37 bh2 molecular orbital diagram
The new orbitals thus formed are known as hybrid orbitals. More significantly, hybrid orbitals are quite useful in explaining atomic bonding properties and molecular geometry. Let us quickly look at the example of a carbon atom. This atom forms 4 single bonds wherein the valence-shell s orbital mixes with 3 valence-shell p orbitals. (2) Determine the most stable molecular structure for CH2. Would you expect BH2 to adopt a similar structure? Hint: Use a correlation diagram (Walsh) to determine how the orbital energies change as a function of bending. (3) Construct the molecular orbital diagrams for (a) AB4 (Td case) and (b) AB6 (Oh case) where A is a first-row transition
Sep 8, 2021 — Walsh correlation diagram is a plot of molecular orbital energy as a function of some systematic change in molecular geometry.
Bh2 molecular orbital diagram
These molecular orbitals are calculated to be only 0.0074 Hartrees (19.4 kJmol -1) apart in energy. The energy inversion is explained by the Natural Bond Orbital analysis, where the constituent terminal hydrogen 1s orbitals in MO #6 are calculated to be at 0.0456 Hartrees higher energy than the constituent bridging hydrogen NAOs in MO #5 Plot MO energies and draw orbitals ... Walsh's correlation diagram: Plot course of MO energies with change in geometry ... e.g. BH2, CH2, NH2, H2O, H2S ...32 pages Calculations done at B3LYP/6-311G+(2d,p). Click on any image above to view the optimized structure. Ethane, a two carbon molecule with a single-bond between the carbons, is the simplest alkane.. To understand the hybridization, start by thinking about the orbital diagram of the valence electrons of atomic, unhybridized carbon.
Bh2 molecular orbital diagram. sp 2 Hybridization. The valence orbitals of a central atom surrounded by three regions of electron density consist of a set of three sp 2 hybrid orbitals and one unhybridized p orbital. This arrangement results from sp 2 hybridization, the mixing of one s orbital and two p orbitals to produce three identical hybrid orbitals oriented in a trigonal planar geometry (). Draw a molecular orbital energy diagram for each. B2-1. F 2. The magnetic property, bond order, and so on can be understood from its molecular orbital diagram. 5) Identify the bond and existence of molecule. From the molecular orbital diagram of N 2, predict its bond order and whether it is diamagnetic or paramagnetic. Download scientific diagram | Frontier molecular orbitals (FMOs) of the tropylium cation (1); phosphatropylium cation (2) and 1,2-diphosphatropylium cation (3). from publication: molecules Effect ... 1: Walsh diagram for AH Fig. · 2: Schematic representation of the molecular orbitals of AH Figure 1 displays the energies of orbitals for molecules AH2 as a ...
(2) Determine the most stable molecular structure for CH2. Would you expect BH2 to adopt a similar structure? Hint: Use a correlation diagram (Walsh) to determine how the orbital energies change as a function of bending. (3) Construct the molecular orbital diagrams for (a) AB4 (Td case) and (b) AB6 (Oh case) where A is a first-row transition (A) BH2 will be linear, like BeH2, because it has the same MO diagram, just with one more electron. The extra electron changes the interactions! (B) BH2 will be ... FIGURE2: Character table for the the point group D3h. B atom in BH3: +s-orbital: with the shape of the sphere, its function is x 2 +y 2 +z 2.Therefore, 2s orbital has a 1 ' symmetry +p-orbital: has 3 orbitals , p x, p y, p z.Therefore, 2p z orbital has a 2" symmetry. 2p x and 2p y orbital are degenerate and have e' symmetry. 3 Hydrogen atoms in BH3: (Ligand group orbitals) Question 1 (50 points total): Using coordinate system shown, derive a molecular orbital diagram (o + ) for the bonding between the carbon and nitrogen atoms in the guanidnium cation ([C(NH2)3]+). Assume that the peripheral nitrogen atoms use only symmetrically similar p-orbitals to interact with the central carbon atom (which can use all of its ...
