38 atomic force microscope diagram
§D. Sarid, Scanning Force Microscopy with Applications to Electric, Magnetic and Atomic Forces , Revised Edition, Oxford University Press, 1994. § U. Dürig, “Interaction sensing in dynamic force microscopy”, New Journal of
Atomic-force microscopy is a reference method for traceable and correlative measurements of nanostructures. The Nanostructure Fabrication and Measurement Group is developing critical-dimension and traceable microscope systems to calibrate probe tips and microscopy standards, and measure diverse devices ranging from waveguides to nanoparticles.
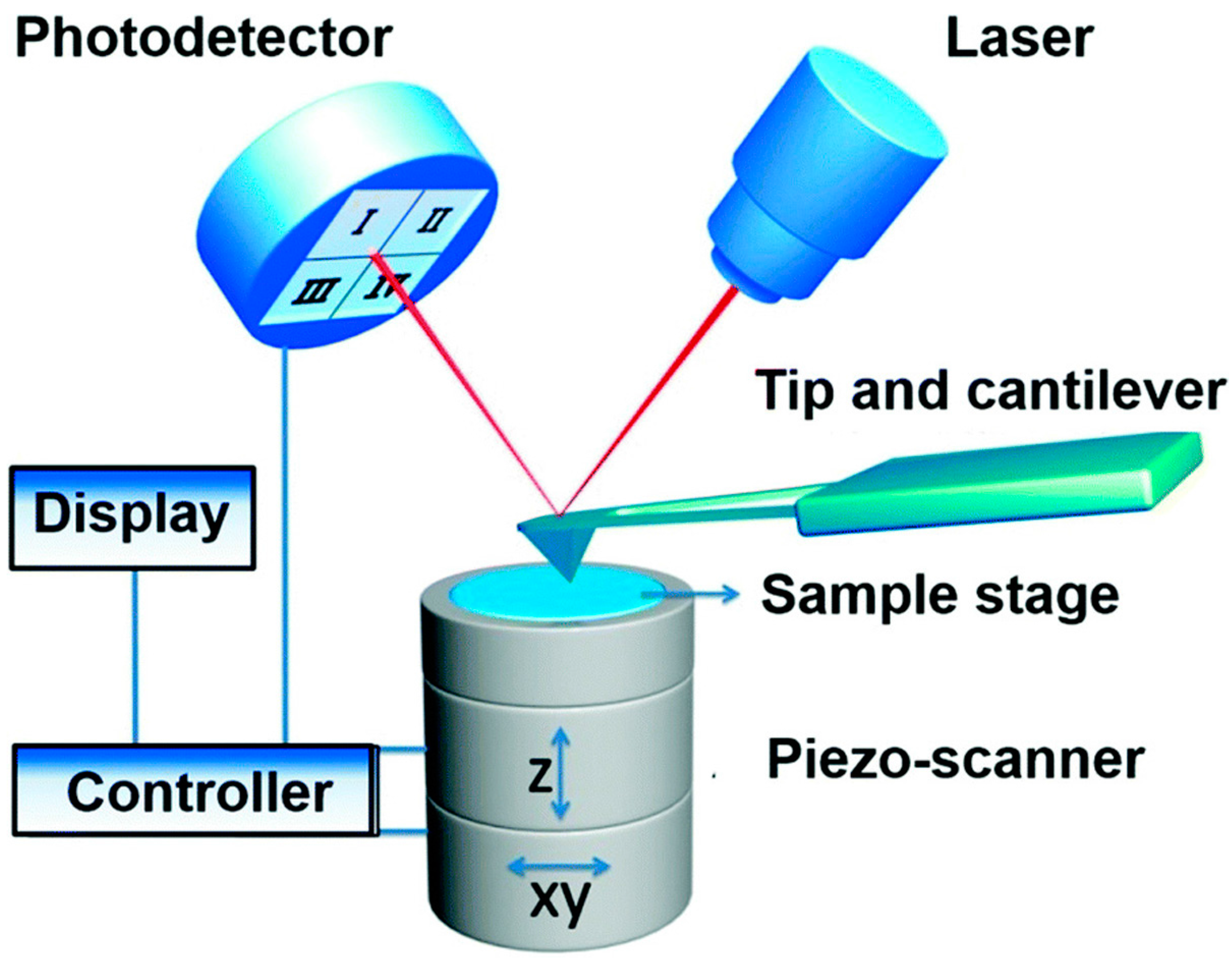
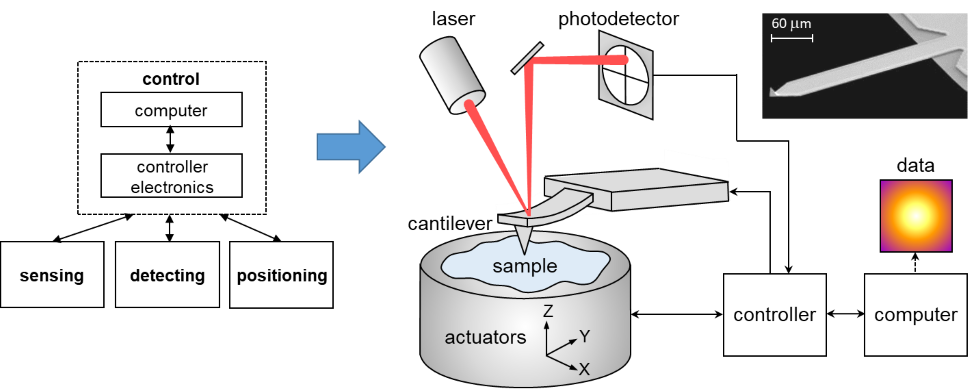
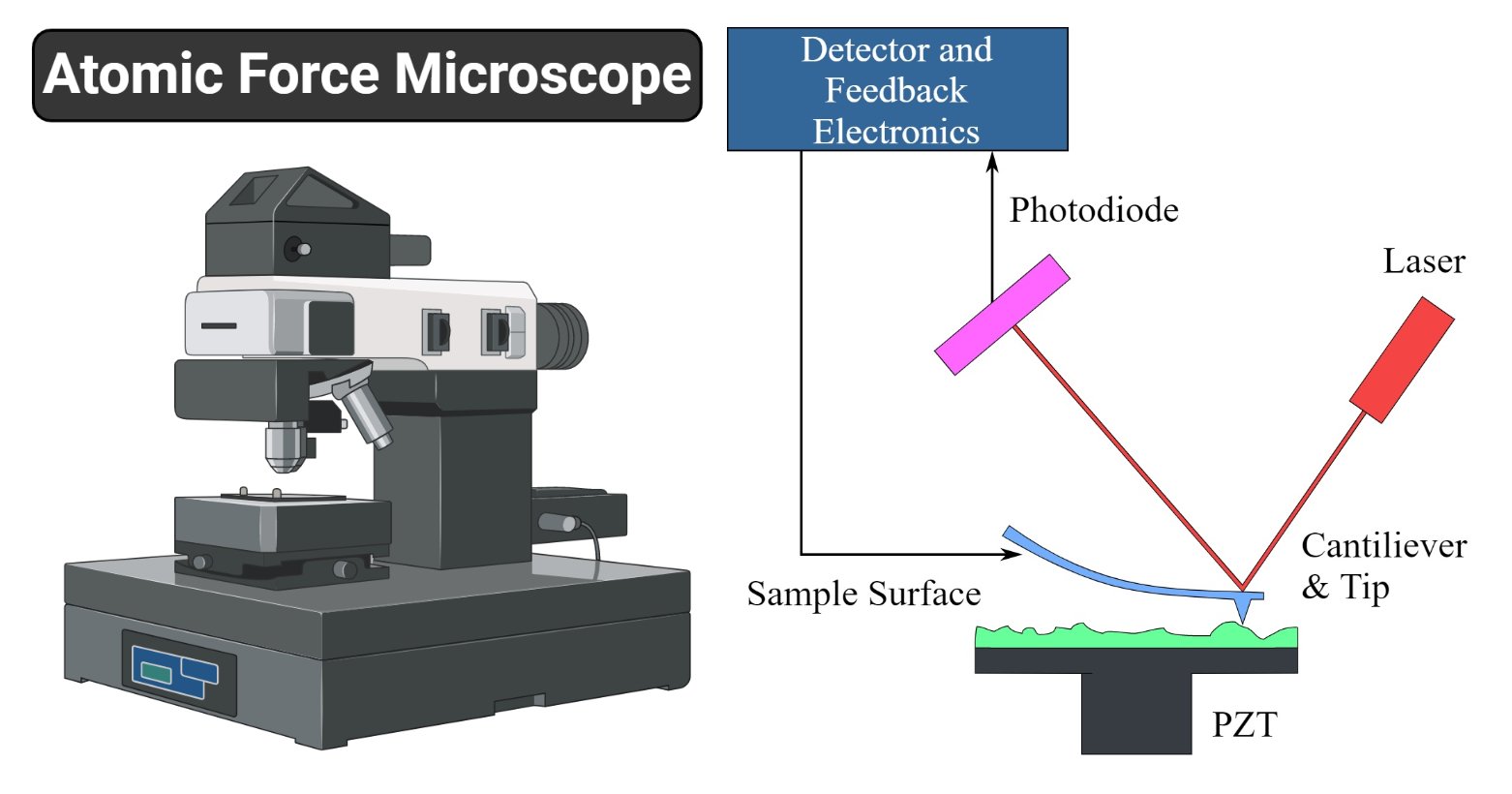
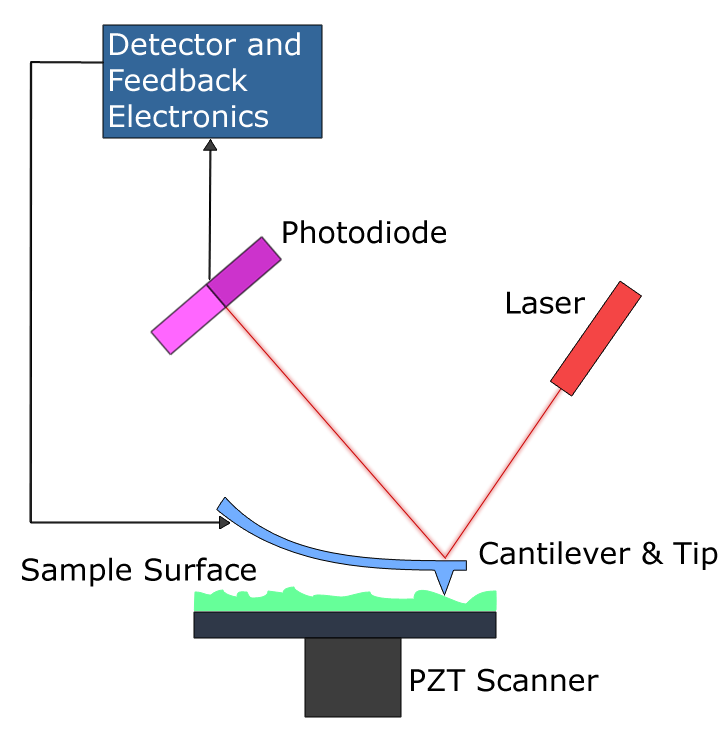
An AFM images the topography of a sample surface by scanning the cantilever over a region of interest. The raised and lowered features on the sample surface ...
Atomic force microscope diagram
21 Mar 2021 — 2 Schematic diagram of probe and surface interaction in contact mode. Tapping Mode. In the tapping mode the cantilever is externally oscillated ...Microscope mode: tappingContact Mode: The contact mode method utiliz...Z-limit max height: 5.064 µm. This can be redu...Noncontact Mode: For noncontact mode the ca...
