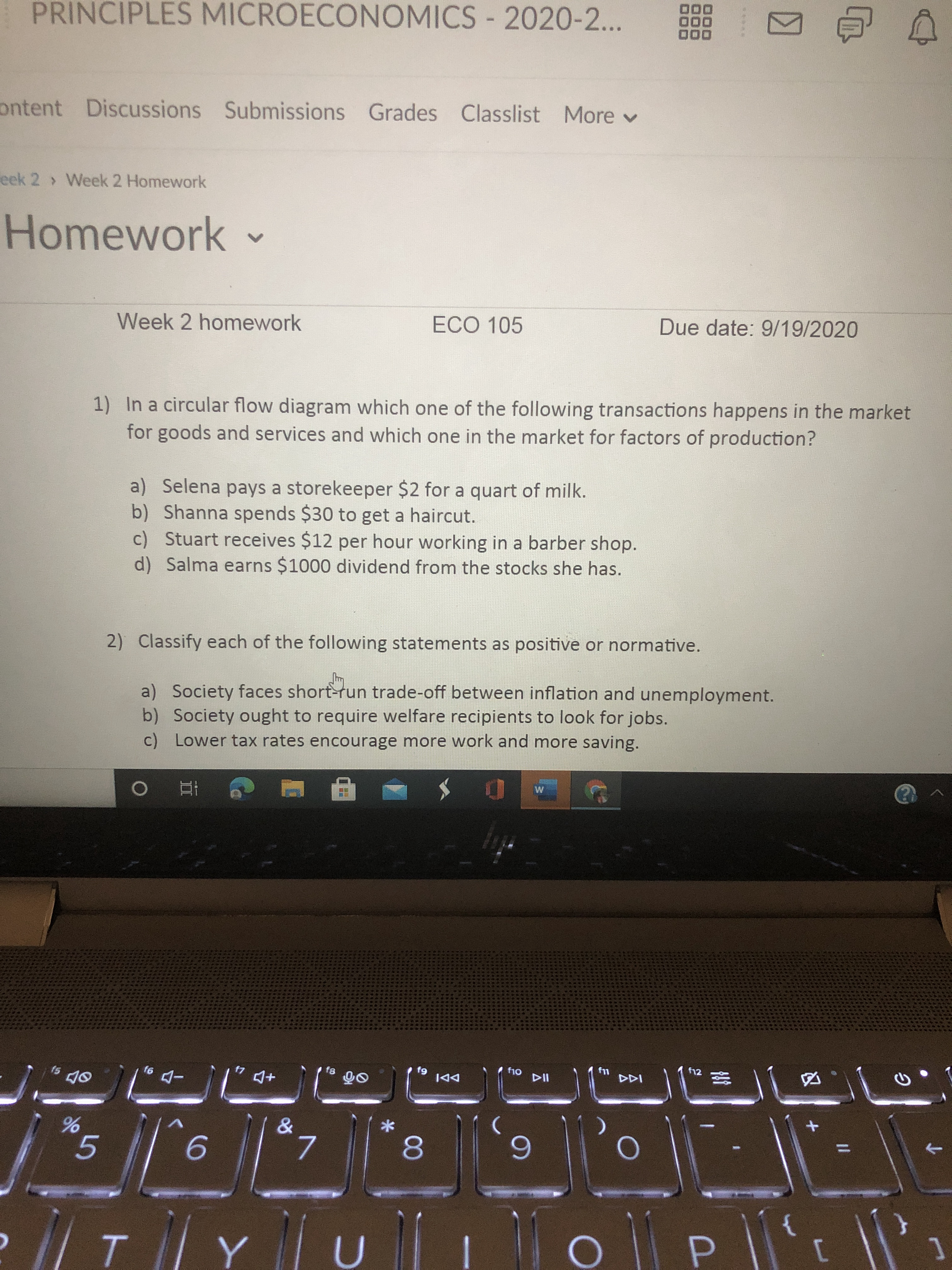
42 in the markets for factors of production in the circular-flow diagram,
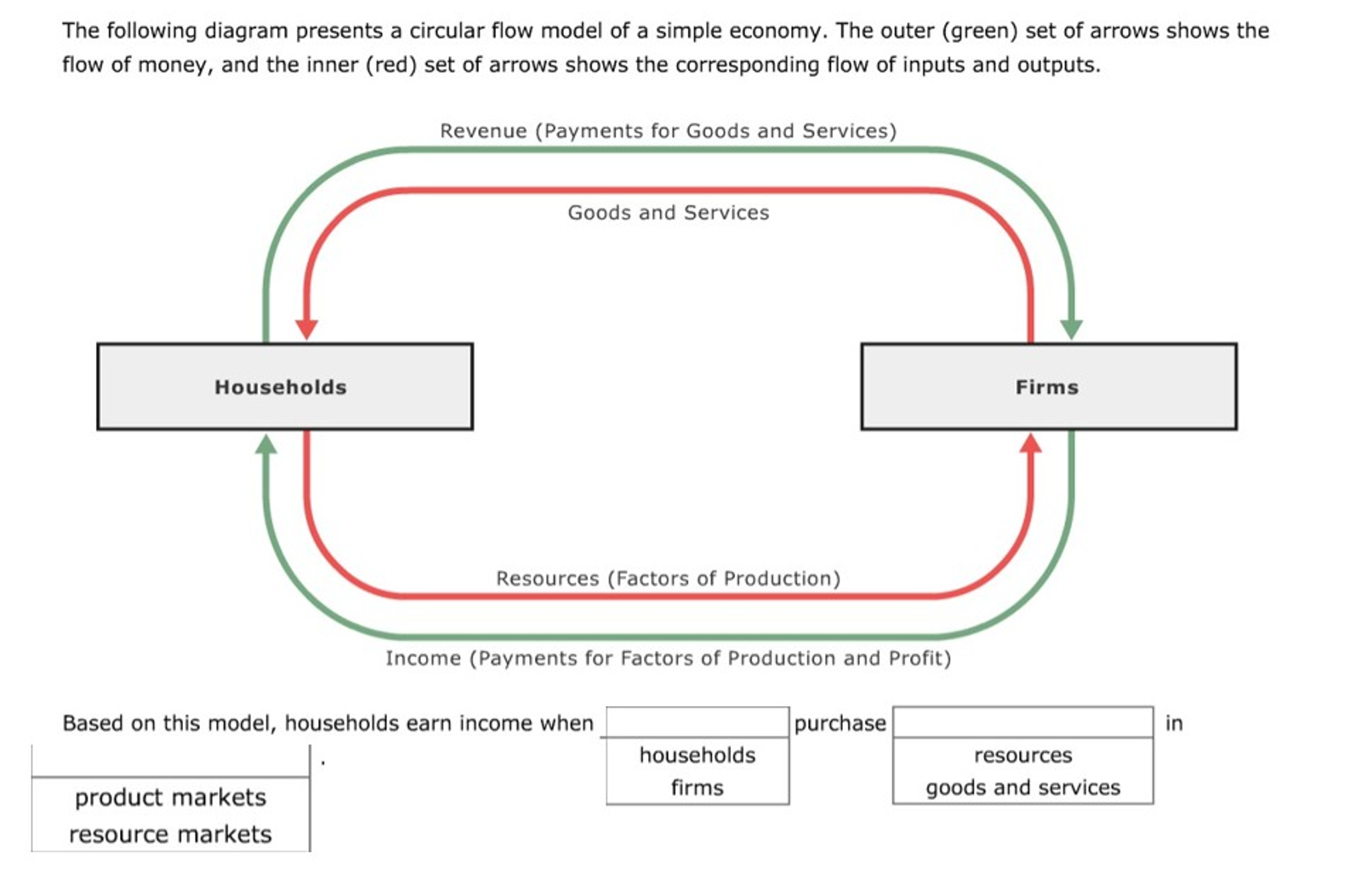
The circular flow model of the economy distills the idea outlined above and shows the flow of Jump To Section. What Is the Circular Flow Model in Economics? 4 Factors of Production. In the simple circular flow model of the free market, money flows in the opposite direction. The circular-flow diagram includes two types of decision-makers only - firms and households. Hence, to say that households are sellers and the firms are buyers in the market for the factors of production is correct.
How do households indirectly `own’ physical capital in the expanded circular flow diagram? A.) Households indirectly own physical capital by renting it to firms B.) Households indirectly own physical capital by providing firms with factors of production C.) Households indirectly own physical capital by funding firms’ investment spending through savings in the market for financial services D.) None of the above The answer sheet is a little confusing, it says the answer is (C) - is this correct?...

