40 diagram that predicts the outcomes of a genetic cross
Inheritance is the process of passing genetic information to offspring. Genes are sections of DNA that code for a protein. Inheritance of genes can be shown in Punnett square diagrams. GENETICS Punnett square The Punnett square is a diagram that is used to predict an outcome of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It is named after Reginald C. Punnet, who devised the approach.The diagram is used by biologists to determine the probability of an offspring having a particular genotype.The Punnet square is a tabular summary of possible combinations of maternal allele 's ...
A diagram used to predict the outcomes of a genetic cross: answer choices ... Pedigree. Venn diagram. Tags: Question 7 . SURVEY . 60 seconds . Q. The allele that is not expressed when the dominant corresponding allele is present: answer choices . dominant. heterozygous. recessive.

Diagram that predicts the outcomes of a genetic cross
The Punnett square is a square diagram that is used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It is named after Reginald C. Punnett, who devised the approach in 1905. The diagram is used by biologists to determine the probability of an offspring having a particular genotype.The Punnett square is a tabular summary of possible combinations of maternal alleles with ... A monohybrid cross involves the crossing of individuals and the examination of a single character (flower color [Figure 1] OR seed color OR pod shape, etc.) in their offspring. The Punnett square is a useful tool for predicting the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in a genetic cross involving Mendelian traits. Constructing a Punnett square is quite easy, as shown in the Web sites below. diagram used by biologists to predict the outcome of a genetic cross: heterozygous: refers to an individual with two Different alleles for a trait: co-dominance: condition in which both alleles for a gene are expressed when present: homozygous: refers to an individual with two alleles that are the same for a trait: allele: an alternative form ...
Diagram that predicts the outcomes of a genetic cross. The phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9:3:3:1. ... A diagram that predicts the expected outcome of a genetic cross by considering all combinations of gametes in the cross. ... Laws of probability help explain genetic events. Normal fruit flies have brownish-yellow bodies, and this body color is dominant. A mutation in the gene for body color can produce flies with an ebony body color. A homozygous normal fruit fly (EE) is crossed with a homozygous ebony fruit fly (ee). What is the predicted outcome of this genetic cross? The genetic makeup of the flower is _____. answer choices . homozygous dominant. heterozygous. pink. homozygous recessive. Tags: Question 16 . SURVEY . 60 seconds . Q. A diagram used to predict an outcome of a cross or breeding experiment. answer choices . pedigree. Punnet Square. Tags: Question 17 . SURVEY . 60 seconds . Q. In this example ... Which of the following diagrams is used to predict the genotypic and phenotypic outcome of a cross? a. Pedigree b. Testcross c. Punnett square
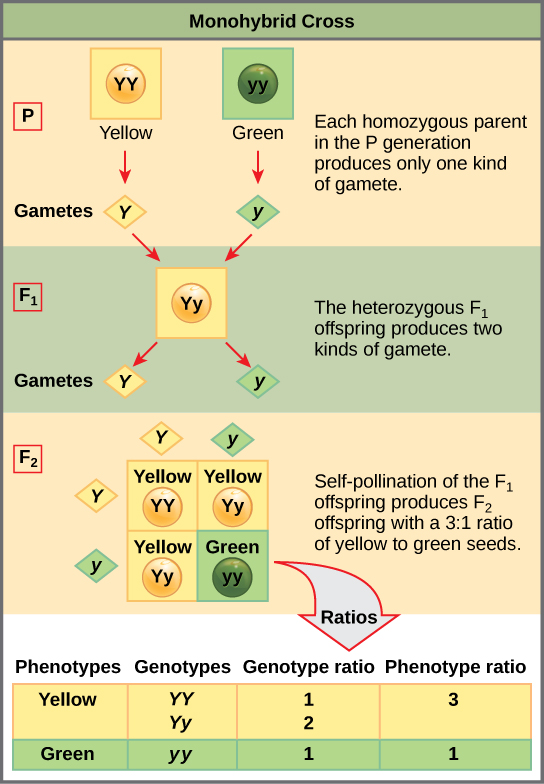
Carrying out a genetic cross Monohybrid crosses. Genetic crosses of single gene combinations (monohybrid inheritance) can be shown and examined using Punnett squares. Diagram used to predict the outcome of a cross. Genotype. Genetic makeup of an individual. Phenotype. Physical expression of genes. ... Diagram used to study the inheritance of traits in a family. Type A. ... Genotypic ratio of a heterozygote cross. 3 green:1 yellow. Phenotypic ratio of a heterozygote cross. Gene. One set of instructions (on ... diagram that predicts the outcome of a genetic cross by considering all possible combinations of gametes in that cross. Nice work! You just studied 5 terms! Now up your study game with Learn mode. A true-breeding, dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one, and the F1 offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted outcome of the F2 is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in the figure, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to each box within the square.
