40 label the axes, phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below.
Label the axes phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below. 100 3 ratings or. This is the diagram that i need to label attached. Label the axes and label the regions in which the solid liquid and gas phases are stable. Label the enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below. And my professor did not explain this at all. Label the axes ... 3.3 Phase Diagram for Water Vapor: Clausius-Clapeyron Equation. The Clausius-Clapeyron Equation. We can derive the equation for e s using two concepts you may have heard of and will learn about later: entropy and Gibbs free energy, which we will not go into here.Instead, we will quote the result, which is called the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation,
Show transcribed image text label the axes phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below. Melt the substance than to separate the molecules. Label the axes phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below. Use this diagram for questions 1 9 1 label each region of the graph as solid liquid or gas. Show transcribed image text label ...
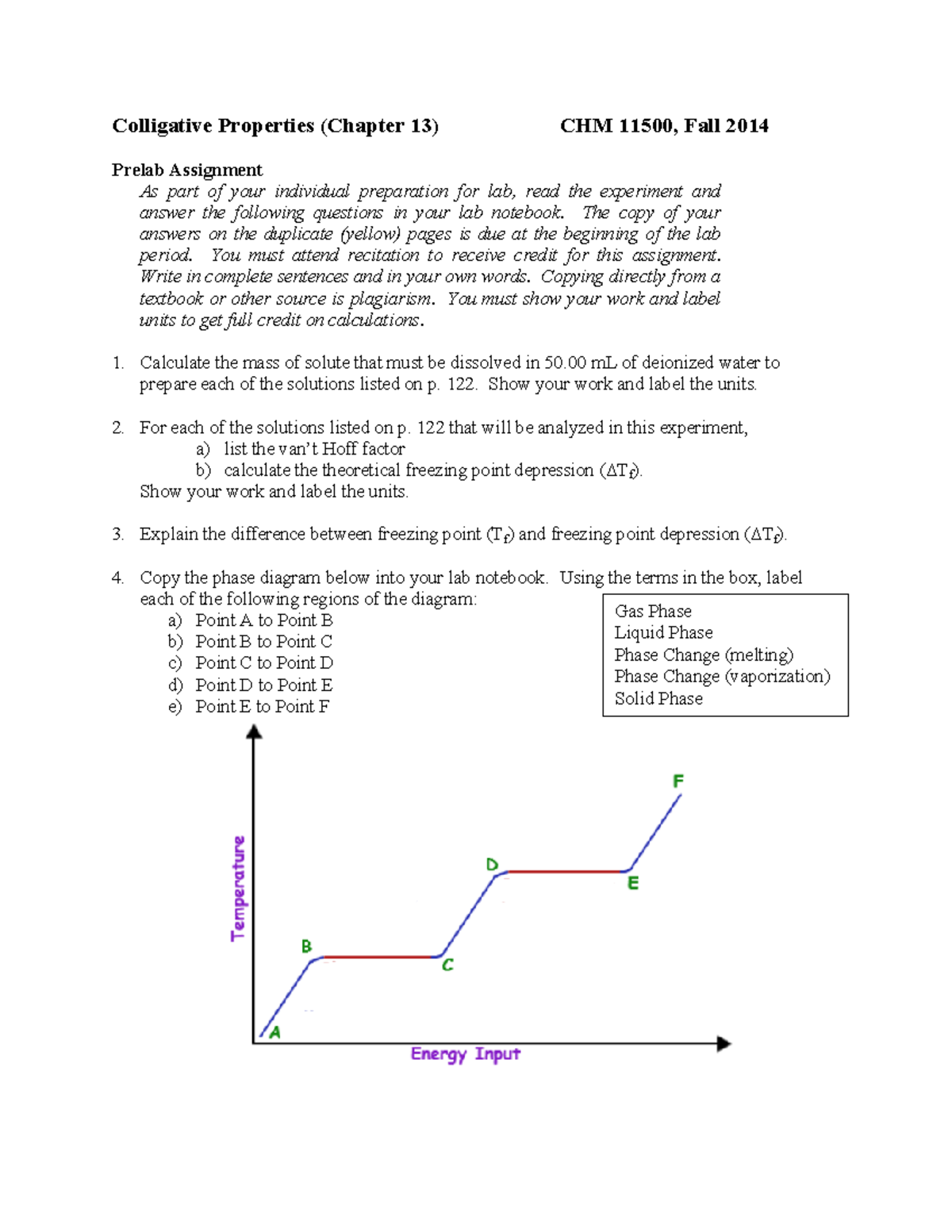
Label the axes, phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below.
