... Draw molecular orbital diagram for F 2 molecule. Also, gives its electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property. Verified 101.4k + views Hint: The Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) explains the formation of the molecule in a better way than Valence Bond Theory (VBT).
CBSE class 11 Chemistry Notes - Toppers CBSE CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Notes are Best ever notes prepared by our awesome team members. We have spend more that 2 years to prepare these Class 11 chemistry notes.After analyzing our notes in deep, we have uploaded our notes on the website.
What is the molecular orbital diagram of O2 and F2? - Quora Qualitative treatments will just use the valence atomic orbitals in (), four from each oxygen atom makes eight. So this sort of treatment will generate eight ...6 answers · 63 votes: Here is the solution, %3E * For O2 molecule, %3E * For F2 molecule, Thanks for reading.
Molecular Orbital Theory - Detailed Explanation with ... The Molecular Orbital Theory (often abbreviated to MOT) is a theory on chemical bonding developed at the beginning of the twentieth century by F. Hund and R. S. Mulliken to describe the structure and properties of different molecules. The valence-bond theory failed to adequately explain how certain molecules contain two or more equivalent bonds ...
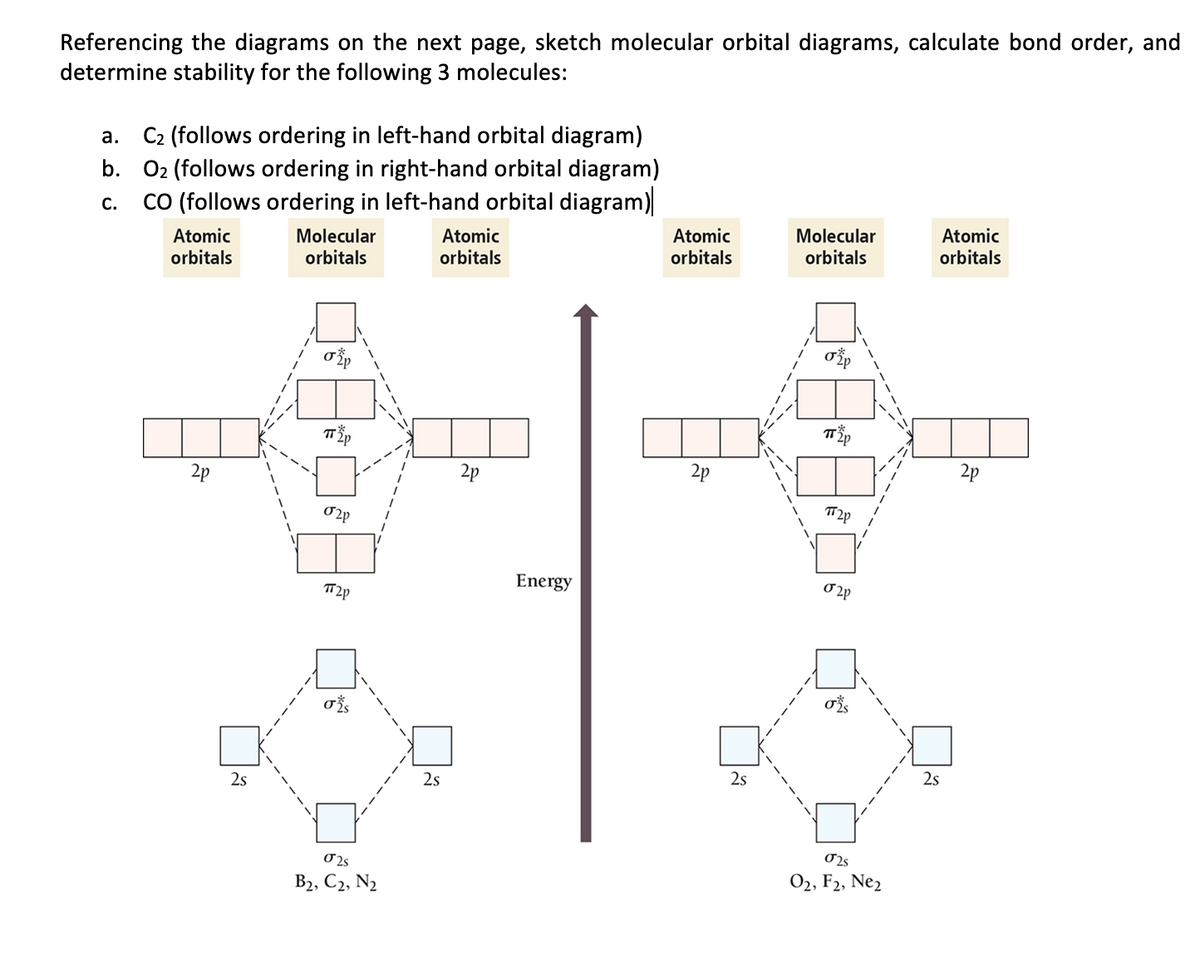
Molecular Orbital Theory - Purdue University The result is a slight change in the relative energies of the molecular orbitals, to give the diagram shown in the figure below. Experiments have shown that O 2 and F 2 are best described by the model in the figure above, but B 2, C 2, and N 2 are best described by a model that includes hybridization, as shown in the figure below.
