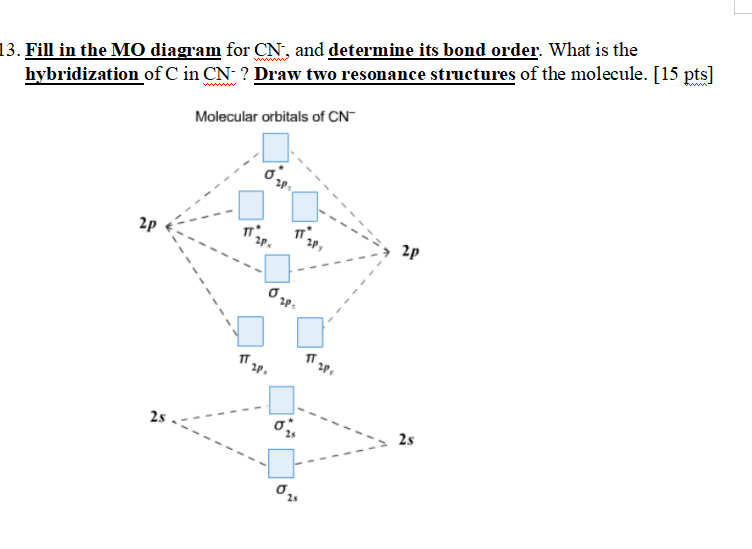
38 mo diagram for cn-
Molecular orbital Diagram Cn-mo diagram of cn hunt research group right you have been asked to draw the mo diagram for cn a heteronuclear diatomic don t panic take it one step at a time and you will have a plete mo diagram before you know it this is meant to be an interactive exercise so arrange for some pieces of blank paper a pencil a pen and an eraser molecular orbital theory heteronuclear ... Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: 2. Draw Lewis structures and MO diagrams for CN+ CN-, and CN. According to the Lewis model, which molecule is most stable? According to MO theory, which molecule ...
How to make molecular Orbital diagramhttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UYC-ndQ6Lww&t=6s
Mo diagram for cn-
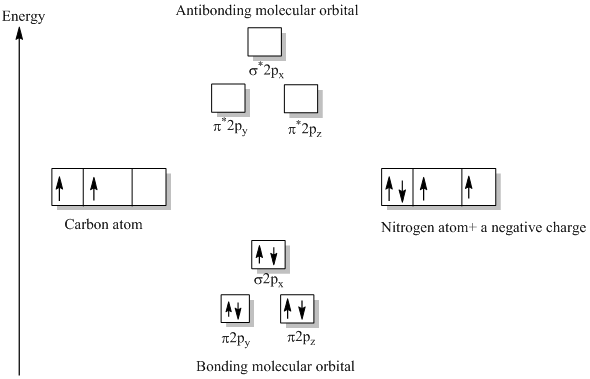
Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion). 21 May 2014 · 3 answersHere is the MO for CN-, just take away a single electron from the MO since CN is neutral. Vijayta Gupta is right, the N atom is lower in energy. 1 answerHey there! To calculate bond order of CN- and predict other properties, we will start by drawing the molecular orbital diagram for the CN- ion.
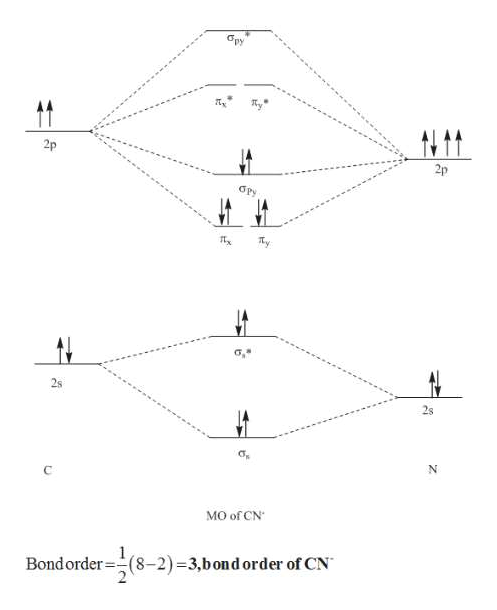
Mo diagram for cn-. So, in this article, we have learned about How to draw CN– lewis structure, its molecular orbital diagram (MO), formal charges, hybridization, and bond order. Here is a quick review of this article. The bond order of CN- is 3. CN– formal charge is -1 according to its lewis structure. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine Answer (1 of 5): \text{Bond order} = \frac{n_{\text{bonding electrons}}-n_{\text{antibonding electrons}}}{2} Here is the molecular orbital diagram of CN-: There are 8 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, therefore B.O.=\frac{8-2}{2}=3 Here’s a guide on how to construct MO diagrams, i... The number of molecular orbitals is always equal to the number of atomic orbitals from which they are formed. Two types of orbitals are bonding and anti-bonding ...1 answer · Top answer: Concepts and reason • The molecular orbital theory explains the bonding in terms of the combination and organization of atomic orbitals of an atom which ...
Cyanide Molecular Orbital Diagram. MO Theory: the bonding orbital will be lower in energy, the an7bonding The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion ). The molecular orbital diagram of (if order of molecular orbital is like that in) is as shown below. We must remember that total number of electrons in ... 3 Jan 2021 — Because each alkali metal (M) has an ns1 valence electron configuration, the M2 molecule has two valence electrons that fill the σns bonding ... The total energy of the molecule must be stabilised. This means that very occasionally an occupied MO can move up in energy as long as the occupied MOs move ... This video is about MO Diagram #3 - CN-
CN Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Polarity, and MO Diagram. CN is known as cyanide which exists as a pseudohalide anion. It belongs to the cyano group and consists of carbon and a nitrogen atom having a triple bond. It carries a charge of -1 and is a conjugate base of hydrogen cyanide (HCN). 1 answerHey there! To calculate bond order of CN- and predict other properties, we will start by drawing the molecular orbital diagram for the CN- ion. 21 May 2014 · 3 answersHere is the MO for CN-, just take away a single electron from the MO since CN is neutral. Vijayta Gupta is right, the N atom is lower in energy. Molecular orbital theory is also able to explain the presence of Figure \(\ PageIndex{6}\): Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagram for HCl. to describe the bonding in the cyanide ion (CN −). mix atomic orbitals on different atoms to get Molecular Orbitals. The resul7ng MO diagram looks like this. CN– (Cyanide ion), NO+ (Nitrosonium ion).

Diagram Orbital Molekul Unduh Gratis Kimia Orbital Molekul Diagram Heteronuclear Molekul Diagram Orbital Molekul Gambar Png

Figure 2 From Photoredox Reactions Of Hg Cn 2 Fe Cn 6 4 And Hgco2 Cn 10 6 Induced By Inner Sphere Metal To Metal Charge Transfer Excitation Semantic Scholar
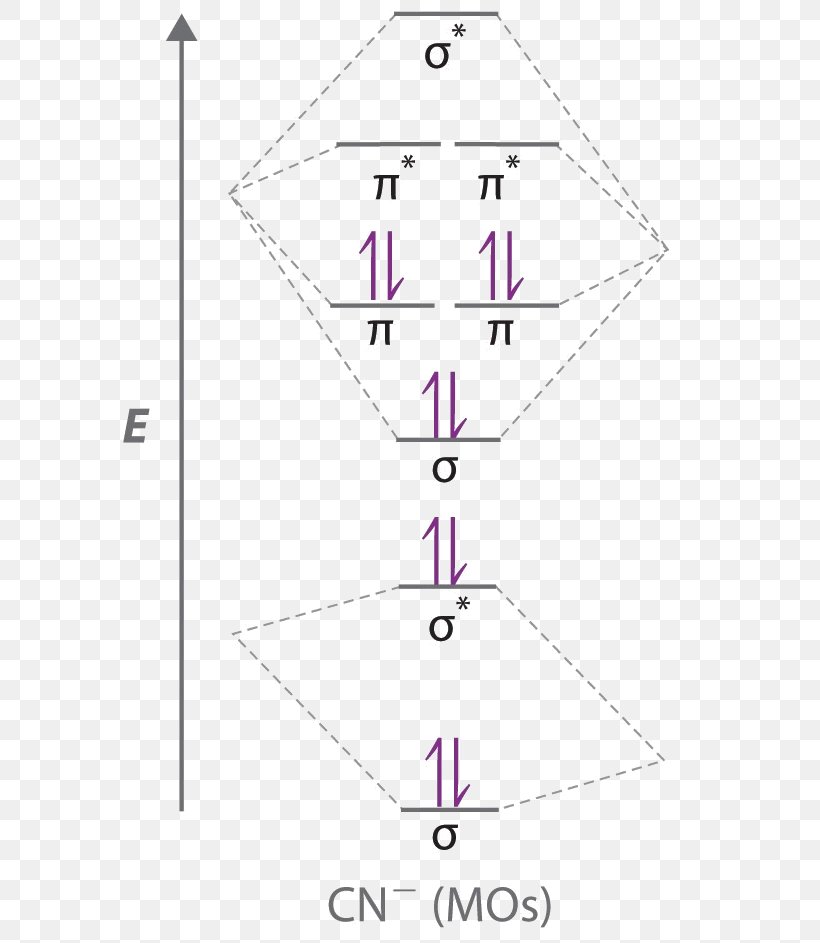
Molecular Orbital Diagram Atomic Orbital Cyanide Png 631x943px Diagram Anion Area Atomic Orbital Bond Order Download