Elemental carbon has one gas phase, one liquid phase, and three different solid phases, as shown in the phase diagram: On the phase diagram, label the gas and liquid regions. Graphite is the most stable phase of carbon at normal conditions. On the phase diagram, label the graphite phase. The reaction whose potential energy diagram is shown in the figure is a two-step reaction. The activation energy for each step is labeled E a1 and E a2 .Each elementary step has its own activated complex, labeled AC 1 and AC 2 .Note that the overall enthalpy change of the reaction is unaffected by the individual steps, since it depends only on the initial and final states. gas Z as shown in the equation below. 2W(g)€ +€ Y(s)€ : € Z(g) The graph below shows how the concentration of Z varied with time at constant temperature. (i)€€€€€ On the axes above, sketch a curve to show how the concentration of W would change with time in the same experiment. Label this curve W.
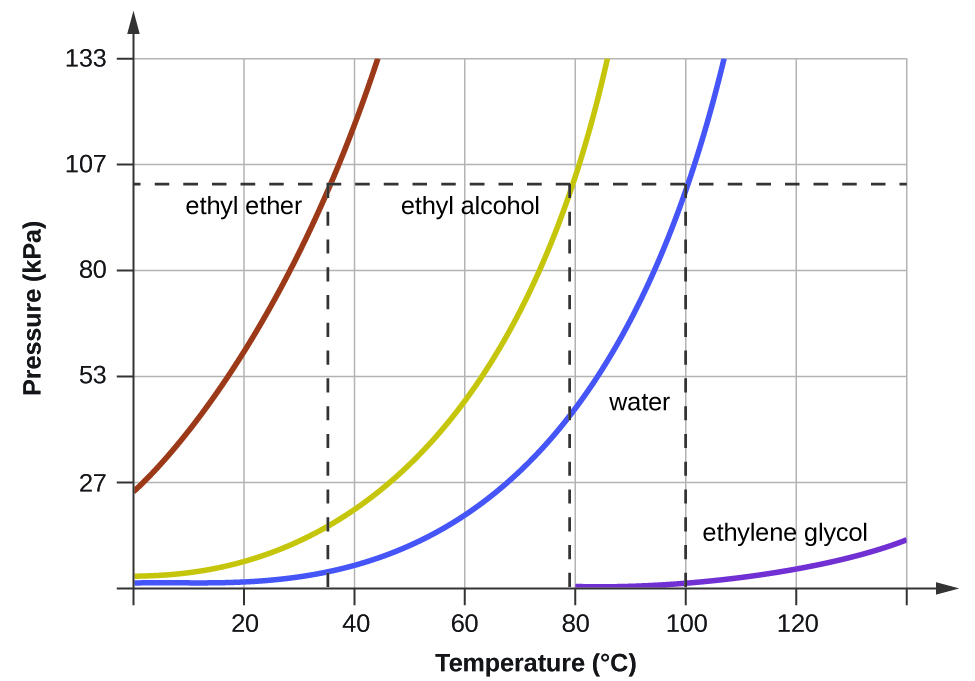
Label the axes, phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below.. Label the Axes, Phases, Phase Changes and Important Points On the Phase Diagram Below. the label gretty rose, label the goldfish, the label ritu kumar, the label network, label the heart game, label the parts of a flower, label the skull, label the x and y axis, label the food worksheet, label johnnie walker, 12 Label The Axes, Phases, Phase ... , as shown below: Now, let us remove the imaginary partition and let the A and B atoms mix. There should be some change in g due to this mixing, and it is given by ∆g. mix = ∆h. mix - T∆s. mix (3) The enthalpy term, ∆h. mix, represents the nature of the chemical bonding, or, put in Heat is added to the cylinder while the pressure is maintained constant until the temperature reaches 300°C, as shown in the following T-v diagram (temperature vs specific volume): From State (1) to State (2) the water maintains its liquid phase and the specific volume increases very slightly until the temperature reaches close to 100°C ... The figure below shows a calculated phase diagram for the system H 2 O-Cu-NaOH-HCl-H 2 in which the X-axis is the molar ratio NaOH/(NaOH+HCl) (which is related to the pH) and the Y-axis is the equilibrium partial pressure of H 2 (which is related to the redox potential Eh).