the heterozygous offspring of a cross or mating between two individuals that breed true for different forms of a trait. ... diagram used to predict the genetic and phenotypic outcome of a cross. ... effect in which the full and separate phenotypic effects of two alleles are apparent in heterozygous individuals. epistasis. How are the principles of probability used to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses? Whenever Mendel performed a cross with pea plants, he carefully categorized and counted the many offspring. Punnett Squares Punnett squares are a useful tool for predicting what the offspring will look like when mating plants or animals. Reginald Crundall Punnett, a mathematician, came up with these in 1905, long after Mendel's experiments. Let's take a look at how Punnet squares work using the yellow and green peas example from Mendel's garden experiments. The Punnett square is a diagram that is used to predict an outcome of a particular cross or breeding experiment. Many biologists and breeders use this method to determine the probability of the progeny (offspring) having a particular genotype.
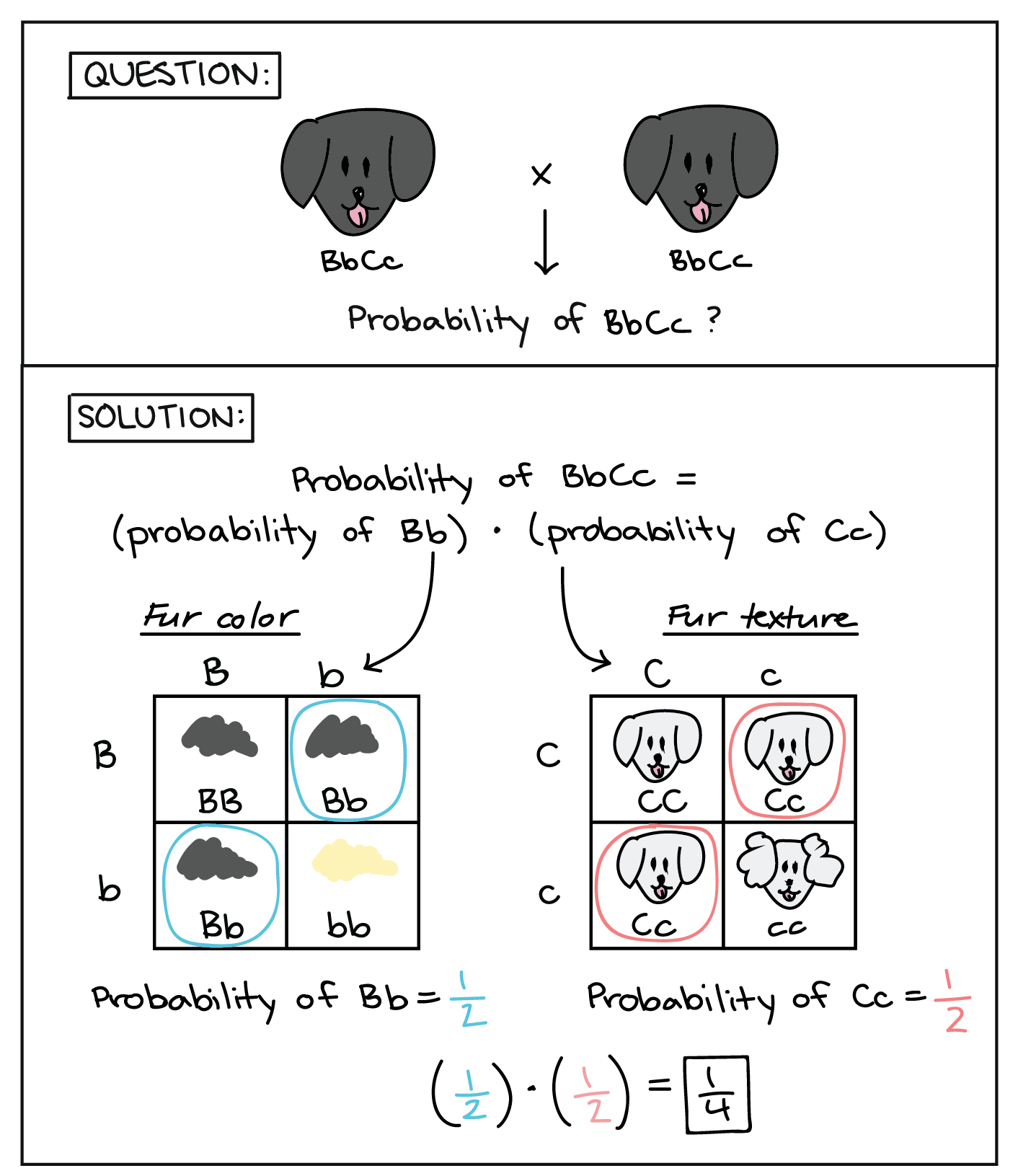
Punnett squares are used for prediction of the genetic probability of a specific phenotype, which arises in a couple's offspring. Punnett squares measure the probability or likelihood of a genetic outcome based on a specific genetic cross. If inheritance is random, math can be applied and the diagram used to predict both possible .
