38 orbital diagram for ni
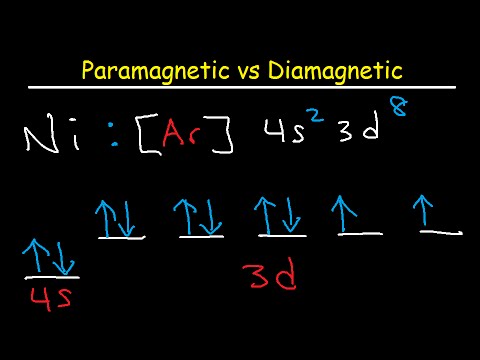
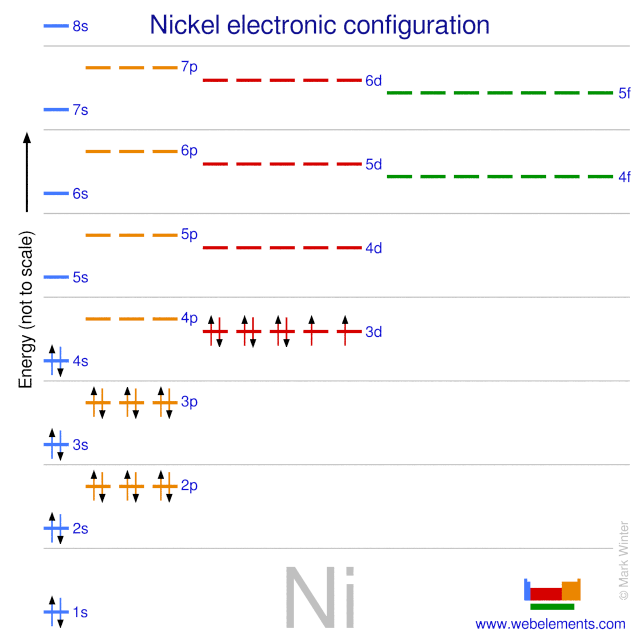
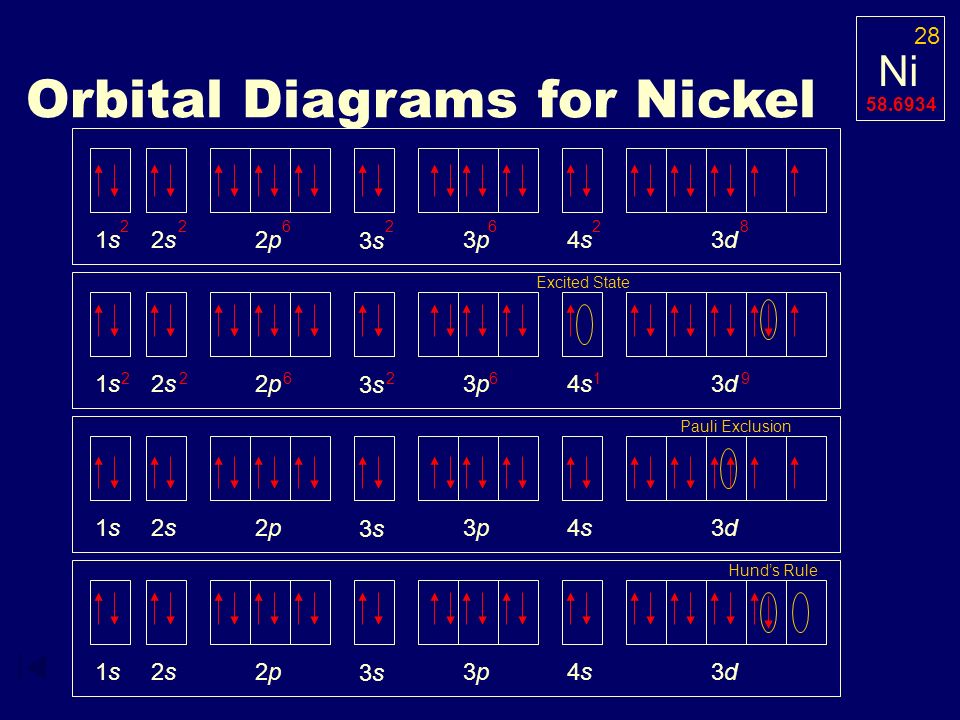
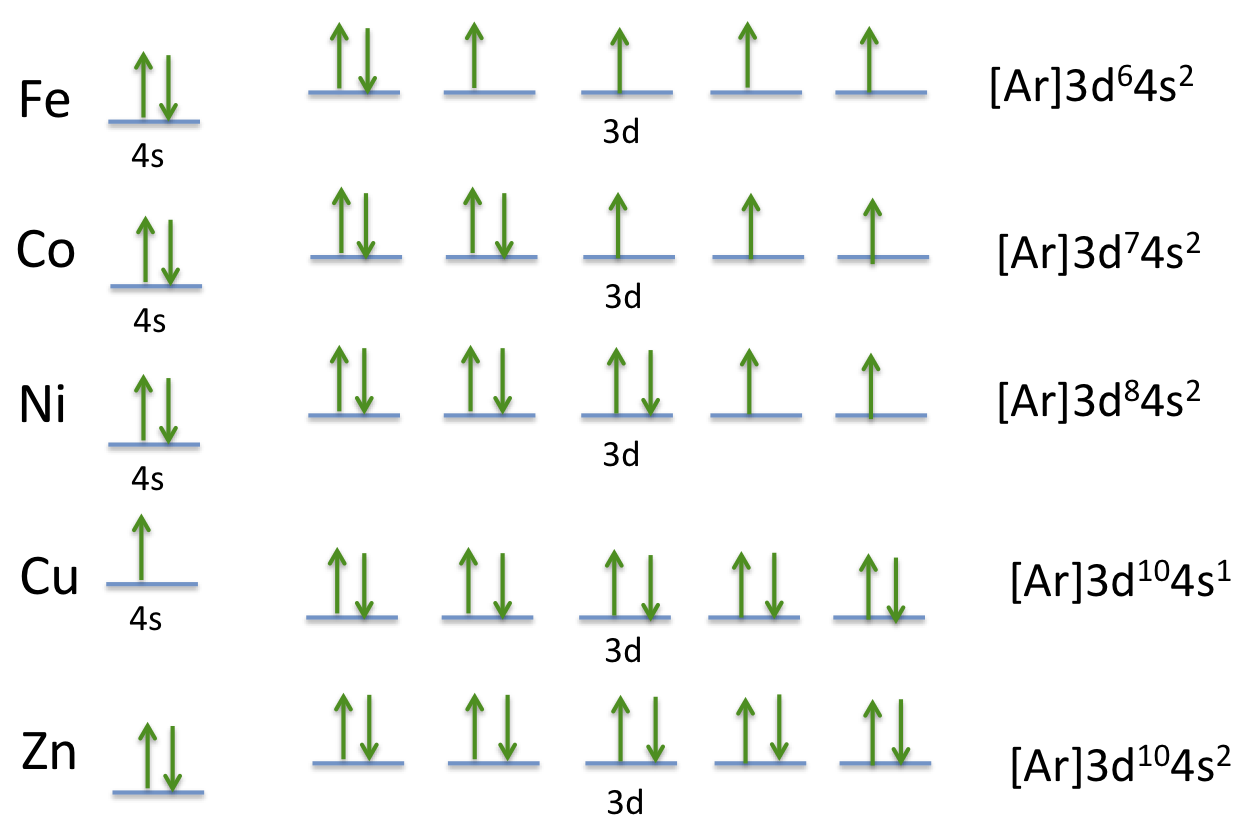
What is the orbital diagram for nickel? Atomic Orbital Diagrams: Atomic orbital diagrams are also known as electron-in-a-box diagrams. These are simplified diagrams of how electrons are arranged ... The orbital diagram for nickel is as follows: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p64s2 3d8. In all of the cases, both up and down arrows are filled,with the exception of the 3d shell, where the last two are.What is the orbital diagram for nickel? | schematron.orgWhat is the orbital diagram for nickel.