a complex MO diagram: B2H6 ... MO diagrams combine two fragments. Symmetry fragments ... fragment =5e therefor keep up to b2 orbital z x y b1 a1 a1 b2. BH2.47 pages Molecular Orbitals for Larger Molecules 1. Determine point group of molecule (if linear, use D2h and C2v instead of D∞h or C∞v) 2. Assign x, y, z coordinates (z axis is principal axis; if non-linear, y axes of outer atoms point to central atom)3. Find the characters of the reducible representationfor the combination of (i) Be2 molecule: The electronic configuration of Be(Z = 4) is: 4 Be 1s 2 2s 1 Be 2 molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. Number of valence electrons in Be atom = 2 Thus in the formation of Be 2 molecule, two outer electrons of each Be atom i.e. 4 in all, have to be accommodated in various molecular orbitals in the increasing order of their energies. Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ...
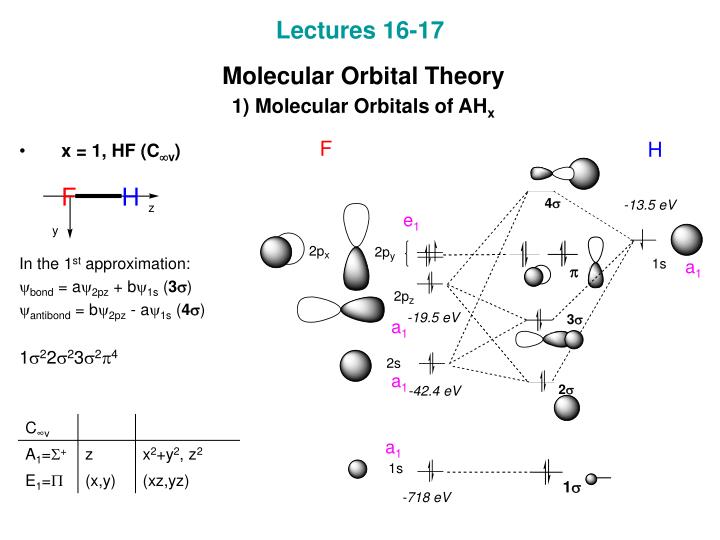
NH, NH2, BH, BH2 and BH3 by P. C. H. JORDANT and H. C. LONGUET-HIGGINS Department of Theoretical Chemistry, University of Cambridge (Received 4 August 1961) This paper describes a semi-emprical quantitative theory of the tow-lying electronic states of the radicals CH, CFI2, CHa, NH, NH,, BFI, BH2 and BHa.
Bonding in Molecules Lecture 3 Molecular shapes Known shape of some AH2 ... better overlap of H 1s orbitals First order effects Walsh diagram mixing can ...
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Transcribed image text: What molecule is illustrated by the following molecular orbital diagram? Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals 2p 2p 2s 2s 2s Provide your answer below.
Answer (1 of 2): * As we see Boron has 3 electrons in its valence shell. * The compound BH3 formation by vbt is shown in below figure, * Now we see that in valence shell ofBH3 there are 6 electrons. * But generally speaking about compounds, they are stable when they attain octate configuratio...
An advanced molecular orbital diagram of BeH2 (beryllium hydride) for the inorganic or physical chemistry student.
Atomic orbitals are labelled 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 3d, etc. where the letter (s, p, d or f)indicates the orbital shape: Molecular orbitals are labelled 1σ, 2σ, 1π, 2π, etc. where the Greek letter (σor π) indicates the orbital symmetry: Molecular orbitals are generated by combining atomic orbitals:
Here are the molecular orbitals for BeH2 from symmetry adjusted linear combinations.
Bh2 Molecular Orbital Diagram. MO diagram of homonuclear diatomic molecules. • Filling the . and lower symmetry, such as BeH2 and H2O. BeH2 2σg. 23σu. 2 linear. BH2. 2a1. 21b2. 23a1. MO Diagram for BeH2.
Beryllium hydride | BeH2 - PubChem. National Center for Biotechnology Information. 8600 Rockville Pike, Bethesda, MD, 20894 USA. Contact. Policies. FOIA. National Library of Medicine. National Institutes of Health. Department of Health and Human Services.