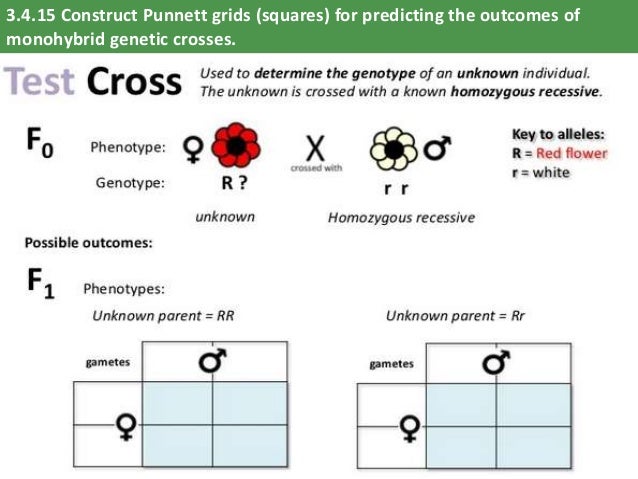
Apply a test cross to determine the genotype of an organism with a dominant phenotype. Predict the results of monohybrid genetic crosses by using probabilities. Analyze a simple pedigree. Punnett Squares A Punnett square is a diagram that predicts the outcome of a genetic cross by considering all possible combinations of gametes in the cross.
A monohybrid cross involves the crossing of individuals and the examination of a single character (flower color or seed color or pod shape, etc.) in their offspring. The Punnett square is a useful tool for predicting the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in a genetic cross involving Mendelian traits. Constructing a Punnett square is quite easy, as demonstrated by the Web sites below.
outcome of a genetic cross but we can predict the possible outcomes using probability •The best ways to predict the outcome of a genetic cross is to use a diagram known as a Punnett Square . How to Punnett Square 1. Write the genotypes that will serve at the parents of the cross 2. Determine what alleles would be found in all possible gametes

Genetics Inheritance Of Characteristics Dominant Recessive Genes Alleles Homozygous Heterozygous Genotype Phenotype Gene Expression Monohybrid Genetic Diagram Punnett Square Mendel Pea Plants Cystic Fibrosis Sickle Cell Disease Anaemia Igcse O Level
The Punnett square is a diagram that is used to predict an outcome of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It is named after Reginald C. Punnett, who devised the approach to determine the probability of an offspring's having a particular genotype (combination of alleles). Dominance in genetics is a relationship between alleles of
Monohybrid crosses. A monohybrid cross is the study of the inheritance of one characteristic. In the genetic diagrams for these crosses: the recessive allele. is represented by a lower case letter
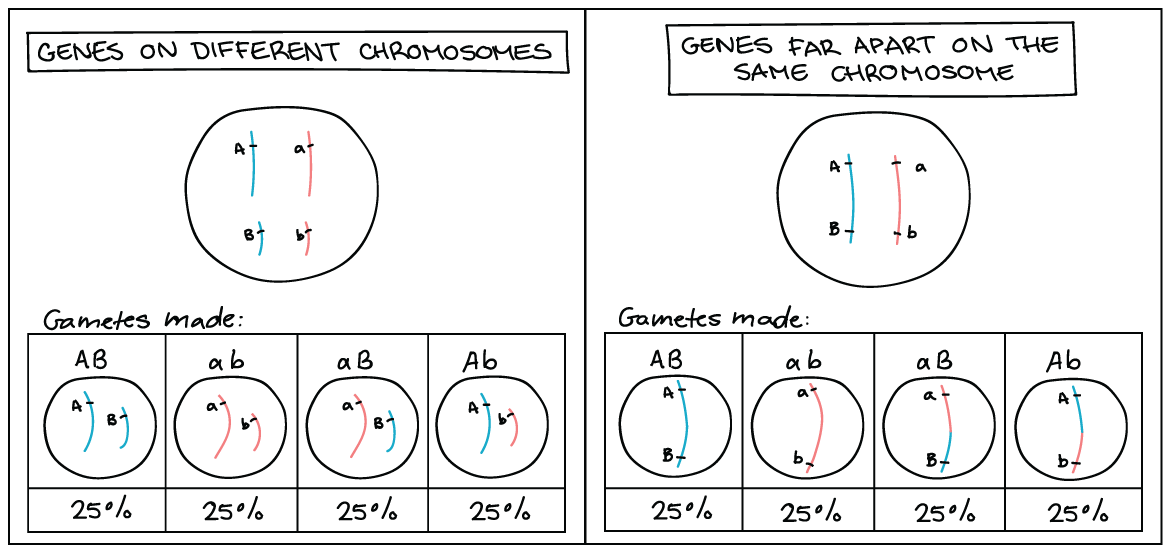
Patterns of inheritance are explained by using genetic diagrams. The results of genetic crosses are analysed statistically using the chisquared test. Studies of human genetic conditions have revealed the links between genes, enzymes and the phenotype. a) explain the terms gene, locus, allele, dominant, recessive, codominant, linkage, test cross ...
