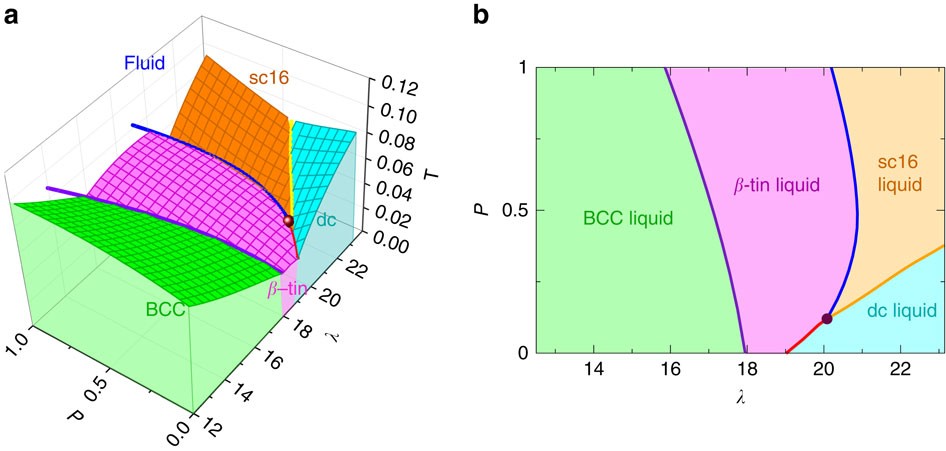
37 examine the following phase diagram and determine what phase(s) exists at point a.
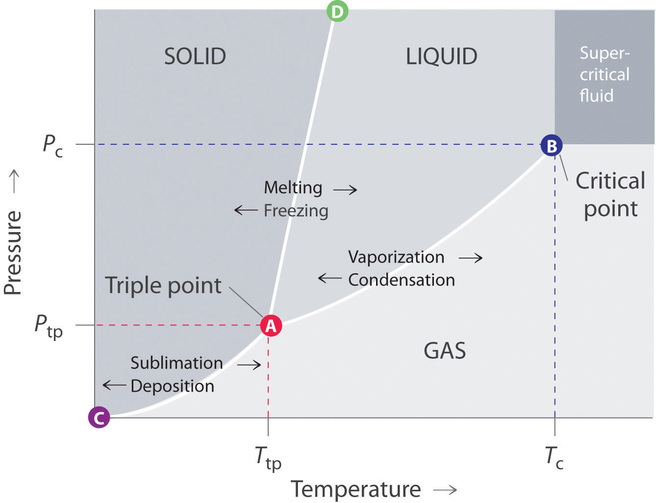
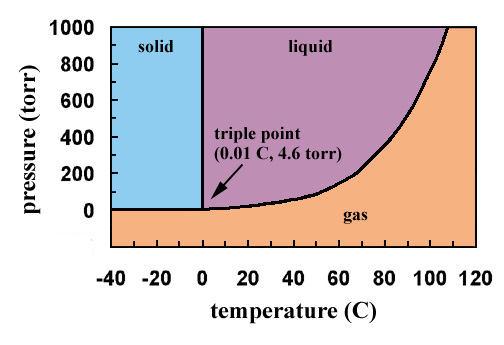
Example: Phase Equilibria For a 99.6 wt% Fe-0.40 wt% C at a temperature just below the eutectoid, determine the following a) composition of Fe 3 C and ferrite (a) b) the amount of carbide (cementite) in grams that forms per 100 g of steel c) the amount of pearlite and proeutectoid ferrite (a) 32 Part G: One of the most important points on a phase diagram is the triple point, where gas, liquid, and solid phases all can exist at once. What are the coordinates ( , ) of the triple point of ammonia in the diagram? Express your answer as an ordered pair. Determine the temperature to the nearest 5 and the pressure to one significant digit.
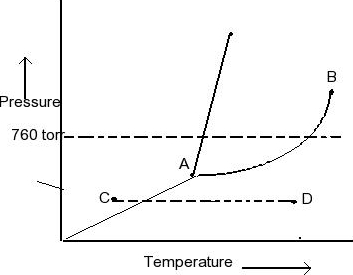
Question: Examine the following phase diagram and determine what phase exists at point 760 som Temperature A) supercritical fluid B) liquid C) vapor+liquid D) vapor E) solid The phase diagram of a substance i s given below. This substance is a at 25°C and 1.0 atm. 1.5 P (atm) 1.0 0.5T -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 T ('C) A) gas B) crystal C ...
