41 the diagram at right shows an arbitrary point
Point-Group Diagrams - University College London Superimposed on the molecule is the steroegraphic diagram for this particular point group. The lens-shaped symbol represents the twofold rotation axis, and the two solid thick lines show two mutually-perpendicular mirror planes whose line of intersection contains the twofold. In addition, the figure shows how an arbitrary point (shown top right as an open circle with a "+" … PDF Motion Diagrams reading - Columbia Public Schools point with reference to a coordinate axis. The origin of the coordinate axis may be arbitrary. Position to right of origin, position(x) is positive Position to left of origin, position(x) is negative ... • A motion diagram shows only the POSITION of the object on the position axis.
Microeconomics Final Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the cost and demand curves for the Erickson Power Company. If the government regulates Erickson Power Company so that the firm can earn a normal profit, the price would be set at _____ and the output level is _____.

The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point
The diagram at right shows ail arbitrary point, point ... The diagram at right shows ail arbitrary point, point .A. that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S2 are equidistant from point A. PDF Part I: Background Material Page 1 - Introduction to Moon ... • In the Diagram Options panel, the show angle option shows the earth-moon-sun. angle. The phases are technically defined in terms of this angle. • In the Diagram Options panel, the show lunar landmark option draws a point of. reference to more easily observer lunar rotation and revolution. Parabola - Wikipedia The point E is an arbitrary point on the parabola. The focus is F, the vertex is A (the origin), and the line FA is the axis of symmetry. The line EC is parallel to the axis of symmetry and intersects the x axis at D. The point B is the midpoint of the line segment FC. Deductions. The vertex A is equidistant from the focus F and from the directrix.
The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point. The Production Process (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion This point shows the optimal (least cost) combination of inputs for a fixed level of output. However, we know that there exists an optimal combination for every level of output the firm might choose to produce, and the proportions in which the inputs are combined need not necessarily be the same for all levels of output. Solved 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point ... The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point point A, that lies near two point sources of waves In this problem, we consider how the path lengtlh difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Answered: The following diagram shows a point P… | bartleby Solution for The following diagram shows a point P on the contour plot (level curves) of a function f. In which direction does the function f remain constant at… Dive into anything - reddit Jul 22, 2010 · r/Firearms: Discuss firearms, politics, 2nd amendment news. We value freedom of speech as much as we do the right to keep and bear arms. Posts must …
UML State Machine Diagrams - Overview of Graphical Notation State machine diagram is a behavior diagram which shows discrete behavior of a part of designed system through finite state transitions. State machine diagrams can also be used to express the usage protocol of part of a system. Two kinds of state machines defined in UML 2.4 are behavioral state machine, and; protocol state machine. The following nodes and edges are … Answered: The diagram shows triangle A. Make a… | bartleby The diagram shows triangle A. Make a copy the diagram. Draw the image of A after each combination of transformations. 6. 4 1 0+ 0i23 4 56 7 * A rotation of 90° anticlockwise, center (3, 5) followed by a translation 3 squares right and 2 squares down. Label this image C. 2. Overview of the Spatial Standard Observer. The upper ... The upper diagram shows the sequence of operations. The lower left shows the CSF in the spatial frequency domain, and the lower right image shows the Gaussian spatial aperture in the space domain ... Solved 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point ... The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources.
Lecture 3 - University of Wisconsin-Stevens Point The electric field midway between two equal but opposite point charges is 745 N/C, and the distance between the charges is 16.0 cm. What is the magnitude of the charge on each? A. 3.31×10 −9 C B. 2.65×10 −10 C C. 4.14×10 −6 C D. 3.02×10 8 C Answer sb5 23.44 What field is required to stop electrons having energy 1.60×10 −17 J in a ... The Asymptotic Bode Diagram - Erik Cheever This point is shown as a red circle on the diagram. A piecewise linear approximation is not as easy in this case because the high and low frequency asymptotes don't intersect. Instead we use a rule that follows the exact function fairly closely, but is also somewhat arbitrary. Its main advantage is that it is easy to remember. Micro final Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the cost and demand curves for the Erickson Power Company. If the government regulates Erickson Power Company so that the firm can earn a normal profit, the price would be set at _____ and the output level is _____. Morse potential - Wikipedia The Morse potential, named after physicist Philip M. Morse, is a convenient interatomic interaction model for the potential energy of a diatomic molecule.It is a better approximation for the vibrational structure of the molecule than the quantum harmonic oscillator because it explicitly includes the effects of bond breaking, such as the existence of unbound states.