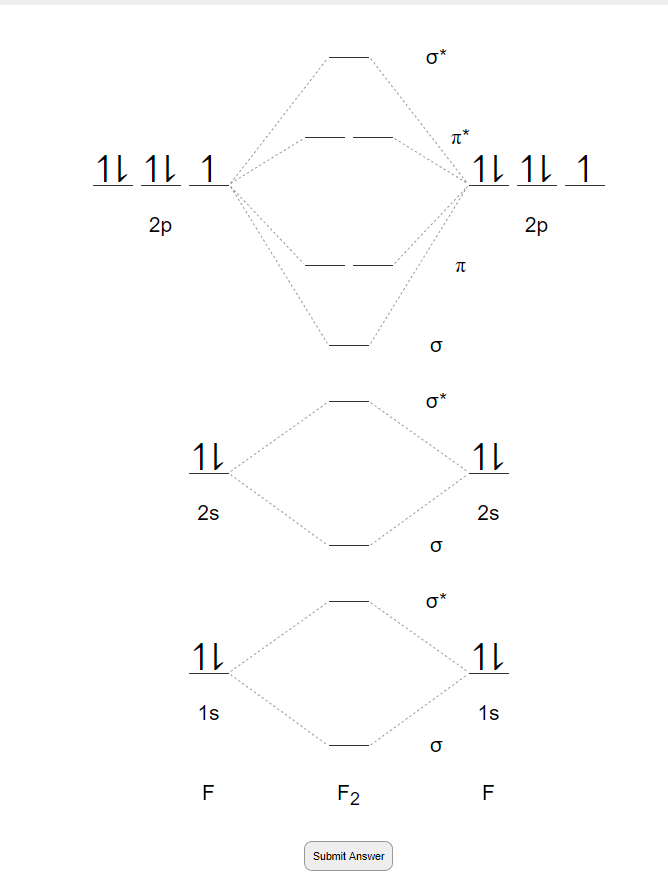
Solved Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram ... Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the F2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons. Question: Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the F2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons.
Metabolomics analysis reveals large effects of gut microflora ... Mar 10, 2009 · Mass Spectrometry Reveals That the Microbiome Has a Broad Effect on Mouse Plasma Biochemistry. Mass spectrometry has become an increasing powerful tool for metabolomics studies due to its wide dynamic range, reproducible quantitative capabilities, and its ability to analyze samples of significant molecular complexity ().
Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which ... In Molecular orbital diagram, we just need to calculate the number of electrons in anti-bonding orbital and bonding orbital, then we can use the formula in order to calculate bond order is: Bond order = (No. of electrons in anti-bonding MO) - (No. of electrons in bonding MO) / 2 Hope this helps!
Answered: PRE-LAB QUESTION After consulting… | bartleby PRE-LAB QUESTION After consulting sections 5.7 of your text, draw the complete MO diagram for the diatomic molecule, H2. Next to each of the MOs in your diagram, draw a picture that describes the constructive or destructive interference of atomic wave functions and indicate the location of any nodes.
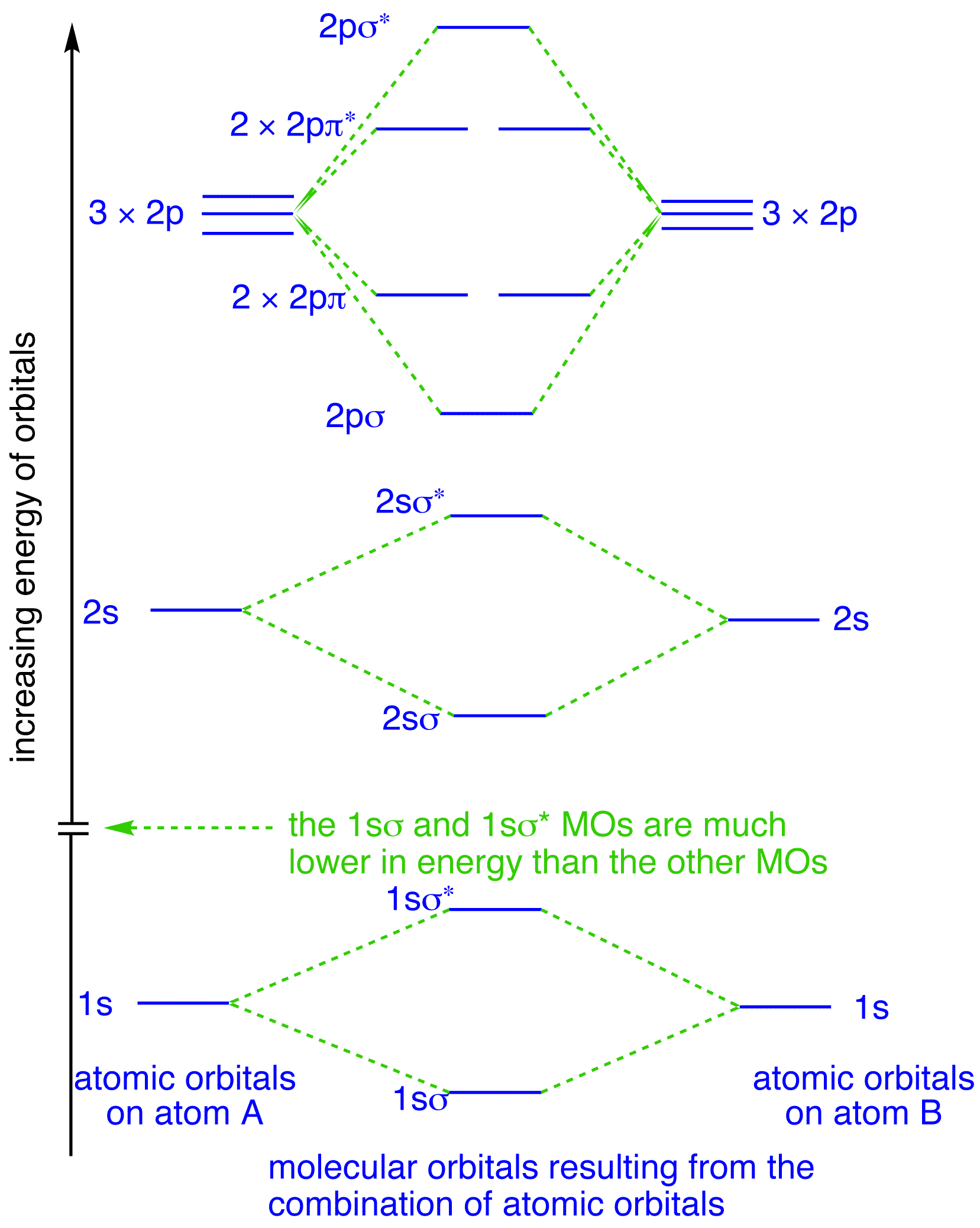
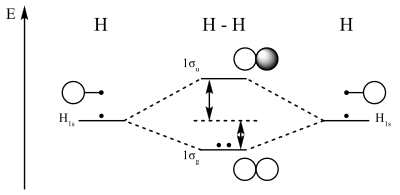
PDF Molecular orbital DiagraM - Magadh University Basis of molecular orbital (MO) approach: Overlap of orbitals occurs for the whole molecule-bonding is thereforeDELOCALISED. Atomic orbitals: Orbitals that are localized on single atoms. Molecular orbitals: Orbitals that span two or more atoms. These are
PDF MO Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
C2H6 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization ... Mar 27, 2022 · The molecular orbital diagram of ethane would be: The molecular orbital is formed from the combination of atomic orbitals, which must have nearly the same energy and are symmetrical about the molecular axis. To understand the MO diagram of ethane, we consider it as a homonuclear diatomic A2 molecule.
Molecular Orbital Theory Flashcards - Quizlet By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for B2, C2, N2, O2, and F2, predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for , , , , and , predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. F2 O2 and F2 O2 and B2 O2
Recitation Week 10 (test 3 - Recitation 2) - GitHub Pages A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic.
Draw molecular orbital diagram of O2 or N2 with magnetic ... Draw molecular orbital diagram of O 2 or N 2 with magnetic behavior and bond order. Medium Solution Verified by Toppr As it can be seen from the MOT of O 2 , The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Also, the bond order can be calculated as [N b −N a ]/2=[10−6]/2=2.
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals - Chemical ... Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... If N b = Na,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order.
7.7 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Fundamentals Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams. The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 7.7.9). For a diatomic molecule, the atomic orbitals of one atom are shown on the left, and those of the other atom are shown on the right.
What is are the intermolecular forces of HF? - Quora Answer (1 of 5): HF is a polar molecule dipole-dipole forces. Hydrogen is bounded to F. Hydrogen bonds exist. There are also dispersion forces between HBr molecules.








![Expert Answer] Draw the molecular orbital diagram for F2 and ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d7a/d377148aa5469a29270f608aa4d77ef6.png)






0 Response to "41 molecular orbital diagram for f2"
Post a Comment