Examine the following phase diagram and determine what phase(s) exists at point a.
PHASE DIAGRAMS • Also called equilibrium or constitutional diagrams • Plots of temperature vs. pressure, or T or P vs. composition, showing relative quantities of phases at equilibrium • Pressure influences phase structure -Remains virtually constant in most applications -Most solid-state phase diagrams are at 1 atm • Note ... Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ... Examine the phase diagram for the substance Bogusium (Bo) and select the correct statement. SEE QUESTION 10 Image A) Bo(s) has a lower density than Bo(l). B) The triple point for Bo is at a higher temperature than the melting point for Bo. C) Bo changes from a solid to a liquid as one follows the line from C to D.
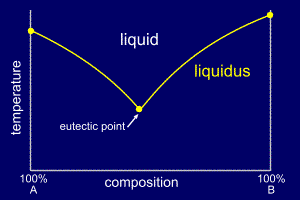
Examine the following phase diagram and determine what phase(s) exists at point a.. Phase Diagrams. The figure below shows an example of a phase diagram, which summarizes the effect of temperature and pressure on a substance in a closed container. Every point in this diagram represents a possible combination of temperature and pressure for the system. The diagram is divided into three areas, which represent the solid, liquid ... (a) That portion of the Cu-Zn phase diagram (Figure 9.19) that pertains to this problem is shown below; the point labeled "A" represents the 90 wt% Zn-10 wt% Cu composition at 400°C. As may be noted, point A lies within the ε and η phase field. A tie line has been constructed at 400°C; its as axes are called phase diagrams. DEF. A phase diagram (or equilibrium diagram) is a diagram with T and composition as axes, showing the equilibrium constitution. The phase diagram of an alloy made of components A and B, for all combinations of T and X B, defines the A-B system. Binary systems have two components, ternary systems three, and so on. 15.A student obtained the following data while cooling a substance. The substance was originally in the liquid phase at a temperature below its boiling point. What is the freezing point of the substance? Base your answers to questions 16 and 17 on the graph below, which represents uniform cooling of a sample of a pure substance, starting as a gas.
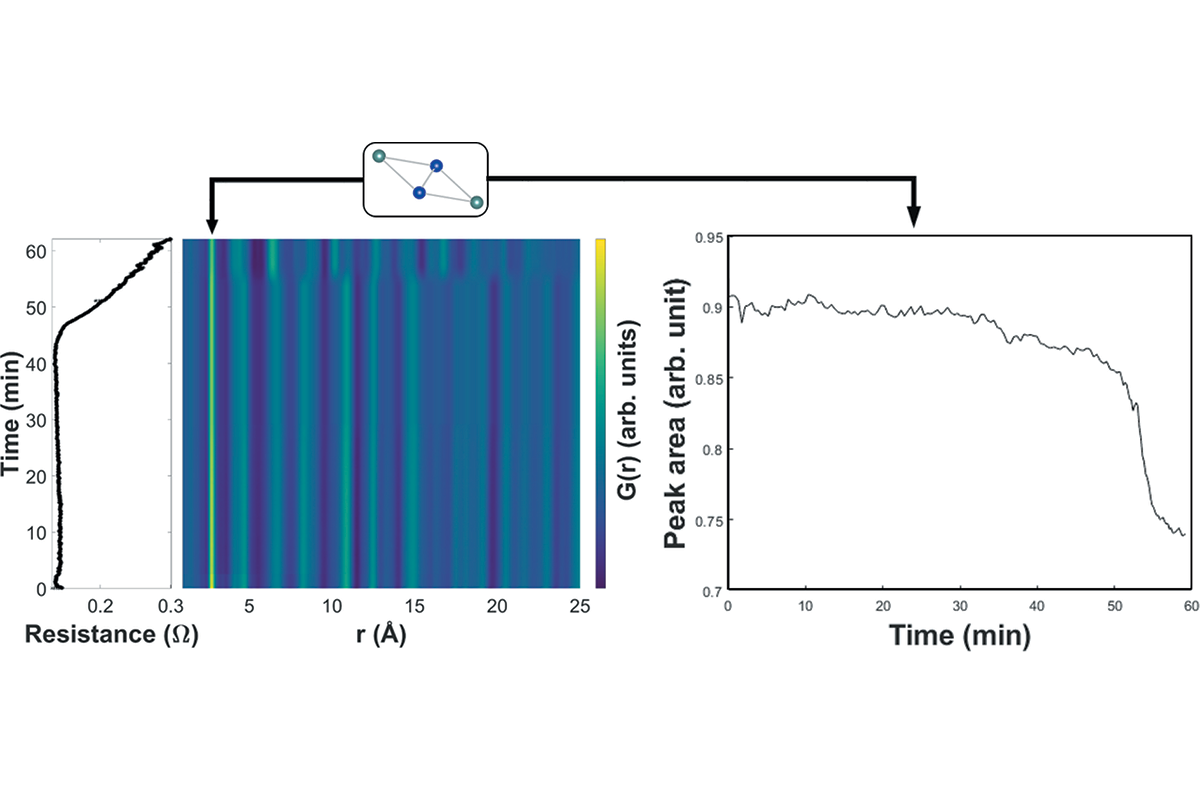
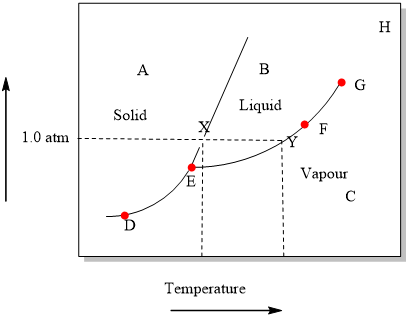
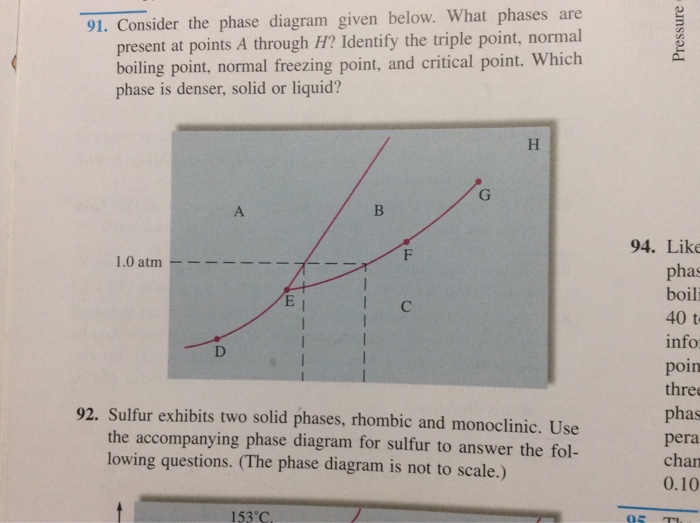
