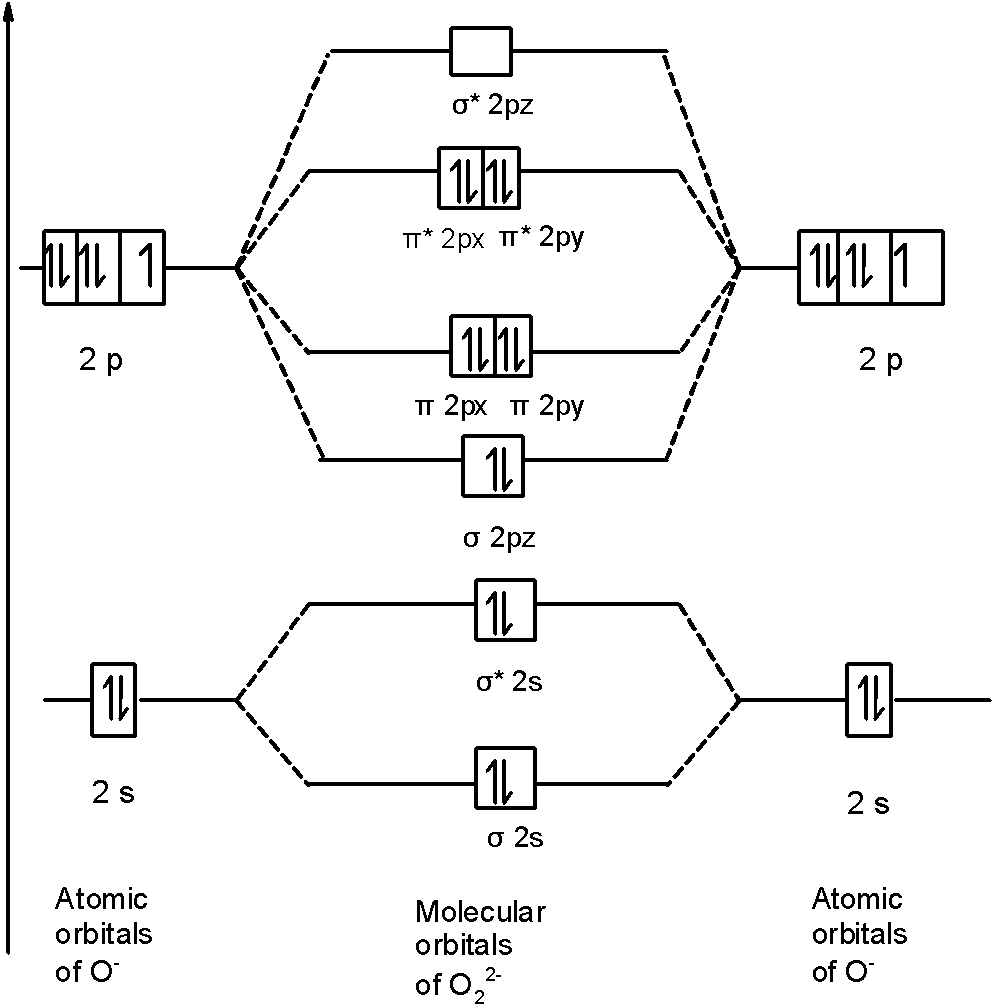
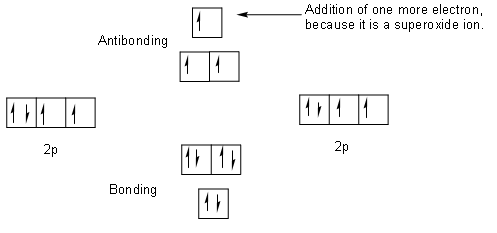
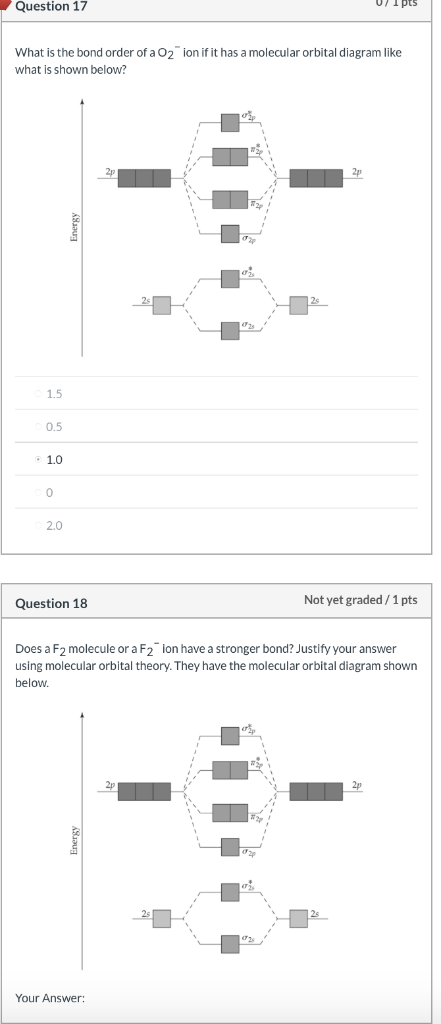
37 molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 . Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 Molecular orbital diagram for ne2 2 ...
