39 diagram of amino acids
25-01-2017 · Can you name the 20 common amino acids from their neutral structures? by sproutcm Plays Quiz Updated Jan 25, 2017 . Rate 5 stars Rate 4 ... Plants Venn Diagram 57; Score Distribution. Your Account Isn't Verified! In order to create a playlist on Sporcle, ... Calculates the molecular weight and percent composition of chemical formulas and amino acids. Molecular Weight Calculator - .NET DLL Version VB.NET DLL version of the Molecular Weight Calculator, supporting a range of molecular weight calculations for both chemical formulas and amino acids. Software Category: Tutorials. Command Line Application ...
Amino acids may be enzymatically removed from the amino end of the protein. Because the "start" codon on mRNA codes for the amino acid methionine, this amino acid is usually removed from the resulting protein during post-translational modification. Peptide chains may also be cut in the middle to form shorter strands.

Diagram of amino acids
Amino Acids - Biology Diagram. Create Biology Diagram examples like this template called Amino Acids - Biology Diagram that you can easily edit and customize in minutes. 15/20 EXAMPLES. General Structure of Common Amino Acids •General structure of amino acids, group and a variable side chain •Side chain determines: protein folding, binding to specific ligand and interaction with its environment •Amino acids consists of a constant COOH (R is side chain) •At neutral pH, H 2 N- protonated to H 3 N+-, and -COOH ... Hydrophobic Amino Acids: What are hydrophobic and polar groups? Amino acids are grouped according to what their side chains are like. The nine amino acids that have hydrophobic side chains are glycine (Gly), alanine (Ala), valine (Val), leucine (Leu), isoleucine (Ile), proline (Pro), phenylalanine (Phe), methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp). Shown at the right is the structure of valine.
Diagram of amino acids. a-Amino Acids Structure: Things to Note 8 • There are some common features of these amino acids that should be noted. • All, but one of these a-amino acids, contain a primary amino group and a carboxylic acid group attached to the same carbon and conform to the general structure above. Structure of Amino acids . All 20 of the common amino acids are alpha-amino acids. They contain a carboxyl group, an amino group, and a side chain (R group), all attached to the α-carbon. Exceptions are: Glycine, which does not have a side chain. Its α-carbon contains two hydrogens. Jan 05, 2022 · The category of the amino acids; The exact names of the amino acids; The basics of the pegword method involve assigning images to letters of the alphabet. So instead of a generic gargoyle for “glycine,” we’ll want to try and find a ‘gl’ word. Ideally this will be the name of a person. Proteins, Peptides & Amino Acids 1. Introduction. Proteins, from the Greek proteios, meaning first, are a class of organic compounds which are present in and vital to every living cell.In the form of skin, hair, callus, cartilage, muscles, tendons and ligaments, proteins hold together, protect, and provide structure to the body of a multi-celled organism.
Amino acids are organic molecules that, when linked together with other amino acids, form a protein.Amino acids are essential to life because the proteins they form are involved in virtually all cell functions. Some proteins function as enzymes, some as antibodies, while others provide structural support.Although there are hundreds of amino acids found in nature, proteins are constructed from ... During protein synthesis, the carboxyl group of the amino acid at the end of the growing polypeptide chain chain reacts with the amino group of an incoming amino acid, releasing a molecule of water. The resulting bond between amino acids is a peptide bond. Peptide bond formation between two amino acids. In a peptide bond, the carbonyl C of one ... Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino (−NH + 3) and carboxylate −CO − 2 functional groups, along with a side chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. The elements present in every amino acid are carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and nitrogen (N); in addition sulfur (S) is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine, and selenium (Se) in the less common ... Constructed from a string of 100 amino acids, the structure is displayed as (A) a polypeptide backbone model, (B) a ribbon model, (C) a wire model that includes the amino acid side chains, and (D) a space-filling model.
The primary structure of a protein is the order of these amino acids in the backbone of each of the polypeptide chains comprising the molecule. The primary structure of a polypeptide chain is delineated beginning with the amino acid occupying the polypeptide's N-terminus. R can be as simple as a hydrogen atom (H) or a methyl group (— CH3) or a more complex structure. The first carbon is the part of the carboxyl group. The second carbon, to which is attached the amino group, is called the α-carbon. The α-carbon of most amino acids is joined by covalent bonds to 4 different groups. Thus, the α-carbon in all ... interactions between the R groups of the amino acids that make up the protein. • Important to tertiary structure are . hydrophobic interactions, in which amino acids with nonpolar, hydrophobic R groups cluster together on the inside of the protein, leaving hydrophilic amino acids on the outside to interact with surrounding water molecules ... Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys.