In the markets for factors of production in the circular-flow diagram,
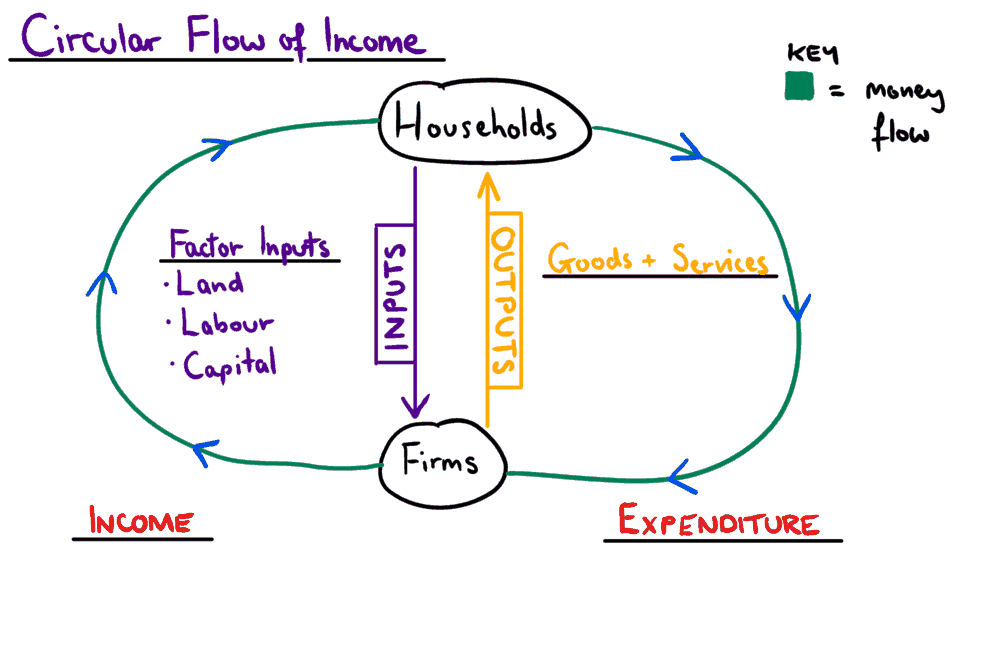
In an economy households provide factors of production, such as labour, to firms. Firms use these factors to produce goods and services which they sell to the households. As you can see in the diagram above, the expenditure on goods and services is equal to the income received by households. */ In this very simple model of the whole economy, it is assumed that the households own all the factors of production. This is shown on the left hand side of the diagram. The green line shows the factors of production going from the households to the firms and the red line shows the money... ...The Gains Rrom Trade 4 The Market Forces Of Supply And Demand 5 Measuring A Nation's Income 6 Measuring The Cost Of Living 7 Production And Growth 8 Savings,investment And The Financial System 9 The Basic Tools Of Finance 10 Unemployment 11 The Monetary System 12 Money Growth.
In the markets for factors of production in the circular-flow diagram,. The circular flow establishes a link between producers and consumers. It is through income that producers buy the services of the factors of production with which the latter, in turn, purchase goods from the Leakages or injections in the circular flow disturb the smooth functioning of the economy. Ideal circular flow:- the firm's demand for factors of production to run the production p... The markets are usually represented with one at the top of the diagram and one on the bottom. Government is usually added in in the middle, government makes the diagram much more... The circular flow model is an economic model that presents how money, goods, and services move between sectors in an economic system. In the basic (two-factor) circular flow model, money flows from households to businesses as consumer expenditures in exchange for goods and services... Visit- www.edunirvana.com, to know more about our latest product- Economics Lab! (Fastest and surest way to learn Economics!)This video consists of small...