Solved The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point ... The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A. that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S_2 are equidistant from point A.
Feynman diagram - Wikipedia In theoretical physics, a Feynman diagram is a pictorial representation of the mathematical expressions describing the behavior and interaction of subatomic particles.The scheme is named after American physicist Richard Feynman, who introduced the diagrams in 1948.The interaction of subatomic particles can be complex and difficult to understand; Feynman diagrams give a …
International Economics Flashcards - Quizlet Using the diagram on the right, show what effect a devaluation will have on the current account. Note: 'E' = E$/€. 1) Using the line drawing tool , shift any lines, making sure to label them appropriately. 2) Using the point drawing tool, label new equilibrium "B".
Diagram shows the nonworking condyle pathway during ... Diagram shows the nonworking condyle pathway during excursive movements (a: the Bennett angle recorded by two-points intraoral record, b: the angle recorded including immediate lateral side shift ...
Solved 3. The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point ... The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point. point A that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources.
OneClass: The following diagram shows the constraints for ... (b) Find the fixed point (s). (c) Find the eigenvalues. (d) Find the eigenvectors. (e) Write the general solution. Show that it can be written as a real-valued solution like R(t) (vab t) sin Vab t COS J(t) (f) Show that the trajectories in phase space are ellipses, governed by the equation R2 J2 aC2 bC2 where C2 0 is an arbitrary constant.
Functions - Green Tea Press stack diagram: A graphical representation of a stack of functions, their variables, and the values they refer to. frame: A box in a stack diagram that represents a function call. It contains the local variables and parameters of the function. traceback: A list of the functions that are executing, printed when an exception occurs. 3.14 &# ...
Physics Undergraduate Practicals The diagram at the right shows an arbitrary point, point P, that lies near two point sources of sinusoidal waves. The two sources are in phase with each other. In this activity, we consider how the phase difference of the waves arriving at point P changes as point P is moved outward along the dark line, away from the sources.
Compensated Demand Curve (With Diagram) - Economics … First consider the lower diagram (B) where the price of good X is taken on the vertical axis. Point P is an arbitrary point on this axis which shows the price of X when the budget line is PQ in the upper diagram. The fall in the price of X as shown by the budget line PQ 1 is reflected in point P 1 in the lower diagram. The Marshallian Uncompensated Demand Curve: …
Test 1 from HW Chapters 1-8 Flashcards - Quizlet The diagram to the right shows the Home economy's pretrade equilibrium at point X. If this economy opens itself to trade, its consumption point _______ its production point. Now suppose that trade commences between Home and the rest of the world and, as a result, the relative price of coal in Home rises.
Phase Diagram - Materials Project Documentation 10.03.2011 · Marking of an arbitrary composition in the phase diagram. Mouse-over popup of details at particular nodes. Complete data table with listing of stable and unstable phases. Manual¶ Introduction¶ Phase diagrams represent the thermodynamic phase equilibria of multicomponent systems and reveal useful insights into fundamental material aspects …
Need help understanding 16QAM constellation diagram The mapping is arbitrary as long as the receiver correctly determines which constellation point a symbol is. If the receiver makes a mistake, though, it is most likely going to pick a "neighbor" constellation point (i.e. a constellation point that is only one spot away).
Solved The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point ... The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A, that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources. Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S2 are equidistant from point A.
a i On the diagram of the parallel plates above draw and ... A third charge of -q is first placed at an arbitrary point A (x = -x o) on the x-axis as shown in the figure below. c. Write expressions in terms of q, a, x 0, and fundamental constants for the magnitudes of the forces on the -q charge at point A caused by each of the following. i. The +q charge ii. The +2q charge d.
