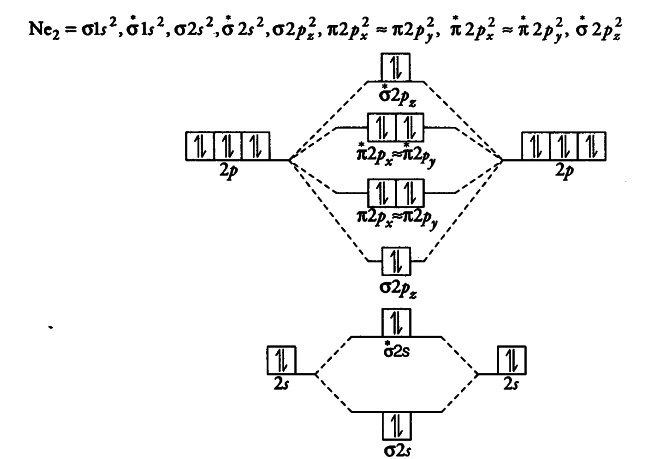
38 molecular orbital diagram for ne2
I’m a little confused on the connection between a molecules molecular orbital diagram and it’s individual atomic hybridization. Can anyone help me? Thank you After reading the theory part draw the MO diagrams for the following diatomic omonuclear molecules: ... Ne2. F2 electron configuration. N. OF. OCCUPIED. MO.13 pages
https://i.imgur.com/GgRlFtK.jpg (Not homework) I am trying to improve by using past papers. Can someone explain how to solve these 3 questions?

Molecular orbital diagram for ne2
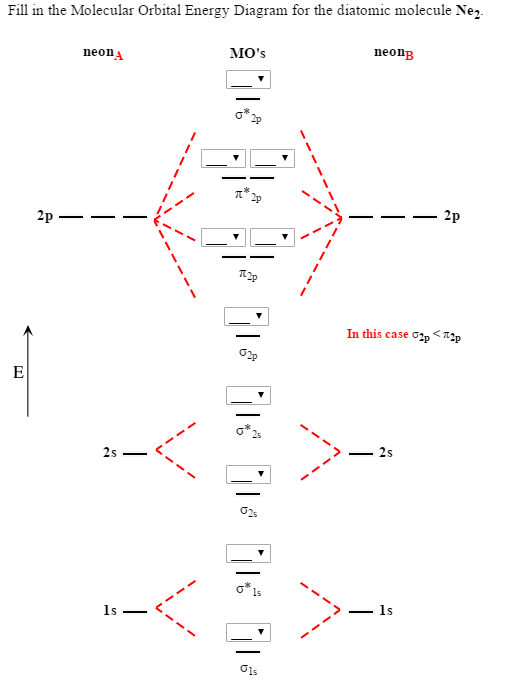
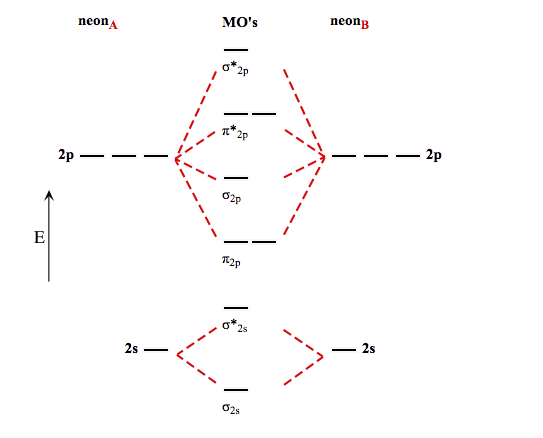
Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule Ne2. (Please fill in all of the blanks using UP OR DOWN ARROWS.) This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. Transcribed image text: Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule Ne2. neonB neonA MO's ?*. In this case ?2p < * ?2s 25 ls ?1s. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways.Draw the molecular orbital diagram for Ne 2 + and determine if the bond between the two atoms will be stable. One of the most essential words in the science of chemistry is bond order. The chemical bonds that exist between two atmos are determined by determining the bond order. Bond order can also be used to get a sense of a molecule's stability, bond energy, bond length, and thermal stability. However, determining bond order via MOT or by drawing molecular orbitals takes time. So, in this article, I've attempted to offer a novel technique to calculating the bond order using applied mathematics and ...
