40 free body diagram mass on inclined plane
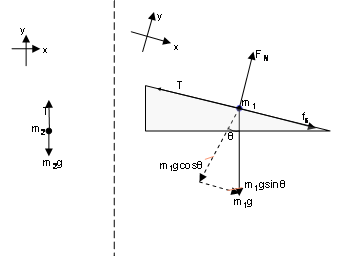
Carefully construct a free-body diagram showing all the forces acting on mass m 2. There are three forces acting on this mass -- the string exerts a force T , the (frictionless) inclined plane exerts a "normal" force n , and gravity pulls down with a force of w 1 = m 1 g. To review, the process for solving inclined plane problems is as follows: Draw a sketch of the problem. Identify known and unknown quantities, and identify the system of interest. Draw a free-body diagram (which is a sketch showing all of the forces acting on an object) with the coordinate system rotated at the same angle as the inclined plane.
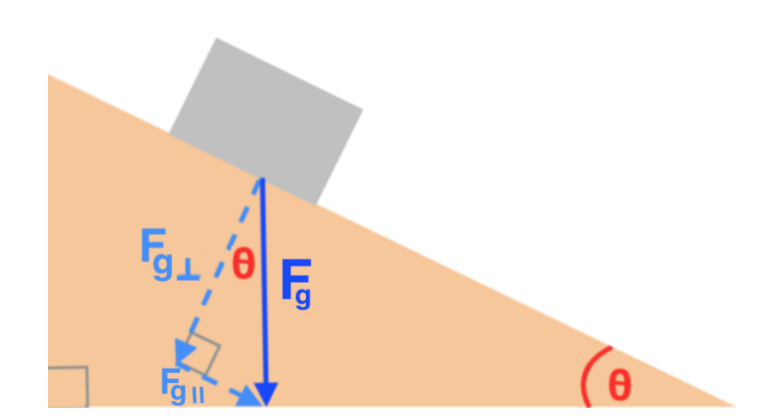
Firstly there are forces that acts on the two masses and are due to their weights. F ( A) = m A g S i n ( w) * (the force in red) is the component of the weight of A parallel to the inclined plane. F ( B) = m B g S i n ( w) (the force in light blue) is the component of the weight of B parallel to the inclined plane.

Free body diagram mass on inclined plane
PhysicsLAB: Freebody Diagrams. In each case, a rock is acted on by one or more forces. On a sheet of paper, draw an accurate vector diagram showing all forces acting on the rock, and no other forces. Use a ruler, and do it in pencil so you can correct mistakes. Refer to the following information for the next two questions. Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in . Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in the problem-solving strategy. Solution. We start by creating a diagram for the first object of interest. In (a), object A is isolated (circled) and represented by a dot. A free-body diagram for a ball resting on the ground: Gravity is acting downward. The ball is at rest. The ground must exert a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction on the ball. This force is called the normal force, n, since it is normal to the surface. Example: A free-body diagram for a mass on an inclined plane: Gravity acts ...
Free body diagram mass on inclined plane. Investigating the free-body diagram of a stationary object on an inclined plane November 2017 3 front face, and there is no need to put emphasis on what is inside it during the activity. The watch we use in this activity is the Apple Watch Series 2 with 38 mm aluminium case, possessing a mass of 28.2g, and the long version of the polymer sport ... Figure 5-24 gives the free-body diagram for four situations in which an object is pulled by several forces ... frictionless plane that is inclined at angle q = 27°. g. (a) What are the magnitudes of the force ... What total mass is accelerated to the right by (a) force , (b) force 21 Visit http://ilectureonline.com for more math and science lectures!In this video I will show the “traditional” and the free-body diagram methods of finding a... Mass on Frictionless Incline One of the insights that comes from the setup of this problem is that the force required to push a mass m up a frictionless incline is equal to mgsinθ. Checking the limiting cases, you find that it takes no force along a horizontal frictionless surface (θ=0), and a force = mg on a vertical frictionless surface (θ ...
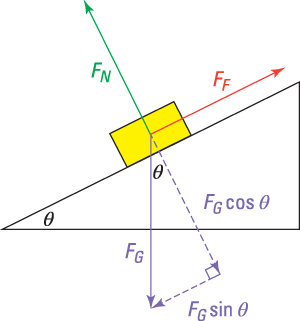
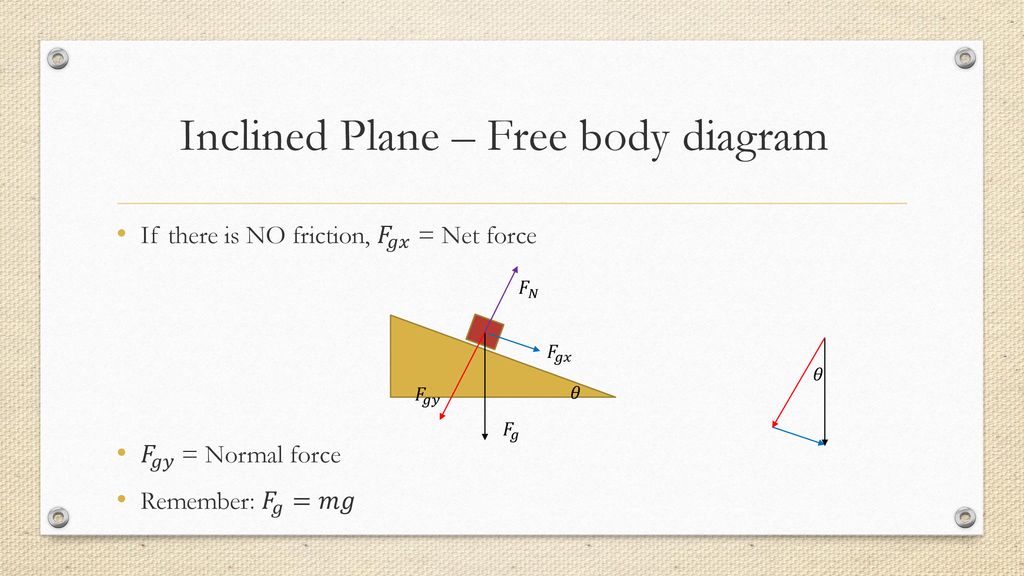
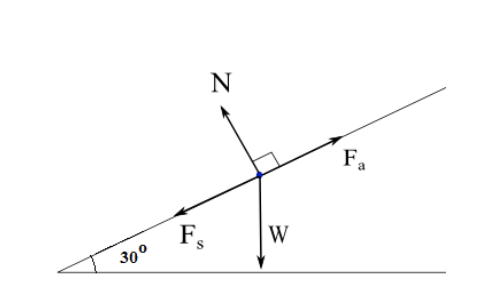
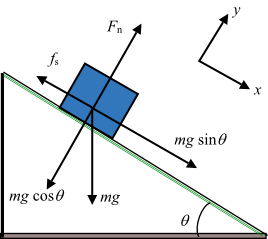
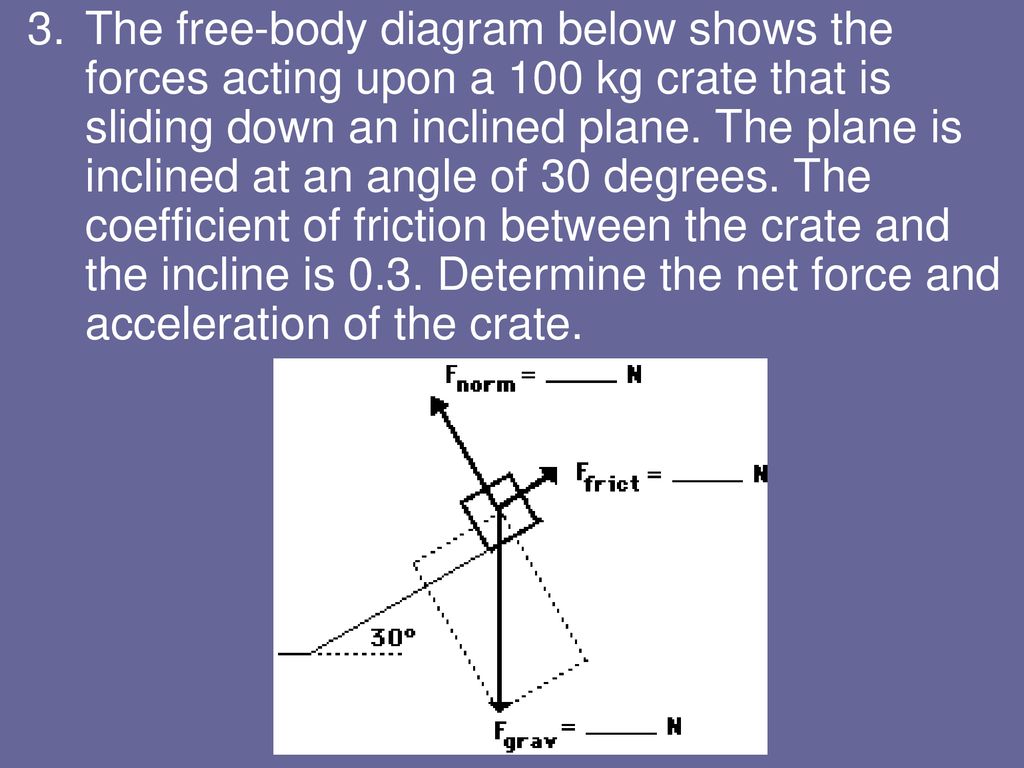
The first peculiarity of inclined plane problems is that the normal force is notdirected in the direction that we are accustomed to. Up to this point in the course, we have always seen normal forces acting in an upward direction, opposite the direction of the force of gravity. But this is only because the objects were always on horizontal surfaces and never upon inclined planes. The truth about normal forces is not that they are always upwards, but rather that they are always directed perpendicular to the surface that the object is on. Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in Figure. Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in the problem-solving strategy. Solution. We start by creating a diagram for the first object of interest. In Figure(a), object A is isolated (circled) and represented by a dot. You will learn how to draw free body diagrams (FBD) when a mass is attached to a string. You will also learn how to draw FBD in case of inclined plane systems The free-body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100-kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the incline is 0.3. Determine the net force and acceleration of the crate. Solution: The force of gravity in the given problem can be calculated as:
This java applet shows the free-body force diagram for a block sits on an inclined plane. Usage: Click the circle near the right edge and drag the mouse up/down to change the angle of inclination theta 。. 