Wiring Diagram Pictures - schematron.org
Molecular Orbital Energies The orbital energies are given in eV, where 1 eV=96.49 kJ/mol. Orbitals with very low energy are core 1s orbitals. More antibonding orbitals than you might expect are sometimes listed, because d orbitals are always included for heavy atoms and p orbitals are included for H atoms.
The wave functions, level energies and Mülliken population analysis of localized molecular orbitals (LMO's) for B4Cl4, 1,5-C2B3H5 and the closo-BnH2-n (n = 6-10, 12) are calculated by using the ...
Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory Transformational properties of atomic orbitals Atomic orbital Transforms as s x2+y 2+z 2 px x py y pz z dz2 z2, 2z 2-x2-y2 dx2-y2 x2-y2 dxy xy dxz xz dyz yz S py • When bonds are formed, atomic orbitals combine according to their symmetry. • Symmetry properties and degeneracy of orbitals and bonds can be ...
BeH2 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, and Polarity. BeH2 is known as beryllium hydride or beryllium dihydride. It is an inorganic compound and comes under the category of alkaline earth hydride. It appears as an amorphous white solid at standard temperature and pressure. It also exists in polymeric form as (BeH2) n.
3) Combine SALCS with orbitals on A For more complex molecules, there may be more than 2 symmetry equivalent types of atoms. In this case, MO diagrams can be constructed from the orbitals of two chemically reasonable fragments. For example, the bonding in [Cl 3Pt(C 2H4)]-can reasonably be considered in terms of the interaction between [PtCl 3 ...
Molecular species No. of valence electrons Shape Known shape of some AH 2 molecules FH 2+ 118 SH 2 92.1 OH 2 104.5 NH 2 103 SiH 2 93 CH 2 110 BH 2 131 Molecular angle species. D∞h C2v. Walsh diagram better overlap of H 1s orbitals poorer overlap of H1s with 2p x remains non-bonding First order effects. Walsh diagram mixing can occur between 2 ...
Figure 10.3.2 : Forming molecular orbitals for \(BeH_2\). Then we can put the Molecular Orbital diagram together, starting with the outside, drawing in bonding, non-bonding and anti-bonding MOs, and filling the electrons (Figure 10.3.3 ). The bond order is 2. Figure 10.3.3 : Molecular orbitals diagram for BeH 2.
