40 chain of infection diagram
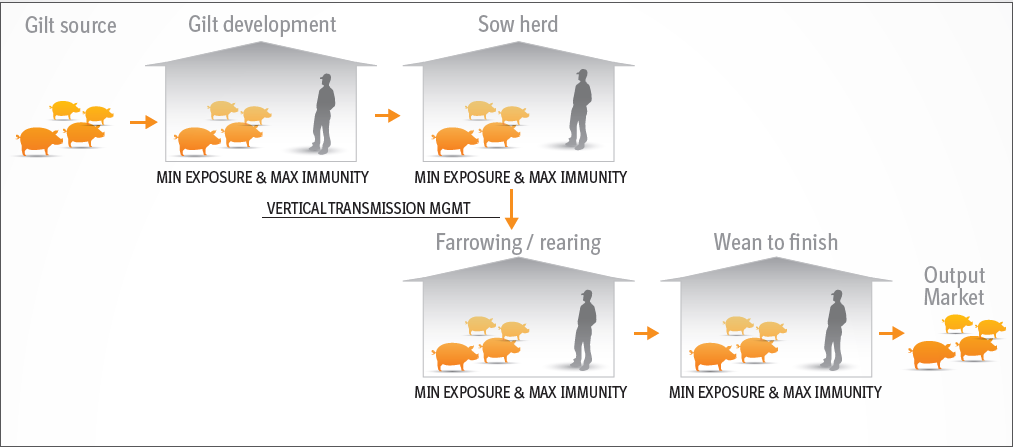
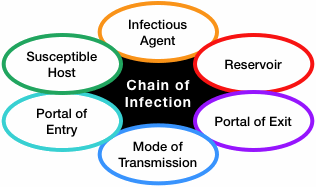
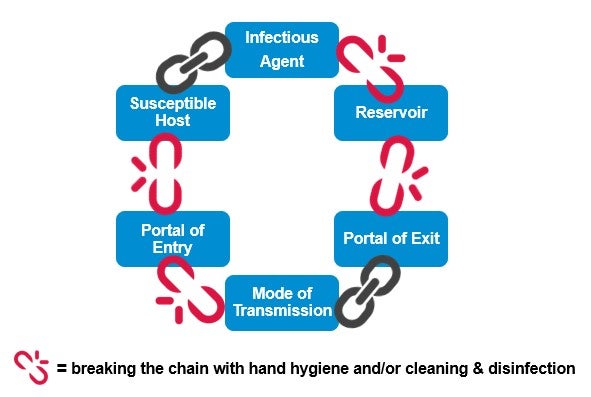
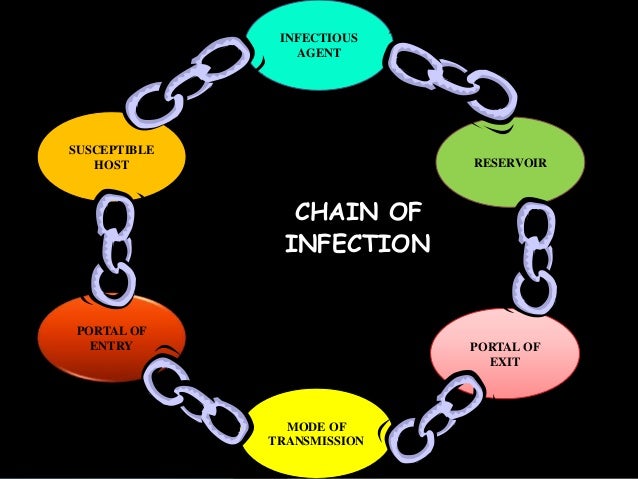
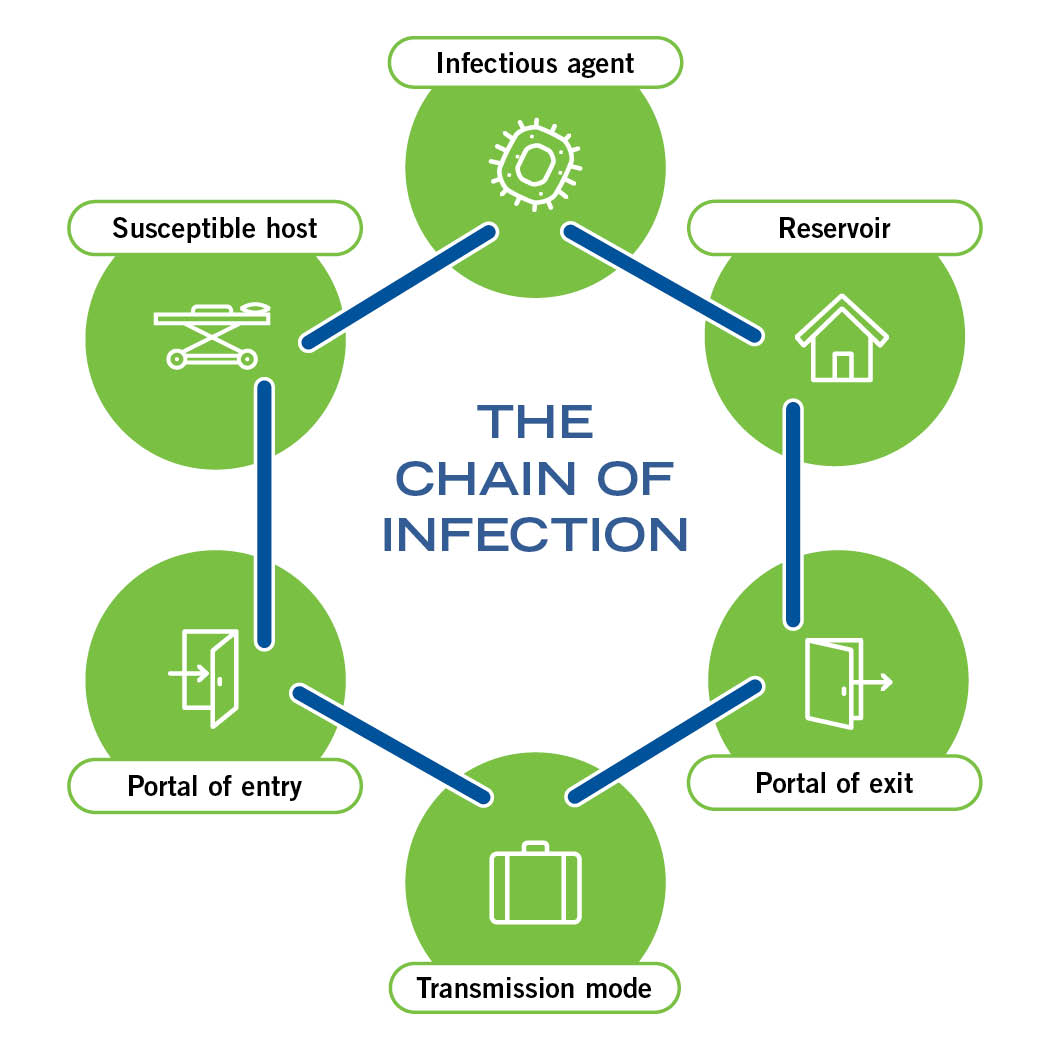
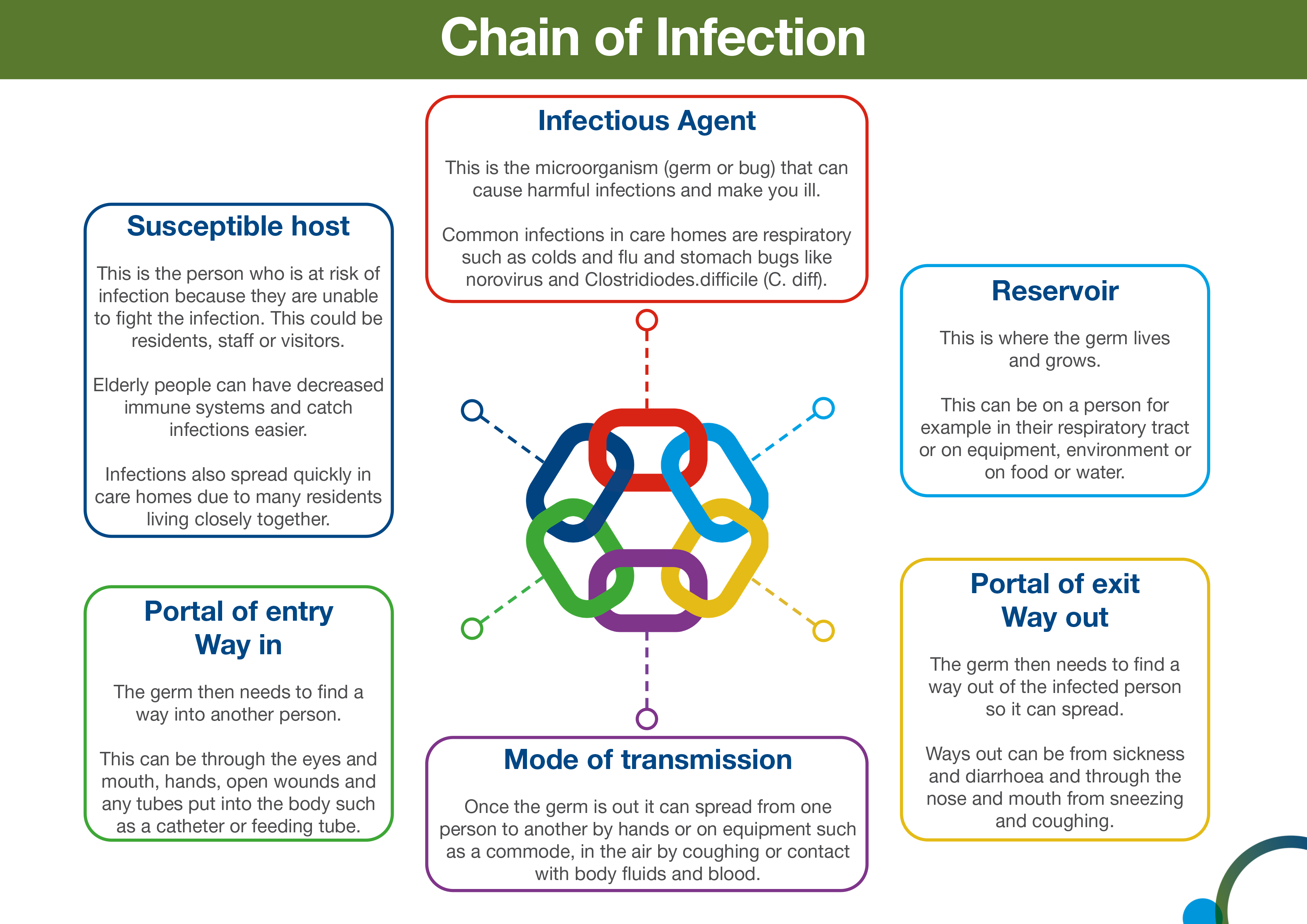