The biologically important amino acids have the amino group attached to the carbon atom next door to the -COOH group. They are known as 2-amino acids. They are also known (slightly confusingly) as alpha-amino acids. These are the ones we will concentrate on. The two simplest of these amino acids are 2-aminoethanoic acid and 2-aminopropanoic acid.
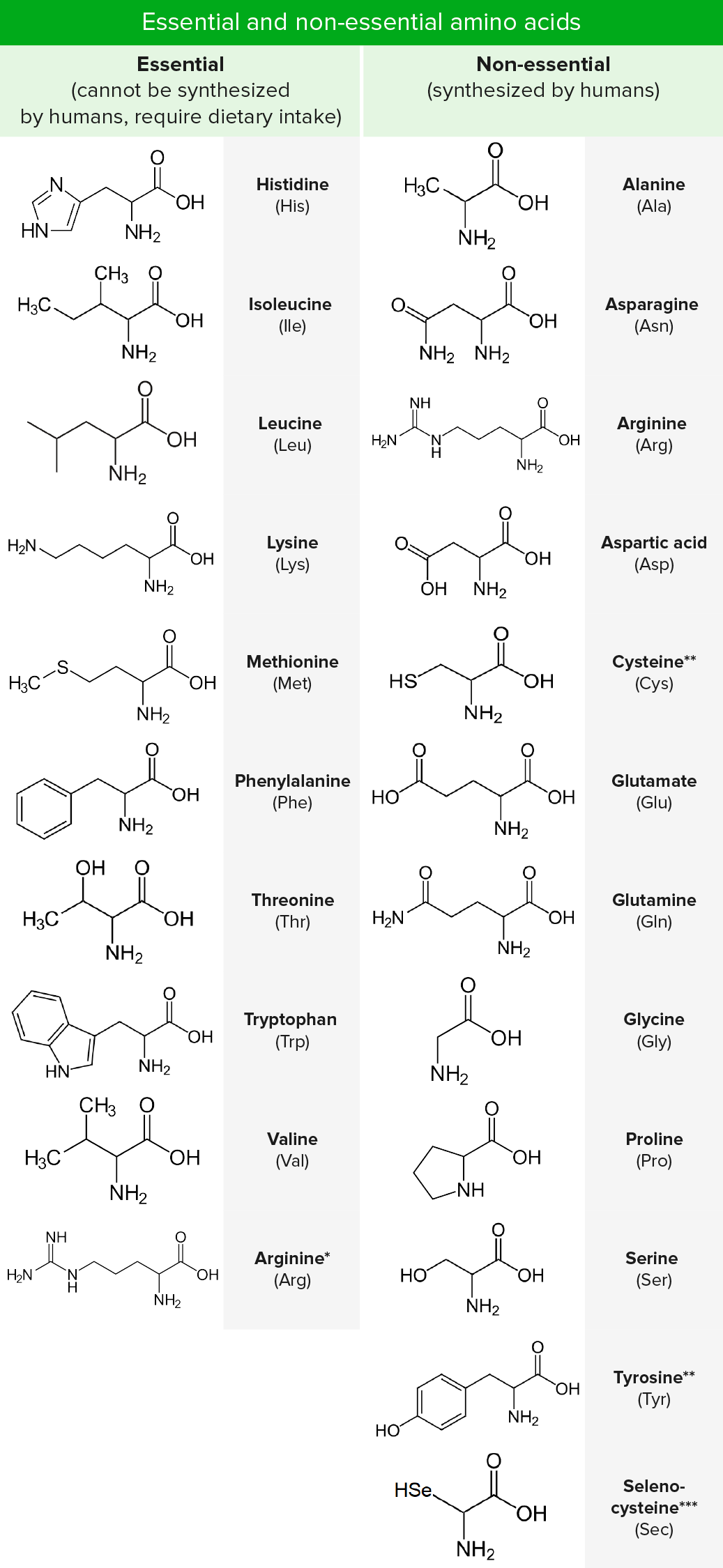
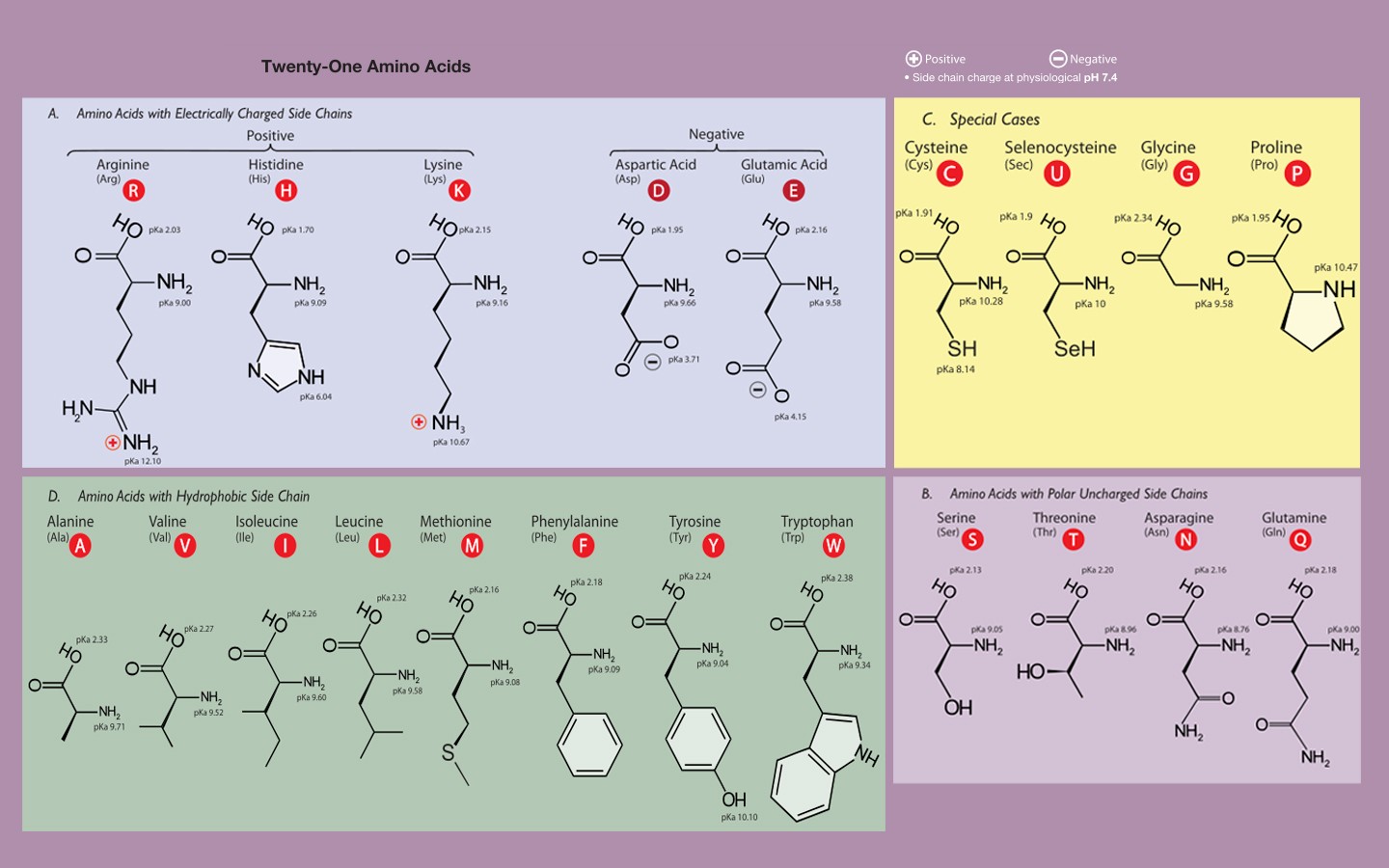
Only 20 amino acids are found in the human peptides and proteins. These naturally occurring amino acids are used by cells to synthesize peptides and proteins. They are typically identified by generic formula: H 2 NCHRCOOH. The primary difference between the 20 amino acids is a different structure of R group.
Many of the amino acids that are common to C and V domains of immuno-globulin chains lie in the core of the immunoglobulin fold and are critical to its stability. For that reason, other proteins having sequences similar to those of immunoglobulins are believed to form domains of similar structure, and in many cases this has been demonstrated by ...

Image from page 724 of "Amino acid pools: distribution, formation and function of free amino acids; proceedings" (1962)
Amino acids contain a free amino group and a free carboxylic acid group that react together with ninhydrin to produce a coloured product. When an amino group is attached to the first, or alpha, carbon on the amino acid’s carbon chain, the amino group’s nitrogen atom is part of a blue-purple product, as shown in Equation 2.

Image from page 168 of "Amino acid pools: distribution, formation and function of free amino acids; proceedings" (1962)
Amino acids that fall under the classification of hydrophobic are alanine, valine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, tryptophan and tyrosine. As their classification suggests, the side chains tend to be repelled from water, so this impacts the positioning of these amino acids in the protein tertiary structure. Properties of polar ...
Amino Acid Abbreviations and Molecular Weights. The average molecular weight of an amino acid is 110Da. Dalton (Da) is an alternate name for the atomic mass unit, and kilodalton (kDa) is 1,000 daltons. Thus a protein with a mass of 64kDa has a molecular weight of 64,000 grams per mole.

Plate 75 from The Plan of Chicago, 1909: Chicago. Diagram of the City, Showing Complete System of Inner Circuits (1909) // Daniel Hudson Burnham, American, 1846-1912 Edward Herbert Bennett, American, born England, 1874-1954
All amino acids have the same basic structure, shown in Figure 2.1. At the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the and attached to it are four groups - a hydrogen, a carboxylic acid group, an amine group, and an R-group, sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain. The α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino groups are ...
Amino acids join together in a linear chain to form proteins. Two amino acids join together with the elimination of a molecule of water forming a special linkage called a peptide bond. In the diagram 3 amino acids are shown linked together through the peptide linkage.
The same amino acid always coded by a particular codon. In fact, one codon (the codon is generated) can be a code the same amino acid, but the same codon shall not code for two or more different amino acids (non-ambiguity). Polarity: The genetic code is polar means that the code always read in a fixed direction. Comma less:
Amino Acid Structure - Amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group, an acidic carboxyl group, and a unique organic side chain. Amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form proteins. The general formula of an amino acid is R-CH(NH2)-COOH.
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. They band together in chains to form the stuff from which life is born. This is a two-step process: first, they get together and form peptides or polypeptides, and it is from these groupings that proteins are made. A total of 20 different kinds of amino acids form proteins, with the types ...
Here is the structure of twenty amino acids with their chemical formula. Sources of Amino Acids Amino acids play an important role in performing several biological and chemical functions in different parts of our body, including building and repairing of the tissues, in the formation and function of enzymes , food digestion, for the ...
a guide to the twenty common amino acids amino acids are the building blocks of proteins in living organisms. there are over 500 amino acids found in nature - however, the human genetic code only directly encodes 20. 'essential' amino acids must be obtained from the diet, whilst non-essential amino acids can be synthesised in the body. by nc nd
Amino acids that contain only the α amino and α carboxyl groups, which act as Brønsted-Lowry acid-base conjugate pairs somewhere within the normal aqueous pH range (meaning that the pK a of the acidic form of the pair lies between 0 and 14), effectively form a diprotic system, with three possible protonation or charge states.
Three amino acids bound into a tripeptide. How amino acids interact with each other and the environment Use the following simulation to test how a polypeptide chain with fold based on the type of solution it is in and the composition of the amino acids. Protein Folding Simulation (CC BY 4.0 Concord Consortium) Levels of structure
All twenty amino acids have this structure. The α-carbon is also attached to a variable structure called the R group. The R group is what differs among the twenty amino acids. α-carbon N C C H R H H O O H Conserved Region R group . Consider the two amino acids drawn below. Can you identify the conserved region and the R
Hydrophobic Amino Acids: What are hydrophobic and polar groups? Amino acids are grouped according to what their side chains are like. The nine amino acids that have hydrophobic side chains are glycine (Gly), alanine (Ala), valine (Val), leucine (Leu), isoleucine (Ile), proline (Pro), phenylalanine (Phe), methionine (Met), and tryptophan (Trp). Shown at the right is the structure of valine.
General Structure of Common Amino Acids •General structure of amino acids, group and a variable side chain •Side chain determines: protein folding, binding to specific ligand and interaction with its environment •Amino acids consists of a constant COOH (R is side chain) •At neutral pH, H 2 N- protonated to H 3 N+-, and -COOH ...
Amino Acids - Biology Diagram. Create Biology Diagram examples like this template called Amino Acids - Biology Diagram that you can easily edit and customize in minutes. 15/20 EXAMPLES.






















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/amino_acid-58b5de935f9b586046ef51d1.png)
/amino_acid-1b0e0369462e47c6aa53a45d404715ae.jpg)
0 Response to "39 diagram of amino acids"
Post a Comment