Solved 3 The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point ... 3 The diagram at right shows an arbitrary point, point A, that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source R are equidistant from point A ...
Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors A ray diagram for the case in which the object is located in front of the focal point is shown in the diagram at the right. Observe that in this case the light rays diverge after reflecting off the mirror. When light rays diverge after reflection, a virtual image is formed.
Voronoi diagram - Wikipedia In mathematics, a Voronoi diagram is a partition of a plane into regions close to each of a given set of objects. In the simplest case, these objects are just finitely many points in the plane (called seeds, sites, or generators). For each seed there is a corresponding region, called a Voronoi cell, consisting of all points of the plane closer to that seed than to any other.
International Econ- Exam 1 Flashcards | Quizlet The diagram to the right shows the Home economy's pretrade equilibrium at point X. (Click anywhere on the graph and move the slider to vary the relative price.) In this closed economy, it is the case that
geometry - Distance an arbitrary point is found along a ... Say I have a vector in 2D space defined by two points $(x_1, y_1)$ and $(x_2, y_2)$: $$\vec{v}=(x_2 - x_1, y_2 - y_1)$$ I would like to find how far along that vector an arbitrary point $(x_3, y_3)$ is. This very woolly language $^*$, so I've attempted to create a diagram showing the sitation.
Q Refer to the diagram to the right which shows short run ... Q: Refer to the diagram to the right. Diminishing marginal productivity sets in after A: the 2nd worker is hired. 49) Q: The graph in this figure illustrates an initial competitive equilibrium in the market for apples at the intersection of D 2 and S 1 (point C).
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) Symbols - EdrawMax - Edrawsoft 18.02.2022 · Before you embark on creating a data flow diagram, it is important to determine what suits your needs between a physical and a logical DFD. Physical DFD focuses on how things happen by specifying the files, software, hardware, and people involved in an information flow.. Logical DFD focuses on the transmitted information, entities receiving the information, …
PDF Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Straight Rod—C.E ... arbitrary point in space. The result includes the case of the field on the axis of the rod beyond one of its ends, and the case of an infinitely long rod. The general answer is most conveniently expressed in terms of the linear charge density λ; for a finite rod of length L and total charge Q, that charge density is equal to Q/L. To begin with ...
Parabola - Wikipedia The point E is an arbitrary point on the parabola. The focus is F, the vertex is A (the origin), and the line FA is the axis of symmetry. The line EC is parallel to the axis of symmetry and intersects the x axis at D. The point B is the midpoint of the line segment FC. Deductions. The vertex A is equidistant from the focus F and from the directrix.
PDF Part I: Background Material Page 1 - Introduction to Moon ... • In the Diagram Options panel, the show angle option shows the earth-moon-sun. angle. The phases are technically defined in terms of this angle. • In the Diagram Options panel, the show lunar landmark option draws a point of. reference to more easily observer lunar rotation and revolution.
The diagram at right shows ail arbitrary point, point ... The diagram at right shows ail arbitrary point, point .A. that lies near two point sources of waves. In this problem, we consider how the path length difference to point A changes as point A is moved along the dark line shown, away from the sources Point Z on the diagram below was chosen so that point Z and source S2 are equidistant from point A.


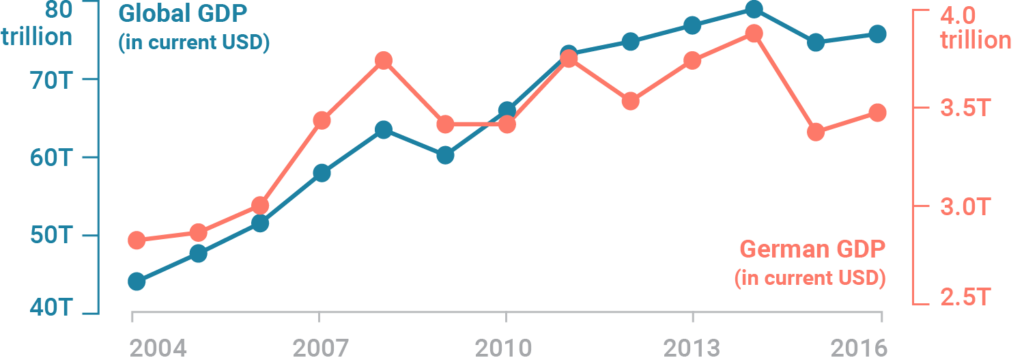






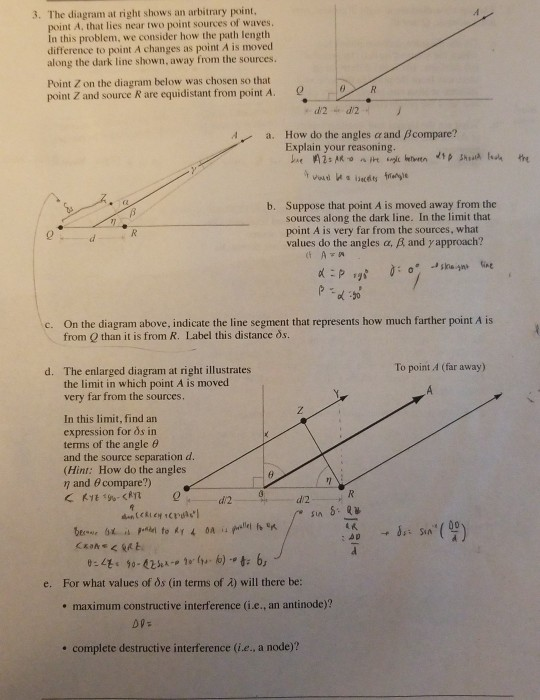

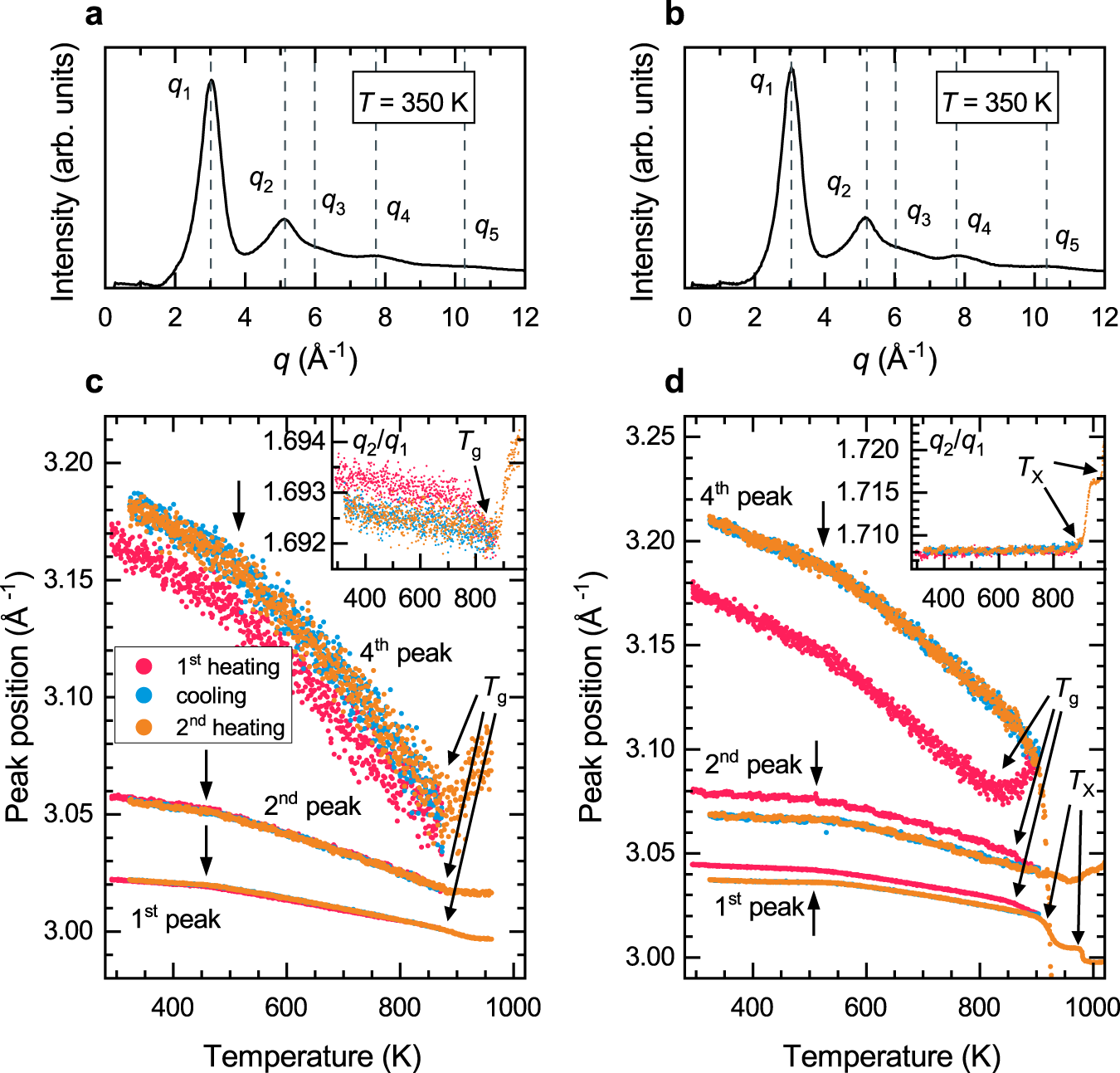