Examine the following phase diagram and identify the feature represented by point A. A. melting point B. critical point C. triple point D. sublimation point E. boiling point 2. Examine the following phase diagram and determine what phase exists at point F. A. vapor + liquid B. vapor C. liquid D. solid E. supercritical fluid in the equilibrium phase diagram of the iron-carbon system because it is a metastable phase, the kinetic product of rapid cooling of steel containing sufficient carbon. • Bainite: first described by E. S. Davenport and Edgar Bain, is a phase that exists in steel microstructures after certain heat treatments. Bainite is one of the decomposition Examine the following phase diagram and determine what phase exists at point F Vapor When the electron cloud of a molecule is easily distorted, the molecule has a high _____________. On any such of diagram, each point represents a state of the material. Once the point has been located, all other thermodynamic properties can be read off. For a single phase, the required point can fall anywhere on the region of the plane representing this phase. Thus, two coordinates are needed to specify a point within that part of the plane.
3. The degree of freedom at triple point in unary diagram for water _____. (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 2 (d) 3 4. Above the following line, liquid phase exist for all compositions in a phase diagram. (a) Tie-line (b) Solvus (c) Solidus (d) Liquidus 5. Following is wrong about a phase diagram. (a) It gives information on transformation rates. Use phase diagrams to identify stable phases at given temperatures and pressures, and to describe phase transitions resulting from changes in these properties. In the previous module, the variation of a liquid's equilibrium vapor pressure with temperature was described. Considering the definition of boiling point, plots of vapor pressure ... 3-Dimensional Depiction of Temperature-Composition Phase Diagram of Bismuth, Tin, and Lead at 1atm. The diagram has been simplified by omission of the regions of solid solubility. Each face of the triangular a eutectic. There is also a peritectic point in the Bi-Pb phase diagram. Figure by MIT OCW. 1. Roughly sketch the phase diagram, using units of atmosphere and Kelvin. Answer. 1-solid, 2-liquid, 3-gas, 4-supercritical fluid, point O-triple point, C-critical point -78.5 °C (The phase of dry ice changes from solid to gas at -78.5 °C) 2. Rank the states with respect to increasing density and increasing energy.
