40 free body diagram of a rocket
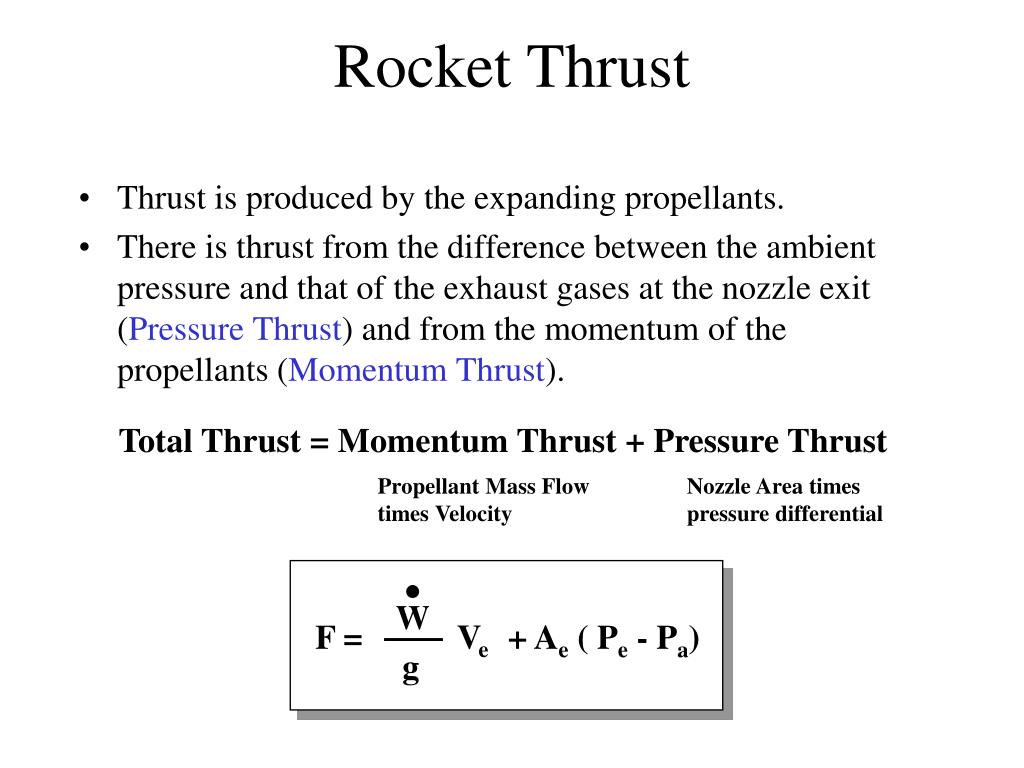
5 Feb 2010 — So I know the rocket thrust equation as: T=(dm/dt)*V_e+A_e(P_e-P_a) where, dm/dt = the mass flow rate V_e = exhaust velocity A_e = Area of ... 20 Oct 2021 · 4 answershere in discussion, we have to call brother free body diagram of our rocket, why it is on the launch pad. And in the second case we have to ...
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
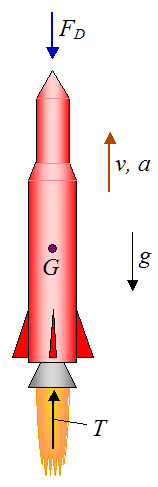
Free body diagram of a rocket
by W Moebs · 2016 — Remember that a free-body diagram must only include the external forces acting on ... A 120-kg astronaut is riding in a rocket sled that is sliding along an ... Free-body diagram of rocket propulsion ... (a) This rocket has a mass m and an upward velocity v. The net external force on the system is −mg, if air resistance ... and air drag of the rocket Free-Body Diagram: 1 . F Net = F a - F o The rocket is decelerating ma = 0 - F g - F drag Force Opposing (F o or F g and F drag) The opposing force is the weight, Fg, and air drag of the rocket. Free-Body Diagram: 2 . F Net = F a - F o Force Opposing (F drag)
Free body diagram of a rocket. A rocket is being launched straight up. Air resistance is not negligible. Draw a free-body diagram for the rocket. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Answer : The fr …. View the full answer. free-body diagram: A diagram that shows all the forces acting upon an object. Newton's first law : If the forces are balanced, the body will stay at rest or continue with the same velocity, neither accelerating nor decelerating. Example: A rocket on the launch pad will not move without an outside force. Our free body diagram looks like: There are only two forces acting on the rocket - the weight of the rocket down (i.e.the force on the rocket due to gravity, F g or mg) and the Normal Force (the force of the launch pad pushing back up on the rocket, F N ). The motion of an object in response to an external force was first accurately described over 300 years ago by Sir Isaac Newton, using his three laws of motion.
... order to begin finding the maximum height, a free-body diagram is used to find all of the forces a rocket body experiences in its flight. This ... A rocket is being launched straight up. Air resistance is not negligible. Draw a free-body diagram for the rocket. Draw the vectors starting at the black dot. The location and orientation of the vectors will be graded. The exact length of your vectors will not be graded but the relative length of one to the other will be graded. Below is a free-body diagram for the rocket during the time interval 0 < t ... This is because the supporting force exerted on the rocket by the launch ... Students are introduced to statics and dynamics, free-body diagrams, combustion and thermodynamics to gain an understanding of the forces needed to lift rockets off the ground. They learn that thrust force is needed to launch rockets into space and the energy for thrust is stored as chemical energy in the rocket's fuel. Then, using the law of conservation of energy, students learn that the ...
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... 8. A large model rocket engine can produce a thrust of 12.0 N upon ignition. This engine is part of a rocket with a total mass of 0.288 kg when launched. a. Draw a free-body diagram of the rocket just after launch. b. What is the net force that is acting on the model rocket just after it leaves the ground? F net! F thrust $ F g! 12.0 N $ (0.288 ... Free-Body Diagram 4 - 4 The first step in the static equilibrium analysis of a rigid body is identification of all forces acting on the body with a free body diagram. • Select the body to be analyzed and detach it from the ground and all other bodies and/or supports. • Include the dimensions, which will be needed 26 Dec 2013 — I made it clear that the force of thrust must be greater than the weight of the rocket for it to liftoff. Moreover, I drew the free body diagram ...
and air drag of the rocket Free-Body Diagram: 1 . F Net = F a - F o The rocket is decelerating ma = 0 - F g - F drag Force Opposing (F o or F g and F drag) The opposing force is the weight, Fg, and air drag of the rocket. Free-Body Diagram: 2 . F Net = F a - F o Force Opposing (F drag)
Free-body diagram of rocket propulsion ... (a) This rocket has a mass m and an upward velocity v. The net external force on the system is −mg, if air resistance ...
by W Moebs · 2016 — Remember that a free-body diagram must only include the external forces acting on ... A 120-kg astronaut is riding in a rocket sled that is sliding along an ...

Smith-Fangruida space tunnel and cosmic multidimensional distortion structure positive or negative, complex generalization

860-880 North Lake Shore Drive, Electrical Riser Diagram (11/28/1949) // Ludwig Mies van der Rohe (American, born Germany, 1886–1969) Associate Architect: Holsman, Holsman, Klekamp and Taylor (American, 20th century) Associate Architect: Pace Associates (American, 20th century) Structural Engineer: Frank J. Kornacker (American, active 1940s–1950s)






















0 Response to "40 free body diagram of a rocket"
Post a Comment