Calculations done at B3LYP/6-311G+(2d,p). Click on any image above to view the optimized structure. Ethane, a two carbon molecule with a single-bond between the carbons, is the simplest alkane.. To understand the hybridization, start by thinking about the orbital diagram of the valence electrons of atomic, unhybridized carbon.
Plot MO energies and draw orbitals ... Walsh's correlation diagram: Plot course of MO energies with change in geometry ... e.g. BH2, CH2, NH2, H2O, H2S ...32 pages
These molecular orbitals are calculated to be only 0.0074 Hartrees (19.4 kJmol -1) apart in energy. The energy inversion is explained by the Natural Bond Orbital analysis, where the constituent terminal hydrogen 1s orbitals in MO #6 are calculated to be at 0.0456 Hartrees higher energy than the constituent bridging hydrogen NAOs in MO #5




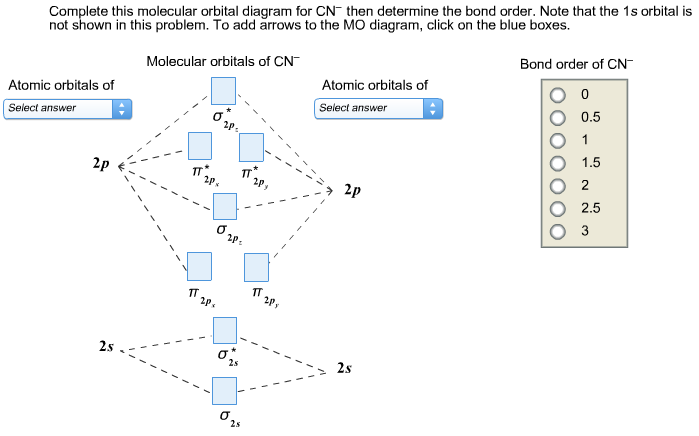
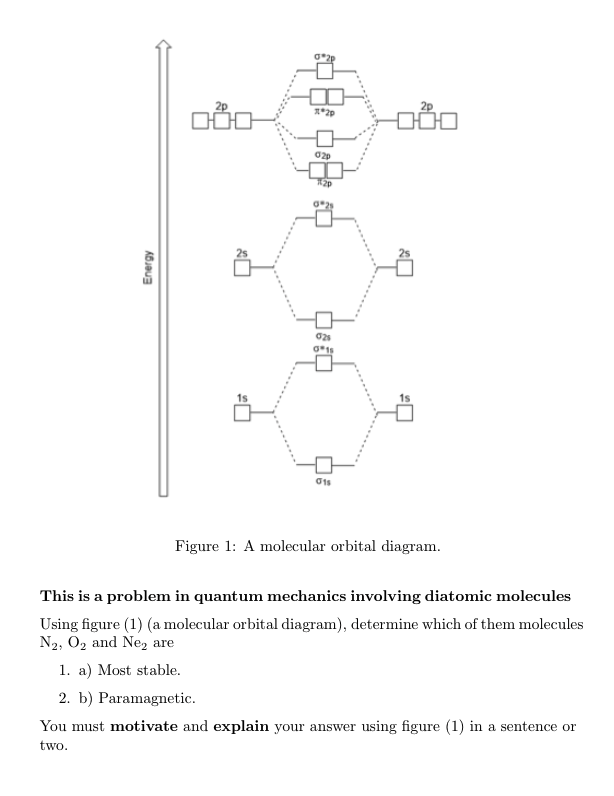

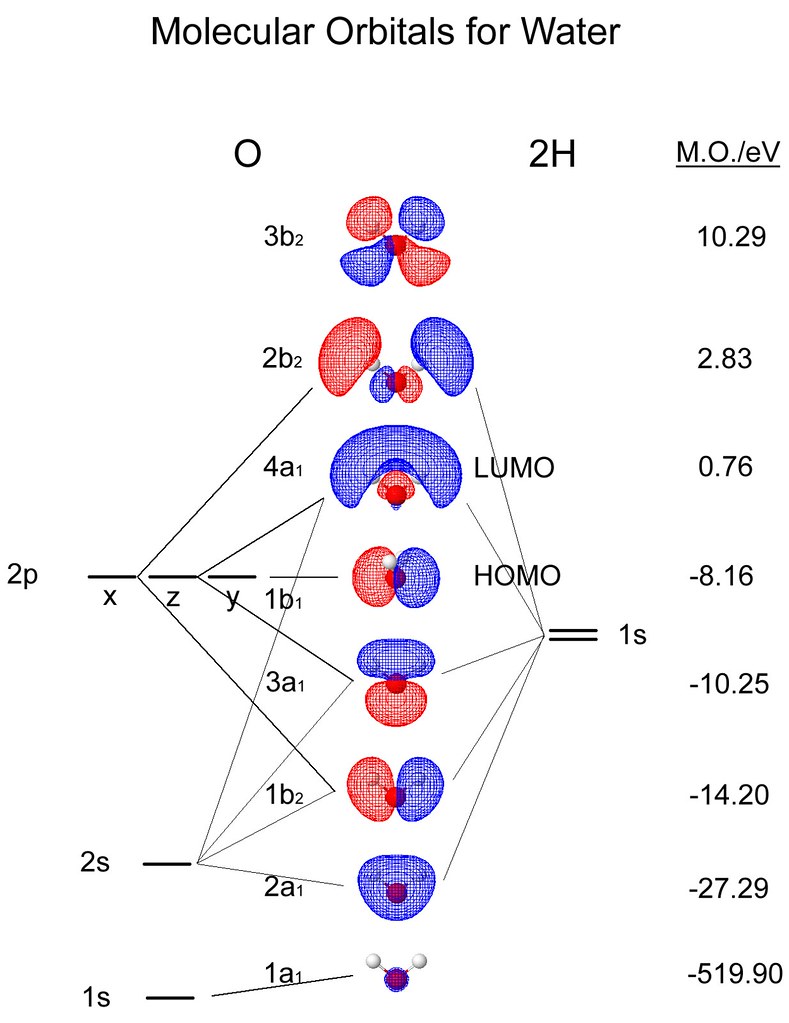






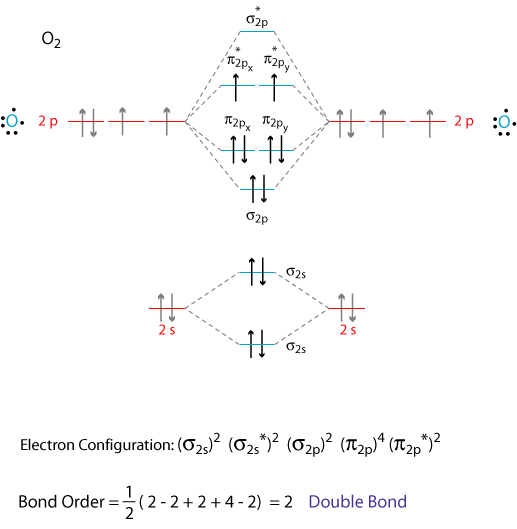


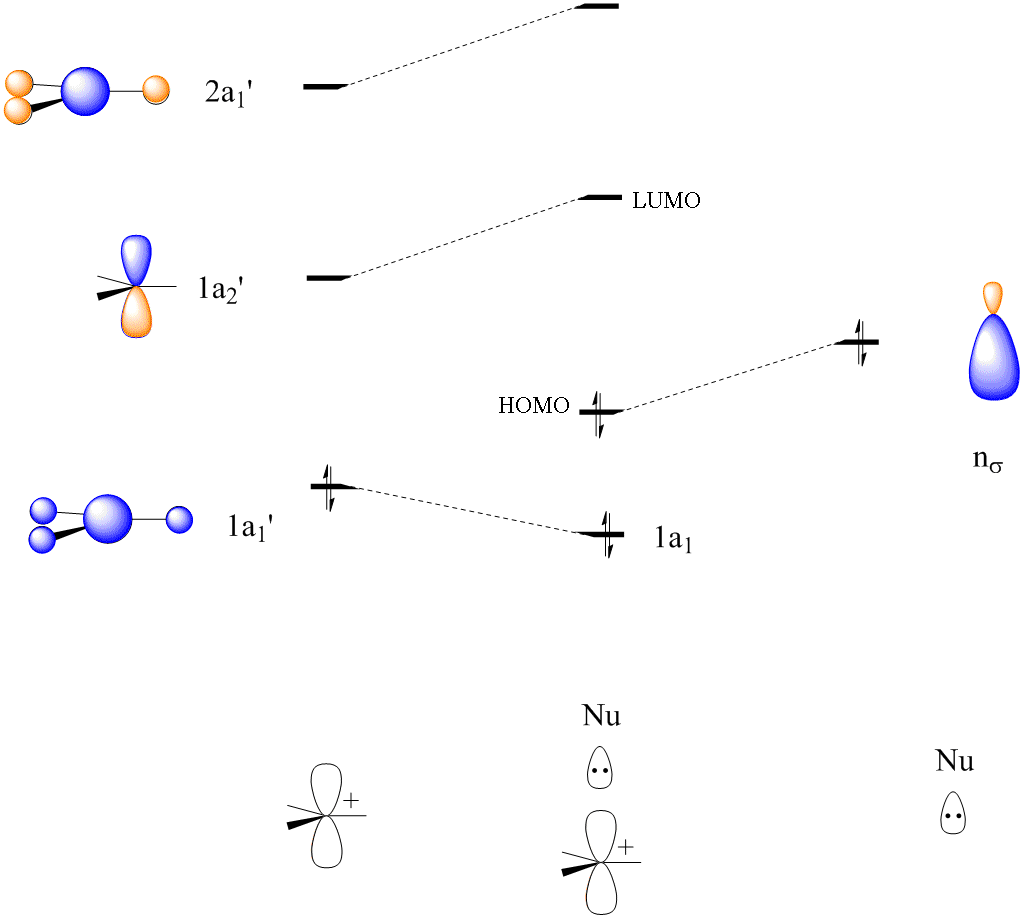










0 Response to "37 bh2 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment