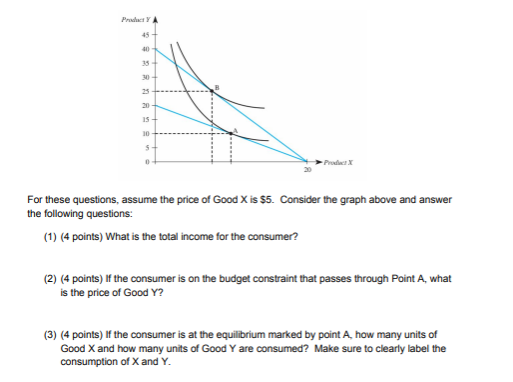
39 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
Coursework Hero - We provide solutions to students Coursework Hero will take good care of your essays and research papers, while you’re enjoying your day. Download it! Hi there! ... in 2-5 days. High Quality. All the papers we deliver to clients are based on credible sources and are quality-approved by our editors. ... Total price: $ 0.00. We can help you reach your academic goals hassle-free. Econ final Flashcards - Quizlet A consumer is in equilibrium and is spending income in such a way that the marginal utility of product X is 40 units and that of Y is 16 units. If the unit price of X is $5, then the price of Y must beA) $1 per unit. B) $2 per unit. C) $3 per unit. D) $4 per unit.
All Grades - EconEdLink Key Concepts: Consumer Economics, Price Ceiling, Price Floor. 150 mins. Feb 22 1:00-3:30pm ET. Webinar . Save Lesson. See On-Demand Webinar . Grades 9-12. Microeconomics - Production Decisions, Market Structures and Labor Markets. In this webinar, you will review Production Decisions & Economic Profit, Market Structures, Labors Markets, and ...

A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.
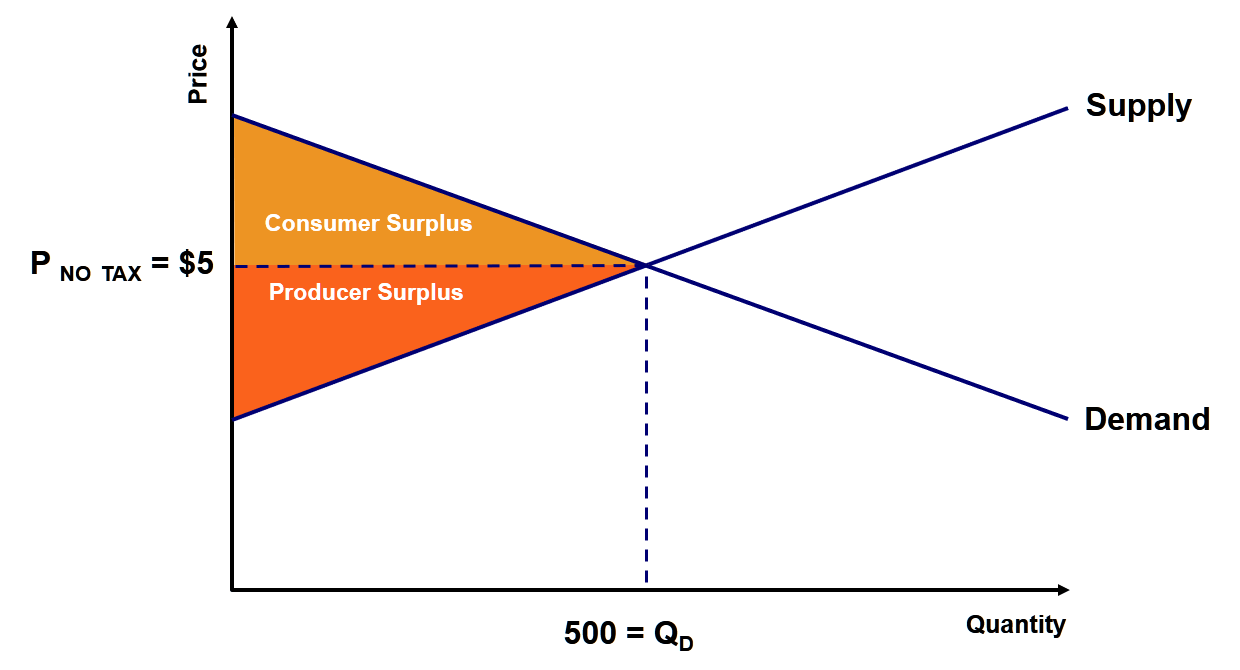
› file › 67099832Chapter 4 HW.docx - Chapter 4 HW 1) A consumer is in ... 3) 4) In the below figure, a consumer is initially in equilibrium at point C. The consumer's income is $400, and the budget line through point C is given by $400 = $100 X + $200 Y. When the consumer is given a $100 gift certificate that is good only at store X, she moves to a new equilibrium at point D. Explanation a. P x = $100, P y = $200 ... PDF ECONOMICS 9708/01 1 hour - XtremePapers A The equilibrium price is zero. B The equilibrium price is P. C The equilibrium price is indeterminate, because the supply curve is vertical. D Consumer surplus from the operations is ODD 1. 12 The diagram shows a demand curve for journeys on a toll road. number of journeys per day toll per journey ($) 5 3 1000 2000 0 Microeconomics Lecture #4 Flashcards - Quizlet Assuming $5 to be the equilibrium price for this market, please shade in consumer surplus (CS), producer surplus (PS), and total surplus (TS). The area above the equilibrium price bound by the demand curve represents the consumer surplus.
A consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5.. a consumer is in equilibrium when - Lisbdnet.com On a supply and demand diagram, consumer surplus is the area (usually a triangular area) above the equilibrium price of the good and below the demand curve. The point at which a price stabilizes-so that both consumers and producers receive maximum surplus in an economy-is known as the market equilibrium. Consumer Equilibrium: Effects On Income, Substitution, Price The slope of budget line is given as: OA / OB = P x / P y. At point E where MRS y,x = P x / P y. Therefore, the consumer is at equilibrium at point E. As the IC2 curve is tangent to the budget line AB, IC2 is the highest indifference curve that a consumer can attain at the given income level and market price of commodities. CHAPTER 3 ECON Flashcards - Quizlet A. move from point x to point y. B. shift from D1 to D2. C. shift from D2 to D1. ... Refer to the diagram. The equilibrium price and quantity in this market will be: A. $1.00 and 200. ... If at the market price of $5 both are running out of beads to sell (they can't keep up with the quantity demanded at that price), then we would expect both ... quizlet.com › 509361733 › chapter-4-flash-cardsChapter 4 Flashcards - Quizlet A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y?$ b. What is the consumer's income?$ c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? d. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B.
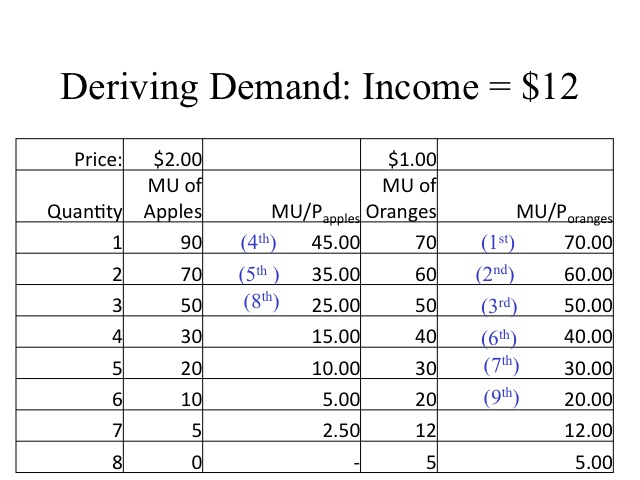
Consumer Equilibrium - CBSE Notes for Class 12 Micro ... It can be seen from the given diagrams that Figure B is derived from Figure A. In figure A, initially, consumer equilibrium is attained at point E, where MU (10) = Price (10). Corresponding to point E, we derive point E 1 in figure B. Due to fall in price (suppose from 10 to 8), MU > Price at the given quantity. A consumer consumes goods X and Y . Given below is his ... The equilibrium condition is satisfied when the consumer consumes the goods in the combination of 1 unit of Good X and 4 units of Good Y. At this level of consumption, the total expenditure of the consumer is : (1 × ` 2) + (4 × ` 1) = 2 + 4 = 6 This is attainable also in his given income of Rs 12. Your favorite homework help service - Achiever Essays Keep up the good job guys. Michelle W. USA, New York. ... you are welcome to choose your academic level and the type of your paper at an affordable price. We take care of all your paper needs and give a 24/7 customer care support system. Admissions. Admission Essays & … Consumer Equilibrium - Commerceiets The units of commodities are 5. The consumer attains his equilibrium by consuming3 units of the commodity. As by consuming 3 units of commodity the price is equals to the marginal utility i.e. 10. DIAGRAMATIC PRESENTATION. The consumer equilibrium in case of single commodity can be explained with the help of following diagram: CONSUMER EQUILIBRIUM
Consumers Equilibrium: Meaning, Graphical Representation ... Therefore, he reaches the equilibrium at point Q on curve IC 3. Notice that at this point, the budget line PL is tangential to the indifference curve IC 3. Also, in this position, the consumer buys OM quantity of X and ON quantity of Y. Since point Q is the tangent point, the slopes of line PL and curve IC 3 are equal at this point. Further ... › questions-and-answers › aAnswered: A consumer is in equilibrium at point A… | bartleby A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? $ b. What is the consumer's income?1 answer · Top answer: Step 1 Since we only answer up to 3 sub-parts, we’ll answer the first 3. Please resubmit the question and specify the other subparts (up to 3) you’d ... PDF LIBS TASK OAECON 03 9708 32 2019 - GCE Guide 5 30 6 30 At which level of consumption would the marginal utility be zero? A 1 B 4 C 5 D 6 5 In the indifference curve diagram point M is the consumer's initial equilibrium, JK and JL are budget lines and MN is the substitution effect of a fall in the price of good X. › a-consumer-is-in-equilibrium[Solved] A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the ... A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the accompanying figure. The price of good X is $5. a. What is the price of good Y? b. What is the consumer€™s income? c. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase?