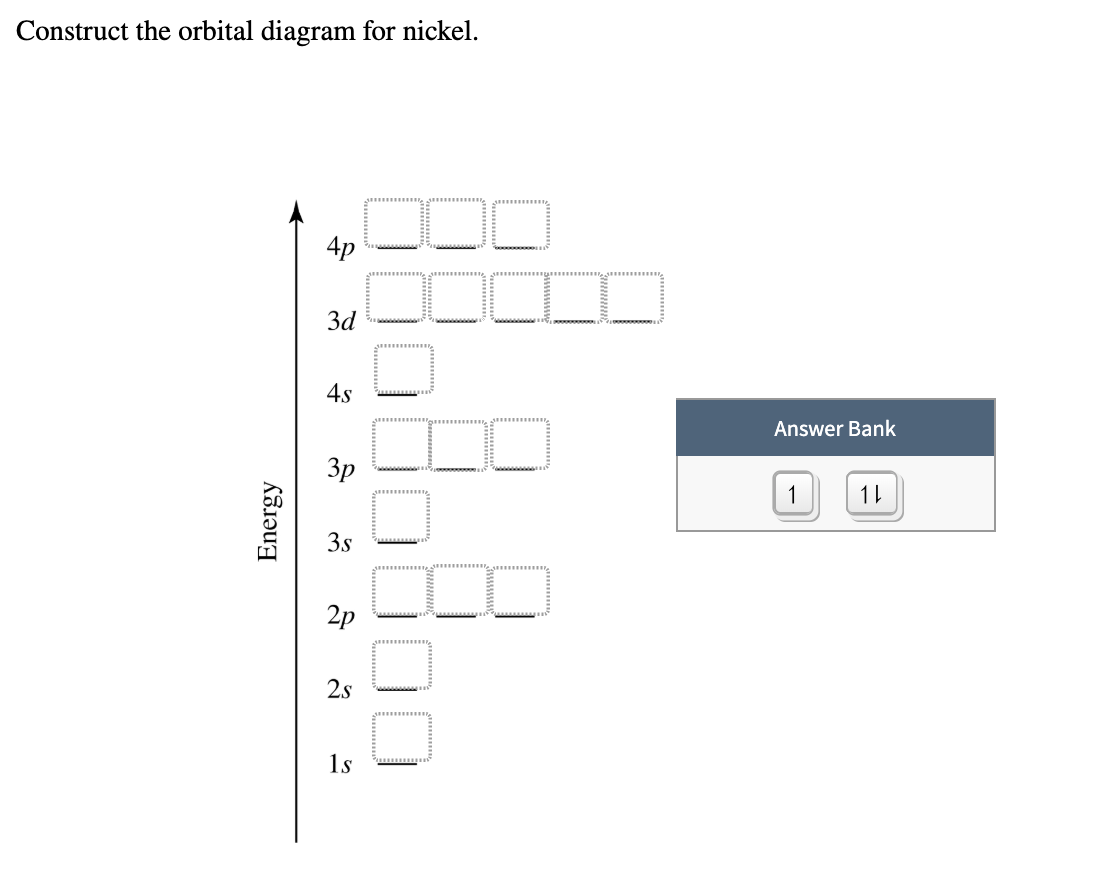
Feb 08, 2016 · Answer to Construct the orbital diagram for Ni. Start by adding the appropriate subshells. For example, carbon is in the 2p block.1. Describe the two differences between a 2p x orbital and a 3p y orbital. The 2px orbital lies on the x-axis. The 3py orbital lies on the y-axis and is larger than the 2px orbital. 2.
Orbital diagram for ni
Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁴ Chemistry questions and answers. Choose the valence orbital diagram that represents the ground state of Ni. 43 3d 11 34 11 13 25 2p 11 45 11|11|1|11 3d 45. 22.10.2021 · Recent studies suggest increasing sensitivity to orbital variations across the Eocene-Oligocene greenhouse to icehouse climate transition. However, climate simulations and paleoenvironmental studies mostly provide snapshots of the past climate, therefore overlooking the role of this short-term variability in driving major environmental changes and possibly biasing model-data …
Orbital diagram for ni. 2. Molecular orbital theory: This is the best model to explain the bonding within the CO ligand as well as in metal carbonyl complexes. There are total three molecular diagrams for carbonyl ligand which were proposed from time to time. Though, all three molecular orbital (MO) diagrams are able to explain the nature of metal-4 We're being asked to construct the orbital diagram for Ni.For that, we first need to determine the electron configuration of Ni.. Recall that for a neutral element, Atomic number = # of protons = # of electrons. The atomic number of Ni is 28 and since it's a neutral element, this means Ni has 28 electrons. This website makes extensive use of JavaScript. The top menus will not function without it and most tools will also not work. If you do not know how to enable JavaScript in your web browser, you should be able find instructions by searching the web for "enable javascript in my browser" (or similar ... The orbital diagram for nickel is as follows. What is the orbital diagram for nickel. In all of the cases both up and down arrows are filled with the exception of the 3d shell where the last two are up. Were being asked to construct the orbital diagram for nifor that we first need to determine the electron configuration of ni.