2. Red Arrow represents the gravitational force. ( which has two green force components). Carefully construct a free-body diagram showing all the forces acting on mass m 2. There are three forces acting on this mass -- the string exerts a force T , the (frictionless) inclined plane exerts a "normal" force n , and gravity pulls down with a force of w 1 = m 1 g. Free Body Diagram Examples. The free-body diagram allows the application of Newton's laws and, with them, determines the state of motion or the rest of the object on which the forces act. ... A block that slides on an inclined plane. Some tables have a slightly slanted table for easy note-taking and reading. ... -For mass 1 (increase): [Free body diagram. Wikipedia] The free-body diagram example was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Physics solution from the Science and Education area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Free Body Diagram On An Inclined Plane

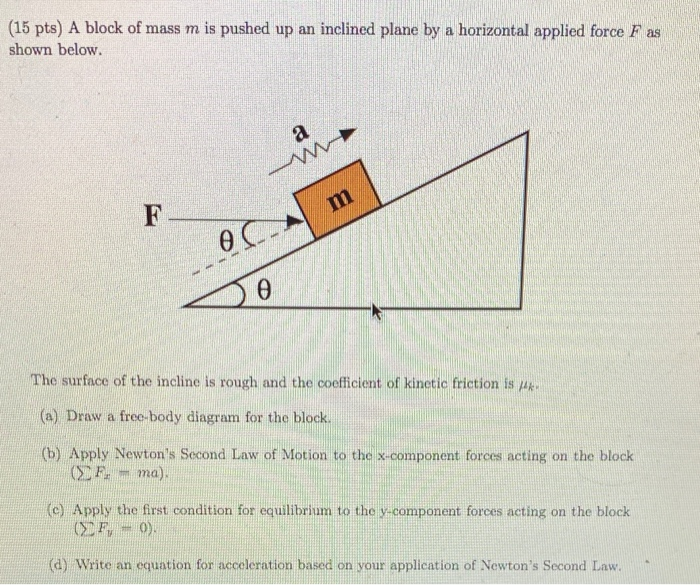
A Box Of Mass M 20kg Is To Be Pushed Up The Inclined Plane By A Horizontal Force F At Constant Speed Of K 0 2 Find The Work Done On The Box By
The torque from is the cross product of the radius vector with. A free body diagram is a picture showing the forces that act on a body. Draw a fbd of the 1000 lb weight. Physicslab Freebody Diagrams 4 Free Body Diagram Inclined Plane Pulley Luxury Free Body Diagram For Solved Load P Is 800n Draw A Free Body Diagram Of Pulley
Homework Statement. For the maximum angle for which you have data draw a free body diagram and explain how the forces add to give the resultant (net) force and show the calculations required to determine the acceleration. The lab was about using Galileo's inclined plane to measure acceleration due to gravity. We rolled the cart down the incline ...