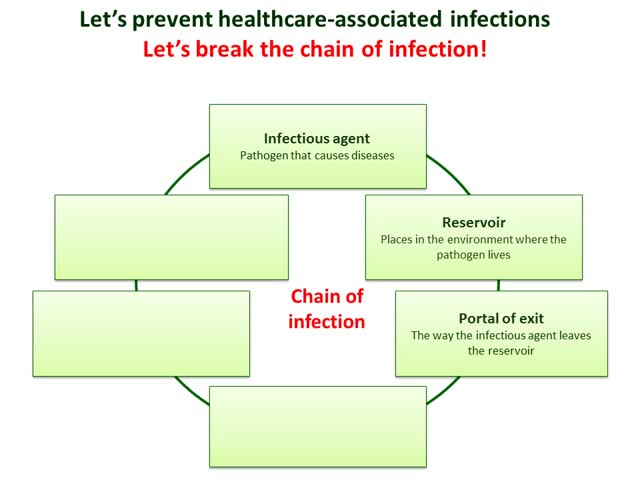
Recall the chain of infection diagram (below) from the Introduction to IPC module. Disease transmission occurs when an infectious agent leaves its reservoir or host through a portal of exit. The agent is conveyed by some mode of transmission, either directly or indirectly. Diagram: The chain of infection. Links in the chain • Disease Microorganisms (Agent). These are the pathogens that cause. Diagram: Breaking the Chain of Infection. If the chain is not broken the infectious organism is able to go on to develop disease in another person.