Molecular orbital diagram for ne2. I know how to draw MO diagrams for certain bonds like NF and CN-, but I don't know how to draw an MO diagram for a bond between a first period element and a second period element. Molecular Orbital Diagram For Ne2. Mar 4, Find an answer to your question Draw and explain the molecular orbital diagram of Ne2. On the basis of molecular orbital diagram, explain. According to Molecular Orbital theory, only those molecule can exists which have net positive bond order while the molecules with negative or. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine I’ve been tasked with drawing rhe MO diagram for Sulfure Oxide and I’m not sure about the energies of the relatove orbitals. Since Oxygen is more electronegative I expect the 2s and 2p orbitals to have much lower energy than the 3s and 3p orbitals sulfur has. But the energy difference would be really high then. So I’m not sure what 2 orbitals combine to form the sigma 3s or sigma* 3s orbital. The difference in energy kevels confuses me as every example I’ve done has the same orbitals (2s,2p’s) c...
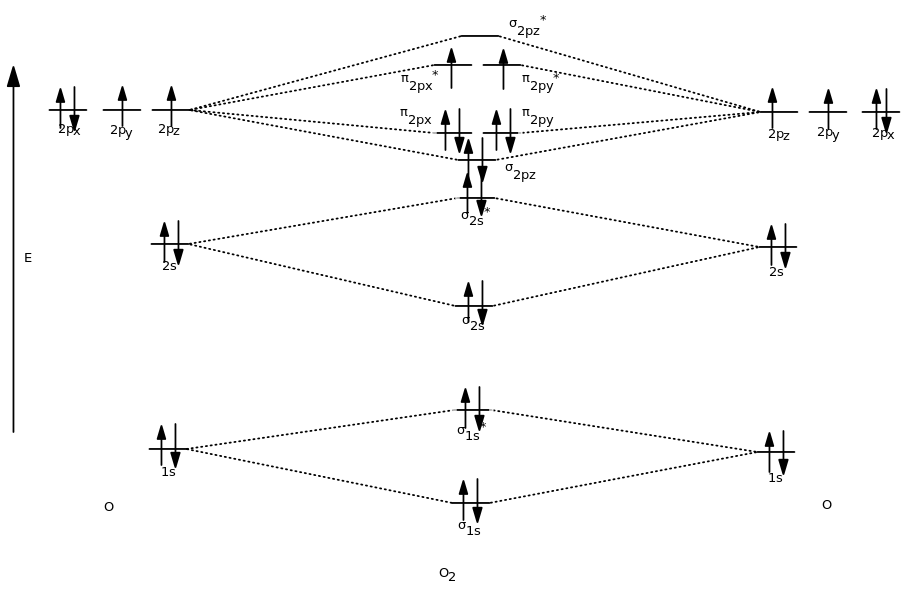
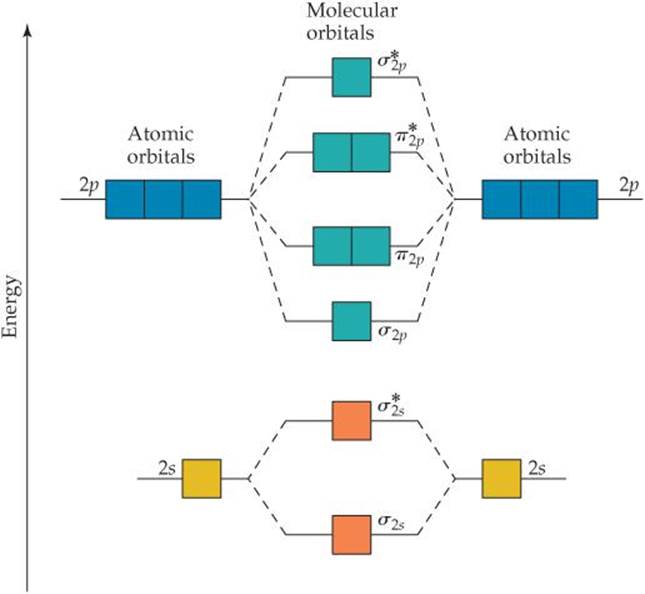
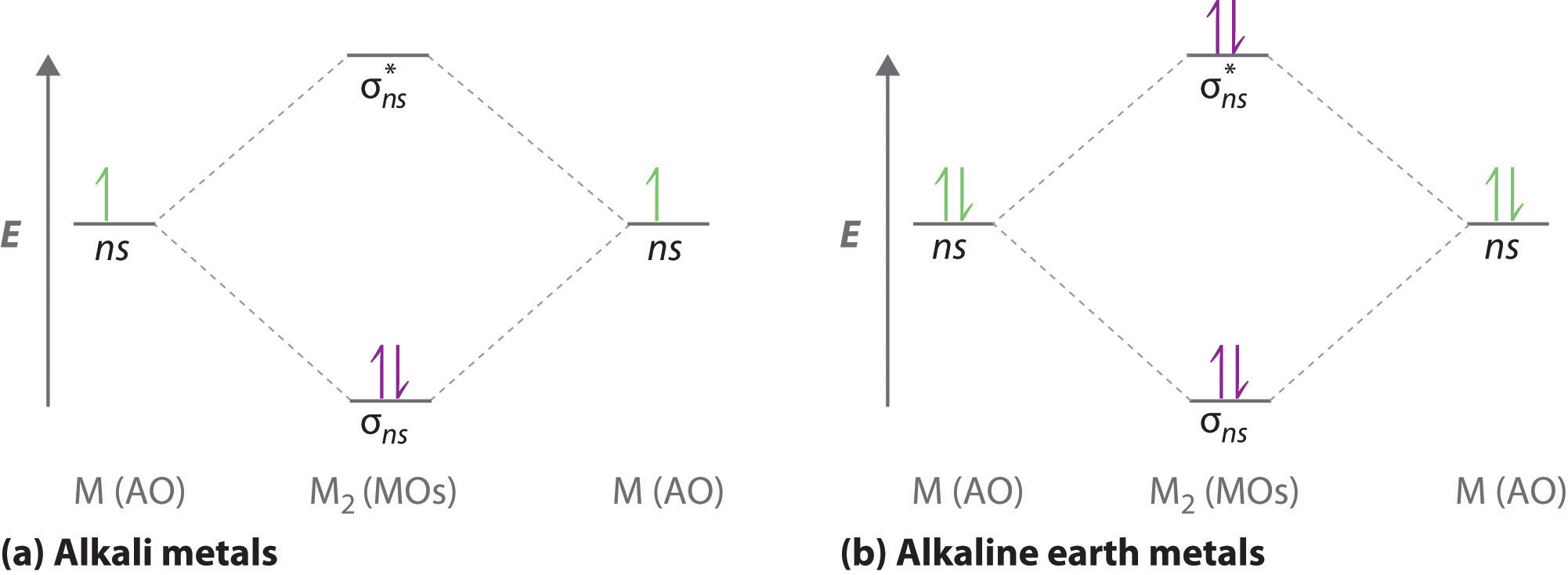
I've been getting the hang of creating MO diagrams and I understand the very basics. My problem is in the 2p orbital's bonding section where sometimes the pi 2p section is lower energy than the sigma 2p section (i.e MO diagram for B2 diatomic molecule). I understand that the lower energy must be filled in first and so my question is, how do I know if the pi 2p is lower energy than sigma 2p? I need to construct the molecular orbital diagram for the hypothetical species Li4, which has the following geometrical arrangement: https://preview.redd.it/npsjre5pch571.png?width=197&format=png&auto=webp&s=c2a7948c2efa04a975bee1db722838fae7482456 The first step is to identify the point symmetry group. In this particular case, we consider that there is only one axis of rotation of order four (actually, other symmetry elements can be observed, but this is a previous consi... Molecular Orbital Diagrams. This scheme of bonding and antibonding orbitals is usually depicted by a molecular orbital diagram such as the one shown here for the dihydrogen ion H 2 +. Atomic valence electrons (shown in boxes on the left and right) fill the lower-energy molecular orbitals before the higher ones, just as is the case for atomic ... Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
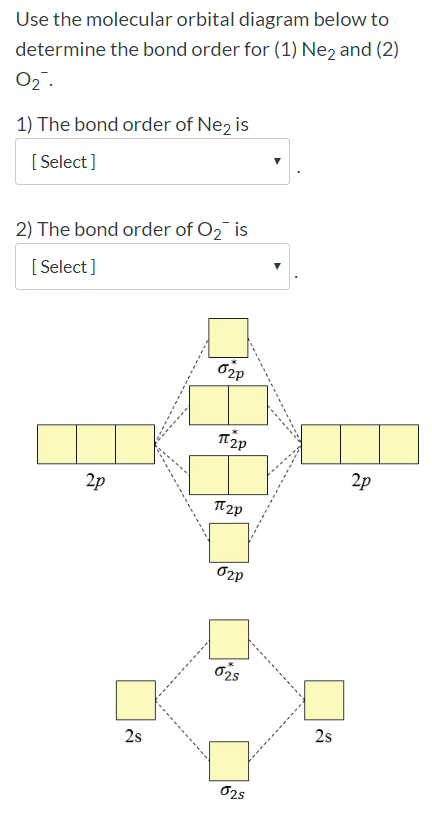
There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).One is for the elements up to Nitrogen. The other is for AFTER nitrogen (start... Hi I am a PhD candidate and I need help making a frontier molecular orbital visualization diagram for the molecule pentacene. I only need 4 molecular orbital visualizations and they are HOMO, LUMO, HOMO-1, and LUMO +1. I am currently using chemissian with the imput from IQMOl but I am having difficulties getting a visual MO composition output. Can anyone help me? Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the Ne2 molecule. Be sure your diagram contains all of the electrons in the molecule, including any core electrons. Energy ; Question: O STRUCTURE AND BONDING Drawing the MO energy diagram for a Period 2 homodiat... Draw the molecular orbital (MO) electron diagram for the Ne2 molecule. Calculate the bond order of Ne2 and determine if you would expect this molecule to exist. Then write out the electron configuration for the molecule, ...4 answers · Top answer: So here we're looking at the molecular orbital theory to describe bonding. So the first example, ...
A) F2; B) F2^2+ C) Ne2^2+ D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. A) O2^2-B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. 10 5 molecular orbital theory chemistry libretexts.