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n... Problem: Construct the orbital diagram for Ni. FREE Expert Solution. Ni → atomic # 28 → 28 electrons. Ni will pass through 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s2, 3d. Following Aufbau principle (fill lowest energy first) and Hund's rule (half-filled first before totally filled) 82% (205 ratings) 22.4.2019 · Show the distribution of electrons in oxygen atom (atomic number 8) using orbital diagram. Nickel atom can lose two electrons to form Ni 2+ ion. The atomic number of nickel is 28. From which orbital will nickel lose two electrons. Which of the following orbitals are degenerate? 3d xy, 4d xy, 3d z 2, 3d yz, 4d yz, 4d z 2 An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.
• MO diagrams can be built from group orbitals and central atom orbitals by considering orbital symmetries and energies. • The symmetry of group orbitals is determined by reducing a reducible representation of the orbitals in question. This approach is used only when the group orbitals are not obvious by inspection. Ni orbital Diagram. what is the orbital diagram for nickel answers the orbital diagram for nickel is as follows 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p64s2 3d8 in all of the cases both up and down arrows are filled with the exception of the what is the orbital diagram for nickel quora what is the orbital diagram for nickel update cancel given the rules the orbital diagram for ni is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8 or ... For example, in the MO diagram provided for the [Ti(H 2 O) 6] 3+ the ns orbital – which is placed above (n − 1)d in the representation of atomic orbitals (AOs) – is used in a linear combination with the ligand orbitals, forming a very stable bonding orbital with significant ligand character as well as an unoccupied high energy antibonding orbital which is not shown. 1. Orbital Filling Diagram 02 Ex. 2, Electron Configuration 02 Ex. (gives the most information) Is (quicker to draw than orbital filling diagrams) Dot Pb 3. Electron Dot shows only the valence (outer energy level) electrons Oxygen atom Ex. 1. Write orbital filling diagrams, electron configurations, and electron dot diagrams for the following ...
Orbital diagram of Nickel (Ni) 29: Orbital diagram of Copper (Cu) 30: Orbital diagram of Zinc (Zn) 31: Orbital diagram of Gallium (Ga) 32: Orbital diagram of Germanium (Ge) 33: Orbital diagram of Arsenic (As) 34: Orbital diagram of Selenium (Se) 35: Orbital diagram of Bromine (Br) 36: Orbital diagram of Krypton (Kr) 37: Orbital diagram of ...

Ni Nickel Element Information Facts Properties Trends Uses And Comparison Periodic Table Of The Elements Schoolmykids
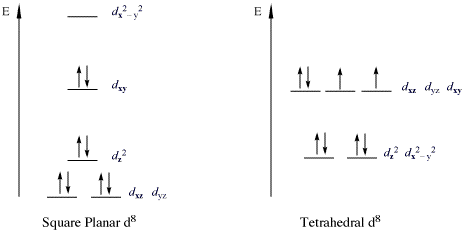
The situation with [ N i ( C N) X 4] X 2 − is that it has square planar geometry, so the two orbitals that are e g in an octahedral complex are separated in energy. This diagram from Chemistry LibreTexts shows it nicely: Because of the separation in energy, the d x y fills completely (two electrons) before any electrons fill the x 2 − y 2 ...
Through the thousand photographs on the web about Orbital diagram for arsenic, selections the best series along side largest quality only for you all, and Gallery for > orbital diagram arsenic is in truth among images libraries inside our best possible footage gallery. Nickel is in the. 4th. energy level, d. block, 7th.