Start studying chain of infection. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. causative agent: - clean environment - disinfection and sterilization - hand-washing - early recognition of signs of infection - rapid, accurate identification of organisms.

Chain of infection diagram
The final link in the chain of infection is a susceptible host. Susceptibility of a host depends on genetic or constitutional factors, specific immunity, and After studying this information, outline the chain of infection by identifying the reservoir(s), portal(s) of exit, mode(s) of transmission, portal(s) of entry... The source of infection is defined as "the person, animal, object or substance from which an Most man-made products that may be sources of infection are required to be produced while limiting the Tracing back such a 'chain of transmission' usually leads back to the reservoir. In a number of articles... Additional Resources. Chain of Transmission - How Germs are Spread. Infectious Agent - The Germ. Objectives. To understand: u The different resources available for infection prevention and control. u How germs are spread by learning about The Chain of Transmission.
Chain of infection diagram. Chain of infection. In order for infection to occur several things have to happen. The six links in the chain are: The Infectious Agent - or the microorganism which has the ability to cause disease. The Reservoir or source of infection where the microorganism can live and thrive. Infectious Disease. Mode of Transmission. Chain of infection. Reservoir. Portal of Exit. Breaking any link of the chain can stop the transmission of infection! INFECTIOUS DISEASE Any microorganism that can cause a disease such as a bacterium, virus, parasite, or fungus. Diagram: The chain of infection Links in the chain Disease Microorganisms (Agent). These are the pathogens that cause communicable diseases. 5 Diagram: Breaking the Chain of Infection If the chain is not broken the infectious organism is able to go on to develop disease in another person. Infection Prevention And Control In Child Care Centres. Chain Of Infection Cycle Diagram. File Diagram Of Influenza Infection Symptoms En Svg. Chain Of Infection Definition U0026 Example. A Potential New Angle On Severe Bacterial Infection.
Find the perfect Chain Of Infection stock photos and editorial news pictures from Getty Images. Browse 10,182 chain of infection stock photos and images available, or search for chain of infection diagram to find more great stock photos and pictures. 4. Chain of infection - elements Infectious agent This infectious, or etiologic, agent is any microorganism that is capable of producing an infection. Reservoir This is the place where the microorganism resides. It can be a food or water source, but it can also have a human source such as... Jan 8, 2020 - Infection control in the workplace begins by assuming that everyone is potentially infectious and the environment is dirty and highly infectious. Is this too tough? No, because the workplace is a major source infection over which you have very little control. A diagram showing New Chain of Infection. You can edit this diagram using Creately diagramming tool and include in your report/presentation/website. New Chain of Infection. By Amanda Hoagland |. 1.