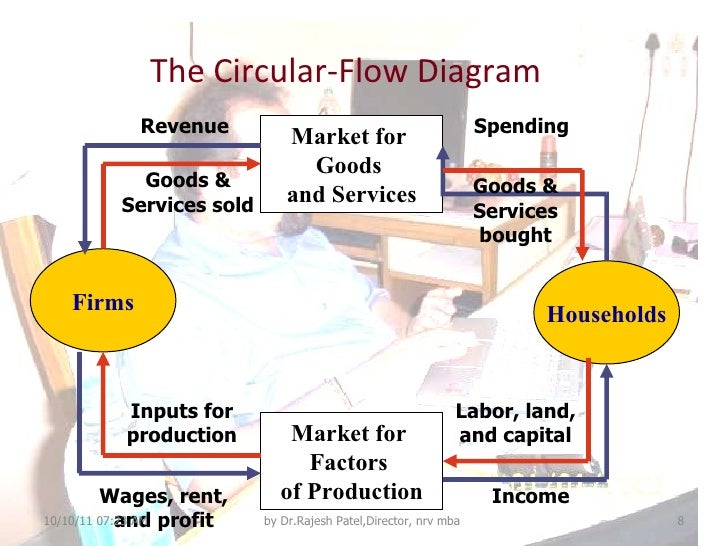
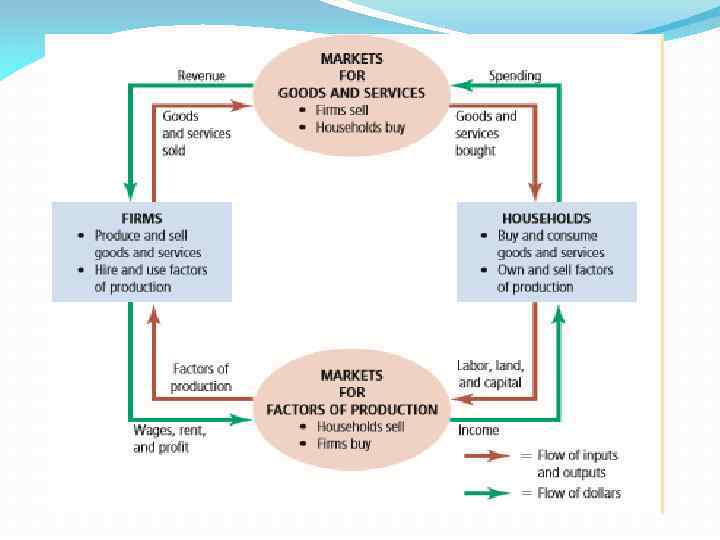
The circular-flow diagram illustrates that, in markets for the factors of production The production possibilities frontier is a graph that shows the various combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce given the available factors of production and production technology. The Circular-Flow Diagram. A visual model of the economy, shows how dollars flow through markets among households and firms. Includes two markets:the market for goods and services &the market for "factors of production" factors of production -the resources that the economy uses to... In a closed economy, goods and services are exchanged in product markets and factors of production are exchanged in factor markets. In this video, we explore how to model this in a straightforward way using the circular flow model. The household sector owns all the factors of production that is land, labor, capital and enterprise. In this way, money flows in a circular manner from the business sector to the household sector and from On the other hand, business firms borrow funds from the capital market for making investment.
In the markets for the factors of production, households are sellers and firms are buyers. In these markets, households provide firms the inputs that the firms use to produce goods and services. The circular flow diagram offers a simple way of organizing all the economic transactions that occur... The term "factors of production" refers to anything that is used by a firm in order to make a final product. Some examples of factors of production are labor (the work was done by In factor markets, households and firms play different roles than they do in the markets for goods and services. A circular flow diagram is a visual model of the economy that illustrates how households and businesses interact through markets for products Markets for factors of production and markets for financial assets c. Another term for factors of production is. The markets for goods and... The Factors of Production are also known as. INPUTS. Some types of labor are scarcer than Entrepreneurship is the innovation and creativity applied in the production of goods and services. Will Smith accepting this role. Is the study of individual markets for goods, services, and resources.
The circular flow of income or circular flow is a model of the economy in which the major exchanges are represented as flows of money, goods and services, etc. between economic agents. The flows of money and goods exchanged in a closed circuit correspond in value, but run in the opposite direction.
Our diagram attempts to correct the problems of the Circular flow model. Moreover, the prices of the. factors of production, through the feedback of market processes, contain information about consumers are imputed back to the factors in the form of prices for factors of production. These.
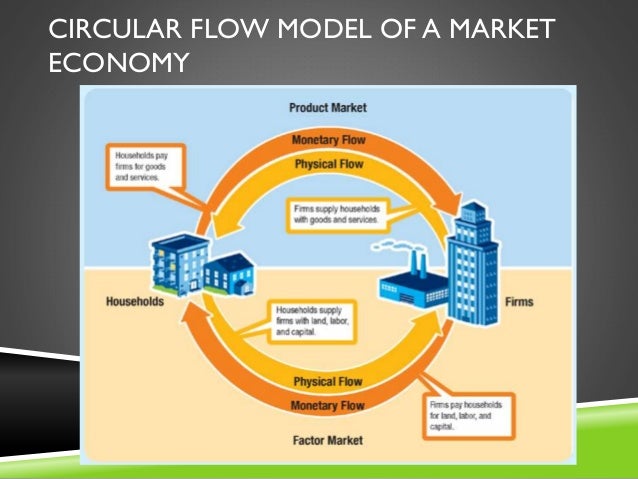
The circular flow model shown in Figure 2.3 illustrates exchanges in two markets, the product market and the factor market. From the circular flow model, it appears that the product market is a single physical location where products are bought and sold.