Tuliskan Konfigurasi Elektron Dan Diagram Orbital Berdasarkan Teori Mekanika Kuantum Untuk Unsur Brainly Co Id
Theory: From H 2 to Data-Storage Alloys The COHP (or COOP) concept is most easily understood by looking at the simple band structure of a "one-dimensional" solid; the following example has been stolen from a classic introduction.Imagine a linear chain of hydrogen atoms, the one-dimensionally periodic analogue of H 2 (whose molecular-orbital scheme is known from the freshmen lecture)!
Answer (1 of 4): Nickel is atomic number 28; therefore, it has 28 electrons in its orbitals. The filling rules are as follows: 1. Aufbau Principle: Lowest energy levels fill first. 2. Pauli Exclusion Principle: Only 2 electrons per orbital, they must have opposite spin. 3. Hund's Rule: Given sev...
Explanation: Electronic configuration of Nickel ( 28Ni) is. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8. After removal of two electrons from outermost shell the electron configuration of Ni2+ is. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s0 3d8. Answer link.
The orbital diagram for nickel is as follows: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8. In all of the cases, both up and down arrows are filled, with the exception of the 3d shell, where the last two are up ...
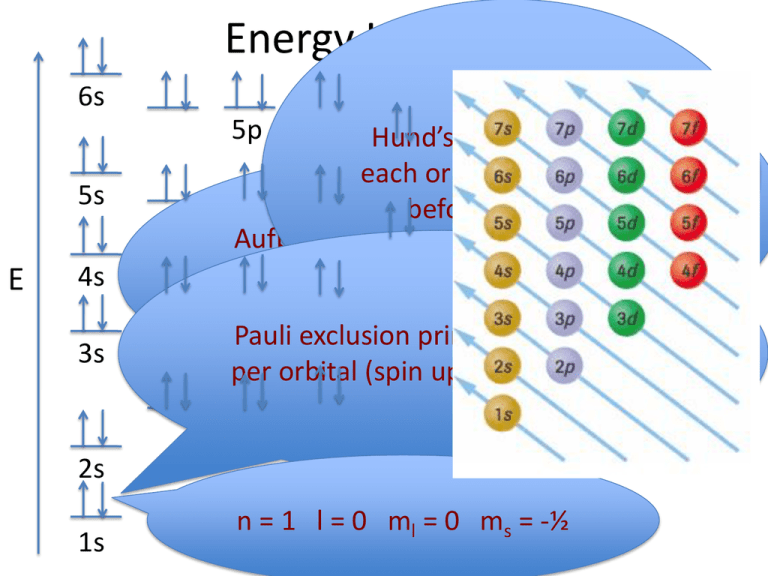
1. The Pauli principle: No more than two electrons can occupy a given orbital. If there are two electrons in an orbital, their spins must be paired (one must have m s = 1 2 and the other, m s = − 1 2). 2. The aufbau (building-up) principle: When electrons are filled in to orbitals in an atom, the orbitals with lower energy are filled first.
This could also be described as a positive "hole" that moves from the e g to the t 2g orbital set. The sign of Dq is opposite that for d 1, with a 2 E g ground state and a 2 T 2g excited state. Like the d 1 case, d 9 octahedral complexes do not require the Tanabe–Sugano diagram to predict their absorption spectra.
In this case, the d z 2 orbital drops even lower in energy, and the molecule has the following orbital splitting diagram. As a result of these distortions, there is a net lowering of energy (an increase in the ligand field stabilization energy) for complexes in which the metal has a d 7 , d 8 , or d 9 configurations, and thus electrons would ...
The next element has two electrons and the second electron fills the 1s orbital because there are only two possible values for the spin quantum number used to distinguish between the electrons in an orbital. He (Z = 2): 1s 2. The third electron goes into the next orbital in the energy diagram, the 2s orbital. Li (Z = 3): 1s 2 2s 1
electrons into the same orbital •Πeis a stabilizing energy for electron exchange associated with two degenerate electrons having parallel spin total 3 e 0 c eg* t2g d4HS eg* t2g d8 eg* t2g d6LS total 7 e 3 c total 6 e 3 c LFSE 3 0.4 O 10.6 O 0.6 O LFSE 6 0.4 O 20.6 O
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom

Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes
Now, let us draw the molecular orbital diagram of ${N_2}$ . Now, first let us understand what magnetic behavior and bond order means. - Magnetic behavior: As we know the electron has an electron magnetic dipole moment, which is generally generated by the electron's spin property, which induces an electric charge into motion. As we can see the ...