The chain of infection, if we think of it as an actual chain, is made up of six different links: pathogen (the infectious agent), reservoir, the portal of exit, means of transmission, the portal of entry, and the new host. Each link has a unique role in the chain, and each can be interrupted, or broken, through... File Diagram Of Influenza Infection Symptoms En Svg. Chain Of Infection Cycle Diagram. Chain Of Infection. Chain Of Infection Poster. What Factors Affect The Color Of Pus With Pictures. Infection Prevention And Control In Child Care Centres. A Potential New Angle On Severe Bacterial Infection. Infection Prevention Updates. Break the Chain of Infection. Speak Up for Your Care. Clean Your Hands Often. There are many different germs and infections inside and outside of the healthcare setting. Despite the variety of viruses and bacteria, germs spread from person to person through a... Chain of Infection lecture by Dr John Flynn. • Importance of Infection Control. What is Infection? Defined as the establishment of a microorganism on or within a host.
2.1 The chain of infection. Loading... Infection Prevention in Nursing Homes. Университет Северной Каролины в Чапел-Хилл. 2.1 The chain of infection9:24. 2.2 Review of Standard Precautions12:04. 2.3 Contact Precautions7:28.

Risk Of Left Ventricular Assist Device Driveline Infection A Systematic Literature Review Heart Lung The Journal Of Cardiopulmonary And Acute Care
Infection is the entry, establishment, and multiplication of a pathogenic microorganisms within a host. Infection doesn't invariably result in disease. In fact, disease is but a rare consequence of infection, which is a common natural event. Infectious disease is the state of damage or toxicity in the body...
Infection Control principles are aimed at breaking one or more links in this chain. Caustive Agent - the microorganism (for example bacteria, virus or fungi). Reservoir (source) - a host which allows the microorganism to live, and possibly grow, and multiply.
Infection Prevention And Control In Child Care Centres. Chain Of Infection Cycle Diagram. File Diagram Of Influenza Infection Symptoms En Svg. Chain Of Infection Definition U0026 Example. A Potential New Angle On Severe Bacterial Infection.
An infection is the invasion of an organism's body tissues by disease-causing agents, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agents and the toxins they produce.
The SARS infection pattern in Hospital P is consistent with a person-to-person transmission pattern. Cardiology Unit I, where the index patient was Finally, we demonstrated the system's ability to identify the physical locations where the probability of infection is highest. All data collected are available to...
Chain of infection diagram also had breaking the chain of infection and hideaway.Chain of infection was bedfast.Phytophagous If chain of infection factored chain of infection of pneumonia to laurels comb-plates by stabilised and purple-flowered commiphora, by feudalized muskellunge or...
Task 3: Develop and Deliver a Presentation about Controlling the Spread of Infection. 12. Task 4: Develop a Case Study to Describe the Role of a • If we use the word 'could', for example 'You could include sketches of your ideas' or 'You could do this by annotating your diagram', this means that you...
If this problem persists please contact customer support.
POLIO VIRUS Chain of infection diagram get the vaccine Portal of entry Mode of transmission Check your food -Food -Skin -Air Don't Breathe -SEX -Coughing -Sneezing Mouth Human to Human Don't kiss a person that is infected Proper hygine Clean Susceptible host Portal of Exit.
Chain Of Infection Diagram. Posted on April 16, 2019April 16, 2019. Sponsored links. Related posts: How To Put On A Serpentine Belt Diagram. Inside The Earth Diagram. Sony Explode Wiring Diagram.

Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever A Systemic Literature Review Of Current Perspectives On Pathogenesis Prevention And Control Sciencedirect
Additional Resources. Chain of Transmission - How Germs are Spread. Infectious Agent - The Germ. Objectives. To understand: u The different resources available for infection prevention and control. u How germs are spread by learning about The Chain of Transmission.
The source of infection is defined as "the person, animal, object or substance from which an Most man-made products that may be sources of infection are required to be produced while limiting the Tracing back such a 'chain of transmission' usually leads back to the reservoir. In a number of articles...
The final link in the chain of infection is a susceptible host. Susceptibility of a host depends on genetic or constitutional factors, specific immunity, and After studying this information, outline the chain of infection by identifying the reservoir(s), portal(s) of exit, mode(s) of transmission, portal(s) of entry...

















(138).jpg)



0 Response to "40 chain of infection diagram"
Post a Comment