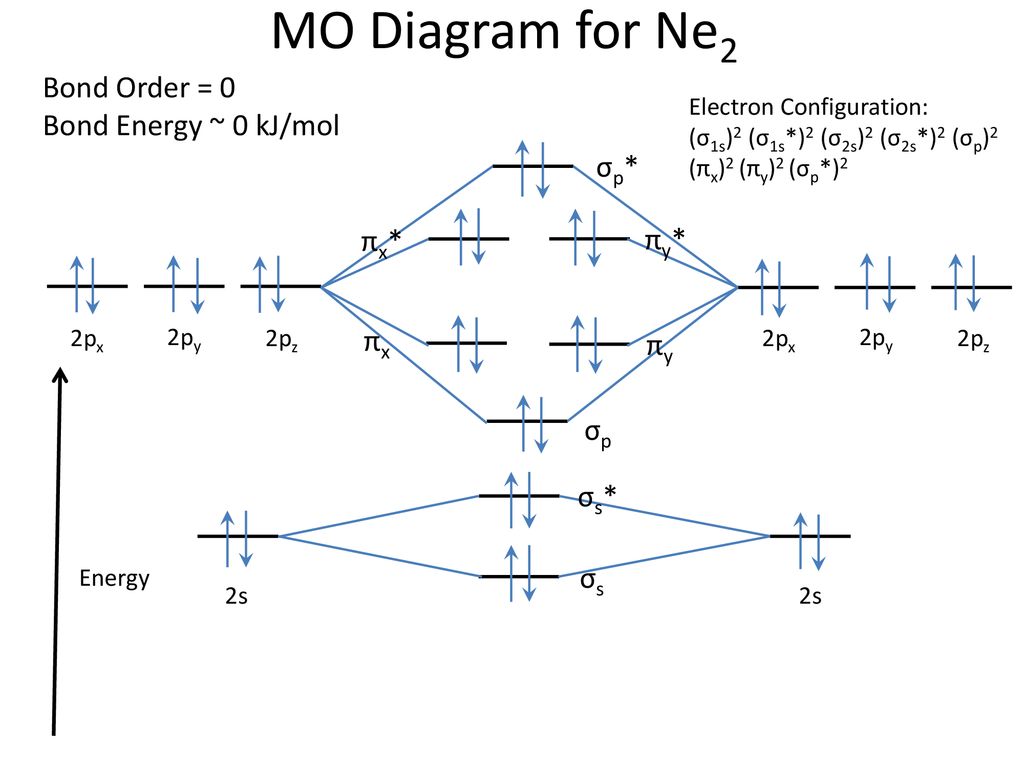
The valence molecular orbital configuration of Ne2+ is:. σ2s2 σ*2s2 σ2p2 π2p2 π2p2 π*2p2 π*2p2 σ*2p1 The bond order of Ne2+ according to molecular orbital theory is: . 0.5; According to the given question, we are asked to show the valence molecular orbital configuration of Ne2+ and also the bond order based on the molecular orbital theory.. As a result of this, we can see that Ne2^+ is ...
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. According to the molecular orbital theory, in a supposed He2 molecule, both the if we draw its MOT DIAGRAM, 2 e's enter the Bonding molecular Orbital and 2 .
Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
Molecular orbital diagram ne2.If ne 2 did form, it would be diamagnetic. Once you have the molecular orbitals and their energy ordering the ground state configuration is found by applying the pauli principle, the what is the molecular orbital diagram for the diatomic neon molecule, ne2?
0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon MoleculeSo as we d...
