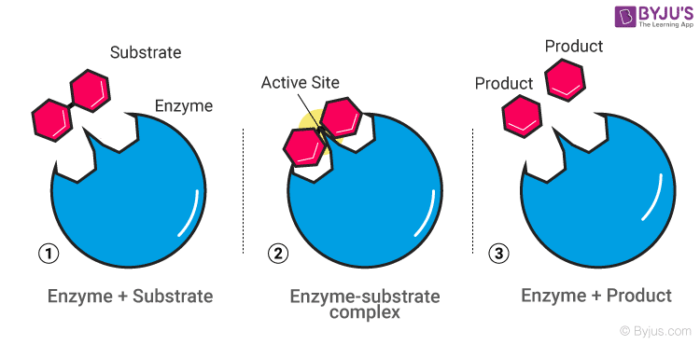
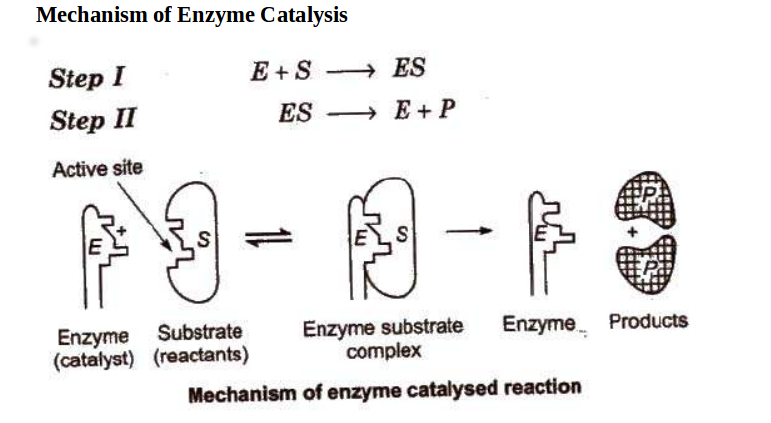
40 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
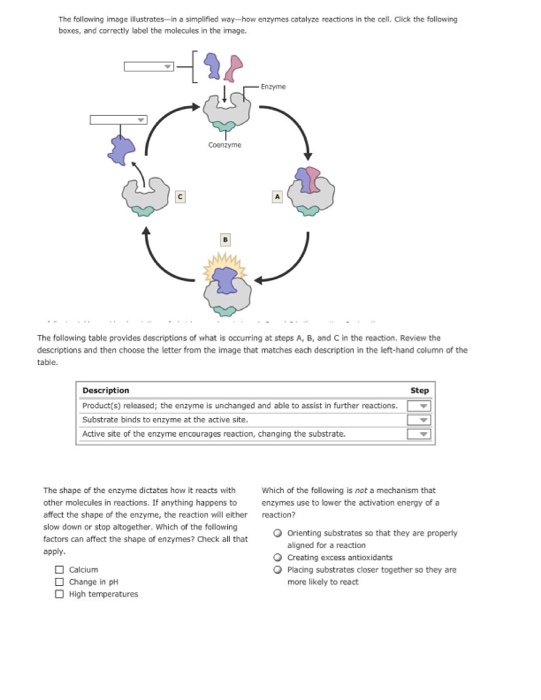
Question: Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P, ... The enzyme's role in the reaction is of biocatalyst. All the reactions, which can otherwise take place if provided with enzyme, simply increase their speed. Enzymes can speed up the reaction rate but they cannot force a reaction to take place. The mechanism involved in the reaction remains the same enzymes only speed up the process.