A system with two blocks an inclined plane and a pulley a free body diagram for block m 1 left of figure below 1 the weight w 1 exerted by the earth on the box. 2 the normal force n 3 the force of friction f. 4 Free Body Diagram For Block With Mass M On Inclined Plane Under.
Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in Figure 5.32. Strategy We follow the four steps listed in the problem-solving strategy. Solution We start by creating a diagram for the first object of interest. In Figure 5.32(a), object A is isolated (circled) and represented by a dot.
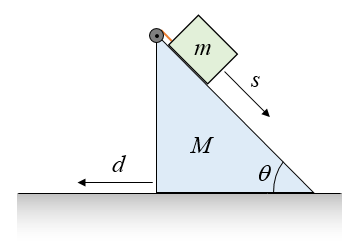
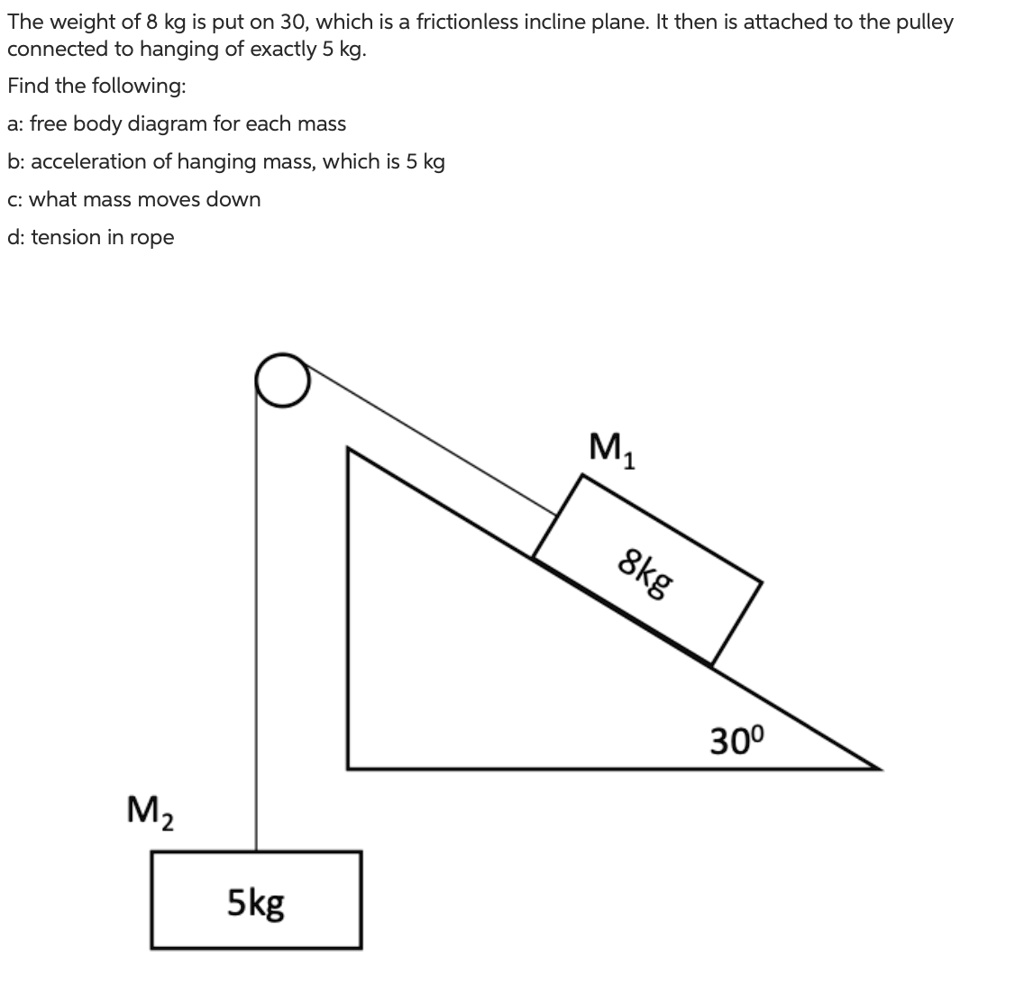
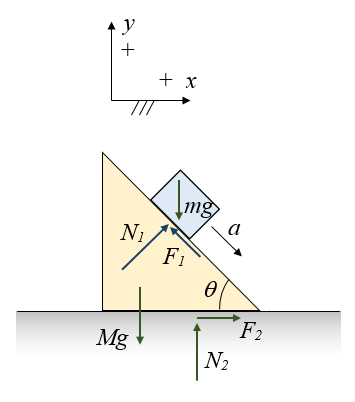
Example 8 : A system with two blocks, an inclined plane and a pulley. A) free body diagram for block m 1 (left of figure below) 1) The weight W1 exerted by the earth on the box. 2) The normal force N. 3) The force of friction Fk. 4) The tension force T exerted by the string on the block m1. B) free body diagram of block m 2 (right of figure below)
An inclined plane is basically a ramp. It is a flat surface that is sloped rather than horizontal. When ... Rotated free body diagram ... 9. A boy and his sled have a combined mass of 65 kg. What is their
The figure below shows the free-body diagram of a block resting on a rough inclined plane. b) From the free body diagram, we can compare the vertical forces acting on the block, and get the ...
Free-Body Diagrams for Inclined Planes. The Free-Body Diagrams for Inclined Planes Concept Builder challenges a learner to utilize an understanding of force types in order to construct a free-body diagram for an object moving along an inclined plane. Learners select force arrows from an arrow bank and label the arrows with a force type.