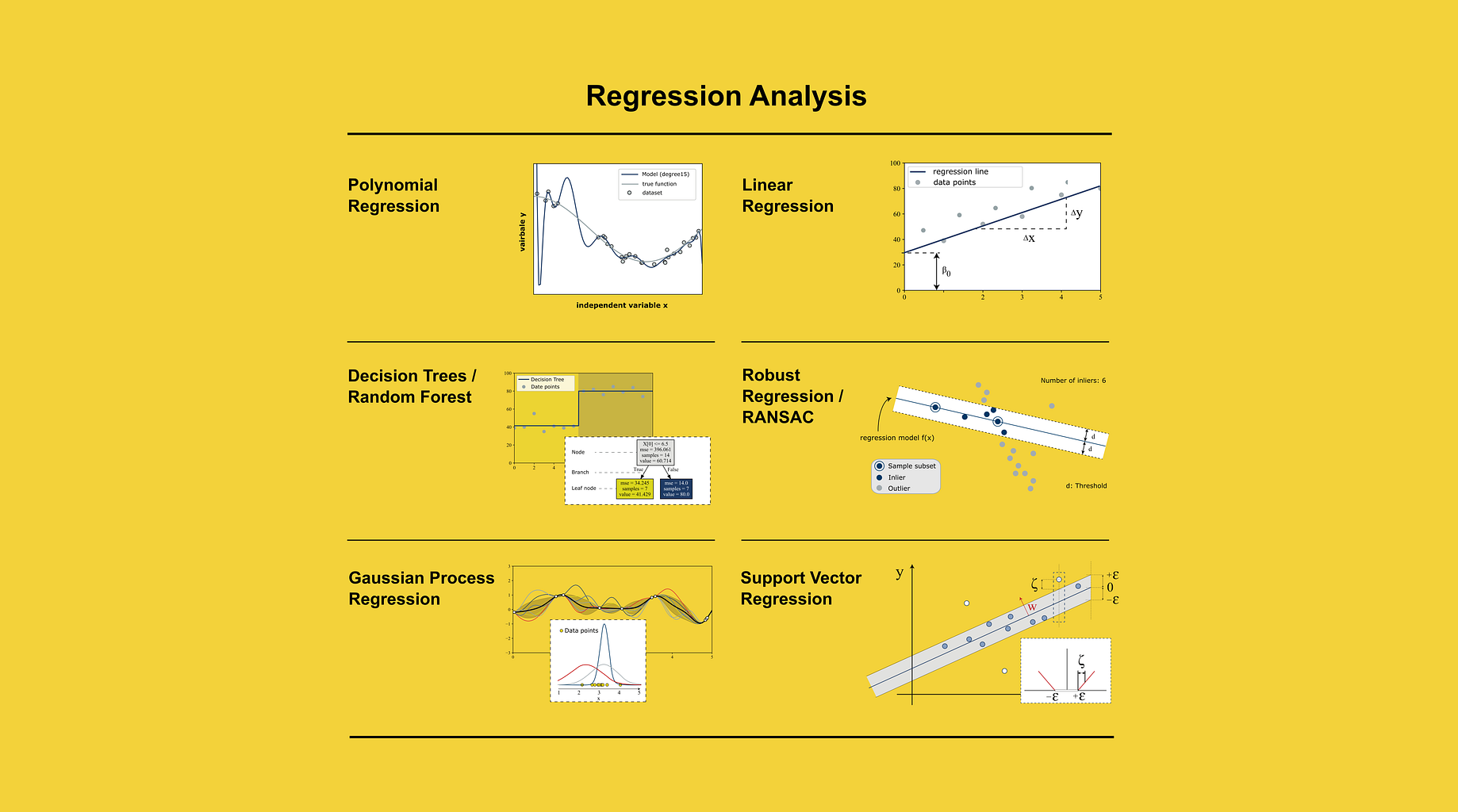




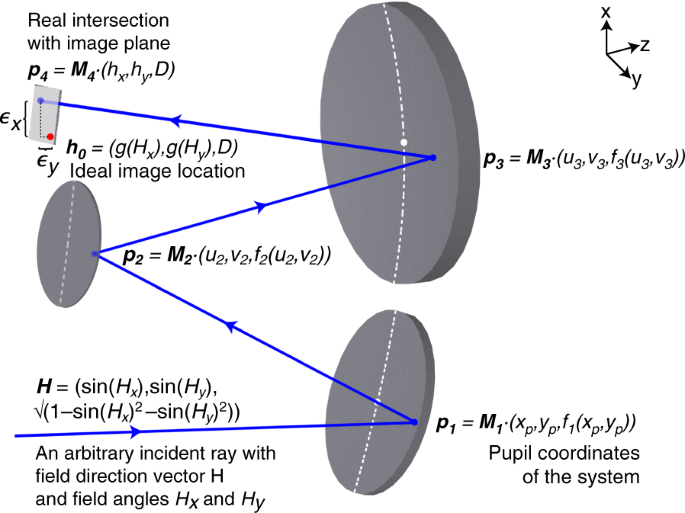
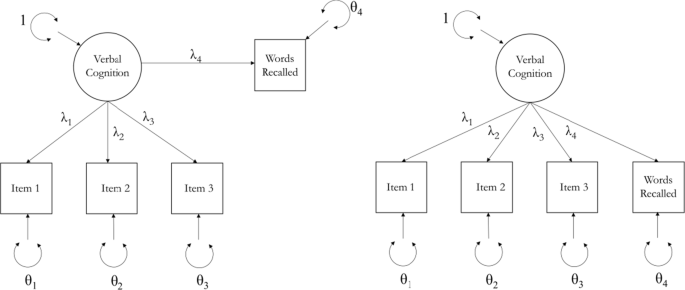








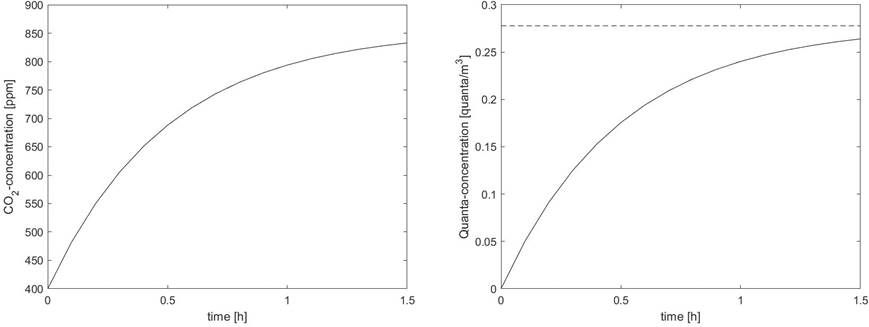



0 Response to "41 the diagram at right shows an arbitrary point"
Post a Comment