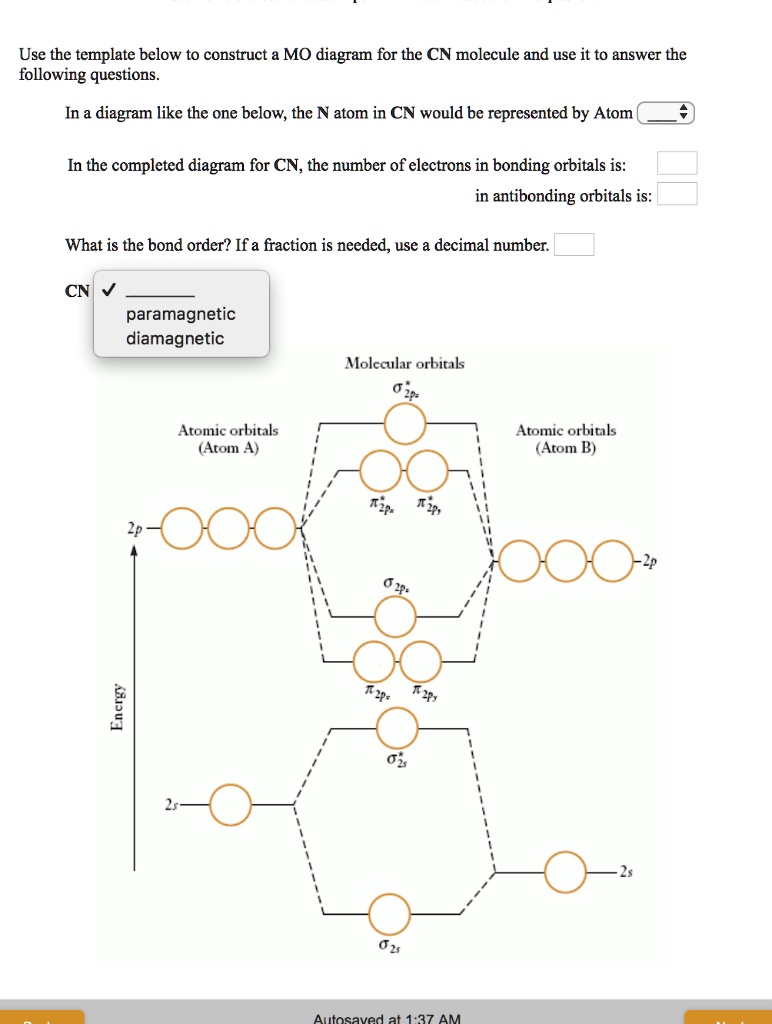
Solved Use The Template Below To Construct Mo Diagram For The Cn Molecule And Use It To Answer The Following Questions Diagram Like The One Below The N Atom In Cn Would Be

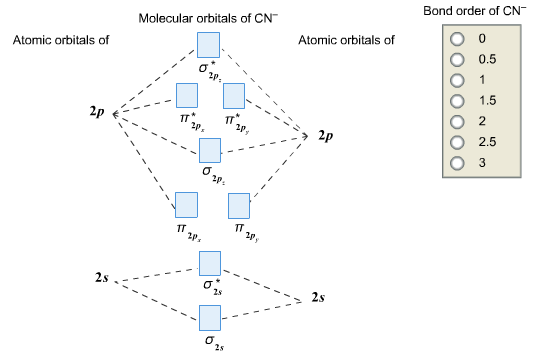
Assuming The Mo Diagram Above Would Apply To Both Species Predict How The Bond Order Will Change Upon Adding An Electron To Cn To Form Cn The Bond Order Will Increase Decrease