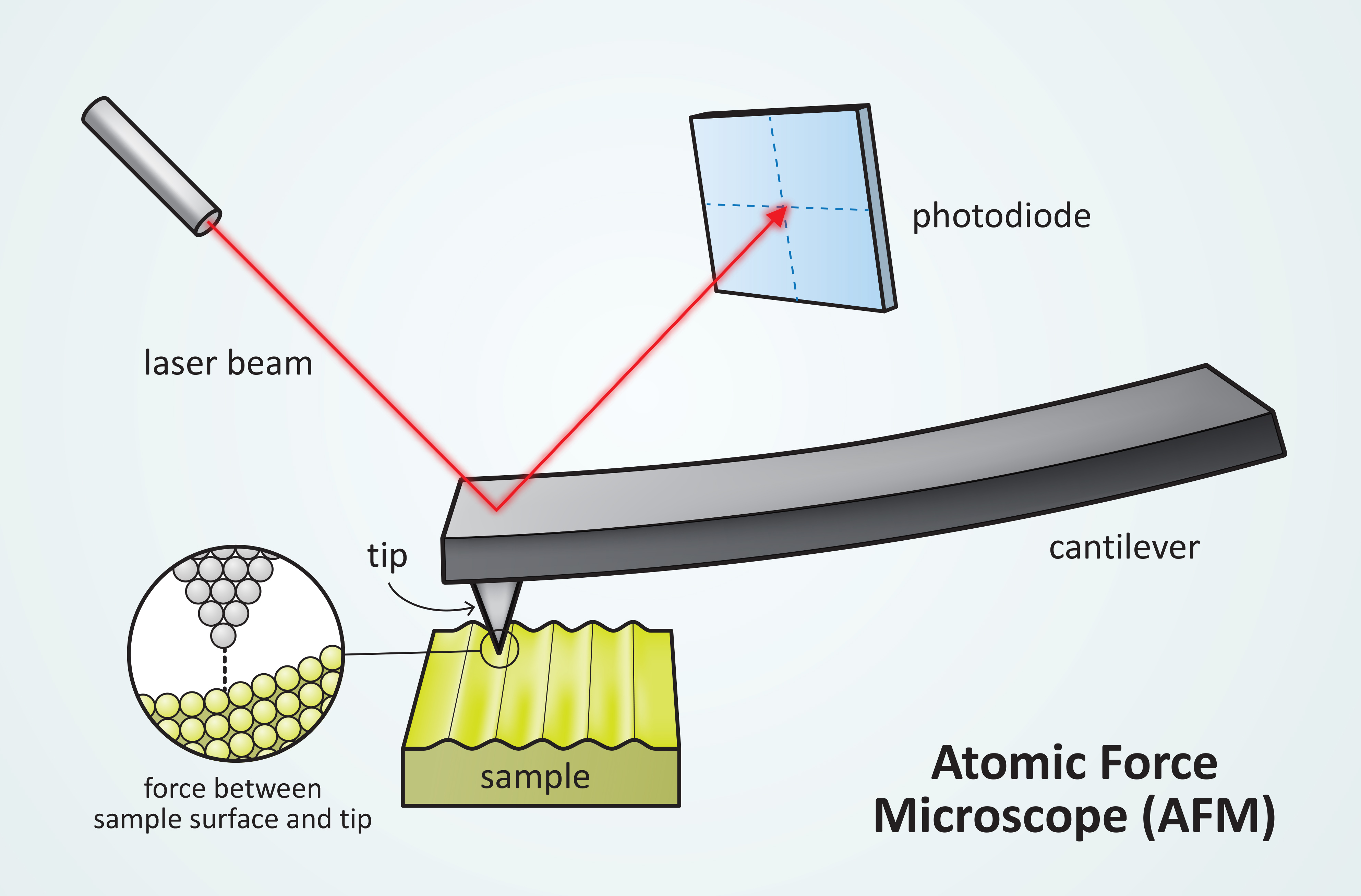
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a powerful technique that enables the imaging of almost any type of surface, including polymers, ceramics, composites, glass and biological samples. AFM is used to measure and localize many different forces, including adhesion strength, magnetic forces and mechanical properties.