Label the axes, phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below. Consider the reaction 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) ⇌ 4H2(g) + Fe3O4(s) If the total pressure is increased by reducing the volume, no change occurs. Elemental carbon has one gas phase, one liquid phase, and two different solid phases, as shown in the phase diagram: (a) On the phase diagram, label the gas and liquid regions. (b) Graphite is the most stable phase of carbon at normal conditions. On the phase diagram, label the graphite phase. Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Label the axes, phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below. appropriate label for the x-axis and y-axis, E a ... a reaction occurs as shown below. 3Fe(s) ... Calculate the activation energy for the forward reaction. b. Draw a labelled potential energy diagram showing the enthalpy change, and the activation energies for the forward and reverse reactions. What Is Required?
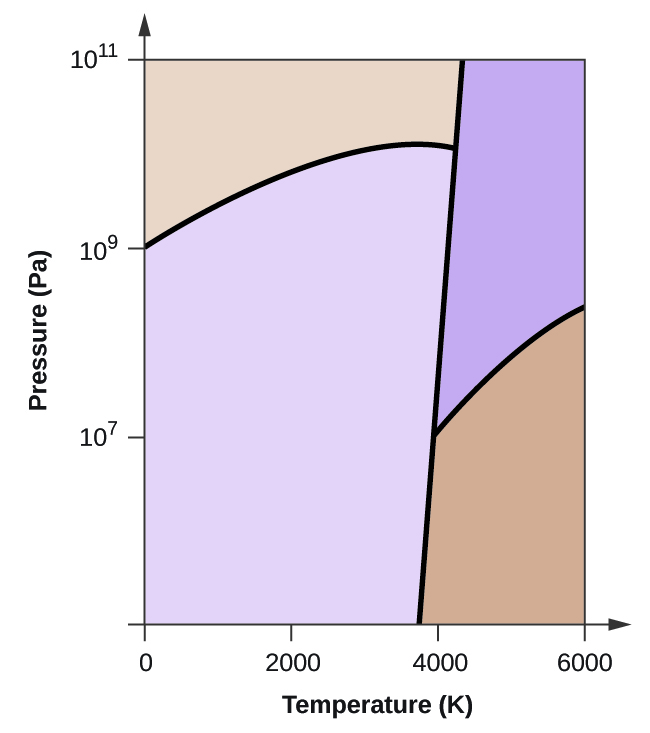
Shown is the phase diagram for phosphorus a indicate the phases present in the regions labeled with a question mark b a sample of solid red phosphorus cannot be melted by heating in a container open to the atmosphere. 1000 points label the axes phases phase changes and important points on the phase diagram below. Shown is the phase diagram for phosphorus a indicate the phases present in the regions labeled with a question mark b a sample of solid red phosphorus cannot be melted by heating in a container open to the atmosphere. 1000 points label the axes phases phase changes and important points on the phase diagram below. Elemental carbon has one gas phase, one liquid phase, and two different solid phases, as shown in the phase diagram: (a) On the phase diagram, label the gas and liquid regions. (b) Graphite is the most stable phase of carbon at normal conditions. On the phase diagram, label the graphite phase. Phase diagram is a graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure. The phase diagram for xenon is shown belowin what. A typical phase diagram has pressure on the y axis and temperature on the x axis. Label the enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below.
Label the enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below. 3. Label the axes, phases, phase changes and important points on the phase diagram below. 4. Label the axes, phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below. Share this link with a friend: Copied! Other Related Materials.
The relative temperature changes of the copper and the water cannot be determined without knowing Tl and T2. 12(s) —Y HI(g) AH=26kJ/m01 HI(g) All=-5.OkJ/m01 64. Based on the information above, what is the enthalpy change for the sublimation of iodine, reprcsentcd below? (A) 15 kJ/m01rx,t (B) 21 kJ/molrxn (C) 31 kJ/m01rxn (D) 42 kJ/molrxn 62
label the axes phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below › ... label the phase changes shown in the diagram below. reset zoom. 32 Label The Phase Changes Shown In The Diagram Below Written By Robert N Greenawalt Monday, August 9, 2021 1 Comment Edit.
A. The enthalpy change of the catalysed reaction is less than the enthalpy change for the uncatalysed reaction. B. The enthalpy change of the catalysed reaction is greater than the enthalpy change for the uncatalysed reaction. C. The enthalpy change of the catalysed reaction is equal to the enthalpy change for the uncatalysed reaction. D.
Let's look at the elements of this enthalpy diagram. First, as noted, the y -axis is labeled 'enthalpy' and the x -axis is labeled 'reaction progress.'. Then we have the actual energy diagram plot ...
a) Draw a potential energy diagram for this reversible reaction. Your starting value for the reactants might be different that is ok, as long as you show the proper E a and ∆H values. b) Calculate the enthalpy change (∆H) for each reaction. i) ΔH forward = 137 kJ/mol
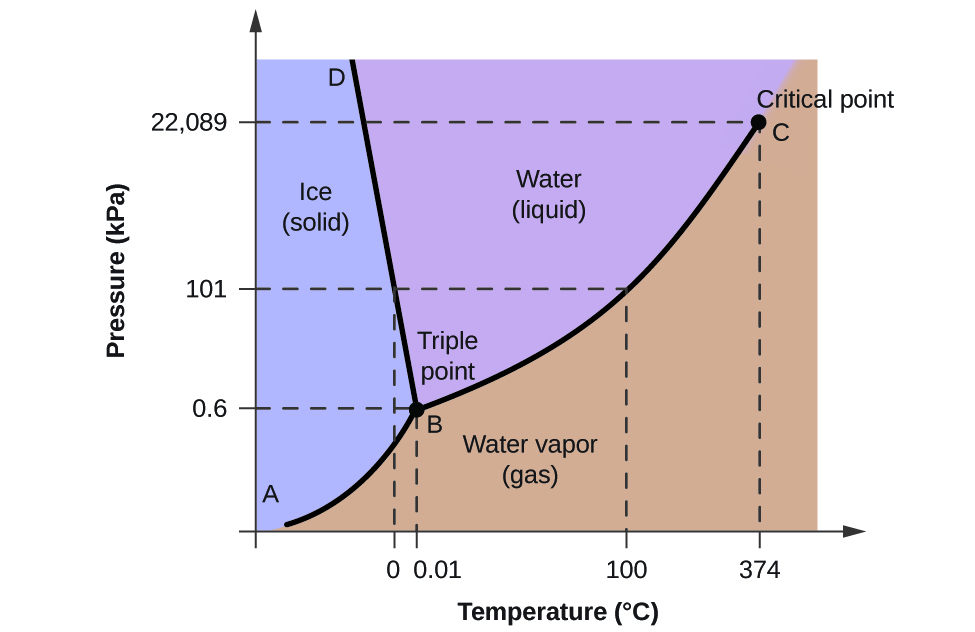
Describe all of the phase changes that occur when water at 0 °C is slowly compressed from 0.500 kPa to 1000 kPa. The vertical dotted line on the phase diagram shows the changes. The temperature is below that of the triple point (A) as is the initial pressure (0.500 kPa). The water is initially a gas.