Genotype. The genetic makeup of an organism as indicated by its set of alleles. Test Cross. A genetic cross of an individual whose phenotype. Probability. The likelihood that a specific event will occur. Phenotype. Observable characteristics of an organism. Punnet Square.
This cross produced the ear of genetic corn shown at the top of this page. Table I is essentially a genetic checkboard called a Punnett square after R.C Punnett, a colleague of William Bateson who devised this method. In 1900, English Geneticist William Bateson had Gregor Mendel's original 1865 paper on the genetics of garden peas translated ...
The punnett square for a monohybrid cross tracks the. 07.11.2021 · they are useful as they can predict the genetic probability of a particular phenotype arising in a couple's offspring. 22.10.2021 · punnett squares are useful in genetics to diagram possible genotypes of the offspring of two organisms.
A punnet square is a diagram showing the gene combination that might result from a genetic cross and it can be bigger than 2x2A diagram that is used to predict an outcome of a particular cross or ...
Mendelian Genetics Biology En Genetics Heredity Mendel Mendelian Punnet Squares Science Glogster Edu Interactive Multimedia Posters
diagram used by biologists to predict the outcome of a genetic cross: heterozygous: refers to an individual with two Different alleles for a trait: co-dominance: condition in which both alleles for a gene are expressed when present: homozygous: refers to an individual with two alleles that are the same for a trait: allele: an alternative form ...
A monohybrid cross involves the crossing of individuals and the examination of a single character (flower color [Figure 1] OR seed color OR pod shape, etc.) in their offspring. The Punnett square is a useful tool for predicting the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in a genetic cross involving Mendelian traits. Constructing a Punnett square is quite easy, as shown in the Web sites below.
The Punnett square is a square diagram that is used to predict the genotypes of a particular cross or breeding experiment. It is named after Reginald C. Punnett, who devised the approach in 1905. The diagram is used by biologists to determine the probability of an offspring having a particular genotype.The Punnett square is a tabular summary of possible combinations of maternal alleles with ...