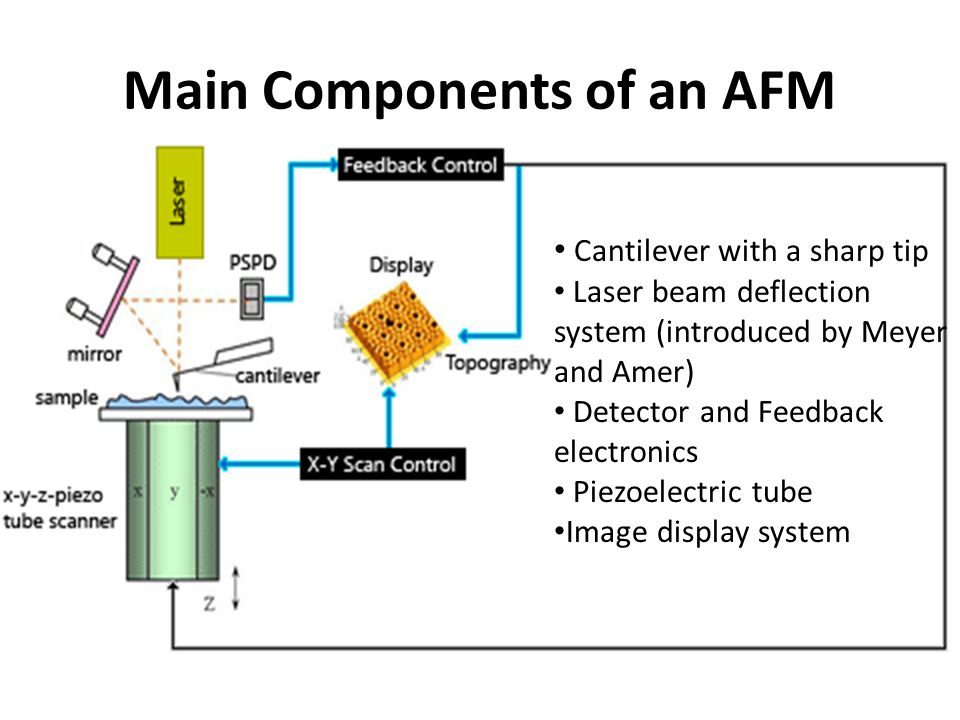
The motion of the probe is monitored and used to create an image of the surface. Figure 1.2. Basic block diagram of an AFM. Force. Sensor. Z motion gener ator.139 pages
Atomic force microscope diagram.
Atomic force microscopy (AFM), a branch of SPM, is a versatile tool of nanotechnology to image both conductive and non-conductive matters with high resolution.
13.2.4.4 Atomic force microscope. AFM is a kind of scanning probe microscope which is used to calculate properties such as the height, magnetic force, surface potential, and friction, and also has the ability to measure intermolecular forces.
Atomic Force Microscopy has a feedback loop using the laser deflection to control the force and tip position. As shown, a laser is reflected from the back of a ...