› homework-help › questions-andSolved A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the | Chegg.com And also budget line touches x-axis at point (20,0). It means that if consumer is spending all his income on good X he is able to buy 20 units of good X. It is …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. Good Y 45 40 35 30-1 B 25 20 15 10 5 - 0 20 ...
Price Elasticity of Demand Questions and Answers - Study.com Assume that the price of good X decreases from $10 to $9 per unit, and the quantity demanded of good X increases from 25 to 30 units. In this price range, the …
Consumer's Equilibrium (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion A consumer is said to be in equilibrium when he feels that he "cannot change his condition either by earning more or by spending more or by changing the quantities of thing he buys". A rational consumer will purchase a commodity up to the point where price of the commodity is equal to the marginal utility obtained from the thing.
Consumer Equilibrium - Meaning, Examples, Conditions and ... 1. Marginal utility of the last rupee spent on each good is the same. 2. Marginal utility of a commodity falls as more of it is consumed. Let us understand the consumer's equilibrium in the case of two commodities with an example. Suppose a consumer has to spend ₹. 24 on two commodities i.e. X and Y.
Consumer Equilibrium: meaning, definition, example, conditions So, the consumer increases the consumption to attain equilibrium. After this level, i.e., at the fourth and the fifth level, MU < Price, e., benefit is less than cost. So, the consumer cuts or decreases the consumption to be in the state of equilibrium. Only at the level of 3 units, the condition of consumer's equilibrium is fulfilled.
Price Ceiling Questions and Answers | Study.com Imposing a price ceiling below the equilibrium price of a good often leads to: a. a greater supply of the good. b. a black market for the good. c. a …
Consumer's Equilibrium under Cardinal Utility Analysis ... Consumer's Equilibrium: Two Commodity Case. In the above table columns, 2 and 3 give marginal utility of X and Y. column 4 and 5 give the ratios of marginal utility to the price of the two commodities, i.e., the marginal utility of a rupee spent on the purchase of two commodities.
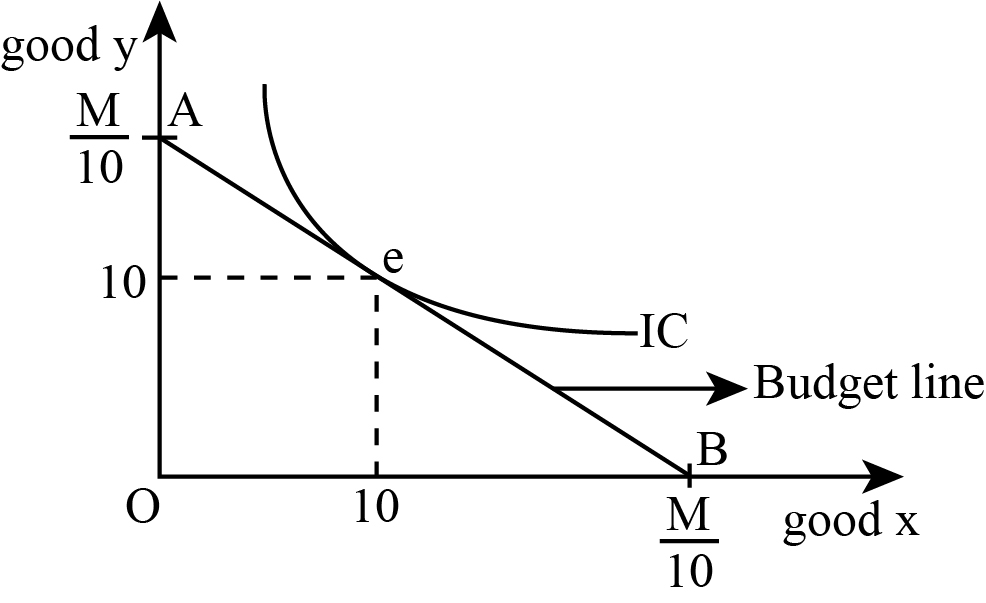
Consumer's Equilibrium: Interplay of Budget Line and ... It means, by moving left or right of point E, a consumer can obtain higher amount of either good X or good Y. Thus point E is not an equilibrium point. A consumer will therefore be in equilibrium when at the point of tangency of indifference curve and the budget line, the indifference curve is convex to the origin.