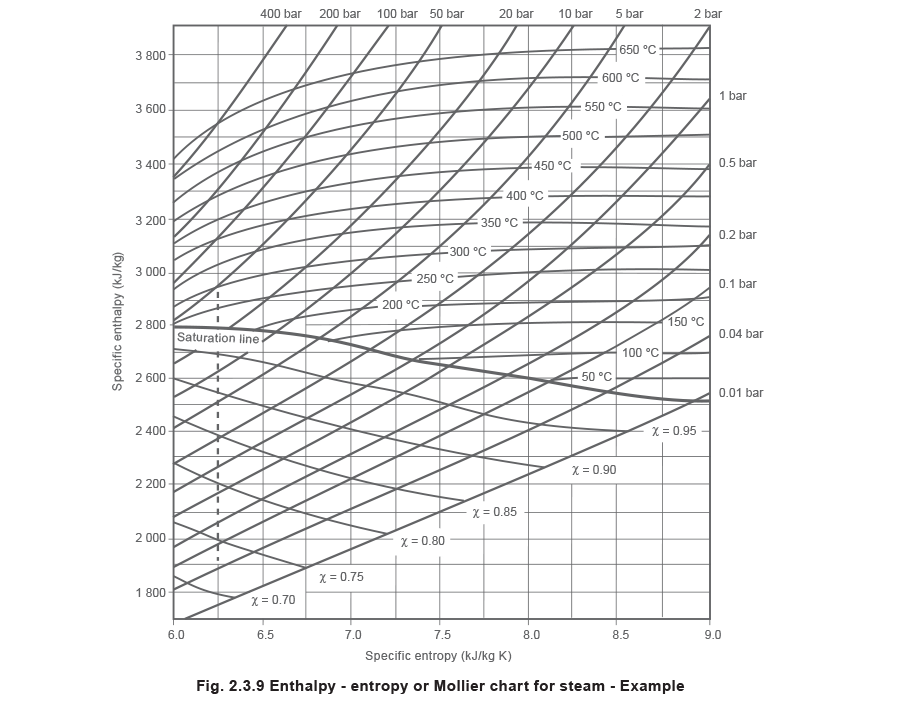
• Phase Diagrams Phase diagrams are graphs that give information on the equilibrium temperature and pressure for a particular compound. The equilibria occur for the solid- liquid plateau, liquid-vapor plateau and solid-vapor plateau. In this experiment, the phase diagram is shown for the solid-liquid equilibrium point, and varies from 100% ...