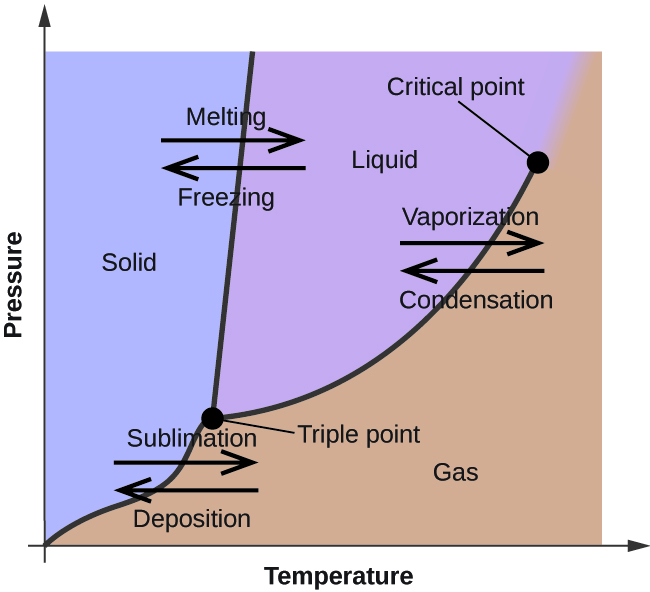
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: Label the phase changes shown in the diagram below. Gas Condensation Vaporization Freezing Deposition Sublimation Melting Liquid Solid.
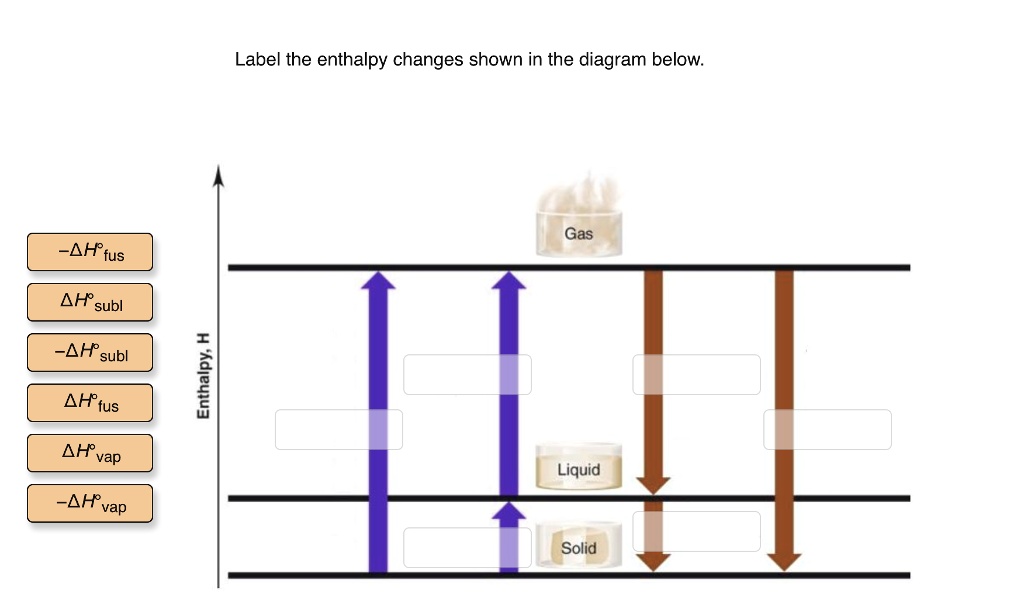
Solved Label The Enthalpy Changes Shown In The Diagram Below Gas Ah Fus Ah Subl Ah Subl Ah Fus Ah Vap Ah Vap Liquid Solid
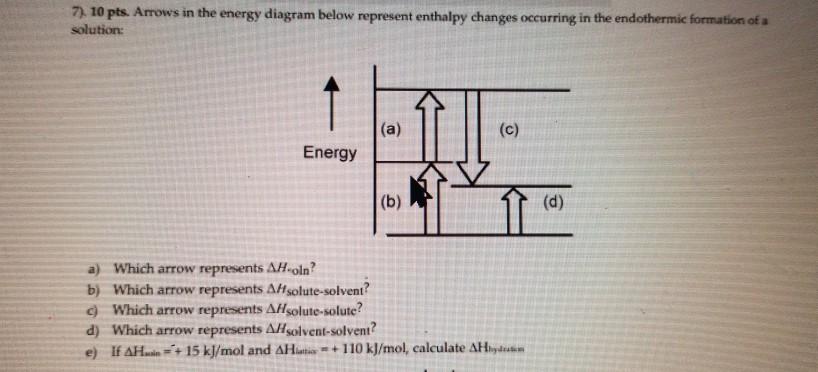
(c) The following enthalpy changes are given. enthalpy change value / kJ mol-1 standard enthalpy change of formation, , for K 3PO 4(s) -2035 standard enthalpy change, -ΔH o, for P(s) + 2O 2(g) + 3e PO 4 3-(aq) -1284 standard enthalpy change, ΔH +o, for K(s) K(aq) + e- -251 Determine the standard enthalpy change of solution of ...
Label the enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below. 32 examine the heating curve for water in section 117 figure 1136. 1000 points label the axes phases phase changes and important points on the phase diagram below.