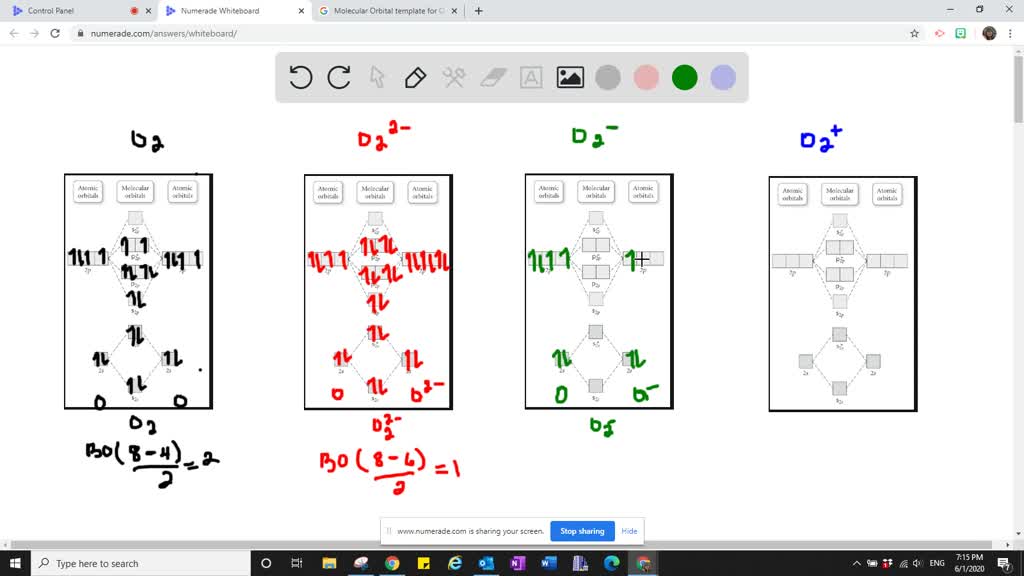
The valence molecular orbital diagram for Li2- is shown. THe molecular orbital bond order for this species is equal to _____ and Li2- is _____ stable than Li2 -1/2-less. correctly describe sigma and pi molecular orbitals-Both atomic s and p orbitals can form sigma molecular orbitals-atomic p orbitals can combine to form either sigma or pi molecular orbitals-a pi bonding molecular orbital has ...

Molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion
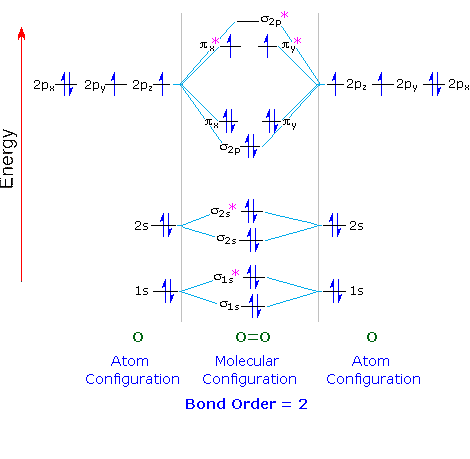
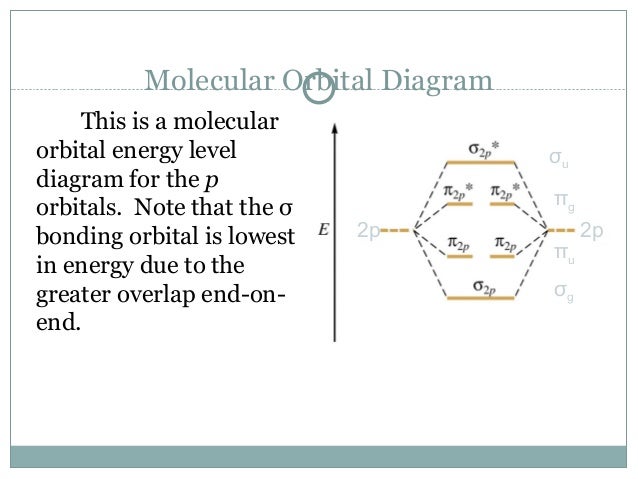
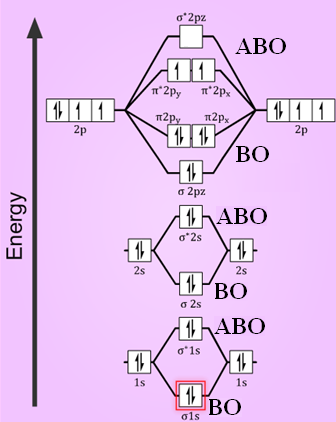
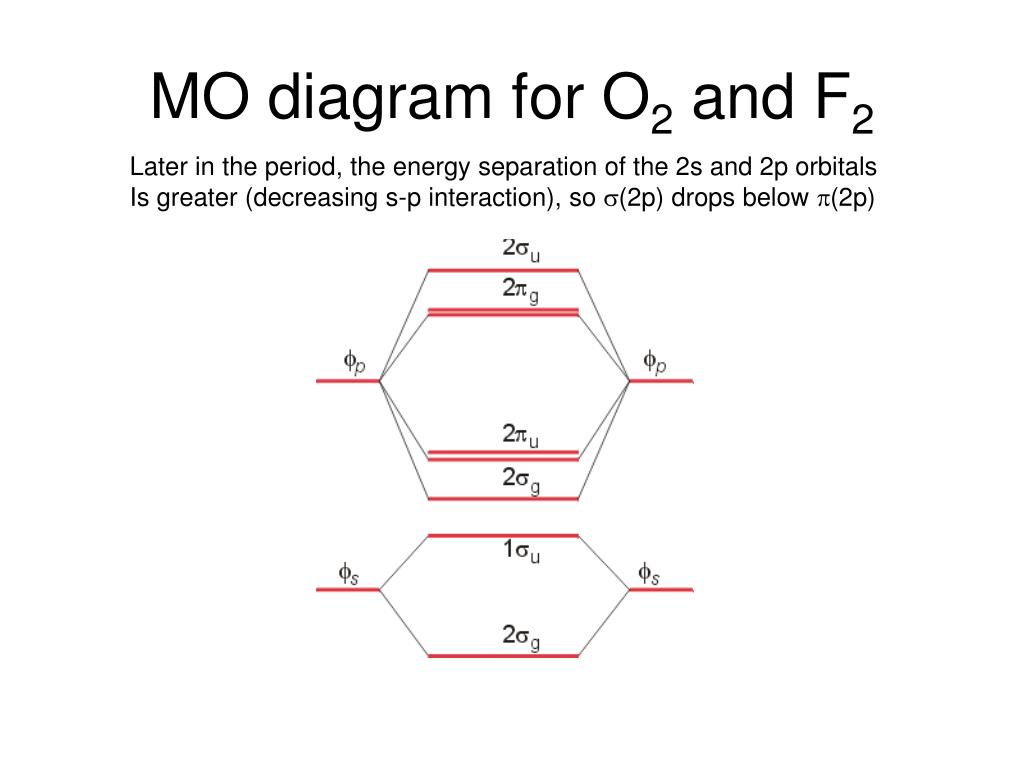
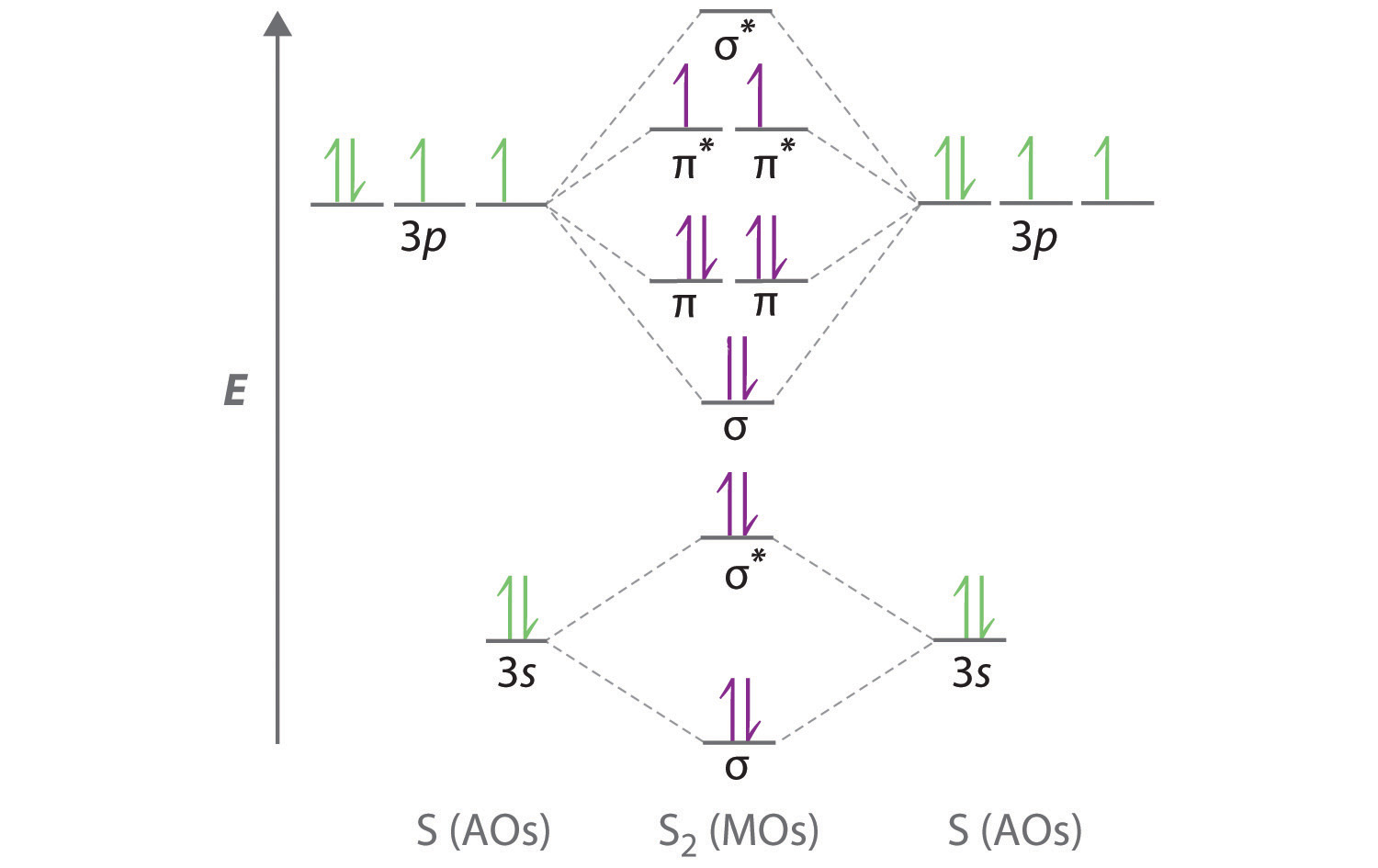
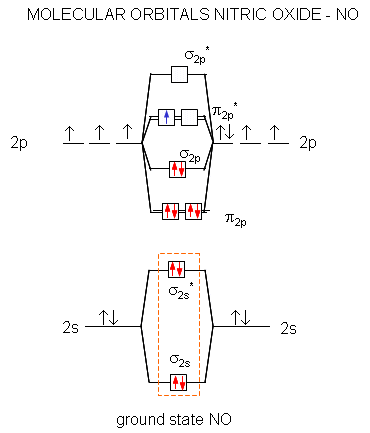
Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Figure 7.7.12. This shows the MO diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases. Between N2 and O2, the order ... 25.09.2016 · "O"_2 is paramagnetic because it has two unpaired electrons. > The Lewis structure of "O"_2 gives a misleading impression. It shows that all the electrons in oxygen are paired, so oxygen should be diamagnetic. Yet oxygen is paramagnetic. The correct explanation comes from Molecular Orbital theory. The atomic orbitals of the "O" atoms overlap to form the σ and π orbitals of the "O"_2 … 20.03.2019 · Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. The first ten molecular orbitals may be arranged in order of energy as follow: σ(1s) <σ ∗ (1s) < σ(2s) <σ ∗ (2s) < π(2p x) = π(2p y) < σ(2p z) < π ∗ (2p x) =π ∗ (2p y) <π ∗ ( 2p z) Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons ...