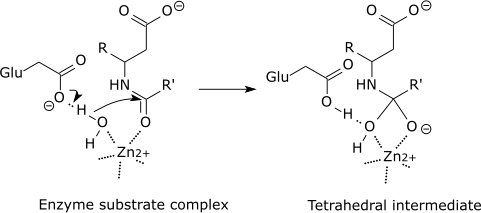
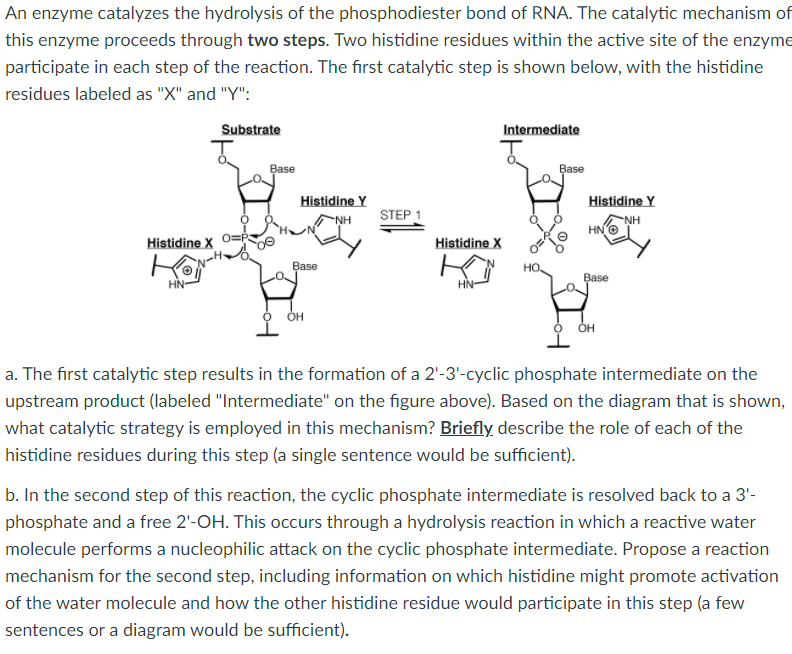
Catalytic Mechanism. In most cases, the hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond is catalyzed by two amino acid residues of the enzyme: a general acid (proton donor) and a nucleophile/base [].Depending on the spatial position of these catalytic residues, hydrolysis occurs via overall retention or overall inversion of the anomeric configuration.
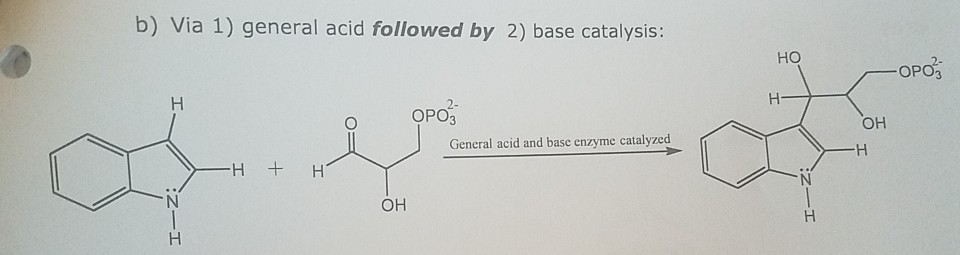
Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction
Enzyme Catalysis: Enzymes are Complex nitrogenous substances (proteins) with a high relative molar mass of the order of 10,000 or even more and are derived from living organisms. Specific reactions may be catalysed either by the microorganisms in bulk like yeast or by the chemical synthesis and extracted from them like yeast extract. Answers. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substrate binds to the enzyme to .... Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. Explain why ... The graph below shows the rate of enzyme activity in relation to pH for two .... This chemical aspect is supported by the well-studied mechanisms of the several enzymatic reactions. Consider the reaction of peptide bond hydrolysis catalyzed ...
Below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Unit 1 Chapter 3 (1st Secondary) Biology. . 1. The following graph shows the effect of altering a factor on the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction. What is shown on the x axis? 2. The following graph shows the effect of a factor on the activity of two enzymes.What are the enzymes (X) and (Y)? 3. Answer (1 of 4): Before moving to understand chemical reaction mechanism, we should understand general meaning of mechanism. General meaning of mechanism :- Typically mechanism means the way of happening something or course of action or work is called as mechanism of that action or work, mechan... Enzyme reactions utilizing [3H]Ins(1,4)P2 as a substrate were loaded onto 0.2 ml ... Enzyme catalyzed reactions and antibody enhanced hydrolysis reactions ... System exhibits a unique low conversion stable steady state corresponding to complete inhibition of the AChE catalyzed reaction by the substrate. A general procedure has been developed to model the behaviour of enzymatic reactions in a membrane bioreactor. The residues involved in substrate binding and enzyme reaction are shown in the model.