Label the axes phases phase changes and important points on the phase diagram below vaporization solid gas triple point liquid condensation critical point freezing. This is quite simple i guess. C trace the phase changes that occur when the pressure on a sample is reduced from point a to b at constant temperature.
gas Z as shown in the equation below. 2W(g)€ +€ Y(s)€ : € Z(g) The graph below shows how the concentration of Z varied with time at constant temperature. (i)€€€€€ On the axes above, sketch a curve to show how the concentration of W would change with time in the same experiment. Label this curve W.
The reaction whose potential energy diagram is shown in the figure is a two-step reaction. The activation energy for each step is labeled E a1 and E a2 .Each elementary step has its own activated complex, labeled AC 1 and AC 2 .Note that the overall enthalpy change of the reaction is unaffected by the individual steps, since it depends only on the initial and final states.
Elemental carbon has one gas phase, one liquid phase, and three different solid phases, as shown in the phase diagram: On the phase diagram, label the gas and liquid regions. Graphite is the most stable phase of carbon at normal conditions. On the phase diagram, label the graphite phase.

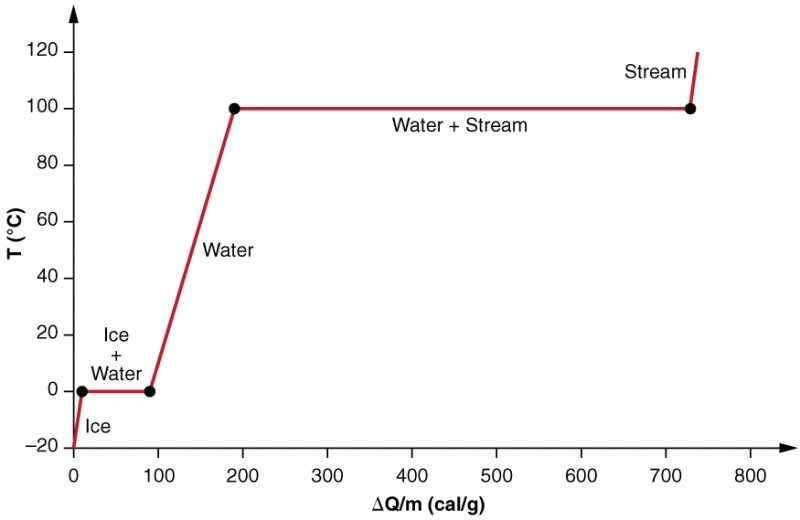
Suppose Water Could Exist In Four States Of Matter At Some Pressure Draw What The Heating Curve For Water Would Look Like Label The Axes And The Graph Study Com

Thermodynamic Forward Modeling Of Retrogressive Hydration Reactions Induced By Geofluid Infiltration Earth Planets And Space Full Text
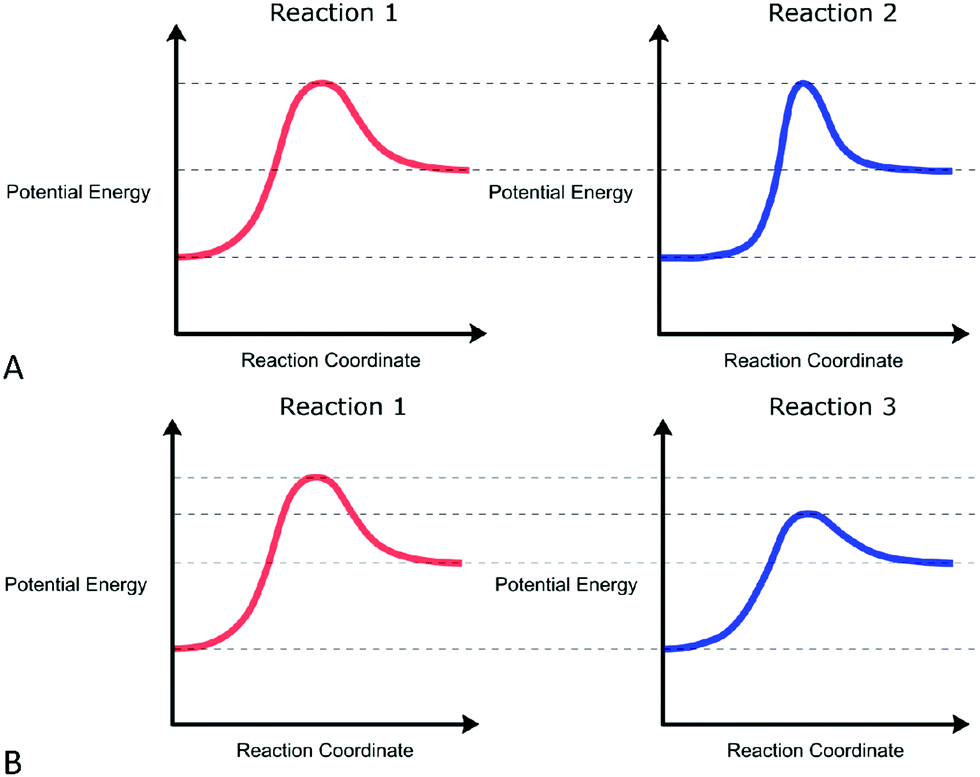
Location Thinking Value Thinking And Graphical Forms Combining Analytical Frameworks To Analyze Inferences Made By Students When Interpreting The Points And Trends On A Reaction Coordinate Diagram Chemistry Education Research And Practice Rsc
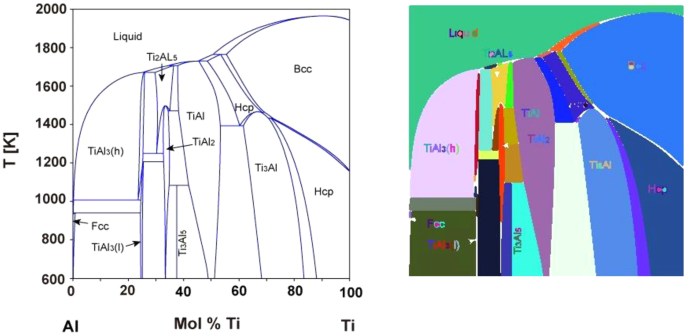
Probabilistic Assessment Of Glass Forming Ability Rules For Metallic Glasses Aided By Automated Analysis Of Phase Diagrams Scientific Reports






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/phase_diagram_generic-56a12a1b5f9b58b7d0bca817.png)












0 Response to "40 label the axes, phases and enthalpy changes shown in the diagram below."
Post a Comment