Some of the factors of production include cocoa beans, land for housing the factory, the building, and laborers for carrying out the production process. This has been a guide to the Circular Flow of Income and its definition. Here we discuss how it works in two-sector, three-sector, and four-sector...
The bottom half of the circular-flow diagram, which represents resource markets, shows that businesses give money to households in exchange for economic resources used as factors of production. For example, when people work for a business, they are supplying their labor as a factor...
The circular flow model demonstrates how money moves through society. Money flows from producers to workers as wages and flows back to It separates the markets that these participants operate in as markets for goods and services and the markets for the factors of production.
The Circular Flow Model or Circular Flow of Income shows how different units in an economy interact and how household consumption is a firm's income. Likewise, markets are placed in two categories: markets for factors of production (also known as factor markets; factors of production include...

100 Boots in the Market (May 17, 1971, 9:30 a.m.; mailed June 7, 1971) // Eleanor Antin American, born 1935
3 Circular Flow Write the following in the circular flow diagram: Households Entrepreneurship 5 buy the factors of production Buyers in the resource market Households Firms buy the factors 16 Use the information below to calculate Nominal GDP in Narvaizland Billions of dollars Exports $367...
The circular flow of income is a way of representing the flows of money between the two main groups in society - producers (firms) and consumers (households). These flows are part of the fundamental process of satisfying human wants. As we have already seen, a free market economy consists of two...
The National Accounts. The Circular-Flow Diagram. Printed Page 102 [Notes/Highlighting]. Households spend most of the income received from factors of production on goods and services. However, in Figure 10.2 we see two reasons why the markets for goods and services don't in fact...
The circular-flow diagram (or circular-flow model) is a graphical representation of the flows of goods and money between two distinct parts of the economy -market for factors of production (such as labour or capital), where firms purchase factors of production from households in exchange for...
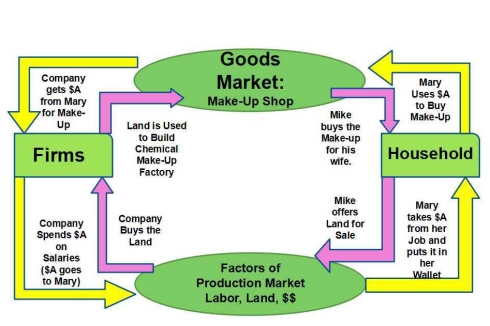
In the traditional high-school Econ classes, we are taught about the circular flow diagram. In essence, let's say there are 2 households and 2 businesses. The households spend in aggregate $100 ($50 each) on products (let's call it Product A) made by the firms. The firms then pay out a portion of the $100 as wages for the product ($90, 45 for each), and then pay out the rest as profit to the owners (which also goes to at least one of the household because the business is owned by at least one h...
The circular flow chart analyses various agents' relationships in an economic scenario regarding The circular flow diagram is a model that traces the inter-connection between the various There are two types of markets, markets for goods and services and markets for factors of production.
GDP Introduction & The Expenditure Approach The Circular-Flow Diagram The Circular Flow Wages, rents, interest, profits Factor services Household Firms nt rnme (production) Taxes Government Goveending Foreigners can also buy stocks and bonds in the U.S. financial markets.
...The Gains Rrom Trade 4 The Market Forces Of Supply And Demand 5 Measuring A Nation's Income 6 Measuring The Cost Of Living 7 Production And Growth 8 Savings,investment And The Financial System 9 The Basic Tools Of Finance 10 Unemployment 11 The Monetary System 12 Money Growth.
*/ In this very simple model of the whole economy, it is assumed that the households own all the factors of production. This is shown on the left hand side of the diagram. The green line shows the factors of production going from the households to the firms and the red line shows the money...
In an economy households provide factors of production, such as labour, to firms. Firms use these factors to produce goods and services which they sell to the households. As you can see in the diagram above, the expenditure on goods and services is equal to the income received by households.















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Circular-Flow-Model-1-590228483df78c5456a9b918.jpg)





0 Response to "42 in the markets for factors of production in the circular-flow diagram,"
Post a Comment