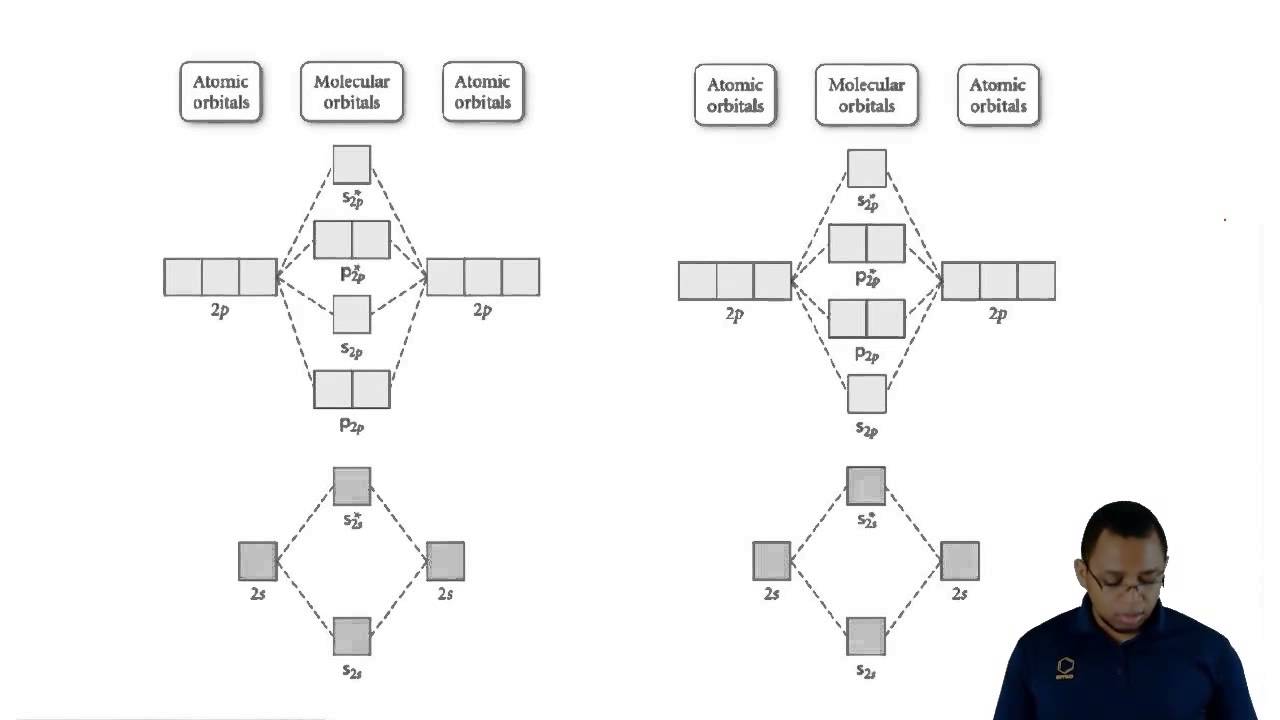
Show activity on this post. I have been taught that the MO diagram is different for molecules with 14 or less electrons than the one used for molecules with 15 or more electrons. For N X 2 the orbitals in increasing energy are: σ 1 s < σ 1 s ∗ < σ 2 s < σ 2 s ∗ < π 2 p x, π 2 p y < σ 2 p z < π 2 p x ∗, π 2 p y ∗ < σ 2 p z ∗ ...
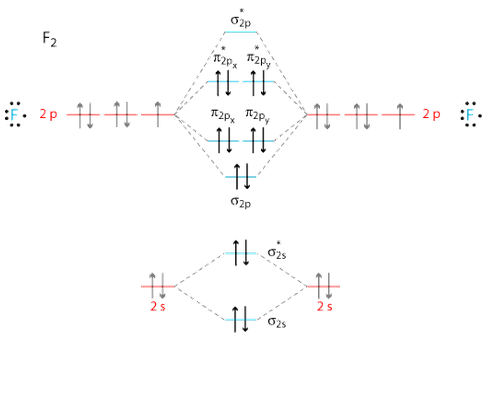
Use the molecular orbital energy level diagram to show that N2 would be expected to have a triple bond, F2, a single bond and Ne2, no bond. · Solution.1 answer · Top answer: Formation of N2 molecule: Electronic Configuration, σ 1s^2<σ *1s^2<σ 2s^2<σ *2s^2<[pi 2px^2 = pi 2px^2]<<σ 2pz^2 Bond order = (Nb - Na)/2 = (10 - ...
19. Refer to the MO Diagrams. Use molecular orbital theory to determine if the molecular are paramagnetic or diamagnetic. c. Li2 d. N2 a. F2 20. Refer to the MO Diagrams. Assuming that the molecular orbital energy diagram for a homonuclear diatomic molecule applies to a hero nuclear diatomic molecule, determine bond order for each below. c. NO ...
A molecular orbital can hold two electrons, so both electrons in the H 2 molecule are in the [latex]\sigma[/latex] 1s bonding orbital; the electron configuration is [latex]{\left({\sigma}_{1s}\right)}^{2}.[/latex] We represent this configuration by a molecular orbital energy diagram (Figure 7.7.10) in which a single upward arrow indicates one ...
place the following molecular orbitals in order of decreasing energy for species of O2, F2, and Ne2. start with the highest energy molecular orbital at the top of the list. 1.) o*2p 2.) pie*2p
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. ... If N b = Na,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals. 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order.
energy level diagram is similar to that of NO (Problem 5.7) without the antibonding π* electron. b. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons.29 pages
Shouldn’t you count the valence electrons for Be (which is 2) and subtract 1 because of the + sign? For O2, N2, NO, F2, etc, you count the number of valence electrons instead of the atomic number. Why is it that for Be, though, you look at the atomic number instead of the number of valence electrons it has? I apologize if this is a stupid question, but I appreciate any clarification on this
Explain your answer here in addition to providing the bond order values. We are asked to determine the bond order from the molecular orbital diagram of Ne2 and to check whether the calculated bond order agrees with the Lewis structure of Ne2. Part A. Draw the Lewis Structure of Ne2. Part B. Determine the bond order from the molecular orbital ...
Problem Details. How can you determine the stability of a compound using the molecular orbital diagram? For example: Using the MO diagram for Ne2 determine if it is stable or not stable. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos.
What happens to the molecular orbital diagram when a metal-ligand complex is oxidized? Oxidation removes an electron, e.g. you go from d8 metal to d7 metal. As consequence the antibonding orbital has an unpaired electron making the complex less stable (weaker M-L bond, since less pi-backdonation), but how does it change the gap between the metal MO and LUMO of ligand, as well as the gap between the metal MO and HOMO of the ligand?
With the help of molecular orbital diagram show that Ne2 cannot exist as stable molecule. (Atomic number of Ne = 10). asked Jan 26, 2020 in Chemistry by SurajKumar ( 66.2k points)
Jan 26, 2020 — With the help of molecular orbital diagram show that Ne2 cannot exist as stable molecule. (Atomic number of Ne = 10). chemical bonding ...1 answer · Top answer: Ne2 (20) = σ1s2 σ*1s2, σ2s2 σ*2s2, σpx2 π 2py2 2π* 2py2π*2py2 2pz2 σ* 2px2 B.O = 1/2 (10 - 10) = 0 Ne2 cannot exist because its bond order is zero.
hey! I have a question: how do i draw a molecular orbital diagram for SO2? i only found examples for diatomic diagrams and im not sure how to do it if i have more then two atoms in the molecule.
Interactive video lesson plan for: MO Diagram for N2+ (Molecular Orbital) Activity overview: There are two MO diagrams you need to memorize for diatoms (N2, O2, Ne2, etc).
Mar 3, 2018 — Molecular orbital diagram of · Neon atom has 10 electrons and its electronic configuration is . When molecule is considered, it has two neon ...2 answers · 20 votes: Bond order of Ne2 = (10-10) =0 So Ne2 is unstable ;Ne2 cannot exist
LCAO MO Energy Diagram for H2 Energy H-H ∆E1 ∆E2 • ∆E2> ∆E1, so the antibonding orbital is always more anti-bonding than the bonding orbital is bonding H2molecule: two 1s atomic orbitals combine to make one bonding and one antibonding molecular orbital. Ha Hb
B) Ne2^2+ C) O2^2+ D) F2^2+ E) None of the above are paramagnetic; 3) Draw the molecular orbital diagram needed, and determine which of the following is paramagnetic. A) B2^2+ B) B2^2-C) N2^2+ D) C2^2-E) B2; 4) Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.
With the help of molecular orbital theory show that Ne2 cannot exist as stable species . Asked by Aashna Anith Kumar | 4th Feb, 2014, 11:50: PM. Expert Answer: According to Molecular Orbital theory, only those molecule can exists which have net positive bond order while the molecules with negative or zero bond order will not exists.
