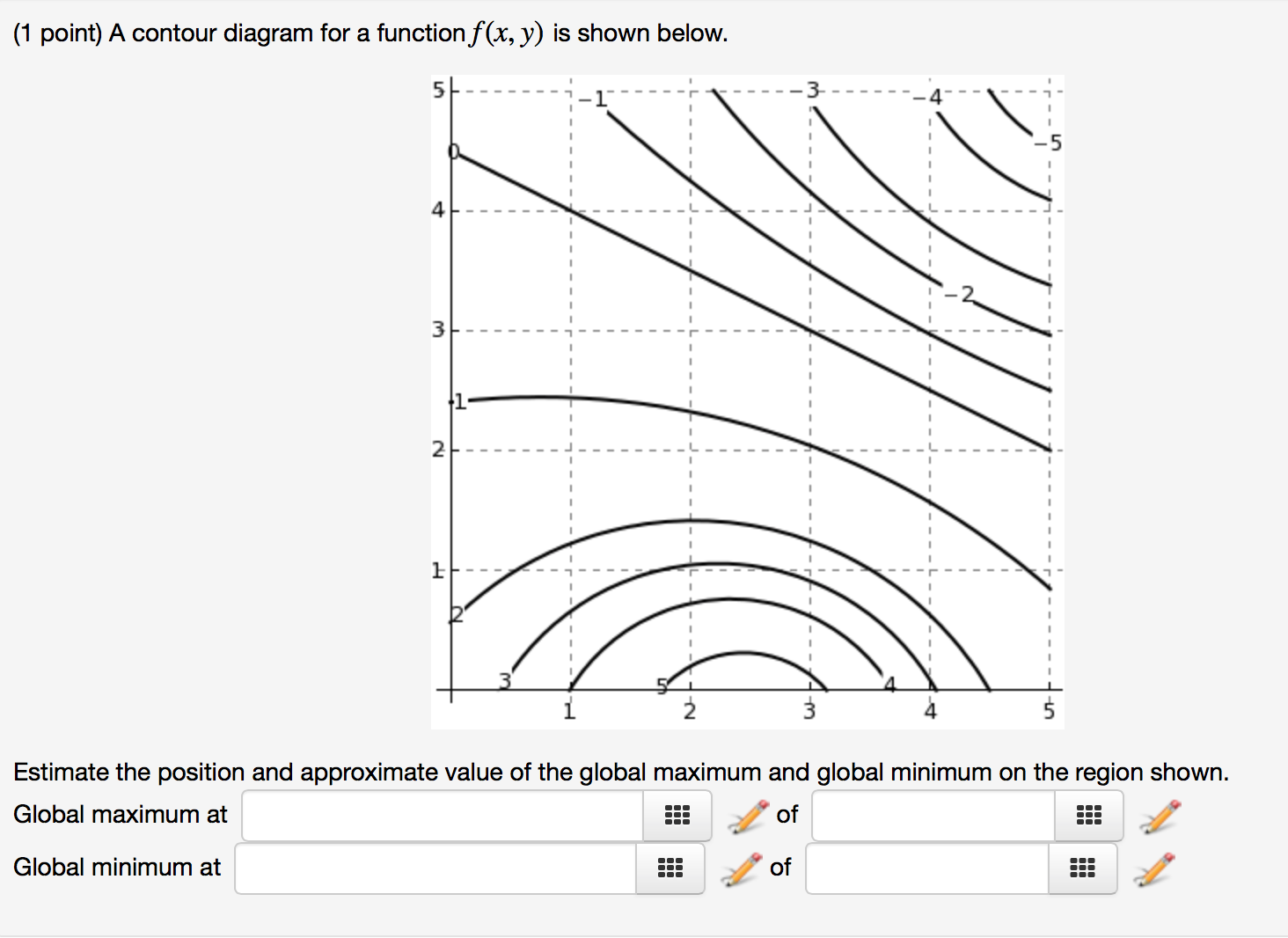
39 a contour diagram for a function f(x,y) is shown below.
Contour diagrams give us the same kind of information about a function. Below is a contour diagram of the same surface shown in above. The level curves are graphs in the x y -plane of curves f ( x, y) = c for various constants c. Each of the squares corresponds to one of the bumps on the surface. [In other words, the values of f(x,y) do not change when y changes, so f(x,y) can be viewed as a function of x alone, which makes f y(x,y) = 0 everywhere.] (c) We already know that f x is everywhere positive, or in other words that f(x,y) increases as x increases with y held constant. Moreover, the spacing of the contours tells us that as x ...
Transcribed image text: A contour diagram for a function f(x, y) is shown below. 51 3 -1 2 1 2 1 3 4 5 Estimate the position and approximate value of the ...

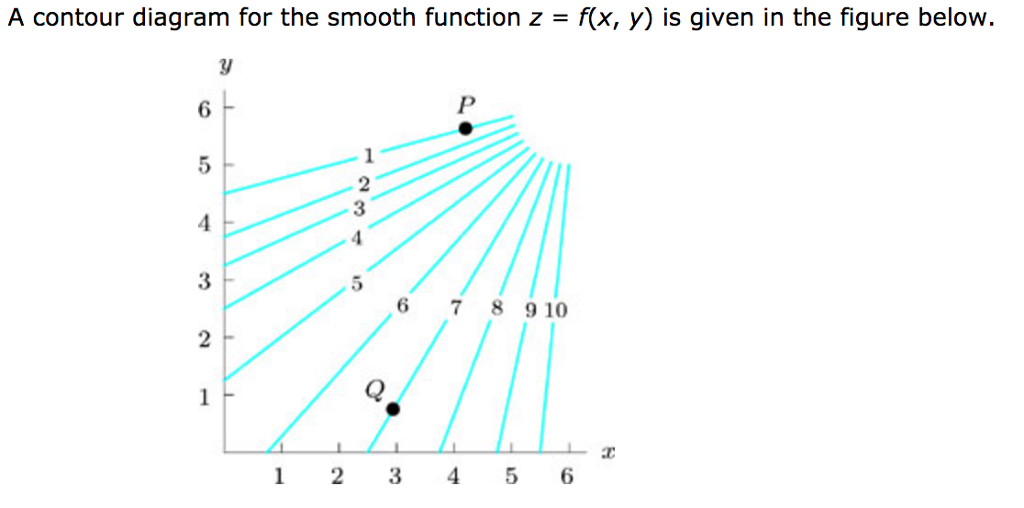
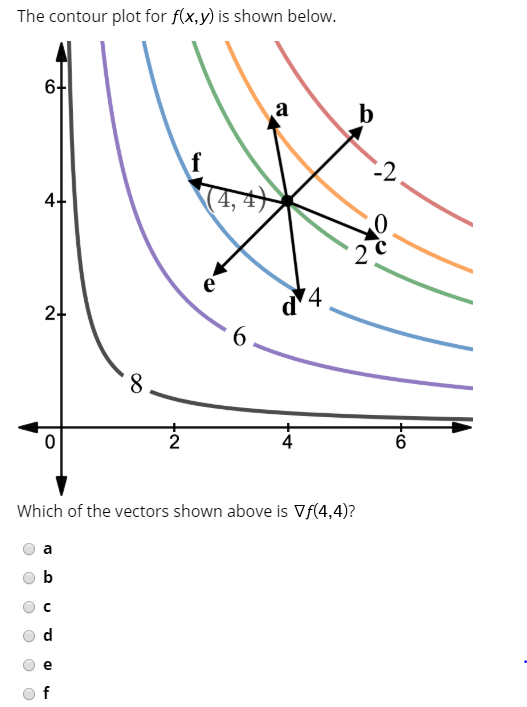
A contour diagram for a function f(x,y) is shown below.
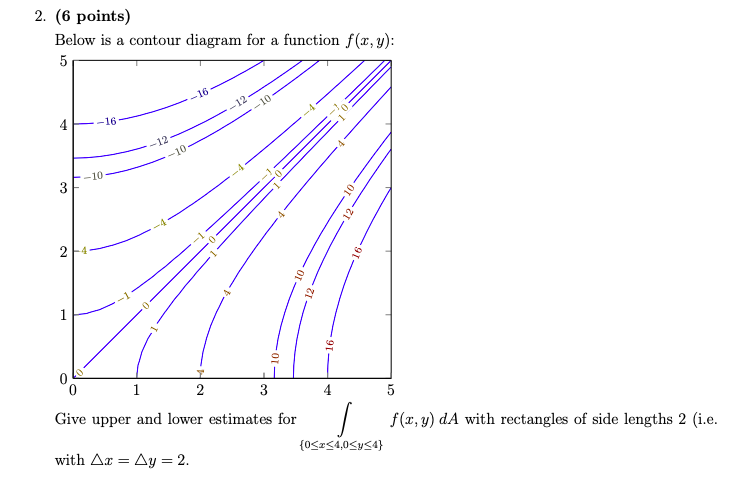
In Problems 2-6, sketch a contour diagram for the function with at least four labeled contours. Describe in words the contours and how they are spaced. 2. f(x;y) = x+ y If we set f(x;y) = c, the contours will satisfy y= c x, or straight lines with slope -1. 3. f(x;y) = 3x+ 3y If we set f(x;y) = c, the contours will satisfy 3y = c 3x, or y= c 3 ... A contour map for a function fis given. Use it to estimate f x(2;1) and f y(2;1). Solution: We can estimate f x by observing that as xgoes from 1.5 to 2.5, with y= 1 xed, f seems to go from about 9 to 12. Therefore f x(2;1) is approximately 3. As ygoes from 0.5 to 1.5, with x= 2 xed, fgoes from about 11 to about 9, so f y(2;1) is roughly -2. 2. Stewart 14.3.70 Ask about how fx changes in the y-direction and about fy. 6. Figure 9.7 is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the x and y axes in the usual directions. At the point P, if x increases, what is true of fx(P)? If y increases, what is true of fy(P)? (a) Have the same sign and both increase. (b) Have the same sign and both decrease.
A contour diagram for a function f(x,y) is shown below.. Problem 7, §12.4, p588. Does the contour diagram shown in the text represent a linear function? Solution. In this contour diagram the contours are all parallel lines. However, the contour lines ... we obtain a formula for our function: z = f(x,y) = −75+5(x − 4)− 5(y − 0) or f(x,y) = −95+5x − 5y. Problem 15, §12.4, p588. Find an ... A contour plot of the function z=f(x,y) consists of a family of curves f(x,y)=c (called level or contour curves) in the xy plane for various values of c. On the curve f(x,y)=c, z=c. A contour plot of the model function is shown below: On each curve in the contour plot z =f(x,y) is constant. On different curves the constant is different. Transcribed image text: A contour diagram for a function f(x, y) is shown below. Estimate the position and approximate value of the global maximum and ... The two images below show the graph of f(x;y) = x2 +y2 being sliced by horizontal planes, and the accompanying contour diagram. The graph of f(x;y) = x2 + y2 Contour diagram for f(x;y) = x2 + y2 Examples: 2. Match the surfaces (a)-(e) in the gure below with their respective contour diagrams
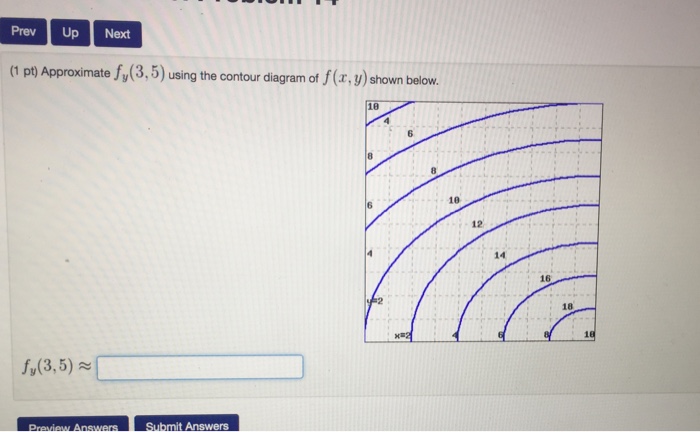
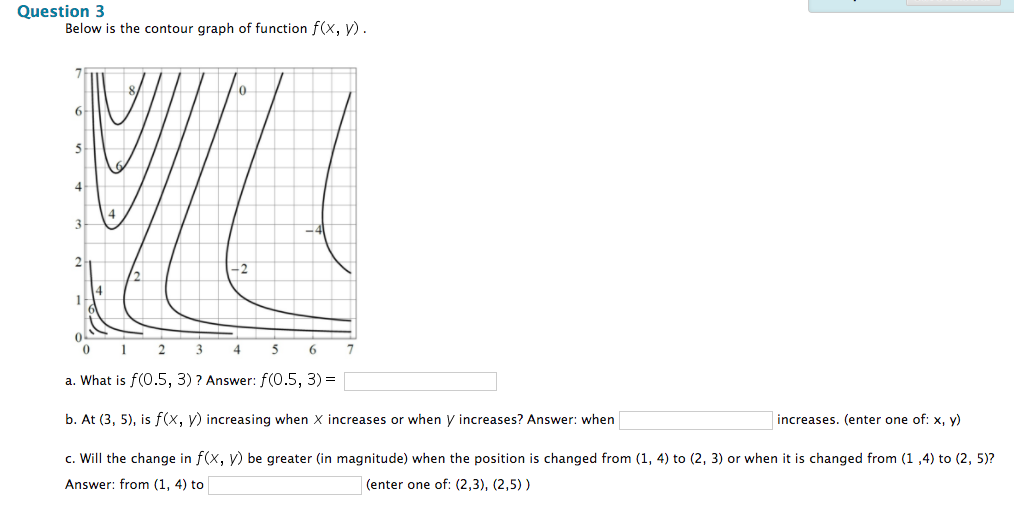
3 3. Determine the sign of f x and f y at the point using the contour diagram of f in the gure below. (a) P (b) Q (c) R (d) S 4. Approximate f x(3;5) using the contour diagram of f(x;y) shown in the gure below. Contour maps give a way to represent the function while only drawing on the two-dimensional input space. Step 1: Start with the graph of the function. Example function graph. Step 2: Slice the graph with a few evenly-spaced level planes, each of which should be parallel to the -plane. way, the graph of a function f of two variables xand yis the set of all ordered points (x;y;z) such that z= f(x;y) and (x;y) is in the domain of f:The graph is a surface in the 3-D space. Example 75.1 Sketch the graph of z= f(x;y) = p 1 x2 y2: Solution. Using a graphic tool such as a computer we nd the surface shown in Figure 75.1. If the following is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the z = 0 contour at the origin, going up by 1 for each concentric circle, approximate the rate of change of f(x,y) at (1,1) in the direction of ... If f is a differentiable function of x and y, then f has a directional derivative in the direction of any unit vector ~u = u1~i+u2~j at any ...
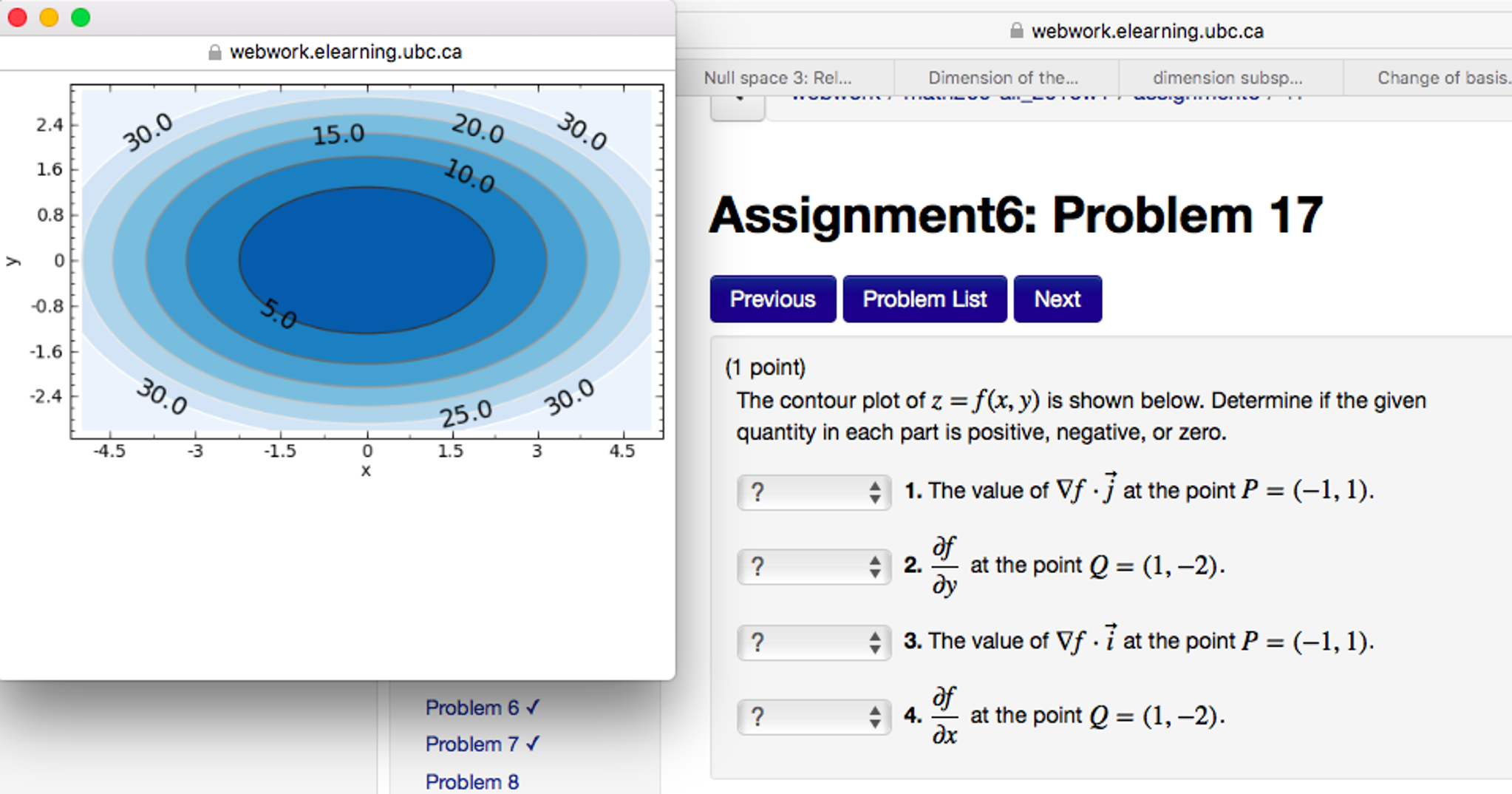
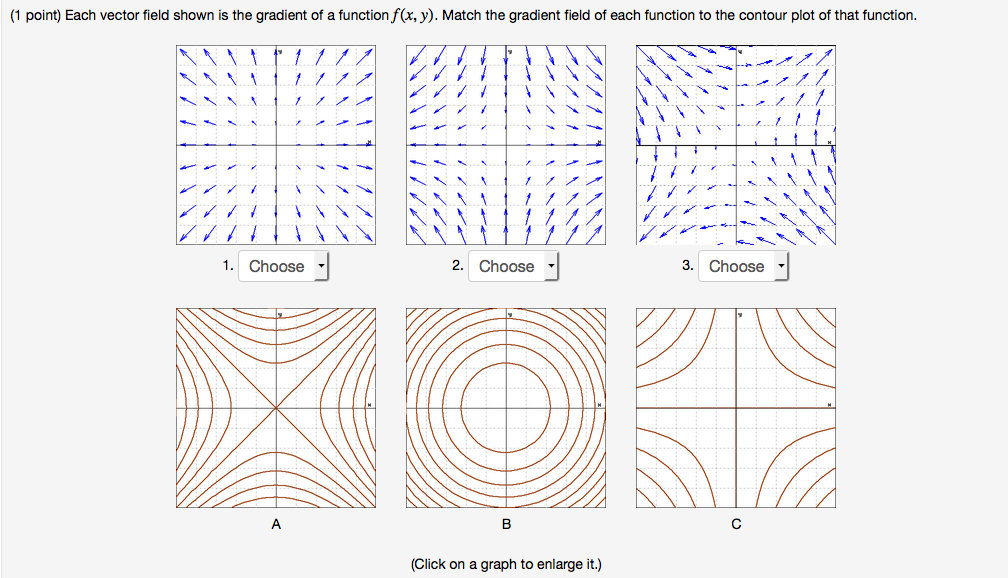
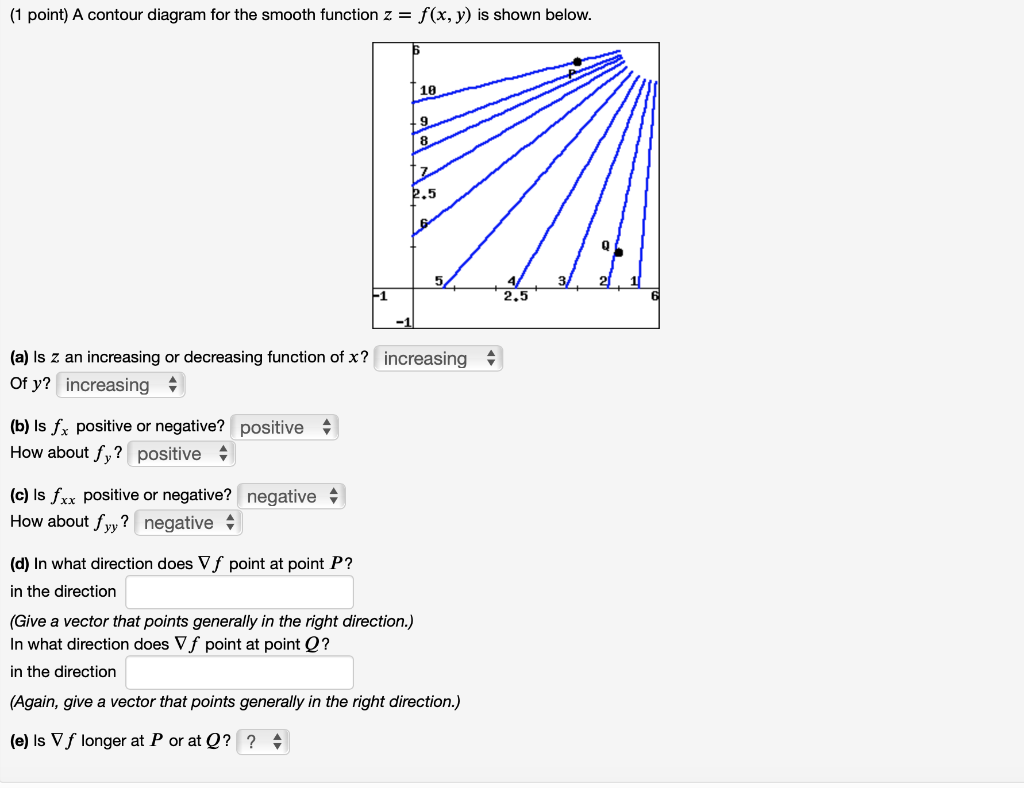
Here are their contour graphs, sketches of f(x;y) = c on the plane for di erent values of c shown. Again, the x and y axes have been scaled the same. The axes have not been marked so focus on the types of curves ... Finally, we have the planes. The rst two below are not really of the form z = f(x;y). x = 2 y = 3 f(x;y) = 1 15. A contour diagram for a function f(x;y) is shown in the gure below. (a) On the graph, sketch a reasonably accurate estimate of the gradient r~f at each of the points A, B, and C. (b) If f(0; 2) = 4 and r~f(0; 2) = 4 5 ^i+ 12 25 ^j, write an equation for the tangent plane to the surface z= f(x;y) at (0; 2). 16. A contour diagram for the smooth function z = f(x, y) is shown below. 2 2.5 7/ 2.5 918 6 F1 (a) Is z an increasing or decreasing function of æ? increasing Of y? decreasing (b) Is fr positive or negative? positive How about fy? negative v (c) Is frz positive or negative? positive How about fyy? negative (d) In what direction does Vf point at point P? in the direction (Give a vector that points ... Get the free "Contour Plot" widget for your website, blog, Wordpress, Blogger, or iGoogle. ... This widget plots contours of a two parameter function, f(x,y). Send feedback|Visit Wolfram ... and copy and paste the Widget ID below into the "id" field: To add a widget to a MediaWiki site, the wiki must have the Widgets Extension installed, as ...

Taken on a trip to Vietnam in 2015. The village of Y Ty is at the extreme north of Vietnam and is well off the normal tourist route. The road overlooks the Chinese border in many places.
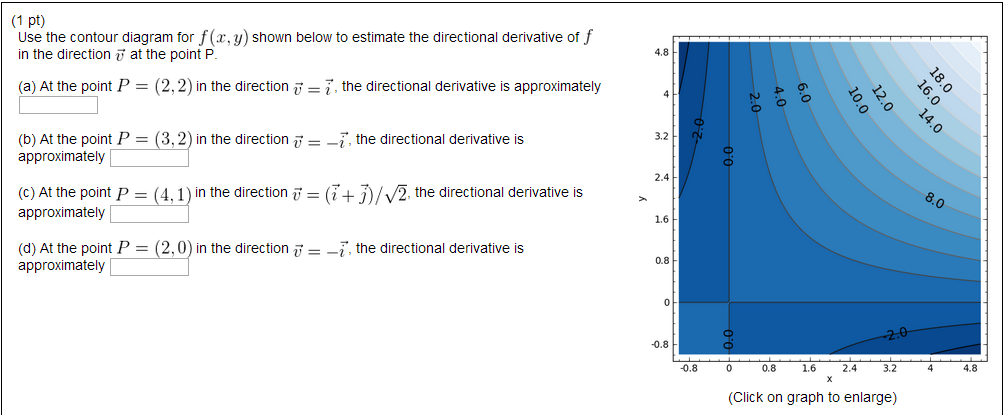
to a domain on which the function is defined. 15. f(x,y) = 3 2 x5 ... In Exercises 1-6, use the contour diagram of f in Figure 14.31 to decide if the specified directional derivative is positive, negative, or approximately zero. 1. At point (−2,2), in direction~i.
Transcribed Image Textfrom this Question. (1 point) A contour diagram for a function f (x, y) is shown below. 5 2 23 2 3 Estimate the position and approximate value of the global maximum and global minimum on the region shown. Global maximum at of Global minimum at of.
Question: A contour diagram for a function f(x, y)is shown below. Estimate the position and approximate value of the global maximum and global minimum on ...
Transcribed image text: (1 point) A contour diagram for a function f(x, y) is shown below. 23------ - - E- - -- A 297 1 3 Estimate the position and ...
Transcribed image text: A contour diagram for a function f(x, y) is shown below. Estimate the position and approximate value of the global maximum and ...
Multivariable Calculus Question 3. (2 pts) The contour diagram for a function, f(x, y) is shown below. Estimate the length of the gradient at point P. Be sure to show or explain your reasoning. 2.4 1.6 pe 0.8 0.8 1.6 2.4 24 1.60.80.8 16 24 2.4 3. (2 pts) The contour diagram for a function, f(x, y) is shown below.
Picturing f(x;y): Contour Diagrams (Level Curves) We saw earlier how to sketch surfaces in three dimensions. However, this is not always easy to do, or to interpret. A contour diagram is a second option for picturing a function of two variables. Suppose a function h(x;y) gives the height above sea level at the point (x;y) on a map.
Question: 1 point) A contour diagram for a function f(x,y) is shown below. Estimate the position and approximate value of the global maximum and global minimum ...
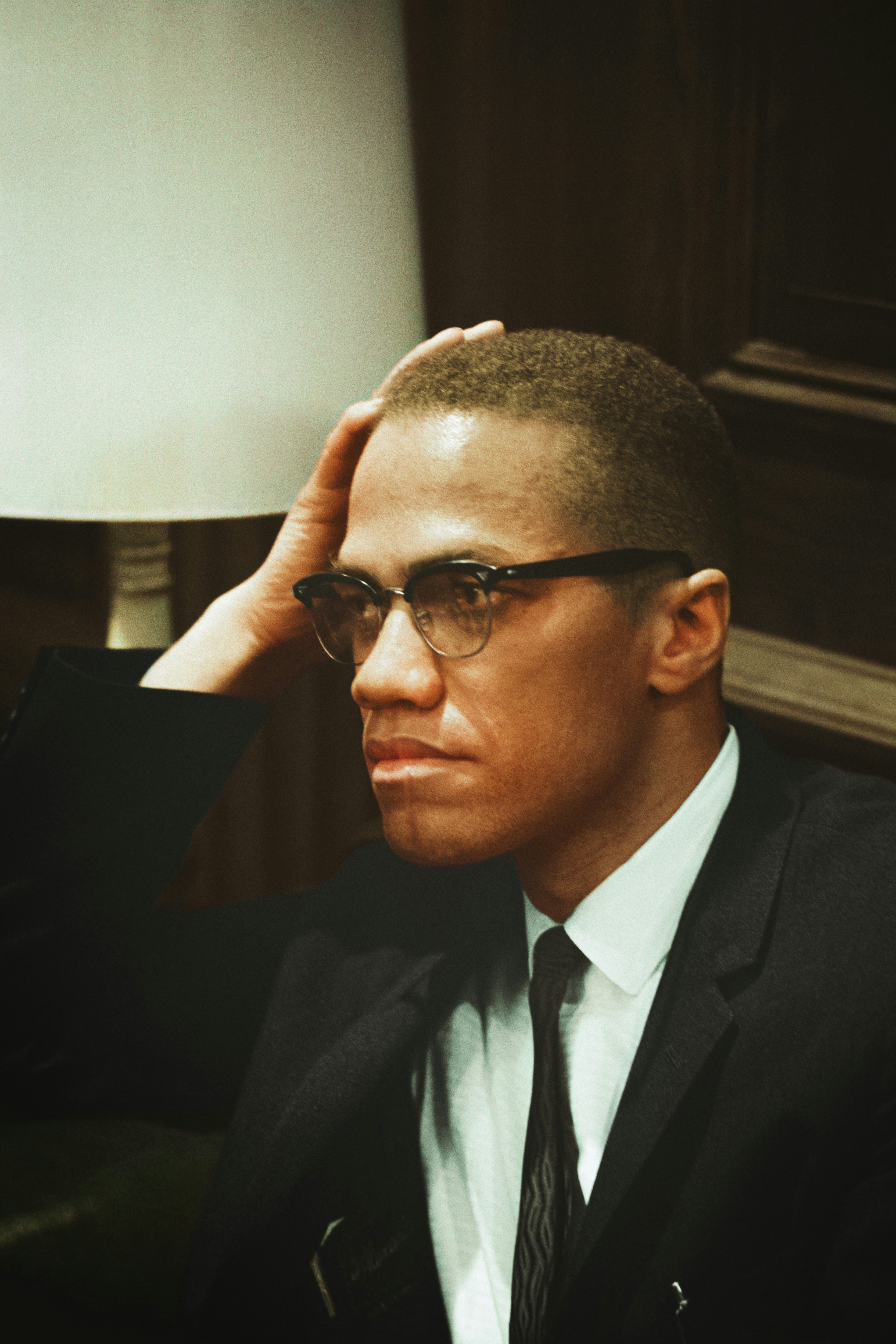

Caption reads, "[Malcolm X waits at Martin Luther King press conference, head-and-shoulders portrait] / [MST]." Original black and white negative by Marion S. Trikosko. Taken March 26th, 1964, Washington D.C, United States (@libraryofcongress). Colorized by Jordan J. Lloyd. Library of Congress Prints and Photographs Division Washington, D.C. 20540 https://www.loc.gov/item/2003688131/
Multivariable Calculus: Sketch the contour map of f(x,y) = 1/(x^2 + y^2). Label the level curves at c= 0, 1, 1/4, 4. We sketch the graph in three space to...
Question: (1 point) A contour diagram for a function f(x, y) is shown below. -21--- 22 23 24 2 28 26 27 4 30 20 2 1 Estimate the position and approximate ...
Section 1-5 : Functions of Several Variables. In this section we want to go over some of the basic ideas about functions of more than one variable. First, remember that graphs of functions of two variables, z = f (x,y) z = f ( x, y) are surfaces in three dimensional space. For example, here is the graph of z =2x2 +2y2 −4 z = 2 x 2 + 2 y 2 − 4.
Front Door - Valencia College
Description. fcontour (f) plots the contour lines of the function z = f (x,y) for constant levels of z over the default interval [-5 5] for x and y. fcontour (f,xyinterval) plots over the specified interval. To use the same interval for both x and y , specify xyinterval as a two-element vector of the form [min max].
12.Below is the contour diagram of f(x;y). x y 1 2 31 1 2 3 2 2 1 1 0 0-1-1-2-2 Sketch the contour diagram of each of the following functions. (a)3f(x;y) (b) f(x;y) 10
Get my full lesson library ad-free when you become a member. https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCNuchLZjOVafLoIRVU0O14Q/join Plus get all my audiobooks, access...
Transcribed image text: A contour diagram for the function f(x,y) is shown below. -35 40- A5- 50- 25 -55 10 15 20 -2 -25- y -3 25 -45- -4 50 ,651 15 170 -6 ...
the contours of f(x, y) = x + y are all straight lines which have a slope of -1 (the coefficient of x) and a y-intercept of c (the z value on that Thus, we get the contour diagram shown below. #2. Setting z = c for z = x y, produces the contours y = (c/x). contours are all hyperbolas, except for x = 0 or y = 0, which form the
The average rate of change of a function f(x) over the interval from a to a + h is given by f(a+h) f(a) h: ... Let P vary along the region of the x-axis shown in the gure below. How does df dx (P) ... Approximate f x (3, 5) using the contour diagram of f (x,y ) in Figure 14.9. 24 68 10 2 4 6 8 10 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 x y Figure 14.9
When we have a contour plot for a function f(x, y), it is possible to sketch a 3D graph of the surface z = f(x, y). To visualize the relationship between a contour plot for a function f(x, y) and the three-dimensional graph z = f(x, y), consider the diagram on the next page. This diagram shows the graph of y = f(x, y) for some function ...
Ask about how fx changes in the y-direction and about fy. 6. Figure 9.7 is a contour diagram for f(x,y) with the x and y axes in the usual directions. At the point P, if x increases, what is true of fx(P)? If y increases, what is true of fy(P)? (a) Have the same sign and both increase. (b) Have the same sign and both decrease.
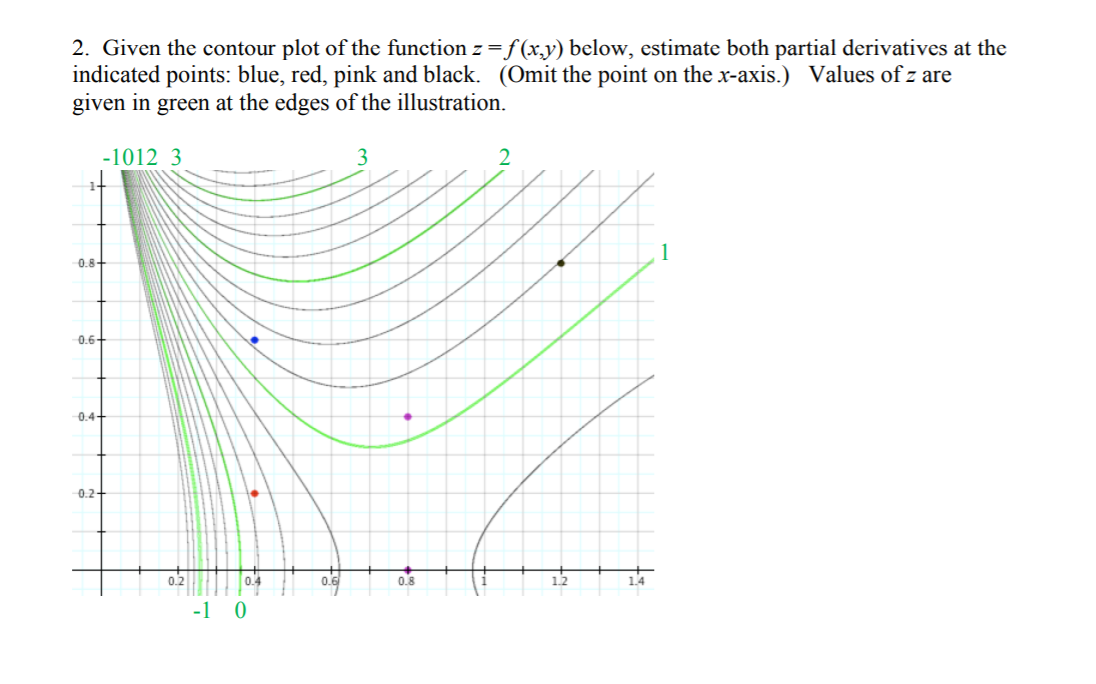
A contour map for a function fis given. Use it to estimate f x(2;1) and f y(2;1). Solution: We can estimate f x by observing that as xgoes from 1.5 to 2.5, with y= 1 xed, f seems to go from about 9 to 12. Therefore f x(2;1) is approximately 3. As ygoes from 0.5 to 1.5, with x= 2 xed, fgoes from about 11 to about 9, so f y(2;1) is roughly -2. 2. Stewart 14.3.70
In Problems 2-6, sketch a contour diagram for the function with at least four labeled contours. Describe in words the contours and how they are spaced. 2. f(x;y) = x+ y If we set f(x;y) = c, the contours will satisfy y= c x, or straight lines with slope -1. 3. f(x;y) = 3x+ 3y If we set f(x;y) = c, the contours will satisfy 3y = c 3x, or y= c 3 ...




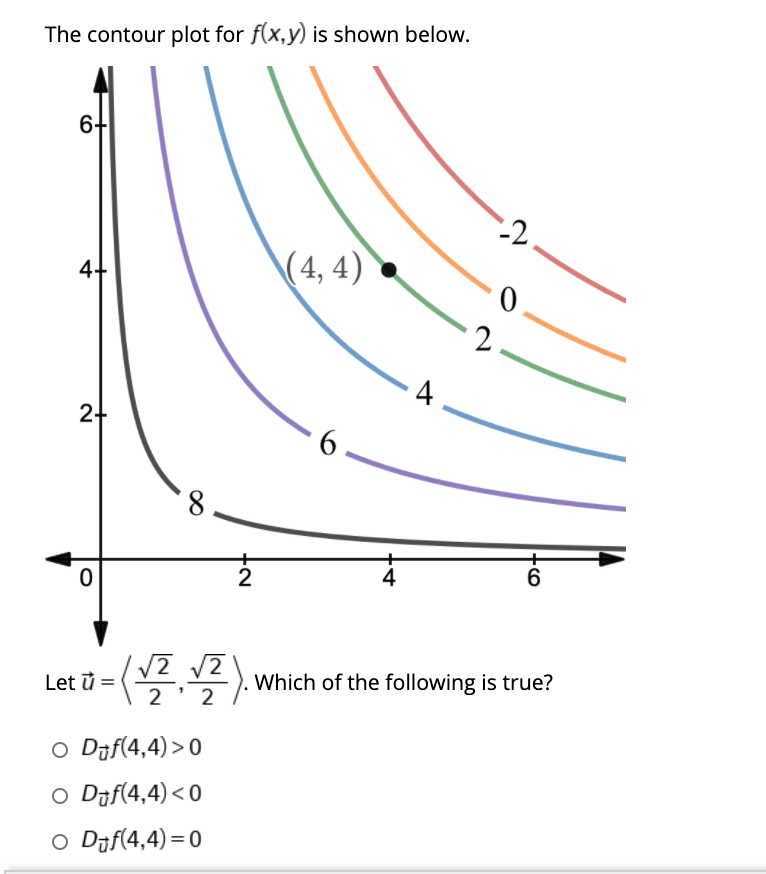
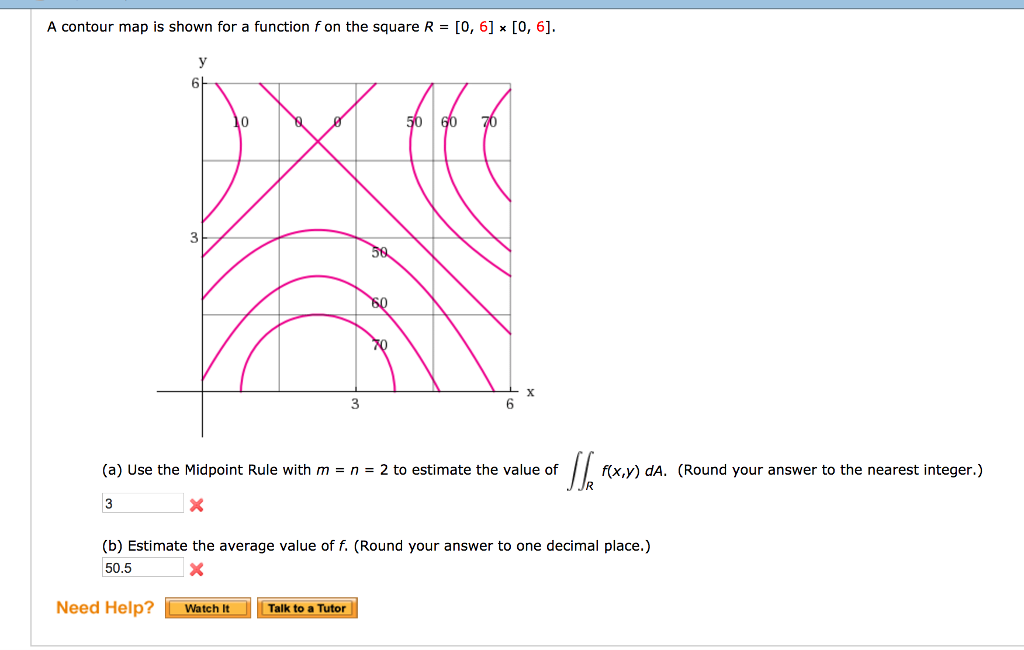


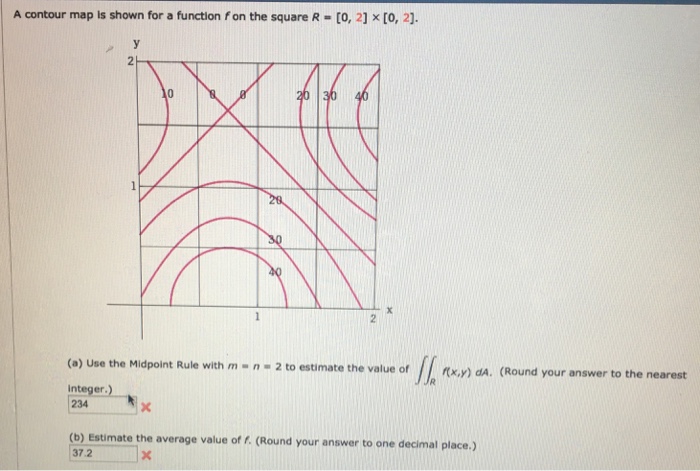




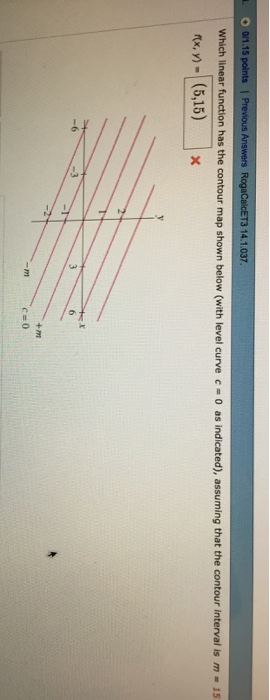


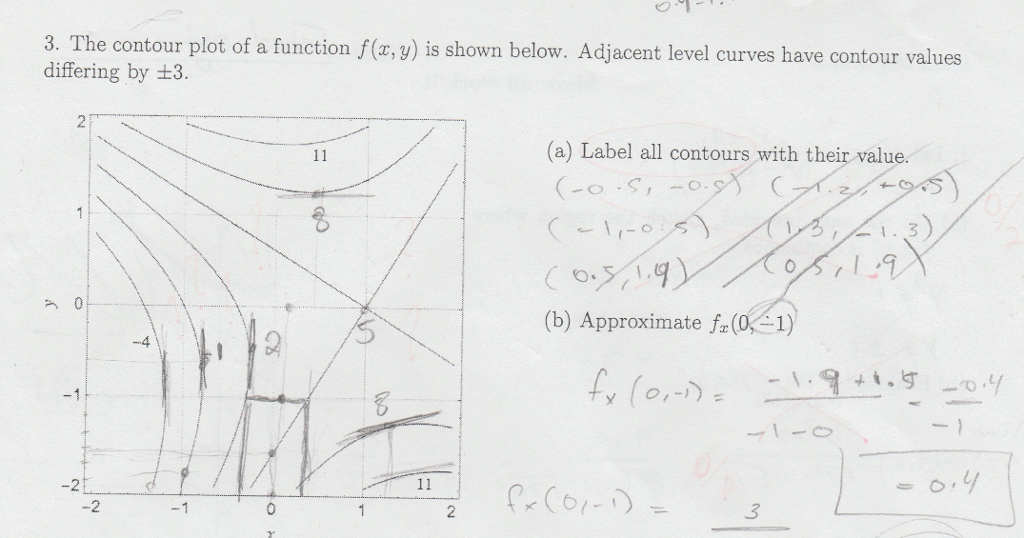
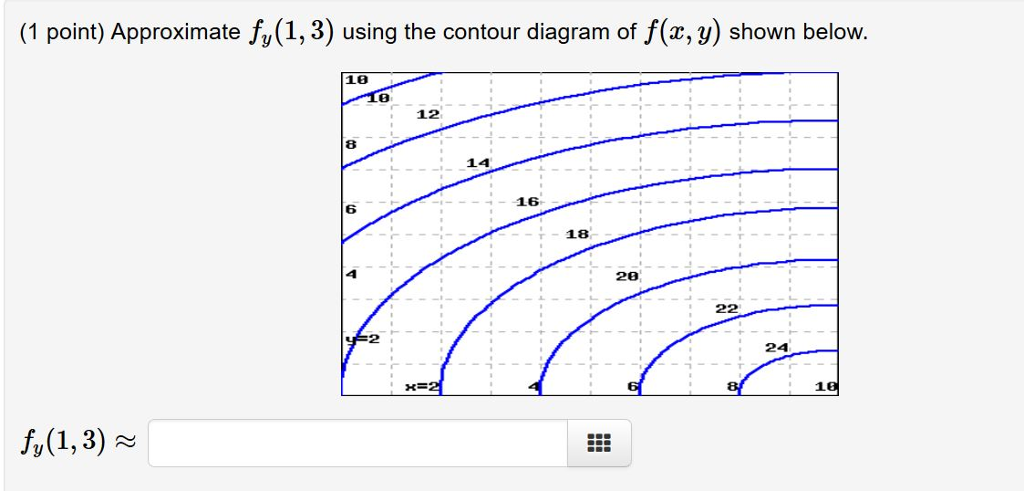
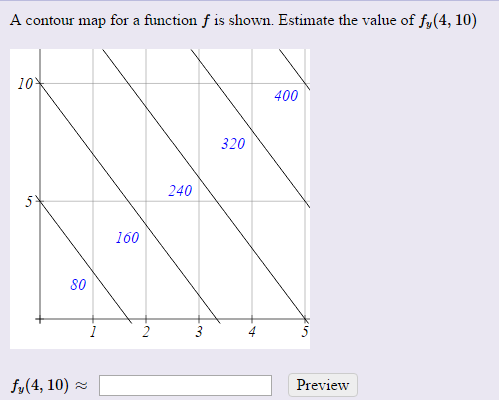

0 Response to "39 a contour diagram for a function f(x,y) is shown below."
Post a Comment