Solution. Figure 11.7 A solid cylinder rolls down an inclined plane from rest and undergoes slipping. The coordinate system has x in the direction down the inclined plane and y upward perpendicular to the plane. The free-body diagram shows the normal force, kinetic friction force, and the components of the weight.
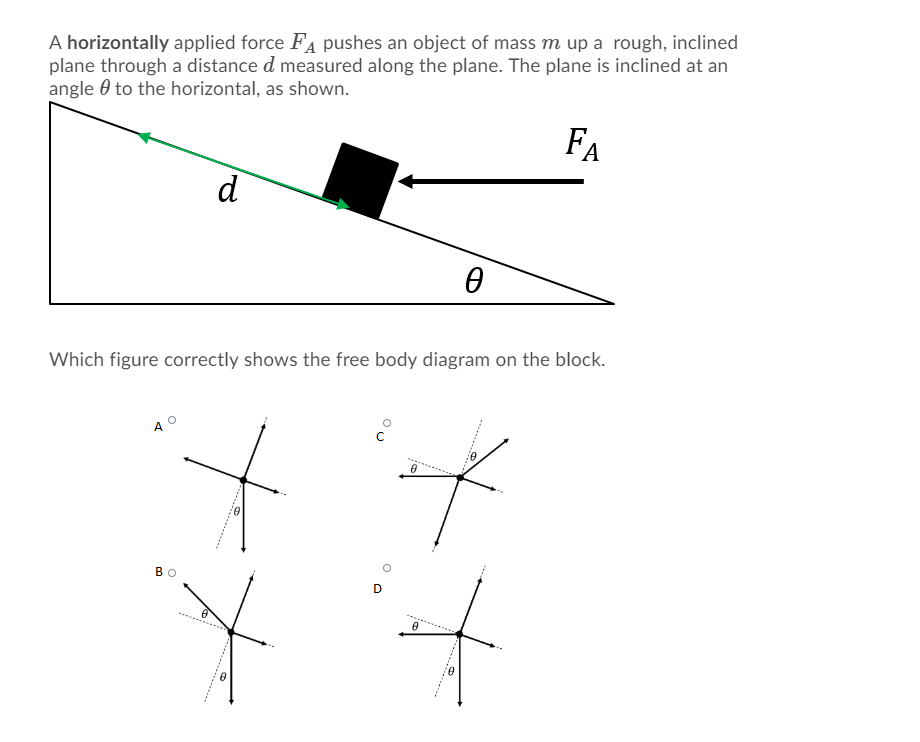
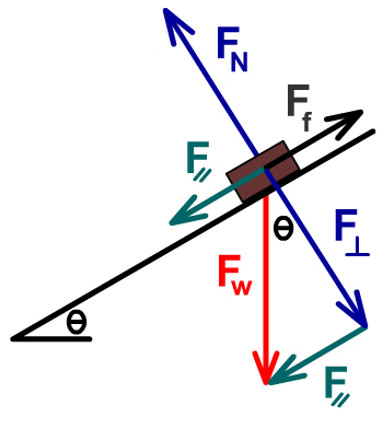
Examples of drawing free-body diagrams. To better understand how to draw free-body diagrams using the 3 steps, let's go through several examples. Example 1. A box is pushed up an incline with friction which makes an angle of 20 ° with the horizontal. Let's draw the free-body diagram of the box. The first step is to sketch what is happening:

In The Figure The Block Of Mass M Is At Rest On An Inclined Plane That Makes An Angle Theta With The Horizontal Draw A Free Body Diagram For The Mass The Force
The free body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100 kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. Bantz explains how to construct a free body force diagram and determine the magnitude and direction of all forces acting on box sitting on an. Gravitys downward force and the corresponding translated downhill force parallel to the surface.
A box of mass M = 10 Kg rests on a 35° inclined plane with the horizontal. A string is used to keep the box in equilibrium. The string makes an angle of 25 ° with the inclined plane. The coefficient of friction between the box and the inclined plane is 0.3. a) Draw a Free Body Diagram including all forces acting on the particle with their labels.
