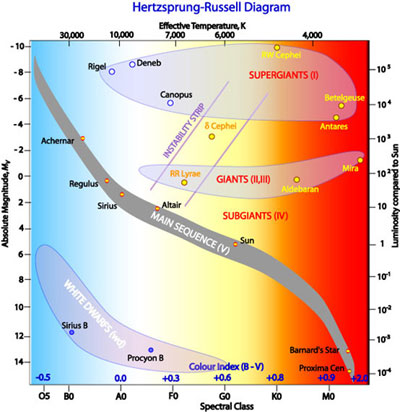
38 on an hr diagram stellar radii
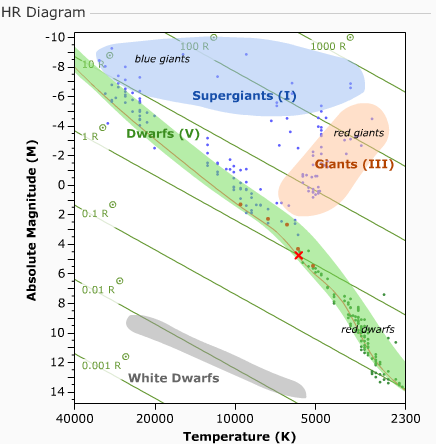
Found in the uppper right of the H-R diagram Main-sequence stars: The majority of stars in our galaxy The Sun, for example A very hot and very luminous star White dwarfs: not much larger in radius than Earth Very hot but very dim. Compared to a main-sequence star with a short lifetime, a main-sequence star with a long lifetime is _____. less luminous, cooler, smaller, and less …
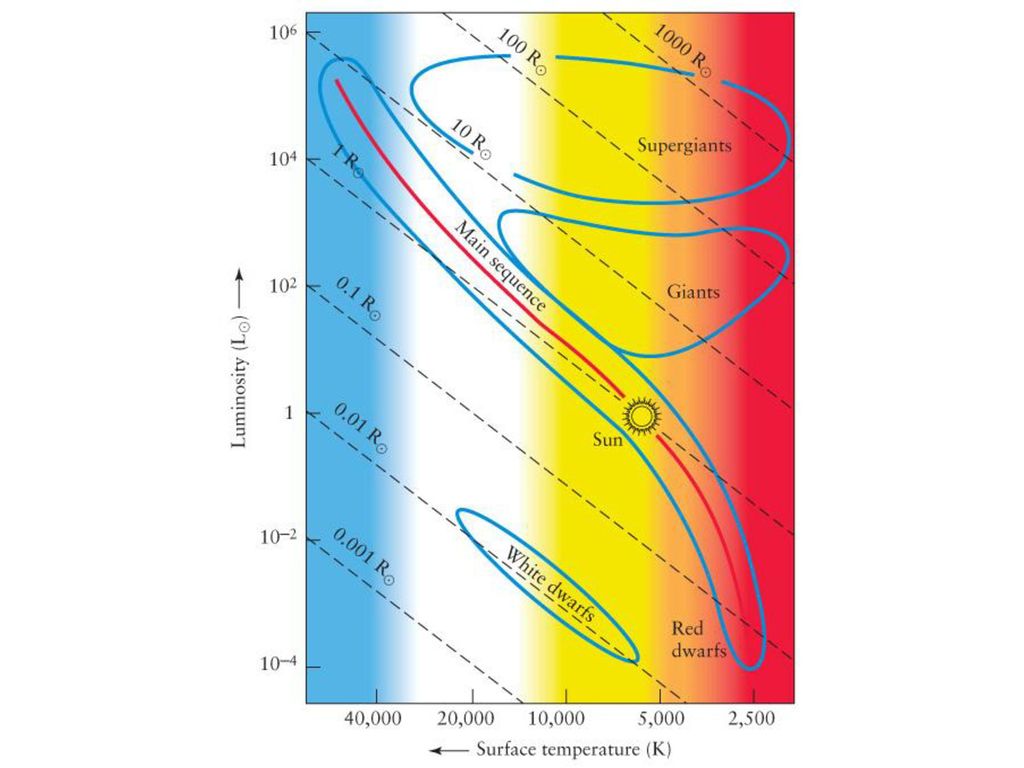
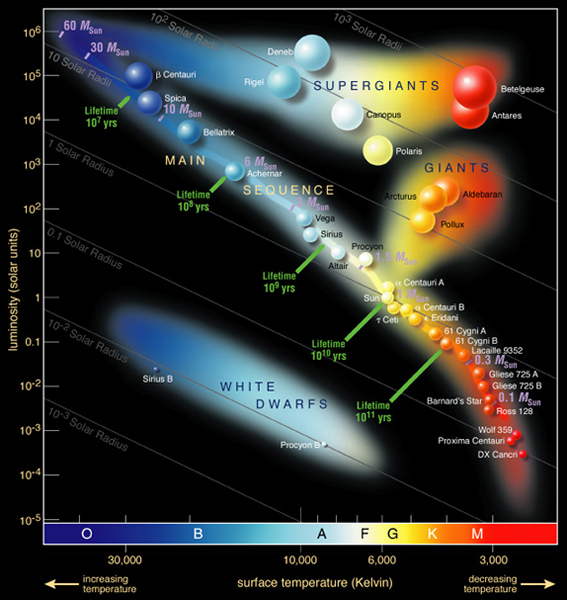