› homework-help › questions-andSolved A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the - Chegg A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. A. What is the price of good Y? $_____ B. What is the consumer's income? $_____ C. At point A, how many units of good X does the consumer purchase? _____ units. D. Suppose the budget line changes so that the consumer achieves a new equilibrium at point B.
Consumer Equilibrium through Indifference Curve Analysis ... So at point C, all three conditions for the stable-consumer's equilibrium are satisfied. Summing up, the consumer is in equilibrium at point C where the budget line PT is tangent to the indifference IC 2. The market basket OH of good X and OE of good Y yields the greatest satisfaction because it is on the highest attainable indifference curve.
Answered: When a small country imposes a tariff… | bartleby A: Given production function q=10L^0.5 K^0.5 Price of labor=$20 Price of capital=$5 question_answer Q: Explain why the FOMC is expected to …
Consumer Equilibrium in Case of Two Commodity ... Let a consumer buy two commodities i.e. X and Y. Then at equilibrium. M u x P x. =. M u y P y. = Marginal utility of the last rupee spent on each good or simply Marginal utility of money (MUM) Similarly, if a consumer buys three commodities such as X, Y, and Z, then the condition of equilibrium will be the simply marginal utility of money or MU ...
Assisting students with assignments online - Success Essays Every sweet feature you might think of is already included in the price, so there will be no unpleasant surprises at the checkout. 24/7/365 Support. You can contact us any time of day and night with any questions; we'll always be happy to help you out. Free Features. $15.99 Plagiarism report. $7.99 Formatting.
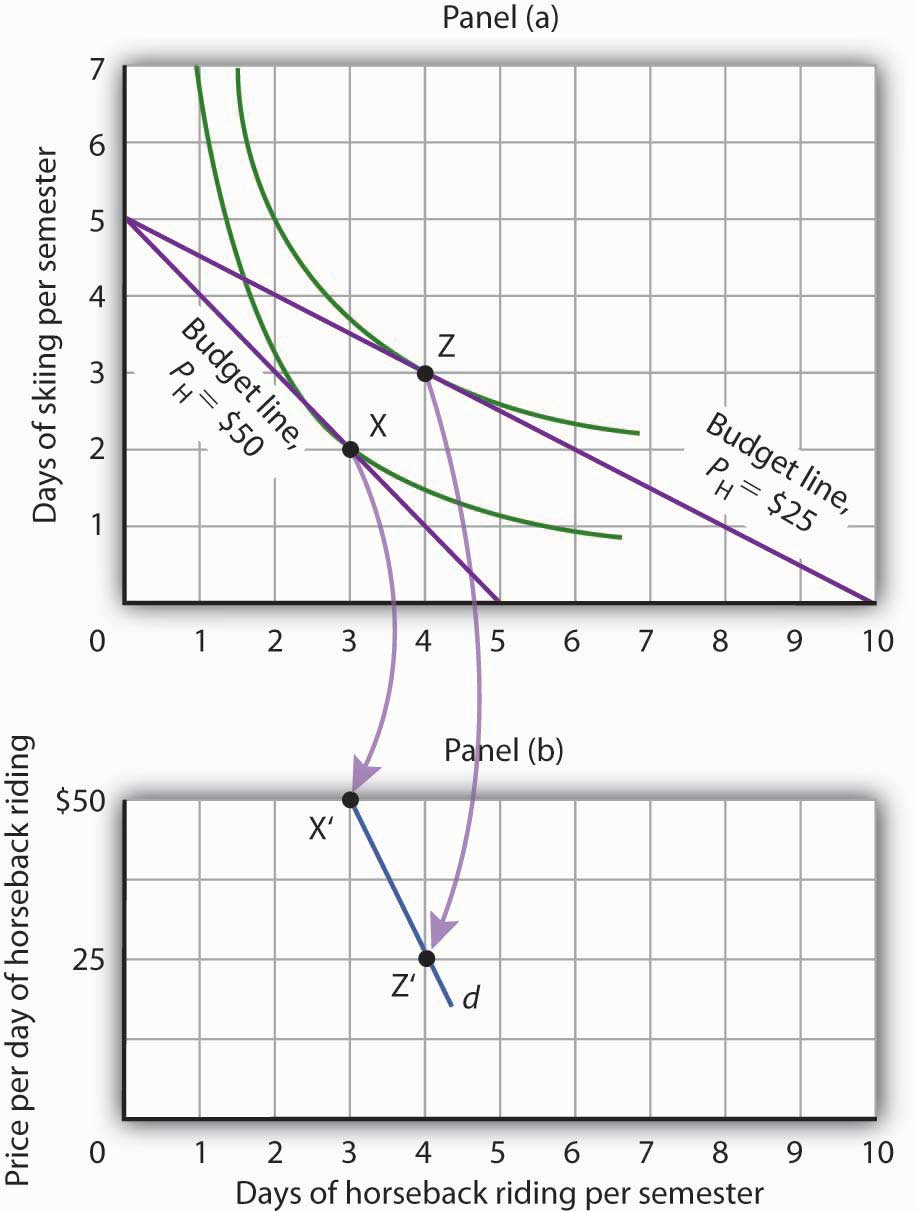
Income Effect of the Consumer (With Diagram) (2) ICC 2 is horizontal from point A, X is a normal good while У is a necessity of which Fig. 23 the consumer does not want to have more than the usual quantity as his income increases further. (3) ICC 1 is vertical from A, Y is a normal good here and X is satiated necessity; (4) ICC 4 is negatively inclined downwards, У becomes an inferior good form A onwards and X is a superior good; and
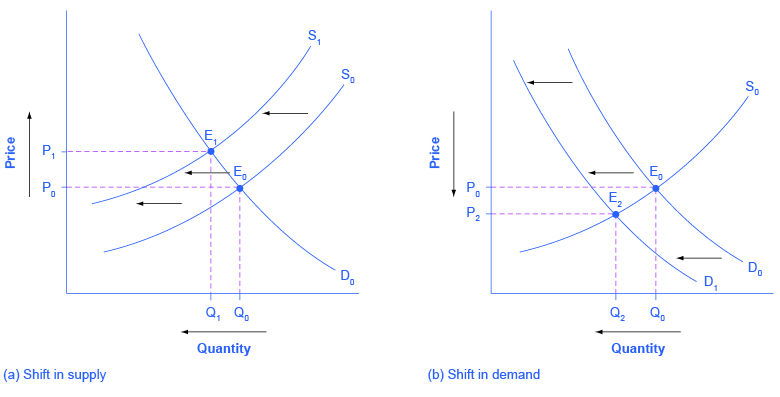
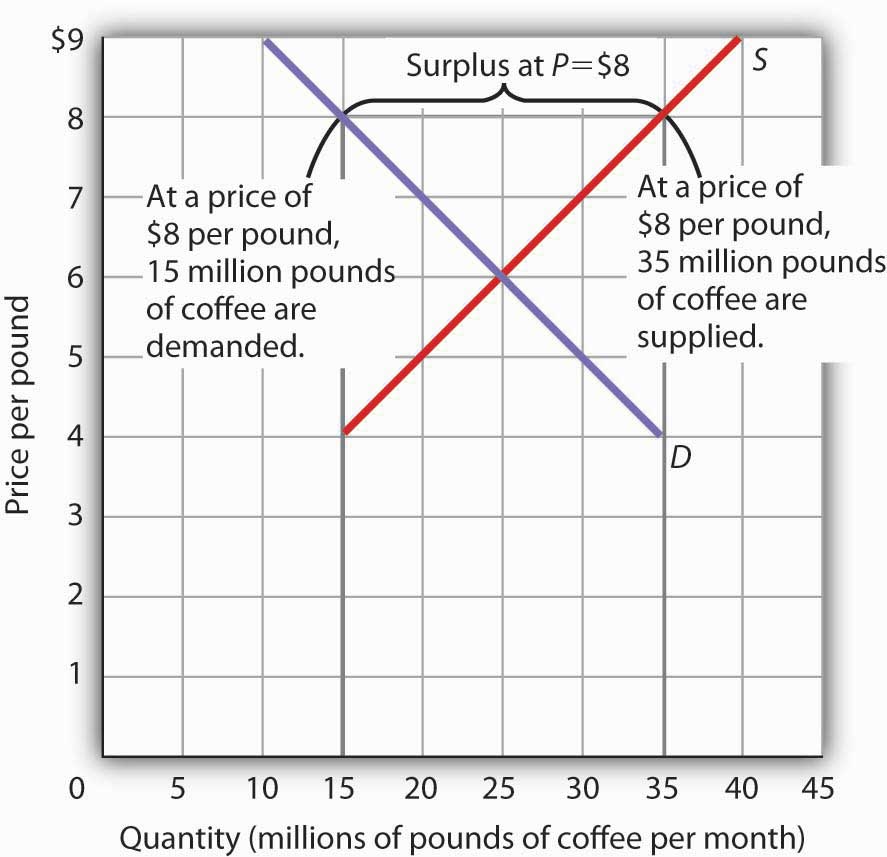
3.3 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium - Principles of ... At a price below the equilibrium, there is a tendency for the price to rise. Figure 3.7 The Determination of Equilibrium Price and Quantity When we combine the demand and supply curves for a good in a single graph, the point at which they intersect identifies the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity.
Graded HW 2 CH 4.docx - 1. A consumer is in equilibrium at ... View Homework Help - Graded HW 2 CH 4.docx from ECN 5150 at University of North Carolina, Pembroke. 1. A consumer is in equilibrium at point A in the diagram below. The price of good X is $5. a. What
3.6 Equilibrium and Market Surplus - Principles of ... Suppose the equilibrium price of good X is $10 and the equilibrium quantity is 60 units. If the price of good X is $4: a) The quantity demanded will be less than 60 units. b) The quantity supplied will be more than 60 units. c) There will be an excess demand for good X. d) There will be an excess supply of good X. 14.
PDF Question Bank 5. A consumer will start buying less of good-X and more of Good-Y, when: (a) MUx/Px = MUm (b) MUx/PxMUy/Py 6. According to IC approach, at the point of equilibrium: (a) slope of IC > slope of price line (b) slope of IC < slope of price line (c) Slope of IC # slope of price line (d) slope of IC = slope of price ...
PDF Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge ... 4 In the indifference curve diagram point M is the consumer's initial equilibrium and MN is the substitution effect of a fall in the price of good X. If good X is a Giffen good which point will be the consumer's new equilibrium point after the fall in
SOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS: Chapter 13 - Geneseo c. If there’s a price ceiling of $9, it has no effect, since the market equilibrium price is $8, below the ceiling. So the equilibrium price is $8 and the equilibrium quantity is 6 million Frisbees. 4. a. Figure 4 shows the market for beer without the tax. The equilibrium price is P1 and the equilibrium quantity is Q1.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Micro Economics Consumer ... A consumer consumes only two goods X and Y and is in equilibrium. Show that when the price of good X rises, the consumer buys less of good X. Use utility analysis. [AI 2014] Answer: As, we know condition for consumer equilibrium is, Necessary Condition Marginal utility of last rupee spend on each commodity is same.
Microeconomics Lecture #4 Flashcards - Quizlet Assuming $5 to be the equilibrium price for this market, please shade in consumer surplus (CS), producer surplus (PS), and total surplus (TS). The area above the equilibrium price bound by the demand curve represents the consumer surplus.
PDF ECONOMICS 9708/01 1 hour - XtremePapers A The equilibrium price is zero. B The equilibrium price is P. C The equilibrium price is indeterminate, because the supply curve is vertical. D Consumer surplus from the operations is ODD 1. 12 The diagram shows a demand curve for journeys on a toll road. number of journeys per day toll per journey ($) 5 3 1000 2000 0
› file › 67099832Chapter 4 HW.docx - Chapter 4 HW 1) A consumer is in ... 3) 4) In the below figure, a consumer is initially in equilibrium at point C. The consumer's income is $400, and the budget line through point C is given by $400 = $100 X + $200 Y. When the consumer is given a $100 gift certificate that is good only at store X, she moves to a new equilibrium at point D. Explanation a. P x = $100, P y = $200 ...



















0 Response to "39 a consumer is in equilibrium at point a in the diagram below. the price of good x is $5."
Post a Comment