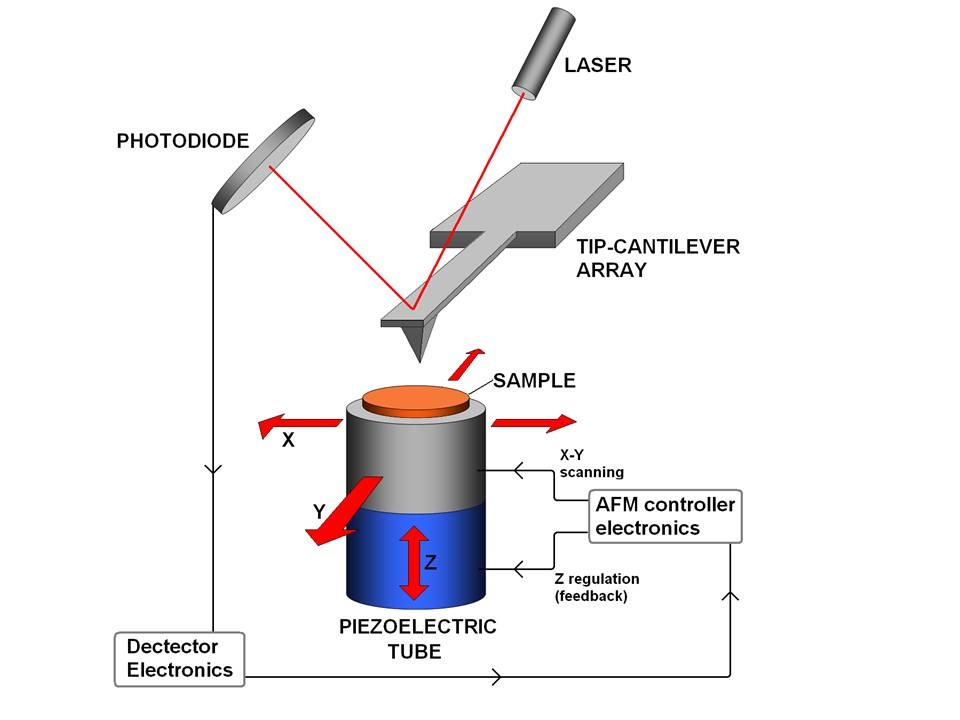
AFM, which uses a sharp tip to probe the surface features by raster scanning, can image the surface topography with extremely high magnifications, up to 1,000,000X, comparable or even better than electronic microscopes. The measurement of an AFM is made in three dimensions, the horizontal X-Y plane and the vertical Z dimension.
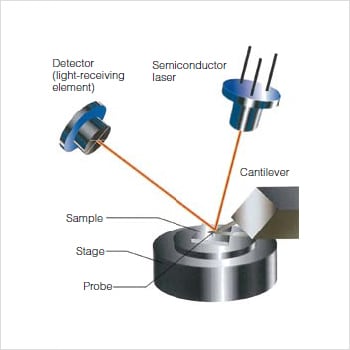
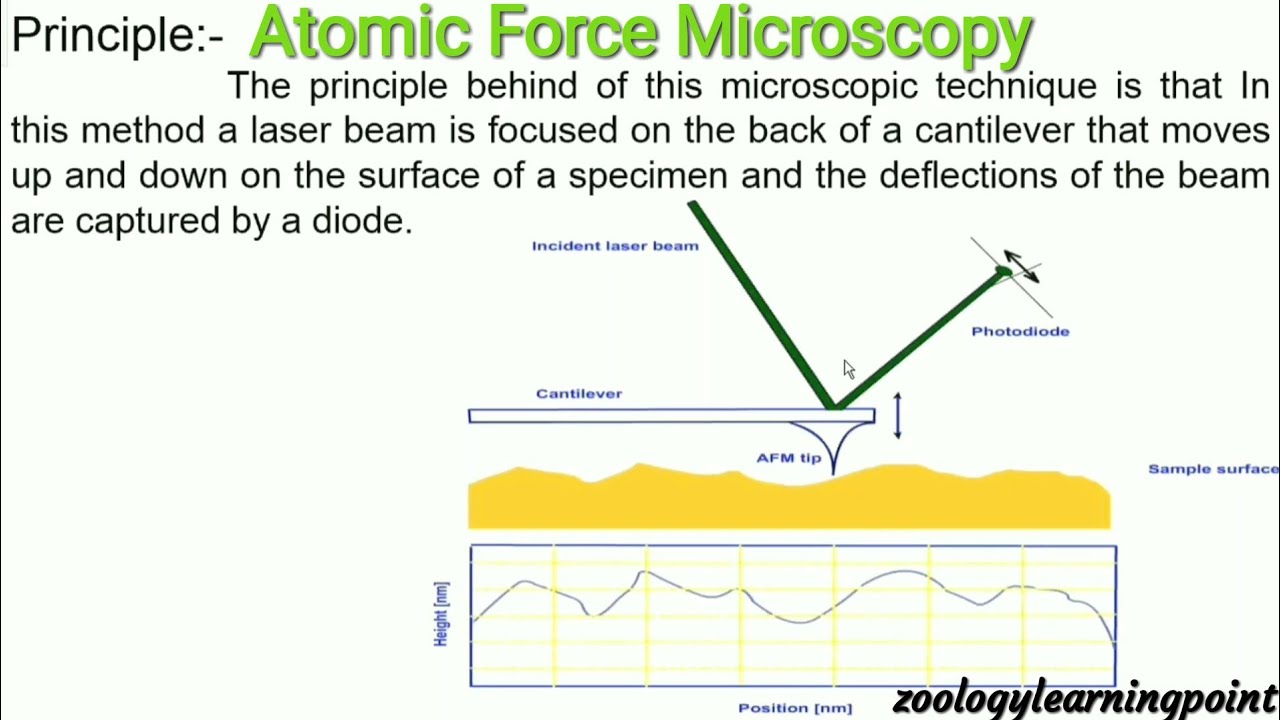
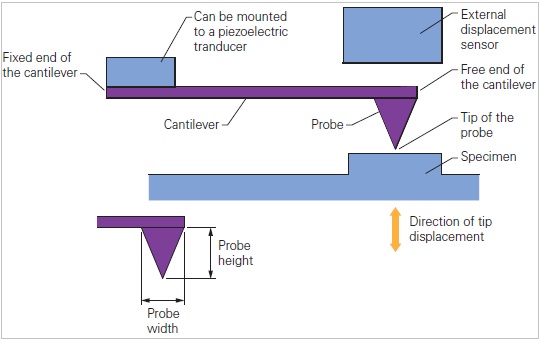
In this article we will discuss about the design of atomic force microscope, explained with the help of a diagram. An atomic force microscope instead of using a lens is provided with a probe to examine the surface of a specimen with a sharp tip which may be several micrometers in and less than 10 nm in diameter at the point near field to be examined. The tip lies at the end of the lever which ...