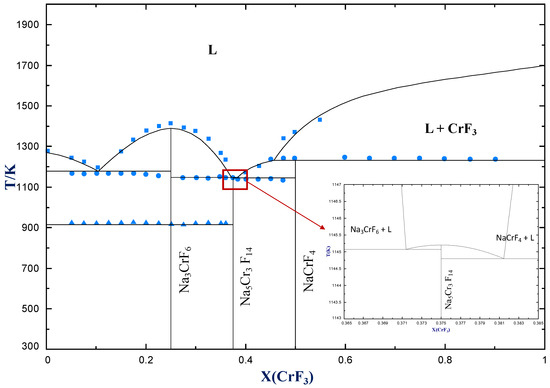
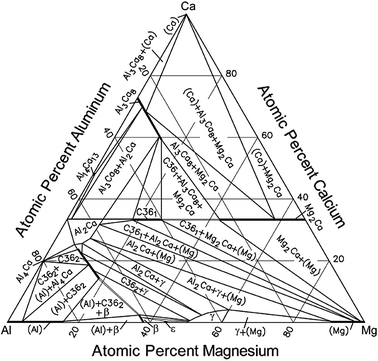
Below is shown the titanium-copper phase diagram (Figure 9.37). There is one eutectic on this phase diagram, which exists at about 51 wt% Cu-49 wt% Ti and 960°C. Its reaction upon cooling is 2 L! TiCu + TiCu There is one eutectoid for this system. It exists at about 7.5 wt% Cu-92.5 wt% Ti and 790°C. This reaction upon cooling is ! " # + Ti2Cu
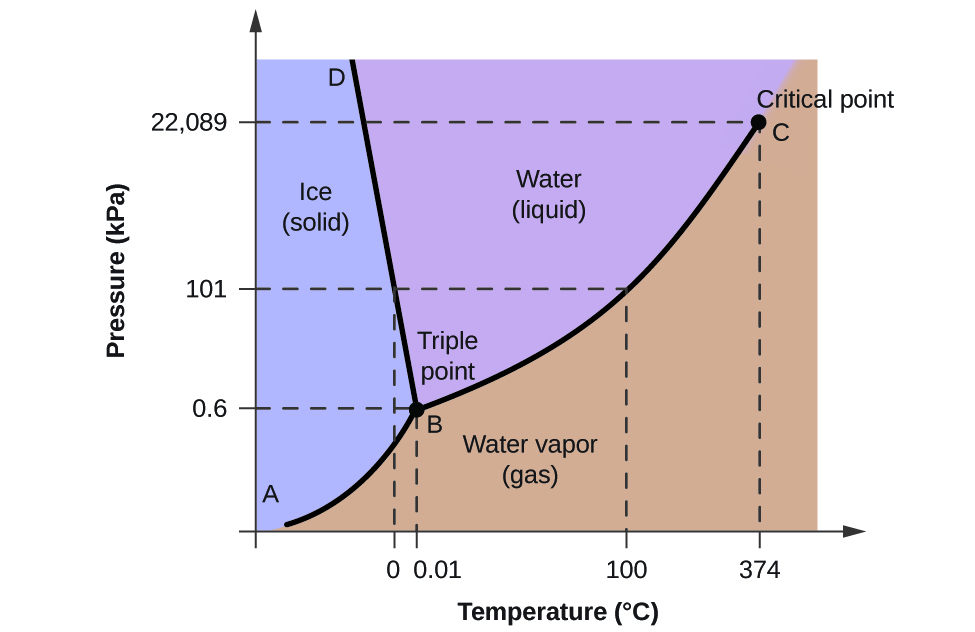
The lines in a phase diagram correspond to the combinations of temperature and pressure at which two phases can coexist in equilibrium. In Figure 11.6. 1, the line that connects points A and D separates the solid and liquid phases and shows how the melting point of a solid varies with pressure. The solid and liquid phases are in equilibrium all ...
2. The ice melts at 0.00 ºC (Phase Change) 3. The liquid water then rises in temperature from zero to 100.0 ºC. 4. The liquid water then boils at 100.0 ºC (Phase Change) 5. The steam then rises in temperature from 100.0 to 120.0 ºC. Each one of these steps will have an energy calculation associated with it.
This chemistry video tutorial explains the concepts behind the phase diagram of CO2 / Carbon Dioxide and the phase diagram of water / H2O. This video contai...
shear and bending moment diagrams. The basic procedure for determining the shear and moment diagrams is to determine the values of V and M at various locations along the beam and plotting the results. In doing so, we will determine critical sections within the beam. A critical section is one where a critical or maximum stress occurs.
This problem asks that we determine the phase mass fractions for the alloys and temperatures in Problem 9.8. (a) From Problem 9.8a, ε and η phases are present for a 90 wt% Zn-10 wt% Cu alloy at 400 °C, as represented in the portion of the Cu-Zn phase diagram shown below (at point A).