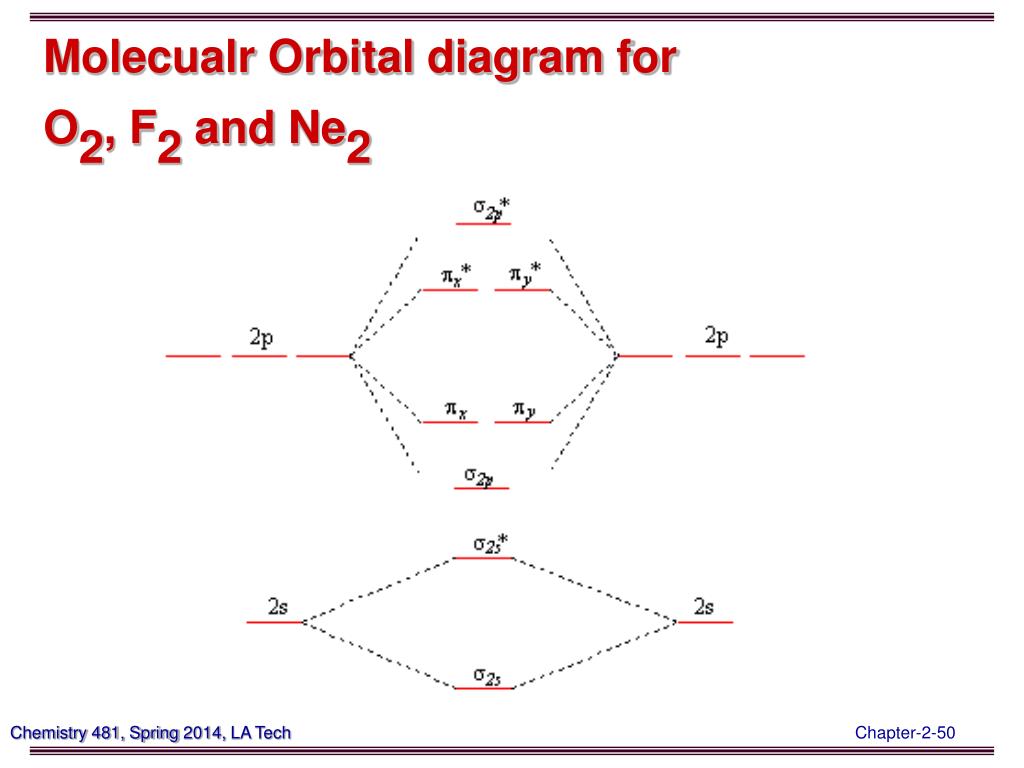
Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways. Page 1. MO Diagrams for Elements Li2 through Ne2. (Don't memorize.) Li2 through N2. O2 through Ne2.
One of the most essential words in the science of chemistry is bond order. The chemical bonds that exist between two atmos are determined by determining the bond order. Bond order can also be used to get a sense of a molecule's stability, bond energy, bond length, and thermal stability. However, determining bond order via MOT or by drawing molecular orbitals takes time. So, in this article, I've attempted to offer a novel technique to calculating the bond order using applied mathematics and ...
Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructed, from N2, O2, F2, Ne2 the complexity of the molecular orbitals develop in two ways.Draw the molecular orbital diagram for Ne 2 + and determine if the bond between the two atoms will be stable.
Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule Ne2. (Please fill in all of the blanks using UP OR DOWN ARROWS.) This is the best answer based on feedback and ratings. Transcribed image text: Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule Ne2. neonB neonA MO's ?*. In this case ?2p < * ?2s 25 ls ?1s.




![Expert Verified] using MOT find out the bond order of Ne2 ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d9f/f4e9ccc0480e0f453254060b5fef8c9a.jpg)














0 Response to "38 molecular orbital diagram for ne2"
Post a Comment