AFM schematic. Modes of AFM Operation. There are two basic modes of imaging surface topography with an Atomic Force Microscope: Static or Contact Mode and ...
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) is a type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the optical diffraction limit. The information is gathered by "feeling" or "touching" the surface with a mechanical probe.
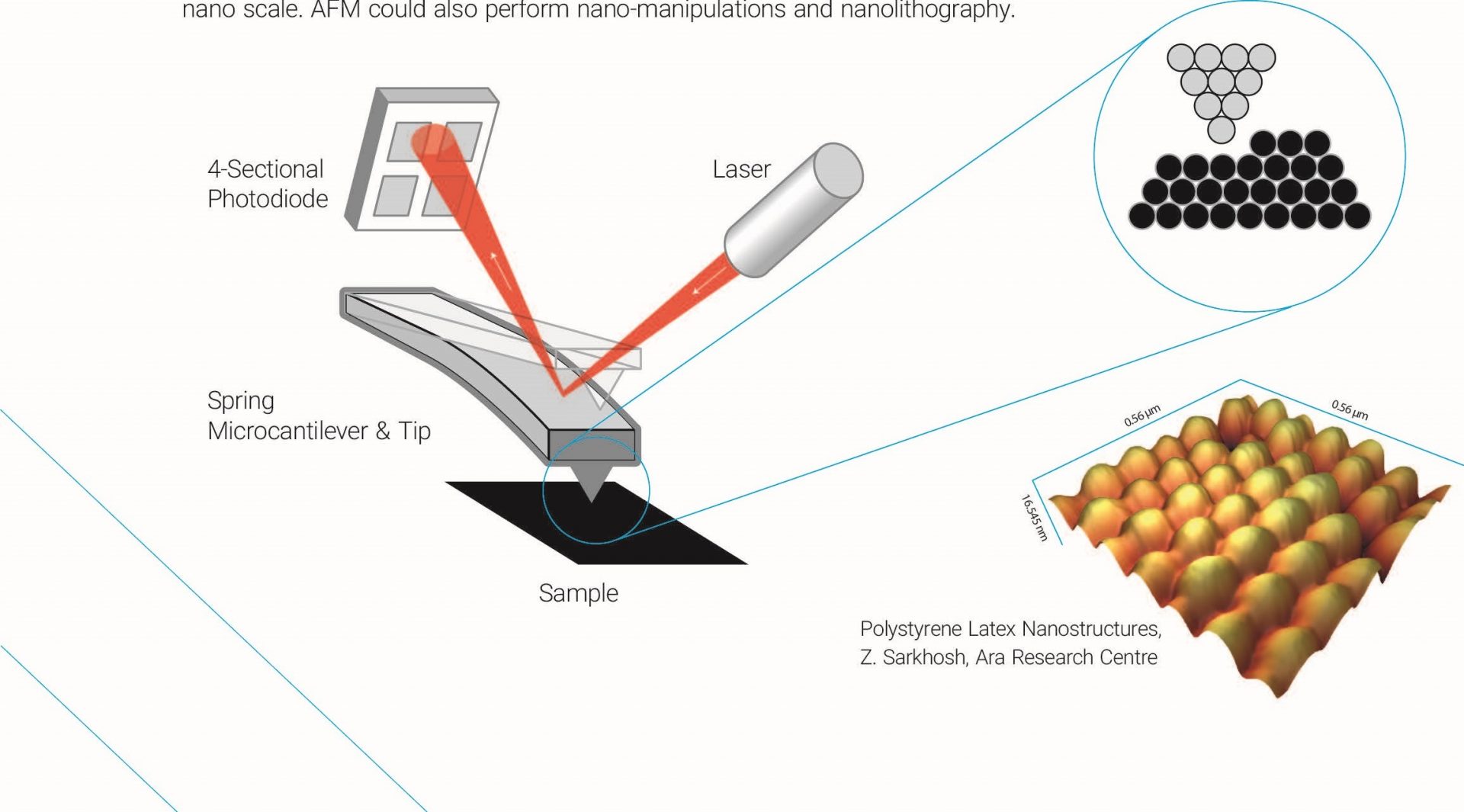
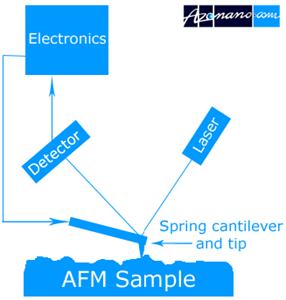
The AFM principle is based on the cantilever/tip assembly that interacts with the sample; this assembly is also commonly referred to as the probe.
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) 1. General Principle The Atomic Force Microscope is a kind of scanning probe microscope in which a topographical image of the sample surface can be achieved based on the interactions between a tip and a sample surface. The atomic force microscope was invented by Gerd Binning et al. in 1986 at IBM Zurich based on ...
Download scientific diagram | Schematic drawing of the atomic force microscope. from publication: Direct Measurement of Interaction Forces between Surfaces in Liquids Using Atomic Force Microscopy ...
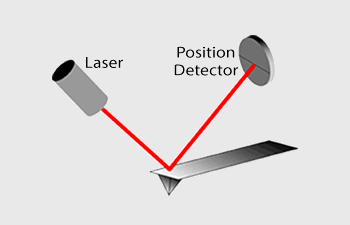
The Atomic Force Microscope (AFM) takes the image of the surface topography of the sample by force by scanning the cantilever over a section of interest. Depending on how raised or how low the surface of the sample is, it determines the deflection of the beam, which is monitored by the Positive-sensitive photo-diode (PSDP).






















0 Response to "38 atomic force microscope diagram"
Post a Comment