Do Now True Or False 1 Certain Acquired Characteristics Such As Mechanical Or Mathematical Skill May Be Inherited 2 Color Blindness Is More Common Ppt Download
Punnett And His Square Segregation Of Genes The Plant Breeder S Method Of Predicting The Future Passel
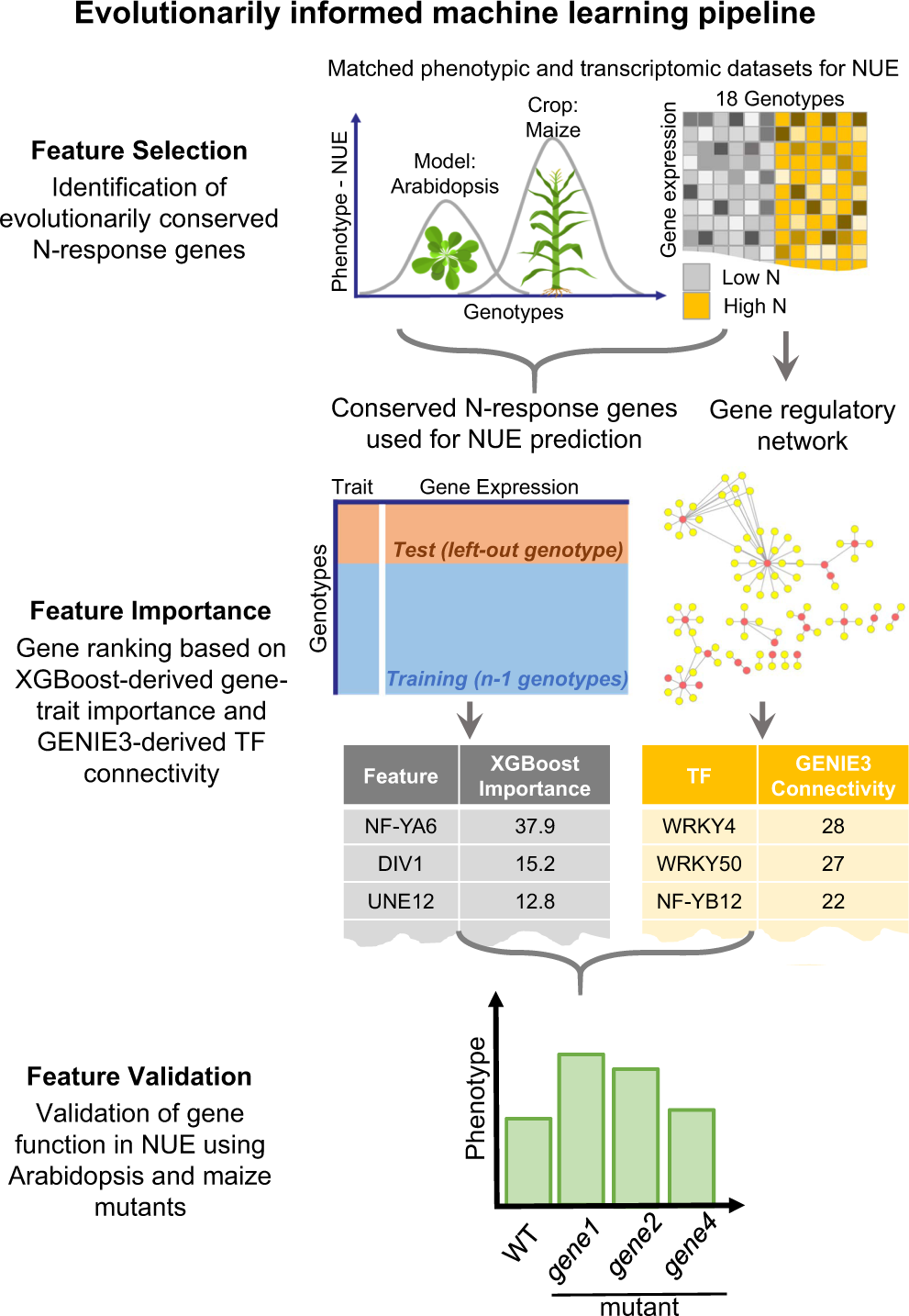
Evolutionarily Informed Machine Learning Enhances The Power Of Predictive Gene To Phenotype Relationships Nature Communications

3 4 Inheritance The Patterns That Genes And The Phenotypes They Generate Can Be Mapped Using Pedigree Charts The Image Show A Small Section Of A Pedigree Ppt Download

What Is A Punnett Square And Why Is It Useful In Genetics Using Punnett Squares To Calculate Phenotypic Probabilities 6 Steps With Pictures Instructables It Can Also Be Used To
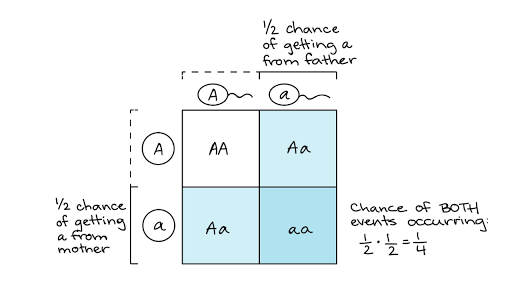
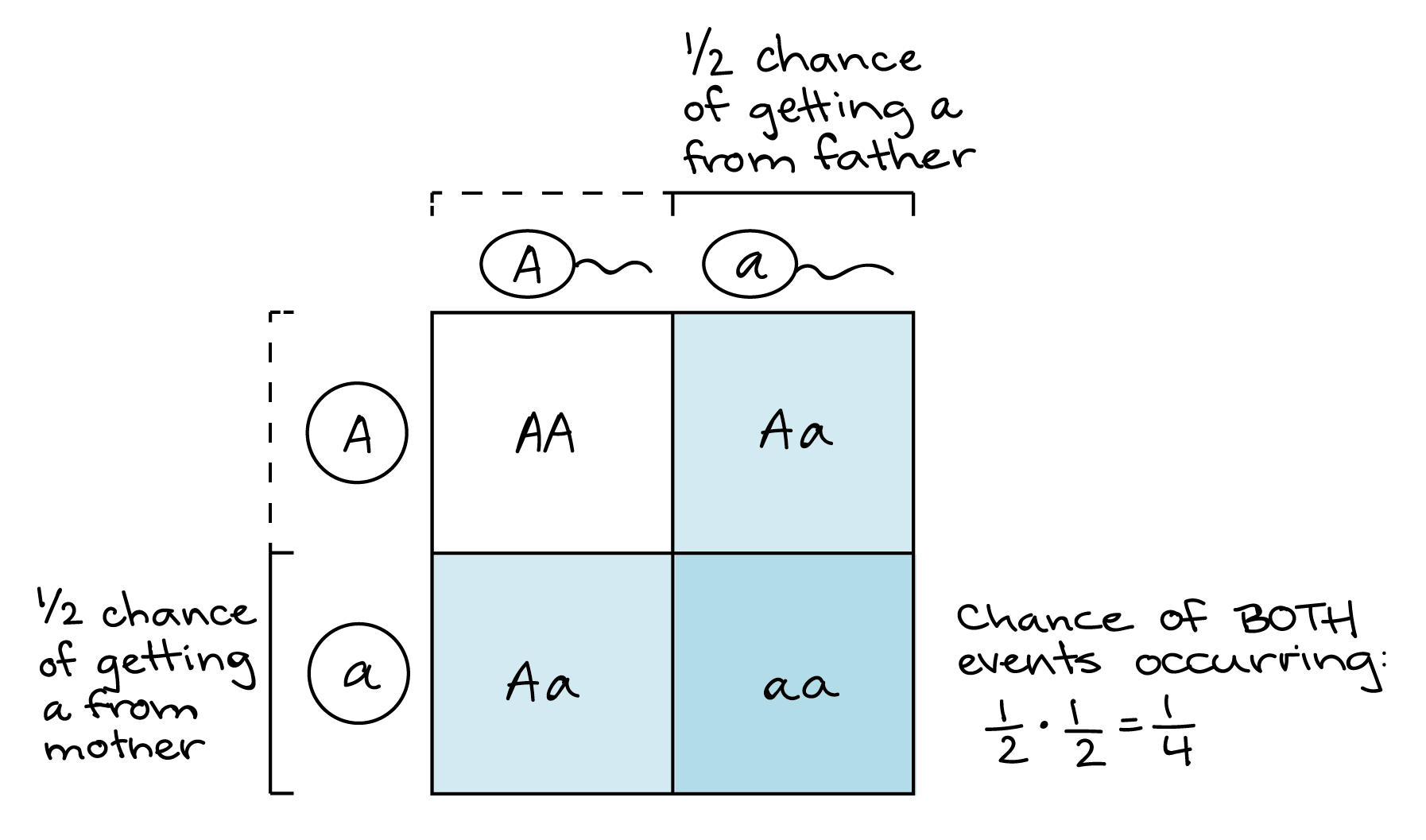





/monohybrid_cross-58d567715f9b5846830d0d91.jpg)



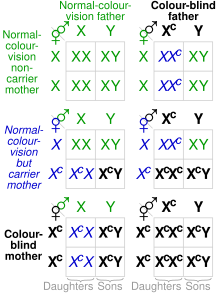



/genetic-crosses-56e97ae13df78c5ba057ca68.jpg)




0 Response to "40 diagram that predicts the outcomes of a genetic cross"
Post a Comment