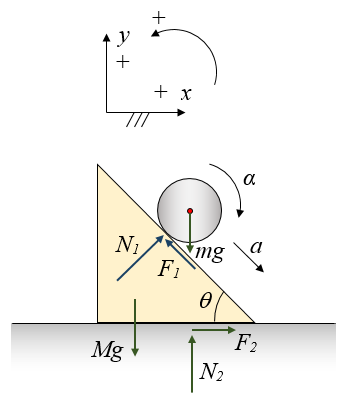
(5). How does mass M move if there is no friction (f = 0)? Draw free-body diagram for mass M with 4 vectors Mg, m_1g, N, and f. (Pay attention to the given x-direction.) If there is no friction, the mass M will move up, move down, or stay at rest on the inclined plane. Draw the free-body diagram for mass M with the same 4 vectors.
A free-body diagram for a ball resting on the ground: Gravity is acting downward. The ball is at rest. The ground must exert a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction on the ball. This force is called the normal force, n, since it is normal to the surface. Example: A free-body diagram for a mass on an inclined plane: Gravity acts ...
A Block Of Mass M Is Placed At Rest On An Inclined Plane Of Inclination Theta To The Horizontal If The Coefficient Of Friction Between The Block And The Plane Is Mew
Two Blocks on an Inclined Plane. Construct the free-body diagram for object A and object B in . Strategy. We follow the four steps listed in the problem-solving strategy. Solution. We start by creating a diagram for the first object of interest. In (a), object A is isolated (circled) and represented by a dot.
PhysicsLAB: Freebody Diagrams. In each case, a rock is acted on by one or more forces. On a sheet of paper, draw an accurate vector diagram showing all forces acting on the rock, and no other forces. Use a ruler, and do it in pencil so you can correct mistakes. Refer to the following information for the next two questions.















0 Response to "40 free body diagram mass on inclined plane"
Post a Comment