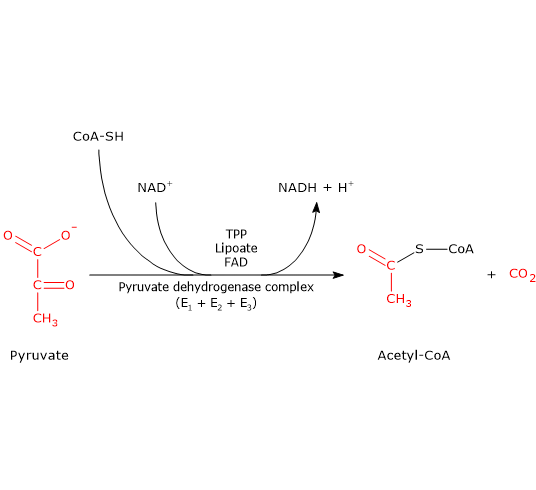
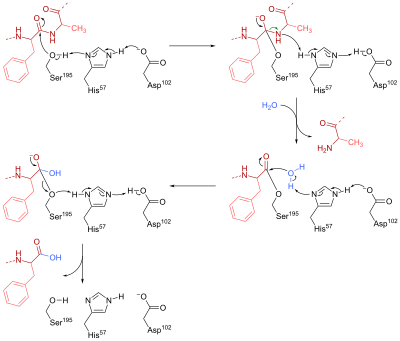
Induced-fit model - an offshoot of the earlier lock-and-key model; states that the substrate induces a change of shape in the enzyme. Lock and key model - theory proposed by Emil Fischer in 1894 ... Many enzymes catalyze reactions by this type of mechanism. Acetylcholinesterase is used as a specific example in the sequence described below. Glucose phosphorylation - In the initial phase, glucose is phosphorylated into glucose-6-phosphate, a usual reaction in glycolysis. It is catalyzed by glucokinase (liver) and hexokinase (muscle). Conversion of Glc-6-P to Glc-1-P - An enzyme Phosphoglucomutase will catalyze the conversion of Glucose-6-P is converted to Glc-1-Phosphate. Provide reasoning to support your claims based on the position of the PDC-catalyzed reaction in the sequence of the cellular ... is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction that converts a precursor of gibberellin to the active form of gibberellin. A ... Construct a diagram below to depict the four possible normal products of meiosis that would ...
Electron Transport Chain Definition. The Electron Transport System also called the Electron Transport Chain, is a chain of reactions that converts redox energy available from oxidation of NADH and FADH 2, into proton-motive force which is used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex through a process called oxidative phosphorylation. Given the oxygen dissociation curves, which of the following statements ... Complete the diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Gluconeogenesis refers to a group of metabolic reactions, some of them highly exergonic and irreversible, which are regulated both locally and globally (by insulin, glucagon, and cortisol). The purpose of this system, localized in both the cytosol and mitochondria, is to maintain blood glucose level constant throughout fasting state. The balance between stimulatory and inhibitory hormones ... This reaction is unique to gluconeogenesis and is the first of two steps required to bypass the irreversible reaction catalyzed by the glycolytic enzyme pyruvate kinase. In the cytosol, oxaloacetate is decarboxylated and rearranged to form phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) via the enzyme PEP carboxykinase.
During glycolysis, a single mole of 6-carbon glucose is broken down into two moles of 3-carbon pyruvate by a sequence of 10 enzyme-catalyzed sequential reactions. These reactions are grouped under 2 phases, phase I and II.
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C 6 H 12 O 6, into pyruvic acid, CH 3 COCOOH. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that does not require oxygen.
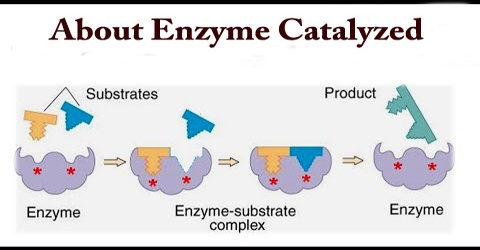
A chemical reaction mechanism with or without enzyme catalysis. The enzyme (E) binds substrate (S) to produce product (P). A two dimensional plot of substrate ...
Gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) with enzyme-like activities are useful glucose oxidase mimics, but the insights into the mechanism of this reaction are limited. Here, the authors show that the process ...
Label ΔH as positive or negative. Figure shows the energy level diagram for the reaction between methane and oxygen. Based on Figure, the following information can be obtained. (a) The reaction between methane and oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water is an exothermic reaction. (b) During the reaction, the temperature of the mixture increases.
Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, "biological machines" also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell.
What is the effect of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction? Effect of catalyst on the rate of reaction: A catalyst is a substance which can alter the rate of a chemical reaction while itself remains chemically unchanged at the end of the reaction. (a) Catalysts can be classified into positive catalysts and negative catalysts (inhibitors). (b) A positive catalystis a catalyst that increases the ...
Metabolism (/ m ə ˈ t æ b ə l ɪ z ə m /, from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms.The three main purposes of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the ...
Enzyme mechanisms; Multienzyme complexes ... undergo changes in bonding and hybridization during a single enzyme-catalyzed reaction 13,14 ... illustrating the general quality of the structure are ...
ATP synthase is the enzymes involved in the synthesis of energy. Enzymes are responsible for the movement of ions across the plasma membrane. Enzymes perform a number of biochemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, etc. to eliminate the non-nutritive substances from the body.
Transesterification reaction is where alcohol and ester react in the presence of an acid or a base to produce a new ester. Here, one ester is converted into another ester. An ester is a molecule that contains a carbonyl carbon, which has a double bond to oxygen. The double bond's oxygen is carbonyl oxygen. In this article, we will look into the ...
Feedback inhibition (in biology) is defined as the process in which the end product of a reaction inhibits or controls the action of the enzyme that helped produce it. In other words, the end products formed in the reaction actually get enzymes to slow down or stop making new products altogether.
This reaction is catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. It is the energy-yielding reaction. Reactions of this type in which an aldehyde group is oxidised to an acid are accompanied by liberation of large amounts of potentially useful energy. During this reaction, NAD+ is reduced to NADH. This is a reversible reaction.
Answer (1 of 2): Catalysts , substances that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change, by definition are not consumed during a reaction, Enzymes, biological catalysts, are usually more complex and may suffer damage during reaction and need ...
Enzyme-catalyzed reactions can be classified according to reactancy, ... reaction is depicted in the following diagram where E' indicates that the enzyme ...
This is known as the Michaelis-Menten mechanism. The potential energy diagram is shown in the figure. Which of the following sets of identifications is correct?
The upper and lower diagrams show faster reacting and slower reacting ... The descriptions below describe the major mechanisms enzymes use to catalyze ...
In eukaryotes, including fungi and animals, the highly conserved glycogen-debranching enzyme (GDE) debranches glycogen by a glucanotransferase (GT) reaction followed by a glucosidase (GC) reaction. Previous work indicated that these reactions are catalyzed by two active sites located more than 50 Å apart and provided insights into their ...
The simulation in water provides a reference to calibrate the EVB parameters (gas phase shift and coupling constant) and the mechanism for the reaction in enzyme. 3.5 The reaction profile catalyzed by LigI. Based on the insight from the reaction profile in water, we know that the proton transfer and the hydroxide attack mostly almost happens in ...
Solution for The diagram shows the mechanism of a general enzyme‑catalyzed reaction. Put the labels in the correct locations. The abbreviations E, P and S…
The corresponding diagram shows the induced fit model of an enzyme. In this case, the enzyme has a certain shape in its active site, which allows the substrate to enter. Once the substrate enters ...
This chemical aspect is supported by the well-studied mechanisms of the several enzymatic reactions. Consider the reaction of peptide bond hydrolysis catalyzed ...
Answers. In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substrate binds to the enzyme to .... Read each question, and write your answer in the space provided. Explain why ... The graph below shows the rate of enzyme activity in relation to pH for two ....

Electrostatic Origin Of The Catalytic Power Of Enzymes And The Role Of Preorganized Active Sites Journal Of Biological Chemistry
Enzyme Catalysis: Enzymes are Complex nitrogenous substances (proteins) with a high relative molar mass of the order of 10,000 or even more and are derived from living organisms. Specific reactions may be catalysed either by the microorganisms in bulk like yeast or by the chemical synthesis and extracted from them like yeast extract.




















0 Response to "40 below is a diagram of the mechanism of a general enzyme-catalyzed reaction"
Post a Comment