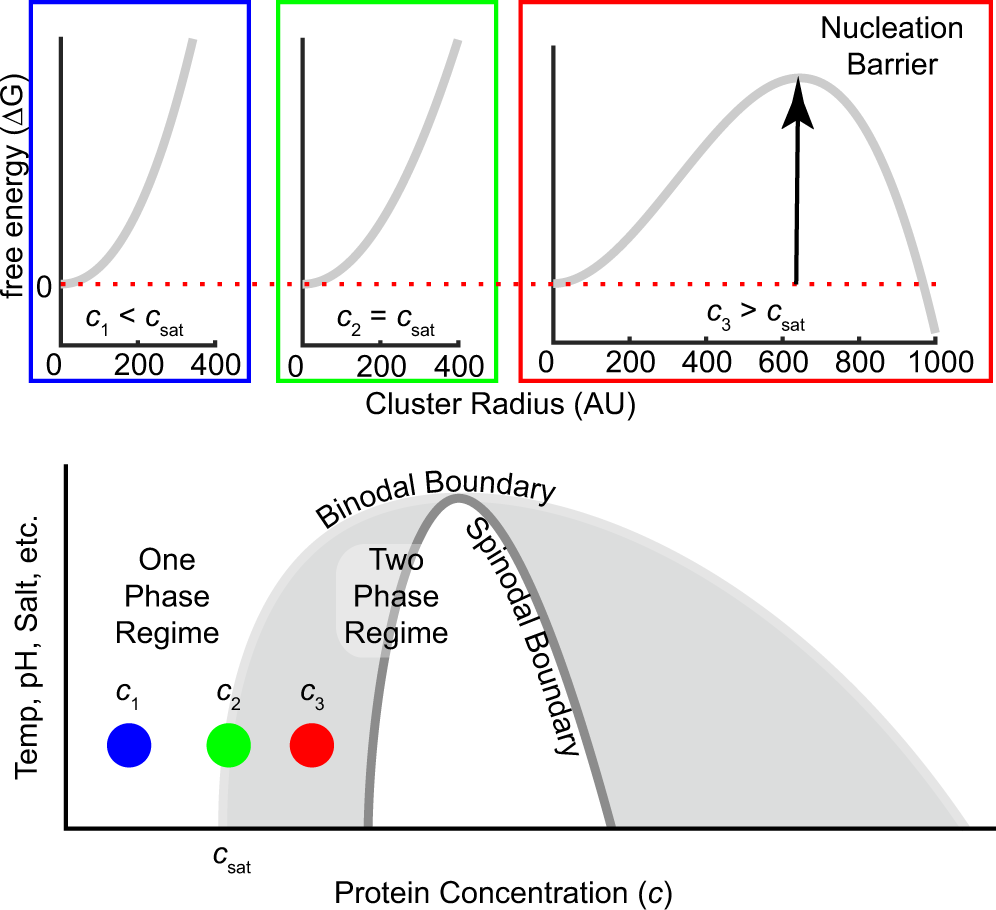
Phase diagrams. A phase diagram lets you work out exactly what phases are present at any given temperature and pressure. In the cases we'll be looking at on this page, the phases will simply be the solid, liquid or vapour (gas) states of a pure substance. This is the phase diagram for a typical pure substance.
Phase Diagrams • Indicate phases as function of T, Co, and P. • For this course:-binary systems: just 2 components.-independent variables: T and Co (P = 1 atm is almost always used). • Phase Diagram for Cu-Ni system Adapted from Fig. 9.3(a), Callister 7e. (Fig. 9.3(a) is adapted from Phase Diagrams of Binary Nickel Alloys , P. Nash
Question. : 12) Examine the following phase diagram and identify the feature represented by point A. 760 torr Temperature A) melting point B) critical point C) triple point D) sublimation point E) boiling point 13) In hydrogen iodide are the most important intermolecular forces A) B) C) dipole-dipole forces London dispersion forces hydrogen ...
38. Examine the following phase diagram and identify the feature represented by point A. A. melting point B. critical point C. triple point D. sublimation point 39. What are the changes in phase going from points A to B to C to D A B D C T P A. melting, vaporization, deposition B. vaporization, freezing, sublimation
Examine the phase diagram for the substance Bogusium (Bo) and select the correct statement. SEE QUESTION 10 Image A) Bo(s) has a lower density than Bo(l). B) The triple point for Bo is at a higher temperature than the melting point for Bo. C) Bo changes from a solid to a liquid as one follows the line from C to D.
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure 5 as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot exist as a liquid ...
PHASE DIAGRAMS • Also called equilibrium or constitutional diagrams • Plots of temperature vs. pressure, or T or P vs. composition, showing relative quantities of phases at equilibrium • Pressure influences phase structure -Remains virtually constant in most applications -Most solid-state phase diagrams are at 1 atm • Note ...













0 Response to "37 examine the following phase diagram and determine what phase(s) exists at point a."
Post a Comment