Orbital diagram. Nickel electron configuration ← Electronic configurations of elements . Ni (Nickel) is an element with position number 28 in the periodic table. Located in the ... Below is the electronic diagram of the Nickel atom Distribution of electrons over energy levels in the Ni atom 1-st level (K): 2 2-st level (L): 8 3-st level (M ...
Answer (1 of 4): Nickel is atomic number 28; therefore, it has 28 electrons in its orbitals. The filling rules are as follows: 1. Aufbau Principle: Lowest energy levels fill first.
Answer (1 of 7): Since there are 2 electrons which are left unpaired, the molecule is paramagnetic in nature.
Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: The Aufbau principle, the Pau...

Write The Abbreviated Orbital Diagrams For The Following Elements And State Whether They Are Paramagnetic Or Diamagnetic A Ni 2 B Ca 2 Study Com
11) What is the magnetic moment of nickel ion in tetraammine nickel(ii) chloride, [Ni(NH 3) 4]Cl 2? 12) Write the hybridisation and magnetic behaviour of the complex Ni(CO) 4 . 13) Question - Amongst following, the lowest degree of paramagnetism per mole of the compound at 298 K will be shown by:
22.10.2021 · Recent studies suggest increasing sensitivity to orbital variations across the Eocene-Oligocene greenhouse to icehouse climate transition. However, climate simulations and paleoenvironmental studies mostly provide snapshots of the past climate, therefore overlooking the role of this short-term variability in driving major environmental changes and possibly biasing model-data …
Chemistry questions and answers. Choose the valence orbital diagram that represents the ground state of Ni. 43 3d 11 34 11 13 25 2p 11 45 11|11|1|11 3d 45.
Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top. 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁴













/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)
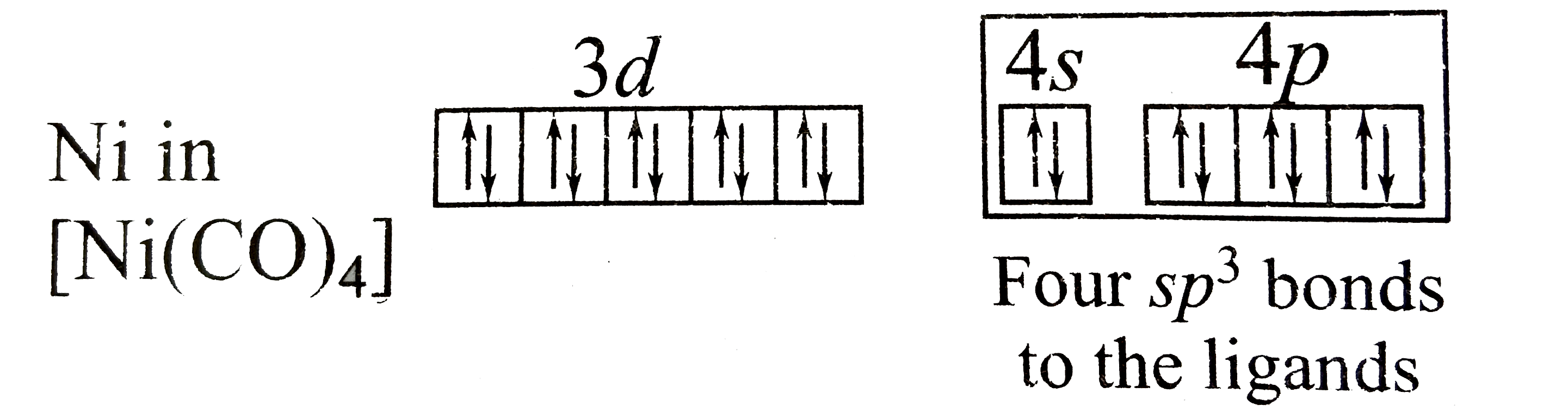






0 Response to "38 orbital diagram for ni"
Post a Comment