The HR Diagram Most (>90%) stars lie on the “main sequence”. A few stars are cool and extremely bright, so, by L = 4 π R2 σ T4, they must be extremely large. A few stars are hot, but extremely faint, so they must be very small.
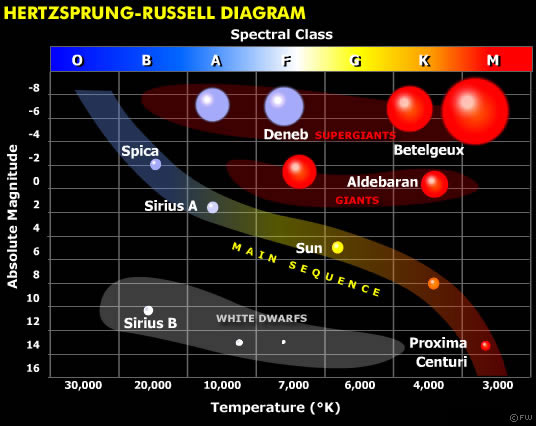
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram ( HR diagram) is one of the most important tools in the study of stellar evolution. Developed independently in the early 1900s by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, it plots the temperature of stars against their luminosity (the theoretical HR diagram), or the colour of stars (or spectral type) against their absolute magnitude (the observational HR diagram, also known as a colour-magnitude diagram).
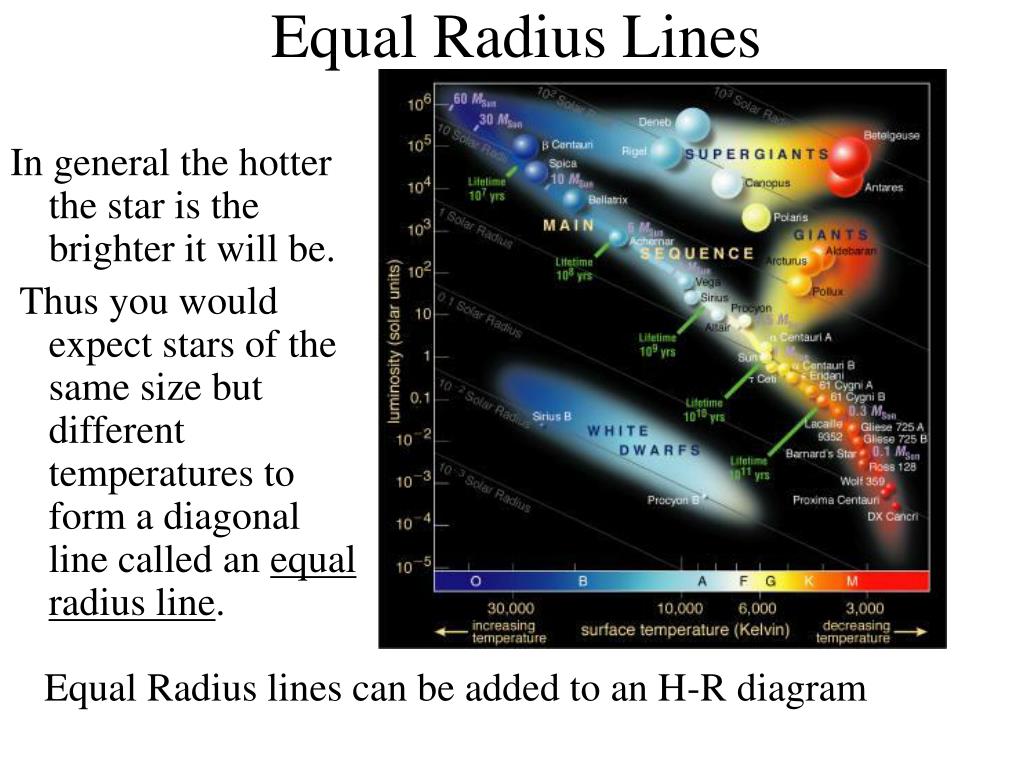
On an hr diagram stellar radii
• The Herzsprung-Russell (HR)diagram • The main sequence • Spectroscopic parallax • Extending the cosmic distance • Luminosity class • Stellar masses . Parallax is the apparent shift of an object relative to some distant background as the observer’s point of view changes It is the only direct way to measure distances to stars It makes use Earth’s orbit as baseline Parallactic ...
Based on its location on the HR diagram, what can we say about Rigel's mass and lifetime? A. We cannot give exact values, but it must be more massive than Betelgeuse because it has a higher surface temperature. B. Its mass is about 5 MSun and its lifetime is about 109 years. C. Nothing, because it is not on the main sequence. D. Its mass is about 5 MSun, but we cannot …
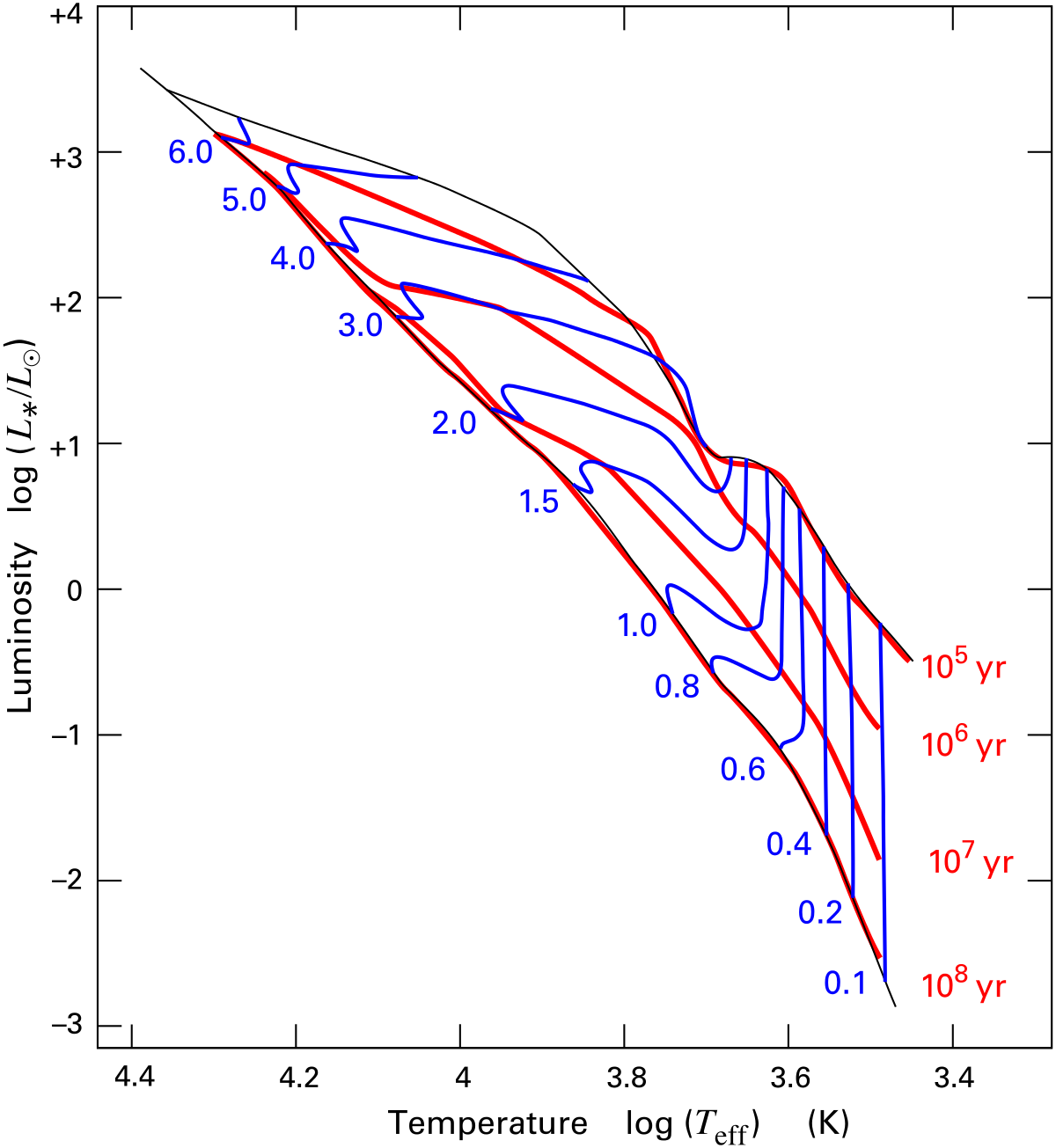
strong stellar winds variable and irregular light curves. A star in the T-Tauri phase can lose up to 50% of its mass before settling down as a main sequence star, thus we call them pre-main sequence stars. Their location on the HR diagram is shown below: The arrows indicate how the T-Tauri stars will evolve onto the main sequence. They begin ...
On an hr diagram stellar radii.
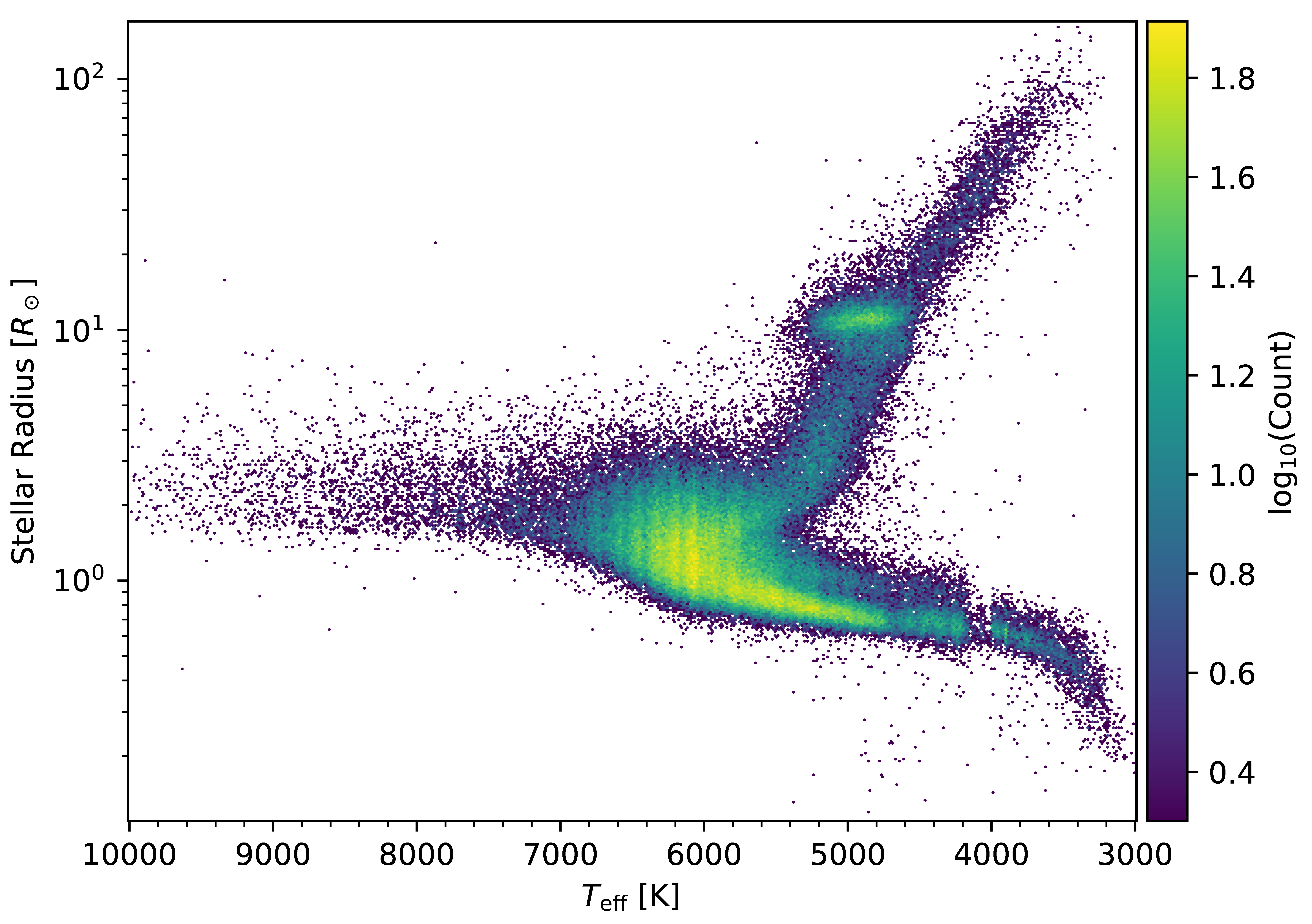
Using the H-R Diagram to Infer Stellar Properties. Let us look at the cool M-class stars as an example. If we look at the H-R diagram below we can see that in fact there are three main groups of these stars. Why do these three groups differ so much in luminosity? The answer to this question depends upon the Stefan-Boltzmann relationship. You may recall from equation 4.4 …
There are also two bands of stars in the H-R diagram that are brighter than Main Sequence stars with the same effective temperatures. The Luminosity-Radius-Temperature relation tells us that the stars in these bands must therefore be larger in radius than Main Sequence stars. There are two groups of giant stars: Giants
On an H-R diagram, stellar radii. asked Sep 23, 2016 in Physics & Space Science by Carmensita. A) are greatest in the lower left and least in the upper right. B) decrease from left to right. C) are impossible to determine. D) increase diagonally from the lower left to the upper right. introductory-astronomy.
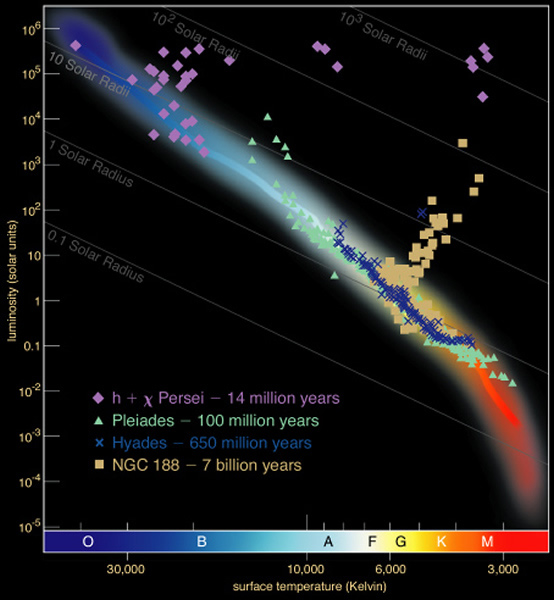
(solar radii) Luminosity (solar luminosity) Approximate main-sequence life span (years) ... The HR diagram spans a rather large range in luminosity, from 10-4 L on the low end to as much as 10 6 L on the high end. This interactive applet might help you visualize some of the properties of the HR diagram. Star size. Of the 12 brightest stars in our sky, most are giants and supergiants. …
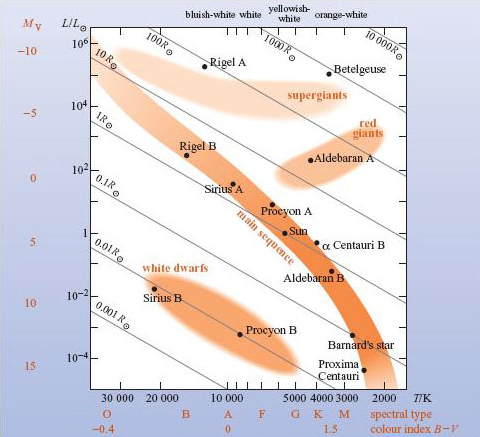
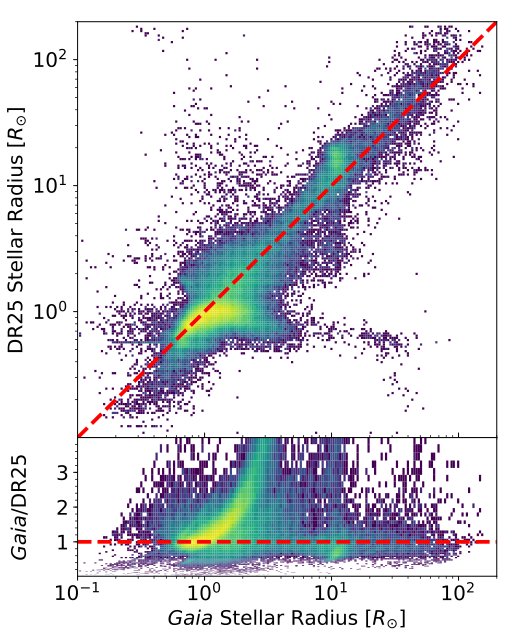
measure stellar radii in units of the Sun's radius, ... Complete the following table based on the HR Diagram on the previous page. By category, we man whether the stars are supergiants, giants, main-sequence or white dwarf stars. Table 1: Stellar Properties Star Name Category L (L⊙) T (K) R (m) R (R⊙) Betelgeuse Deneb Rigel Arcturus Pollux Spica Sirius A Sun MS 1.0 …
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines.Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength …
Supergiant stars can be identified on the basis of their spectra, with distinctive lines sensitive to high luminosity and low surface gravity. In 1897, Antonia C. Maury had divided stars based on the widths of their spectral lines, with her class "c" identifying stars with the narrowest lines. Although it was not known at the time, these were the most luminous stars.













![Mean stellar radii for [F e/H] ≥− 0.5 (squares). The small symbols ...](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Angel-Alonso-14/publication/234226885/figure/fig2/AS:738807288700931@1553156792302/Mean-stellar-radii-for-F-e-H-05-squares-The-small-symbols-correspond-to-the_Q640.jpg)


0 Response to "38 on an hr diagram stellar radii"
Post a Comment