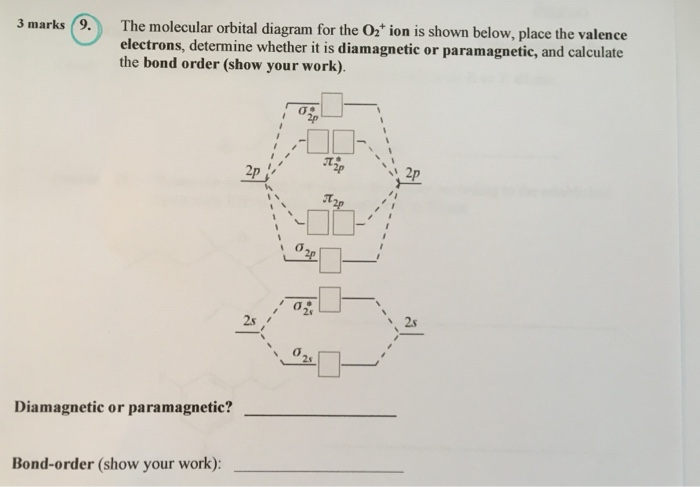
Molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion. 17.11.2021 · Molecular orbital diagram practice worksheet Cyanide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CN‾ ion. It is a member of the Cyano group. It is lethal for every living thing and smells like bitter almonds. In this article, we will study the Cyanide (CN-) lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram(MO), its bond order, formal charges, and hybridization. Cyanide can be a colorless gas in the form of hydrogen cyanide, sodium ... 07.02.2015 · Pt l O2 l H+ ll OH- l O2 l Pt In this case, the half reactions are O2 + 2H2O +4e- --> 4 OH-O2 + 4H+ +4e- -->2H2O How would you know that O2 and H+ should be on the same side of the half-reactoin? And how would you know how to write these reactions without it being clear which substance is oxidized or reduced in the cell diagram. Thanks! 04.09.2021 · Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. This switch in orbital ordering occurs because of a phenomenon called s-p mixing. s-p mixing does not create new orbitals; it merely influences the energies of the existing molecular orbitals.
**Physical Chemistry** **Thermodynamics, Structure, and Change 10th Edition Solutions Peter Atkins, Julio de Paula** **ISBN-13: 9781429290197** Download the Solutions manual for this textbook **Order it via email: markrainsun"@"gmail(.)com** &#x200B; **Table of Contents** **Foundations** A Matter B Energy C Waves **Part 1 Thermodynamics** **1. The properties of gases** Topic 1A The perfect gas Topic 1B The kinetic model Topic 1C Real gases **Impact** …O... 20.03.2019 · Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals. The first ten molecular orbitals may be arranged in order of energy as follow: σ(1s) <σ ∗ (1s) < σ(2s) <σ ∗ (2s) < π(2p x) = π(2p y) < σ(2p z) < π ∗ (2p x) =π ∗ (2p y) <π ∗ ( 2p z) Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons ... 25.09.2016 · "O"_2 is paramagnetic because it has two unpaired electrons. > The Lewis structure of "O"_2 gives a misleading impression. It shows that all the electrons in oxygen are paired, so oxygen should be diamagnetic. Yet oxygen is paramagnetic. The correct explanation comes from Molecular Orbital theory. The atomic orbitals of the "O" atoms overlap to form the σ and π orbitals of the "O"_2 … Obtain the molecular orbital diagram for a homonuclear diatomic ion by adding or subtracting electrons from the diagram for the neutral molecule. Figure 7.7.12. This shows the MO diagrams for each homonuclear diatomic molecule in the second period. The orbital energies decrease across the period as the effective nuclear charge increases and atomic radius decreases. Between N2 and O2, the order ...












0 Response to "37 molecular orbital diagram for o2- ion"
Post a Comment