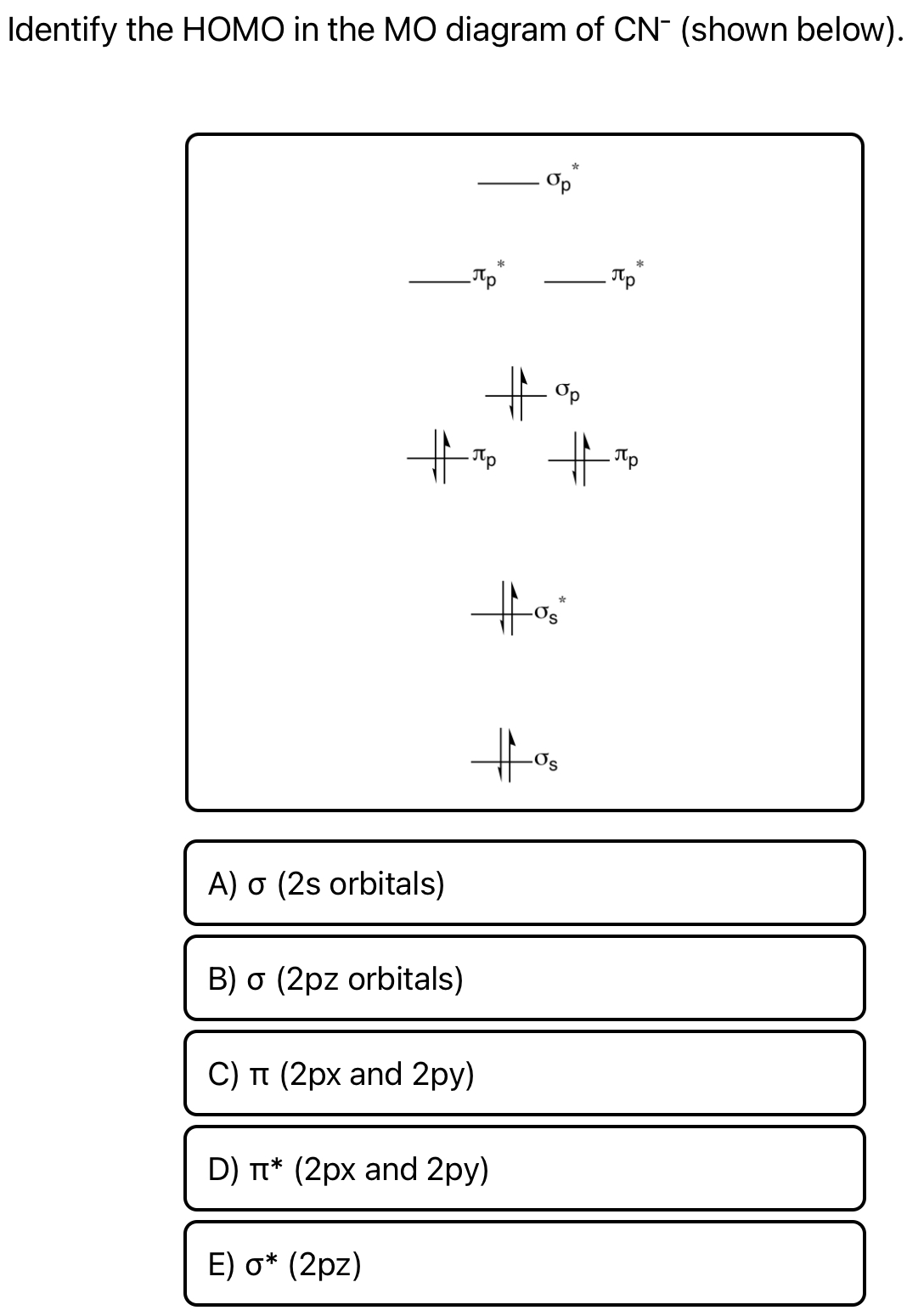
How Can One Tell From The Mo Diagram Of The Cyanide Ion That The Homo Is Carbon Centred Chemistry Stack Exchange

Which Atom Bears The Negative Charge In Cyanide I Am Confused By The Mo Diagram Chemistry Stack Exchange

Complete This Molecular Orbital Diagram For Cn Then Determine The Bond Order Note That The 1s Homeworklib
Consider The Following Molecules No No And No Using The Molecular Orbital Theory How Do You Evaluate Them In Terms Of Bond Energy And Stability Quora













0 Response to "38 mo diagram for cn-"
Post a Comment